Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Prod TE
Transféré par
akshaybj4396Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Prod TE
Transféré par
akshaybj4396Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Third Year (Production Engineering) Revised FIRST SEMESTER (PART I)
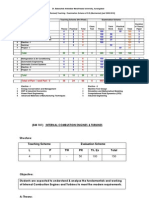
Machine Design-I Teaching Scheme: Lectures: 4 Hours / week Practicals: 2 Hours / week Term work: 25 Marks Examination Scheme Theory: 100 Marks, 3hrs Class Test: 20 Marks
1. Introduction: Design Process, steps of design process. (1 hrs) 2. Design Considerations: Basic Design equation induced and design stress factors of safety A) Simple stress situation: Tensile, compressive, shear and bearing stresses acting one at a time and induced due to direct loading, bending and twisting and design equation related to them. B) Effect of combined stresses: Different possible combinations such as i) Direct and bending stresses. ii) Normal and shear stresses, principal stresses, maximum shear stress and design equations using them.C) Variable or fluctuating loads and stresses (3 hrs) 3. Selection of Material: Basis of selection, I.S.S. and designation of commonly used materials such as steel, C.I. Aluminum, brass, bronze and other bearing materials, Principle of local quality. (2 hrs) 4. Theories of Failure: Maximum principal stress, Maximum shear stress, maximum strain, Maximum total strain energy and maximum energy of distortion theories of failure. Their statements and derivations of design equations and applications comparison. (3 hrs) 5. Design of component under simple stresses: Design of cotters, pins, levers, keys shafts subjected to only twisting subjected to only direct loading, shearing and tension. Design of simple assemblies subjected to simple stresses such as cotter and knuckle joint, couplings. (3 hrs) 6. Combined Stresses -Direct and Bending:Design of parts subjected to combined bending and direct stresses, e.g. C-clamp frame, screw press frame etc. (3 hrs) 7. Fatigue Loading: Endurance test, S.N. diagram, endurance limit. Soderberg diagram, Goodman diagram and equation for design under fluctuating load. Modified Goodman, diagram. Low cycle and high cycle fatigue, life and load, relationship during
high cycle fatigue designing for a definite life. Basquins equation designing for variable combined stresses. Notch sensitivity stress concentration, methods to reduce the stress concentration methods to improve fatigue strength, Interpretation of brittle fracture, Miner equation of cumulative damage, short time testing. (7 hrs) 8. Design of Power Screw: Types of threads used, standard square and Acme Efficiency of screw, Use of maximum shear stress the maximum energy of distortion theory buckling of screw of nut, materials, single and multistart differential and come right and left handed type efficiency, in power screw, self locking of power screw. (4 hrs) 9. Design of Bolted, Riveted and Welded Joints: Coarse, fine, extra fine series used in threaded fasteners, types of threaded fasteners, preloading of bolts, empirical design equations and exact analysis load to open the joint, improvement of factor of safety by preloading for bolted assembly subjected to fluctuating loads. Riveted joints, types, strength of joint, welded joints, types, weld symbols, methods to reduce the distortion and warping in welding, stress concentration, strength of arc welds subjected to direct, bending and twisting loads. (4 hrs) 10. Springs: Functions, types and spring rate. Close coiled helical springs, design equation, Wahl's correction factor, springs in parallel and series. Variable loading, effect of end turns, surging of compression springs, optimum design, springs with non-circular sections. Leaf spring, design equations, construction, extra full-length leaves, stress equations. Torsion springs, design equations. (5 hrs) 11. Manufacturing Considerations: Limitations of manufacturing processes such as Forging, Casting, Welding, Machining, Heat Treatment and their effect on design of the component. (2 hrs) 12. Standardization: Preferred numbers, company, national and international standards, practical aspects of standardization, interchangeability. (2 hrs) 13. Aesthetic and Ergonomic consideration in design: Appearance, functional requirements, design of display and controls. (1 hr) Term Work Term work shall consist of A. Two imperial size sheets consisting of details and assembly and a report of the calculations; based on any two projects out of the following. Sheet: I At least two problems of the following: Cotter joint (different types), knuckle joint, levers spring loaded or lever loaded safety valve, Details and assembly. Thermodynamic concept in design of valve not to be considered Sheet: II
One-problem details and assembly out of Screw jack, Screw press, Coupling, Toggle jack, Shaft straightner. B. Assignments on the following. 1. One problem on variable loading 2. One prob1em each on coil and leaf spring design 3. One problem each on bolted, welded and riveted joint 4. Design process with respect to one identified need Recommended Books. 1. Design of Machine Elements by J, E. Shigley, TMH Publication 2. Design or Machine Elements by M. F. Spotts 3. Machine Design TMH Schaum Series 4. Machine Design by Pandya and Shah, Charotar Publication. 5. Machine Design by V.B.Bhandari, TMH Publication.
COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN / COMPUTER AIDED MANUFACTURING (CAD /CAM) Teaching Scheme: Examination Scheme: Theory: 4 Hrs/ week Theory: 100 Marks, 3 Hrs. Practical: 2 Hrs / week Class Test: 20 Marks Term Work: 25 Marks Practical: 25 Marks 1. Introduction to CAD; CAM, CIM and CAE, Product cycle, Mathematical model for product life cycle. (1 hr) 2. Fundamentals of CAD: The basic design process and computer, Principles, of concurrent engineering, the manufacturing date base benefits of CAD. (2 hrs) 3. Hardware in CAD: Hardware configuration of a CAD system, display devices like raster scan devices, Direct view storage devices, plasma panels, liquid crystal displays. Types of images like- halftone, grayscale, color, Memory requirement for raster scan graphics terminal. Concept of pointing and positioning. (4 hrs) 4. Software in CAD: Ground rules for graphics software, software configuration of a graphics system, functions of a graphics package, geometric model, coordinate representation. 20 and 3D transformations including homogenous transformation matrix (4 hrs) 5. Curves and Surfaces: Parametric and non-parametric representation of Bezier curves, Bspline curve, Bezler curve Bspline surface. (4 hrs) 6. 3 D Modelling: Wire frame modelling, solid modelling, representing solids, Boolean operations, primitive instancing sweep representations, boundary representations, cell decomposition, constructive solid geometry (4 hrs) 7. Standard for CAD: Introduction, need, GKS, IGES, STEP (ISO10303) (1 hr) 8. Robotics: Physical configuration, basic robot motion, technical features of a robot, methods of robot programming, introduction to direct, and inverse kinematics, forward kinematics using transformation matrices, end effectors. industrial applications. (5 hrs) 9. NC Machine tools: Basic components of NC, CNC and DNC system NC coordinate systems, Nt motion control systems, drive of NC systems, NC Part programming: Manual, APT, Post. Processor (9 hrs) 10. Group Technology and CAPP: Introduction, concept & methods grouping of Part families, part classification and coding, OPITZ, MICLASS, computer aided process planning. (5 hrs) 11. Computer control Applications: Introduction to CAQC,CIMS (1 hr) Term Work
Performing minimum' 8 experiments out of the following and preparing a record of these experiments. 1. Study of input & output hardcopy devices of a CAD system. 2. Developing program in C for 2D transformations. 3. Developing program in C for 3D transformations. 4. Creating a 2-D model on any drafting package and get its hardcopy output. 5. Developil1g program in C for graphical output of anyone type of curve / surface. 6. Developing program in C forward Kinematics of a Robot. 7. Developing and executing a part program for contouring on an NC milling machining. 8. Developing and executing a: part program for an NC lathe machine. 9. Developing and executing a part program for point to point on NC drilling machine or milling machine. 10. Study Classification and Coding of a part family using Optiz coding system. 11. Assignments on Chapter No.11 Practical Examination Practical Examination will consist of a oral based on the above syllabus and the record of the experiments / assignments submitted by the candidate. The assessment will be based on 1. Record of experiments / assignments submitted by the candidate 2. Viva- Voce based on the syllabus. Recommended Books 1. CAD /CAM- by Zimmer & Groover, PHI Publications. 2. Elements of Computer Graphics - By Rogers OF and Adams JA - McGraw Hill Pub. 3. Numerical Control Machines - P. S. Pabla, PHI Pub. 4. Numerical Control machine tools -Yoran Koran &Joseph Ben 5. CAD/CAM/ClM - RadhaKrishnan. 6. Computer Graphics - Donald Hem, M Pauline Baker (PHI) 7. Computer Graphics - Principles and Practice - Foley, Van Dam, Fringer, 8. Computer aided Manufacturing - P.N. Rao, N.K. Tiwari, T.K. Kundra (TMH) 9. CAD / CAM-Principles, Practices & Mfg. Management Chris McMahon and Jimmie Browne (Addison Wesley) 10. Principles of Interactive Computer Graphics: William M Newman, Robert F Sproull (McGraw Hill Books Co.). 11. Robotics-Control, Sensing and Intelligence - K.S. fu, R.C. Gonzalez, Lee 12. CAD / CAM 'Theory & Practice --lbrahim Zeid (TMH) 13. Group Technology In The Engineering Industry - John L Burbridge, Mech. Engg. Publication, London 14. Automation, Production Systems and Computer Integrated Manufacturing Mikell P. Groover. (PHI).
