Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
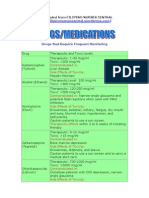
Drugs That Require Frequent Monitoring: Contraindicated In: Side Effects of Toxicity
Transféré par
Rhene GazmenDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Drugs That Require Frequent Monitoring: Contraindicated In: Side Effects of Toxicity
Transféré par
Rhene GazmenDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Drugs that Require Frequent Monitoring Drug Therapeutic and Toxic Levels
Therapeutic: 1-30 mcg/ml Toxic: >200 mcg/ml Acetaminop Contraindicated in: hen Liver disease (Tylenol) Side Effects of Toxicity: Hepatic Necrosis Alcohol (Ethanol) Therapeutic Level: 100 mcg/ml Toxic: >400 mcg/ml
Therapeutic: 120-250 mcg/ml Toxic: >500 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Narrow-angle glaucoma and potential fatal reactions when used with MAO inhibitors Amitriptylin Side Effects of Toxicity: e (Elavil) Drowsiness, sedation, lethary, fatigue, dry mouth and eyes, blurred vision, hypotension, and tachycardia. Caution patients to use a sun screen. Therapeutic effects within 2 to 6 weeks of initiating therapy. Therapeutic: 8-12 mcg/ml Toxic: >15 mcg/ml Carbamazep Contraindicated in: ine Bone marrow depression (Tegretol) Side Effects of Toxicity: Drowsiness, dizziness, and ataxia. Caution patients to use a sun screen and to carry a medical alert card. Therapeutic: 700-1000 mcg/ml Toxic: >5000 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Chlordiazep Comatose patients with CNS depression, narrow-angle glaucoma oxide Side Effects of Toxicity: (Librium) Drowsiness and dizziness. Alcohol Withdrawal Treatment: Assess patients for signs and symptoms of delirium tremors (DTs).
Therapeutic: Variable Toxic: >7 mcg/ml Desopyrami Contraindicated in: de Cardiogenic shock, 2nd and 3rd degree heart blocks, sick sinus (Norpace) syndrome Side Effects of Toxicity: Signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure. Therapeutic: 100-1000 mcg/ml Toxic: >5000 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Comatose patients with CNS depression, narrow-angle glaucoma Side Effects of Toxicity: Sedation with ataxia, dizziness, and slurred speech. Therapeutic effects within 1 to 2 weeks of initiating therapy. Therapeutic: 20-35 ng/ml Toxic: >45 ng/ml Contraindicated in: Uncontrolled ventricular arrhythmias, AV block Side Effects of Toxicity: Abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances, bradycardia, and other arrhythmias. Therapeutic: 0.8-1.5 mcg/ml Toxic: >2 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Uncontrolled ventricular arrhythmias, AV block Side Effects of Toxicity: Abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances, bradycardia, and other arrhythmias. Therapeutic: 30-150 mcg/ml Toxic: >500 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Narrow-angle glaucoma Side Effects of Toxicity: Sedation, fatigue, blurred vision, hypotension, dry mouth, and constipation. Caution patients to use a sun screen. May cause hypotension, tachycardia, and potentially fatal reactions
Diazepam (Valium)
Digitoxin
Digoxin
Doxepin
when used with MAO inhibitors Therapeutic effects within 2 to 6 weeks of initiating therapy. Contraindicated in: Serious infections Signs of adrenal insufficiency: Hypotension, weight loss, weakness, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, lethargy, confusion, restlessness. Side Effects: Glucocortic Depression or euphoria, personality changes, hypertension, decreased oids wound healing, petechiae, ecchymoses, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, hypernatremia, fluid retention, aseptic necrosis of joints, osteoporosis, cushingoid appearance (moon face, and buffalo hump) Monitor blood sugars, BUN, creatinine. Advise patients that medication should NOT be abruptly discontinued by tapered off over 2 to 4 weeks. Therapeutic: 125-250 mcg/ml Toxic: >500 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Narrow-angle glaucoma Imipramine Side Effects of Toxicity: (Tofranil) Disturbed concentration, confusion, restlessness, agitation, convulsions, drowsiness, mydriasis, arrhythmias, fever, hallucinations, vomiting, and dyspnea. Caution patients to use a sun screen. Therapeutic effects within 2 to 6 weeks of initiating therapy. Therapeutic: 0.6-1.2 mcg/ml Toxic: >2 mcg/ml Serum levels should be monitored twice weekly during initiation of therapy and every 2 to 3 months durgin chronic therapy. Contraindicated in: Severe cardiovascular or renal disease, dehydrated or debilitated patients Side Effects of Toxicity: Vomiting, diarrhea, slurred speech, decreased coordination, drowsiness, muscle weakness, and twitching. Therapeutic effects within 1 to 3 weeks of initiating therapy.