Teaching scheme Theory Lectures / week: 4 Hrs. Practical / week: 2 Hrs. Term Work : 25 marks
Engineering Metallurgy Examination scheme Theory: 100 marks,3 Hrs Class Test: 20 marks Practical: 25 marks
1. General engineering: Properties of metals like Y.S.T.C. Toughness, impact strength, creep and Fatigue resistance etc. and their relevance in the selection of materials. (2 hrs) 2. Classification of Metallurgy as Ferrous and Non Ferrous Metallurgy, Brie[idea about Iron and Steel Making, Cast Iron Manufacture, Extraction of Nonferrous metals,Importance of Non Ferrous metals in engineering applications.' (2 Hrs) 3. Equilibrium Diagrams: Their construction with reference of solidification of metals and alloys; Cooling curves, equilibrium diagram for systems like isomorphism, eutectic, peritectic, etc. Lever rule and its application. (3 Hrs) 4. Iron-carbon Diagram: study of different types of invariant reactions, study of different phases and compounds, Critical temperatures and their significance during heating and cooling:Introduction to, classification of ferrous materials. Concept of Structure -" Property co-relationship. (8 Hrs) 5. Heat Treatment of Steels: Necessity of heat treatments, transformations of steels during heating and cooling, Non-equilibrium cooling and transformation products of austenite, TTT diagrams Different hardening methods, quenching media, tempering of plain Csteels and its effects, other heat treatments like annealing, normalizing etc., concept of hardenability, critical diameter, Jommy End quench test; metallurgical aspects of weldments and their heat treatments. (8 Hrs) 6. Surface/Case Hardening, of steels: Necessity of surface/case hardening to engineering components, Principles of case hardening- changing and without changing the composition, Classification of the process, Flame and Induction Hardening, ,Solid, Liquid, Gas Carburizing, Nitriding, Carbo-nitriding processes. Relative merits and demerits, Selection of the process for an engineering component. (3 Hrs) 7. Defects in Heat-treatment: Defects during heating, Over heating of steels, Grain coarsening;decarburization, oxidation, remedies, ASTM Grain size, control and measurement, Defects during cooling, warping, cracking, Section sensitivity, remedies. (3 Hrs) 8. Classification of plain C-steels and alloy steels, Specifications and their, significance. (IS, BS, AISI, En series), some well known specifications. (1 Hr)
9. Alloy steels: classifications of alloying elements effect of alloying elements on Fe-C, TTT diagrams, study of tool steels like HCHC, Micro alloyed steels, Free-cutting steels, spring steels,HSLA steels, Maraging steels, and their heat treatments, properties and uses. HSS, their heat Treatment, subzero treatment, Stainless Steels, classification, Problem, of Sensitization weld decay and its remedies. (4 Hrs) 10. Cast irons: Maurer's diagram, classification of cast irons, effect of shape, size and distribution, of graphite on the properties. Gray C.I., Mechanite, malleable C.I. Nodular C.I. their manufacture and applications. Comparison of steels and C.I, (3 Hrs) 11. Engineering Non-ferrous metals and alloys: Copper alloys, Phase diagrams for Cu-Zn and CU-Sn systems, Brasses, Bronzes, Aluminum alloys, Al-Si, Al-Cu systems, Age hardening, Bearing.materials and their essential properties, Important heat treatments of non- ferrous alloys. (3 Hrs). Term Work The term work shall consist of the experiments based on the above Syllabus as mentioned below 1. Study of the different Crystal Systems. 2. Study of the Metallurgical Microscope. 3. Preparation of the specimen for the microscopic examination. 4. Mounting of the specimen in a plastic mould. 5. Study of the microstructures of the plain carbon steels. 6. Study of the microstructures of Alloy steels. 7. Study of the microstructures of Cast Irons. 8. Study of the microstructures of the Non-ferrous alloys. 9. Observation in the change of mechanical properties due to the change in the microstructures. 10. Study of the change in the structures due to Surface/Case hardening of steels. Practical Examination It shall consist of the Practical/Oral based on the syllabus, mentioned above. Recommended Books 1. Metallurgy and Material Sciences By V.D. Kodgire, Everest Publishing. 2. Introduction to Engineering Materials By B.K.Agrawal, Tata Mc Graw Hill Publication. 3. Material Science and Engineering, By V. Raghvan, PHI Publication. 4. Physical Metallurgy; By S. Avner, Mc Graw Hill Publication. 5. Physical Metallurgy, Clarke- Warney, CBS Publication. 6. Engineering Metallurgy By Higgins R.A. 7. Engineering Physical Metallurgy and Heat Treatment By Y.U. Lakhtin. 8. Physical Metallurgy, By Albert Guy. 9. ASM Handbook - Vol. 12, Materials Characterization. 10. ASM Handbook - Vol. 12, Properties and Selection.
Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer Teaching Scheme: Examination Scheme Lectures: 4 Hours / week Theory: 100 Marks (3 hrs) Practicals : 2 Hours / week. Term work: 25 Marks Class Test: 20 Marks, Practical: 25 Marks 1. Fundamentals of fluid mechanics.Properties of fluid, classification of fluids. capillarity. 2. Fluid Statics: Pascals Law, hydrostatic forces on Immersed plane surface, centre of pressure, buoyant force, condition of equilibrium. (2 hrs) 3. Dynamic of fluid flow. Equation of motion, Euler's equation, Bernoullis equation, practical application of Bernoulli's theorem assumptions, momentum and energy correction factors, Application of momentum equation as force in pipe bends. (3hrs) 4. Kinematic of fluid flow: Types of flow, visualization of flow pattern, stream lines, equipotential lines, stream and velocity potential function, continuity equation in Cartesian and cylindrical co-ordinates. . (3 hrs) 5. Dimensional Analysis and model testing: Dimensions of fluid parameters, Buckingham pie Theorem, Physical meaning of dimensionless groups of fluid mechanics. Model analysis and types of similarities. (4 hrs) 6. Flow Through pipes and piping Design: Introduction, Major and minor losses in pipes, Concept of equivalent length of pipe for minor losses, Arrangement of pipes in series, parallel, power transmission through pipes. (4 hrs) 7. Introduction to Pumps: Principle of opcr3tion, main parts, Working, applications, advantages, limitations of Centrifugal pump, Reciprocating pump, Gear pump, Vane pump, Submersible pump, Jet pump. (3 hrs) Heat Transfer 8. Introduction to heat transfer, different modes of heat transfer, application of heat transfer, electrical analogy. (2 hrs) 9. Conductive Heat Transfer. Steady state heat transfer, Thermal conductivity, variation of thermal conductivity, general heat conduction equation, Cartesian, cylindrical coordinates, Unidirectional heat conduction, without and with internal heat generation, heat conduction with heat
dissipation to surrounding fluid. Extended surfaces single lump heat capacity system for unsteady state heat transfer. (6 hrs) 10. Radiation Heat transfer Definition of terms used in radiation, law of radiation shape factor; concept of radiocity, and irradiation in electrical analogy, radiation shields. (4 hrs) II. Convective heat transfer Introduction to convective heat transfer, determination convective heat transfer, coefficients by laboratory method and using empirical relations and hence evaluating heat transfer. (4 hrs ) Viscosity, surface tension and(1 hr) 12. Heat Exchangers. Introduction, Types, classification of Heat exchanger LMTD, Overall heat transfer coefficient design criterion, effectiveness NTU. (4 hrs) Term Work. The record of at least 8 experiments performed from the following ( minimum four from fluid mechanics and four from Heat transfer covering conduction, Radiation '& convection and Head exchanger). 1. Measurement of flow by orifice and venturimeter. 2. Reynoldss experiment. 3. Flow through notches. 4. Red Wood Viscometer. 5. Verification of Bernoulli's theorem 6. Study of flow of fluids through pipes. 7. Determination of Conductivity of material. 8. Determination of effectiveness of fin. 9. Experiment on forced convection apparatus. 10. Determination of emissivity of test pipe 11. Stefan - Boltzman's apparatus. 12. Experimentation on parallel and counter flow heat exchanger. Practical Examination The practical examination shall consist of performing an experiment based on the practical work during the course, viva-voce based on syllabus and term work. The assessment will be based on I. Performing an experiment. 2Viva-voce on the syllabus. Recommended Books I. Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines - Modi and Seth. 2. Fluid Mechanics - K.L. Kumar. 3. Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics - Dr.R.K. Bansal 4. Heat Transfer - Gupta and Prakash. 5. Heat Transfer - S.P. Sukhatme. 6. Heat Transfer - S.C. Arora. 7. Heat Transfer - J.P. Holman.
Industrial Economics & Management Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme Theory lecture / week: 4 Hrs. Theory: 100 marks, 3Hrs Class Test: 20 marks 1.Management and Organization: Definition, Difference between Management, Administration and Organization, Levels of management, scientific management, Contribution of F. W.Taylor; Henry Fayol.Organization: Definition, Principles of organization, types of organization. (4 hrs) 2. Industrial Ownership: Types, concepts, advantages, disadvantages and applications of Different types of owner-ship like Propertiorship, Partnership, Joint Stock Company, State & Central Government owned. (2 hrs.) 3. Functions of Management: Planning, Forecasting, Co-ordinating, Directing, Decision Making, Communication, Controlling, Motivation etc. (2hrs) 4. Industrial Psychology: Definition, Concepts, objectives, scope, individual difference in behavior, group dynamics, Theory X and Y, Motivation, Industrial fatigue, working conditions communication. (4hrs.) 5. Job Evaluation and Merit Rating: Definition, Concepts, objectives, Procedure and methods of Job Evaluation and Merit Rating. (2hrs) 6. Industrial labour Legislation: Important and necessity, types of laws, study of different acts, (3hrs.) 7. Industrial safety: Definition and need, accidents, cost, causes, and types of accidents, accident prevention and accidents proneness. (2 hrs.) 8. Costing: Elements of Cost, Direct material Cost, Direct Labour Cost, overheads, Classification of overheads, Methods of apportionment of overheads, Machine Hour rate, Cost estimate sheet.Depreciation: Definition, need, methods of calculating depreciation. (4hrs.) 9. Replacement Analysis: Introduction, reasons for replacement; factors, factors affecting on replacement, various methods for selecting alternative (seven methods), uniform gradient series, selection of best alternative using uniform gradient series. (5hrs) 10. Introduction to Modem Management Concept: Just- In-Time Manufacturing, Kaizen, POKA YOKE, Bench Marking, Business Process Reengineering (BPR), BPO, MBO. (6 hrs.)
11. Nature and Significance of Economics: Science, Engineering and Technology, their Relationship with economic development. Basic economic concepts, human wantsEconomic goods, utility, value, price, cost, wealth, and capital. Demand, supply, elasticity of demand and supply. Concept of profit and revenue, economics of scale. (6hrs.) Recommended Books: 1. Industrial Management - Earnest Dale, McGraw Hill Publishers. 2. Industrial Engineering and Management- O.P. Khanna, Dhanapt Rai & Sons. 3. Industrial Engineering and Management. A new perspective - Hicks, McGraw Hill Publishers. 4. Principles of Management- Koontz and O'Donnel-TATA McGraw Hill 5. Personnel administration- Pogors and Mayers, Mc:Graw Hill 6. Management of organizational behavior- Hersey and Blanc-hard, 1981 ,Prentice Hall. 7. New Patterns of Management-Renis Lickert. 8. Industrial Engineering and Management Systems - S. Dalela and Mansoor Ali, Standard Publishers, New Delhi. 9. Organization & Management - R.D. Agrawal, TMH.
WORKSHOP-V Teaching Scheme : Practical: 2Hours/ week. Examination Scheme Term work: 25 marks
1 Study of the machine tools: Milling machine, shaper, grinding machine (cylindrical, surface vertical, horizontal, face etc. ), tool and cutter grinder, radial drill machine, slotting machine, planer, broach, boring machine etc. available in the workshop. Also study of different tools and fixtures of each machine and study of the different attachments used on all above machine tools. Prepare job on the machines involving at least the following operations: Milling, indexing in milling, shaping, surface or cylindrical grinding, slotting (If more machine tools are available; operations on them are recommended) 2Grinding of single and multiple, point tools on Tool and Cutter Grinder. The jobs can be, composite jobs, involving more than one operation on them. The work must be sufficient to create complete awareness about the machine tools and operations done on them. The blanks must be prepared by turning.(e.g.: A job can have preparation of gear blank by turning, external milling of gear teeth involving calculations for indexing, drilling, boring, internal splines cut on a slotting machine and surface grinding can finish the faces, Another job for grinding a tool on the tool and cutter grinder) . 1. Term work shall comprise of completing and submitting of the jobs mentioned above designed by the Workshop Superintendent of the Institute and a workshop diary containing details of the work done, duly certified by the Workshop Superintendent.