Lithium
Lidocaine Therapeutic: 1.5-6 mcg/ml (Xylocaine) Toxic: >6-8 mcg/ml
Contraindicated in: Advanced AV block Side Effects of Toxicity: Confusion, excitation, blurred or double vision, nausea, vomiting, ringing in ears, tremors, twitching, convulsion, difficulty breathing, severe dizziness or fainting, and slow heart rate. Contraindicated in: Hypermagnesemia, hypocalcemia, anuria, and heart block Side Effects of Toxicity: Magnesium Decreased respiratory rate, bradycardia, arrhythmias, hypotension, sulfate drowsiness, flushing, sweating, and hypothermia. Monitor neurologic status before and throughout therapy. Institute seizure precautions. Therapeutic: Variable Toxic: >454 mcg/ml (48 hours after high dose) Contraindicated in: Pregnancy and lactation (teratogenic effects) Side Effects of Toxicity: Methotrexat Hyperuricemia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, stomatitis, hepatotoxicity, e pulcomary toxicity, nephrotoxicity, anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and folic acid deficiency Caution patients to use a sun screen. Rescue Drug to Prevent Fatal Toxicity: Leucovorin (folinic acid) Therapeutic: 15-40 mcg/ml Toxic: Varies 35-80 mcg/ml Phenobarbit Contraindicated in: al Comatose patients with CNS depression Side Effects of Toxicity: Confusion, drowsiness, dyspnea, slurred speech, and staggering. Therapeutic: 10-20 mcg/ml Toxic: Varies with symptoms Contraindicated in: Sinus bradycardia and heart block Side Effects of Toxicity: Nystagmus, ataxia, confusion, nausea, slurred speech, and dizziness. Caution patients to carry a medical alert card.
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Therapeutic: 5-12 mcg/ml Toxic: >15 mcg/ml Procainamid Contraindicated in: e AV block and myasthenia gravis (Promestyl) Side Effects of Toxicity: Confusion, dizziness, drownsiness, decreased urination, nausea, vomiting, and tachyarrhythmias. Therapeutic: 5-10 mcg/ml Toxic: >15 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Primidone Porphyria (Mysoline) Side Effects of Toxicity: Ataxia, lethargy, changes in vision, confusion, and dyspnea. Caution patients to carry a medical alert card. Therapeutic: Varies Toxic: Vaires Contraindicated in: Uncompensated congestive heart failure, pulmonary edema, Propranolol cardiogenic shock, bradycardia, and heart block (Inderal) Side Effects of Toxicity: Bradycardia, severe dizziness or fainting, severe drowsiness, dyspnea, bluish fingernails or palms, and seizures. Caution diabetic patients to monitor blood sugar. Therapeutic: 2-6 mcg/ml Toxic: >8 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Conduction defects and digitalis glycoside toxicity Side Effects of Toxicity: Tinnitus, hearing loss, visual disturbances, headache, nausea, and dizziness. Cardiotoxicity signs include QRS widening, cardiac asystole, ventricular ectopic beats, idioventricular rhythms, paradoxical tachycardia, and arterial embolism. Therapeutic: Varies Toxic: Varies Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity to aspirin or other salicylates, bleeding disorders or
Quinidine
Salicylate
thrombocytopenia Side Effects of Toxicity: Tinnitus, headache, hyperventilation, agitation, mental confusion, lethargy, diarrhea, and sweating. May take 2 to 3 weeks for maximum effectiveness. Therapeutic: 10-20 mcg/ml Toxic: >20 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Uncontrolled arrhythmias and hyperthyroidism Theophyllin Side Effects of Toxicity: e Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, diarrhea, confusion, headache, restlessness, flushing, increased urination, insomnia, tachycardia, arrhythmias, and seizures. Tachycardia, ventricular arrhythmias, or seizures may be the first sign of toxicity. Therapeutic: 50-100 mcg/ml Toxic: >100 mcg/ml Contraindicated in: Valproic Hepatic impairment Acid Side Effects of Toxicity: (Depakene) Anorexia, severe nausea an dvomiting, yellow skin or eyes, fever, sore throat, malaise, weakness, facial edema, lethargy, unusual bleeding or bruising, or seizures. Antibiotics that Require Frequent Monitoring (Aminoglycosides) Drugs Amikacin Gentamicin Kanamycin Neomycin Streptomycin Tobramycin Troughs 5 mcg/ml 2 mcg/ml 5 mcg/ml 2 mcg/ml Varies 2 mcg/ml Peaks 35 mcg/ml 10 mcg/ml 35 mcg/ml 16 mcg/ml 25 mcg/ml 20 mcg/ml
Vancomycin
5-10 mcg/ml
25 mcg/ml