Third Year (Production Engineering) Revised SECOND SEMESTER (PART II) Machine Design-II Teaching Scheme: Lectures : 3 Hours I week Practicals : 2 Hours / week Practical: 25 Marks. Examination Scheme: Theory: 100 Marks,3 Hrs. Class Test: 20 Marks Term work: 25 Marks
1. Gearing: Spur gear. nomenclature. force analysis. types of failures. Beam and wear strength equations, dynamic effect. Buckinghams Spott's equation, design of gear blank. methods of gear cutting, material, Different approaches used in design. Helical gear, formative number of teeth, force analysis Design equations. Bevel gear, Bevel factor, relations of different angles, force analysis, Design equations. Worm Gearing: Geometry, force analysis, efficiency, design for beam strength, wear consideration and heat dissipation, empirical relationship, materials. (10 Hrs) 2. Gear Trains and Gear Reducer Design: Types of gear trains, compound, reverted, non parallel axes, planetary. Gear box design principles, different arrangements, selection of arrangement, materials, lubrication. (4 Hrs) 3. Bearings and Lubrication: Viscosity, Petroffs law, hydrodynamic theory, Reynolds equation, Sommerfeld number, hydrodynamic bearing performance, use of Raimondi and Boyde' s charts and tables, hydrostatic lubrication. (4 Hrs) 4. Rolling contact Bearing: Hertz contact stresses, Striebeck equation, elements of rolling contact bearings, applications, life, static and dynamic capacity of rolling contact bearing, relationship between life and dynamic load, equivalent load, variable load acting on rolling contact bearing. Nomenclature and selection. (4 Hrs) 5. Belt, Rope and Chain Drive: Types of belt drives, ratio of belt tensions, effect of centrifugal force, centrifugal tension, condition for maximum power transmission, initial tension, creep, length of belt in open and cross. belt drive, stress induced in flat belt, materials design based on catalogs -belt construction, design equations and use of manufactures catalog rope drive. Design of flat and V belt pulleys and pulleys used for rope drive. Construction of roller chains, design equations, polygonal action. (4 Hrs)
6. Brakes: Types, short shoe brakes, frictional torque, long shoe brakes, internal and external shoe brakes, frictional torque and force analysis, simple, differential and additive type of band brakes.Heat dissipation in brakes, material for lining.(4hrs)
7. Clutches: Friction clutches uniform intensity of pressure and uniform rate of wear in; conical and flat pivot, and their applications in clutches. Materials and design equations for single, multiple plate, cone and centrifugal clutch. (4 hrs) 8. Optimum Design: Introduction to optimum design for mechanical element adequate and optimum design, primary and subsidiary design equation, .limit equation, design problems with non specification for axial loading, bending and twisting moment combined loading, the procedure of optimum design redundant specifications. ( 4 Hrs) 9. Statistical Consideration in Design: Probability theories, random variation, the normal distribution, population combination, statistical factor of safety based on reliability. (2 hrs) Term Work Term work shall consist of Two imperial size sheets consisting of details and assembly and a report of the calculations, based on any two projects out of the following. Single plate clutch, multiplate clutch, centrifugal clutch, belt drive, band brake, short and long shoe brake, spur gear drive, helical gear drive, gear drive, gear train etc. Practical Examination Practical Examination shall consist of Oral based on above term work and syllabus. The assessment will be based on Viva-voce based on the syllabus and term work. Recommended Books. . I. Design of Machine Elements by J. E. Shigley, TMH Publication 2. Design of Machine Elements by M. F. Spotts 3. Machine Design TMH Schaum Series 4. Machine Design by Pandya and Shah, Charotar Publication 5. Machine Design by V.B.Bhandari., TMH Publication 6. Optimum Design - R.C. Johnson
Theory of Machines-II Teaching scheme Theory/ week: 4 Hrs. Practical/week: 2 Hrs Class test : 20 marks Examination scheme Theory: 100 marks,3Hrs Term work: 25marks Practical: 25marks
I. TOOTHED GEARING: Gear terminology, types of gears, field of applications. Spur Gear: Condition for correct gearing, conjugate profiles, cycloidal, Involutes. Interference and undercutting. Methods of eliminating interference, determination of length of path of contact, length of path and arc of approach and recess. Spiral Gear: Spiral angles, Normal pitch, and centre to centre distance. Efficiency of power transmission, force analysis. Helical and Herringbone gears. their relative merits and demerits over spur gear. (6Hrs) 2. GOVERNOR: Working principle of centrifugal and Inertia type governor. Watt, Porter, Powel. Spring loaded governors, controlling force diagrams, sensitivity and stability. (4Hrs) 3. GYROSCOPE: Gyroscopic couple. gyroscopic effect in vehicles, ships, planes, gyroscopic stabilization. (4 Hrs) 4. FLYWHEEL: Torque - crank angle diagram for different I.C.and steam engines, fluctuation of energy, use of flywheel, coefficient of fluctuation of energy, determination of mass of flywheel for different applications. (4 Hrs) 5. FRICTION: Sliding and rolling friction, laws of sliding friction, friction circle, friction axis, friction in screw threads. (4 Hrs) 6. BRAKES AND DYNOMOMETERS: Short shoe brakes, band brakes, band and block brakes, force analysis of all types of brakes. Absorption and transmission type of dynamometers, power calculations. (4 Hrs) 7. BELT, ROPE AND CHAIN DRIVES: Types of belts, slip in belt drives, velocity ratio, belt tension ratio, types of pulleys used in belt drives, power transmission in belt drives. Rope drives, ratio of tension in rope drives, kinematics of chain drives, angular velocity ratio, construction of Bush and Roller chain, power transmitted by chain (4Hrs)
8. VIBRATIONS: Introduction, cause, effects and terminology. Single degree of freedom system: undamped tree vibration, development of differential equation of motion and its solution for different undamped systems, computation of natural frequency. Damped free vibrations: differential equation of motion, logarithmic decrement, damping methods, damped natural frequency of vibrations (analysis of viscous damping only) Forced Vibrations: vibration due to harmonic force excitation centric mass excitation, support excitation, steady state response curves, phase lag angle, motion and force transmissibility, seismic instruments. (10 Hr) TERM WORK AI least ten out of the following experiments shall be conducted during the course and a record of the same shall be submitted by the candidate and Term work. I. To generate involute tooth profile with the help of a rack on gear blank. 2. Study of interference and undercutting. 3. Determination of gyroscopic couple. 4. To determine moment of inertia of a disc by using a) Single rotor system b) Trifillar suspension c) Compound pendulum 5. To determine moment of inertia of a uniform rod by using a) Bifilar suspension b) Compound pendulum 6. To determine equivalent mass of a spring for a spring mass system. 7. To determine the damping coefficient for a spring mass dash pot system. 8. To obtain experimentally, a) Frequency response curves, b) Transmissibility curves 9. Determination of gyroscopic couple. 10. Assignment problems on chapter 4 11. Assignment problems on chapter 5 12. Assignment problems on chapter 6 13. Assignment problems on chapter 7 PRACTICAL EXAMINATION The practical examination shall consist of performing an experiment based on the practical work done during the course, viva voce based on the syllabus and term work. The assessment will be based on a. performing an experiment b. viva voce based on the syllabus and record.
RECOMMENDED BOOKS I. Theory of Machines. S.S.Rattan, TMH Publication 2. The Theory of Machines, T. Beven, CBS Publisher 3. Theory Of Machines and Mechanisms, J.E. Shiglay / Vickers, Mc Graw Hill Publication 4. Theory of Machines, P. Ballaney, Khanna Publication 5. Mechanical Vibration. G.K.Groover, New Chand and Brothers 6. Theory Of Machines and Mechanisms, Dr. Jagdish Lal , Metropolitan Publication
CASTING AND WELDING TECHNOLOGY Teaching Scheme: Examination Scheme Lectures: 4 Hours / week Theory : 100 Marks,3 hrs Practical: 2 Hours / week. Class Test: 20 Marks Term work: 25 M 1. Pattern and pattern making practices: Materials, design considerations, allowances, molding sand - types, properties, binding materials, testing; cores - types, core sands, core baking. Furnaces - Types and Selection of furnaces. (5 hrs.) 2. Mould and mould making practices: Methods of molding, types of moulds, molding process, forces acting on moulds and cores, mould metal reactions. . (5 hrs.) 3. Solidification of casting: Mechanism of solidification, solidification of pure metal, alloy and eutectic, Directional solidification, progressive solidification, role of runners, risers, chills, chaplets, exothermic compounds and insulators. (4 hrs.) 4. Principles of gating and Risering: Function of gating and risering system, types of gating systems, design of gating system, design of risering system. Design considerations, specific applications. (4 hrs.) 5. Casting defects: Casting defects, residual stresses in casting, heat treatment of castings, Inspection and testing of casting design considerations in castings. (2 hrs.) 6. Introduction to Welding: Definition, Classification of welding processes, Selection of welding processes, Commonly welded base metals, Welding as compared to Riveting and Casting. Other joining processes like Soldering and Brazing. (3 hrs.) 7. Welding Processes: Review of Principles, working , merits and demerits of different Welding Processes like - Gas Welding ,Arc Welding ,Resistance Welding, Solid State Welding ,Thermo chemical Welding, Radiant Energy Welding. (4 hrs.) 8. Weld ability: Concept of Weld ability, Effects of the alloying elements on weld ability, Weld ability tests - Hot cracking test, The Murex test (2 hrs.) 9. Welding of Steels: Metallurgical aspects and Weld ability of carbon steels, welding of Low, medium and high carbon steels, welding of steel castings. Brief introduction to alloy steels, effect of alloying elements, hardenability, welding processes used for HSLA steels, Tool steels, Introduction to Stainless steels, Classification, Welding of Austenitic stainless steel, weld decay and its prevention. (3 hrs.)