Aminoglycosides must be monitored carefully for side effects including ototoxicity (vestibular and cochlear), nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, and hypersensitivity reactions. Monitor patients for tinnitus, vertigo, hearing loss, rash, dizziness, or difficulty urinating. Renal lab tests that must be monitored include urinalysis, specific gravity, BUN, creatinine, and creatinine clearance. Liver lab tests that must be monitored include , AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT), serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinien, and LDH concentrations. Trough# levels are referred to as the minimum drug concentration that proceeds the administration of a single dose of medication. Trough levels should be drawn just prior to the next dose. Peak* levels are referred to as the maximum drug concentration that follows the administration of a single dose of medication. Peak levels should be drawn 1 hour after IM injections and 30 minutes after a 30-minute IV infusion is completed. Drugs that Require an Antidote Drug Acetaminophen Anticholinesterases (Cholinergics) Antidote Acetylcysteine Atropine, Pralidoxime
Antidepressants (MAO inhibitors and tryamine-containing foods may lead to hypertensive crisis including symptoms of chest pain, severe Phentolamine headache, nuchal rigidity, nausea and vomiting, photosensitivity, and enlarged pupils) Benzodiazepines Cyanide Flumazenil Amyl nitrite, sodium
nitrite, sodium thiosulfate Digoxin, digitoxin Fluorouracil (5FU) Heparin Ifosfamide (Adverse effects cause hemorrhagic cystitis) Iron Lead Methotrexate (Adverse effects cause folic acid deficiency) Opioid analgesics, heroin Thrombolytic agents Tricyclic antidepressants Warfarin (Coumadin) Digoxin immune Fasb (Digibind) Leucovorin calcium Portamine sulfate Mesna Deferoxamine Edetate calcium disodium, dimeraprol, succimer Leucovorin calcium Nalmefene, Naloxone Aminocaproic acid (Amicar) Physostigmine Phytonadione (Vitamin K)
Insulins Insulin Regular IV Regular SC NPH Onset 10-30 min 30 min-1hr 1-4 hr Peak 15-30 min 2-4 hr 6-12 hr Duration 30-60 min 5-7 hr 18-28 hr
Lente Ultralente
1-3 hr 4-6 hr
8-12 hr 18-24 hr
18-28 hr 36 hr
Monitor patients for onset of HYPOGLYCEMIA reaction that typically occurs during the Peak Phase following administration of insulin. Signs and symptoms of HYPOGLYCEMIA include mental confusion, hallucinations, convulsions, pale, cool, clammy skin, tachycardia, and anxiety. Treatment includes the administration of oral glucose. Severe hypoglycemia is lifethreatening and requires treatment with IV glucose, glucagon, or epinephrine. Signs and symptoms of HYPERGLYCEMIA include polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia, hot, red, and dry skin. Treatment includes insulin administration. Severe hyperglycemia is usually caused by missing, miscalculating or mistiming doses of insulin or oral medication or by overeating or drinking. Severe hyperglycemia is life-threatening and requires treatment with IV replacement and IV insulin.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRAL: Drugs That Require Frequent MonitoringDocument8 pagesDownloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRAL: Drugs That Require Frequent MonitoringFilipino Nurses CentralPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs That Require Frequent MonitoringDocument22 pagesDrugs That Require Frequent MonitoringNader Smadi100% (7)
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcD'EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs That Require Frequent MonitoringDocument14 pagesDrugs That Require Frequent MonitoringnurseoncervixPas encore d'évaluation
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesD'EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyChristine PunsalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acetazolamide drug profileDocument33 pagesAcetazolamide drug profileAshley Topp100% (1)
- Epinephrine: Uses, Dosages, Side EffectsDocument15 pagesEpinephrine: Uses, Dosages, Side EffectsDennise Juayang100% (1)
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric NameDibb Fabiania Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument15 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsJAy TootPas encore d'évaluation
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIID'EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument16 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsJosepPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency DrugsDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugsjheverly123100% (1)
- Emergency Drugs Drug StudyDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugs Drug StudyCathrine Sandile Tangwara100% (1)
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument39 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyJenny Rose GriñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs For EmergencyDocument25 pagesDrugs For EmergencyJunathan L. DelgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Icu Drug StudyDocument23 pagesIcu Drug StudyApril LebrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument7 pagesAntimalarial DrugsHilmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyHennah Reblando100% (3)
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument14 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study CCUDocument5 pagesDrug Study CCUKrishna Faith P. DelaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Psych Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- Atenolol drug infoDocument3 pagesAtenolol drug infoPoinsithia OrlandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyDiana Laura LeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Amiodarone Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesAmiodarone Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amlo Cloni PregaDocument4 pagesAmlo Cloni PregaKym Karla PatrizyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsStacy MC PelitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument34 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsMei-mei ZhuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam AntibioticDocument9 pagesPiperacillin-Tazobactam Antibiotic배기숭Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Drug StudyDocument19 pages8 Drug StudyLoyloy D ManPas encore d'évaluation
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- ClonazepamDocument3 pagesClonazepamapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: Aminophylline, Amiodarone, Atropine, BumetanideDocument33 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: Aminophylline, Amiodarone, Atropine, BumetanideNicole GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaPas encore d'évaluation
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument8 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyShaine WolfePas encore d'évaluation
- IndicationDocument4 pagesIndicationDallas WarnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Zyrtec: Tablet Core: Tablet CoatingDocument5 pagesZyrtec: Tablet Core: Tablet CoatingDwi WirastomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Metoprolol to Tenecteplase Cardiac Drug GuideDocument5 pagesMetoprolol to Tenecteplase Cardiac Drug GuideGilbert NeahPas encore d'évaluation
- Paracetamol IV administration side effects nursing considerationsDocument7 pagesParacetamol IV administration side effects nursing considerationsCharm LorenzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solian SMPCDocument20 pagesSolian SMPCyanal.bisharat.mspharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bruce Raymond L. Juele BSN 2-DDocument36 pagesBruce Raymond L. Juele BSN 2-DAno NymousPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency MedsDocument24 pagesEmergency MedsNursyNurse100% (1)
- Drug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesDrug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- CARDIAC DRUGS ATROPINE SULFATE Isopto Atropine Classification Anticholinergics Dosage Bradycardi1Document11 pagesCARDIAC DRUGS ATROPINE SULFATE Isopto Atropine Classification Anticholinergics Dosage Bradycardi1Angeley SabutananPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- MetoprololDocument3 pagesMetoprololapi-3797941100% (3)
- Adult: IV: Bradycardia PoisoningDocument28 pagesAdult: IV: Bradycardia PoisoningArthur William Tell BarbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medication-Induced Movement Disorders TreatmentDocument73 pagesMedication-Induced Movement Disorders TreatmentferdzeptrpPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimenhydrinate injection summaryDocument8 pagesDimenhydrinate injection summarymayra chipanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bisoprolol FumarateDocument3 pagesBisoprolol Fumarateapi-37979410% (1)
- Hesi NR292 ESE Study GuideDocument16 pagesHesi NR292 ESE Study Guidenaijababy89100% (12)
- Metoclopromide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoclopromide Drug Studymarklesterdeguzman087Pas encore d'évaluation