10. Welding of Cast Irons: Characteristics of Cast irons, Weld ability of Grey Cast iron, Process and techniques for welding of G.C.I., metal arc Welding, welding electrodes, Gas welding, Braze welding, Thermit-welding ,welding of Malleable, Nodular and alloy cast Irons. (3 hrs.) 11. Welding of Non-ferrous metals and alloys: Weld ability of Aluminum and its alloys, Processes used, Weld ability of Copper and its alloys, processes used,. Concept and metallurgical problems in welding dissimilar metals. (3 hrs.) 12. Defects and Heat Treatment: Defects in welds, Cracks, Distortion, Incomplete penetration, Inclusions, Porosity, Poor fusion, etc, causes and remedies, Pre and Post weld heat treatment. (2 hrs.) TERM WORK It shall consists of at least ten assignments on above syllabus. I) Minimum two industrial visits to Foundries and Fabrication Units. II) A report on above two industrial visits. RECOMMENDED BOOKS 1. Principles of Metal Casting, By Hein. Lopper, Rosanthai (TMH Pub.) 2. Foundry Technology, By O.P. Khanna, Dhanpatrai Pub. 3. Foundry Technology, By D. Kumar. 4. Welding Technology, By O.P. Khanna, Dhanpatrai Pub. 5. Welding Technology, By Rossi E. Boniface. 6. Manufacturing Engineering, By P. N. Rao, TMH Pub. 7. Welding and Welding Technology, By Richard D. Little.
Mechatronics-I (Sensors and Actuators) Teaching scheme Theory lectures/ Week : 4 Hrs. Practical/week : 2 Hrs Term work ; 25 marks Examination scheme Theory : l00 marks (3hrs) Class test : 20 marks
I. Introduction: Mechatronics: Definition, need. Importance, concurrent system. Difference between Mechatronic and concurrent system, Components of a Mechatronic system, function of each component. Examples of mechatronic system. (3 Hrs.) 2. Measurement and measurement systems: Significance, types, methods, classification, analog and digital mode, functions of instrument and measurement, elements of generalized measurement system.(2 Hrs.) 3. Static characteristics of instrument and measurement systems: Accuracy, static error, reproducibility, drift, sensitivity, errors in measurements, linearity, hysterisis, bias, input and output impedance, loading effect. (2Hrs.) 4. Detector Transducers: Primary and secondary transducers, mechanical transducers, resistive transducers, inductive transducers, capacitive transducers, photoelectric transducers, piezoelectric transducers, optical transducers. (4Hrs.) 5. Signal conditioning and data presentation D.C and A.C. Type signal conditioning system, amplifiers, and filters. Data presentation: - Type of output, galvanometers, ohmmeters, attraction type and repulsion type instruments, C.R.O. , Recorders: galvanometer type, potentiometer type, strip chart, magnetic tape recorder, ultra violet recorder. (4Hrs.) 6. Measurement of force, torque and power- methods and devices. Measurement of pressure and vacuum- methods and devices. Measurement of flow - methods and devices. Measurement of temperature - methods and devices. Measurement of speed- methods and devices. Measurement of velocity and acceleration- methods and devices. Strain gauges and their application in measurement. 7. Sensors: Introduction, proximity sensors and switches, digital optical encoder, strain gauges, potentiometers, Wheatstone bridge. (3Hrs.) 8. Solenoids and relays, D.C. Motors, permanent magnet D.C. Motors, Pulse width modulation (PWM) amplifier, stepper motors, selection of a motor. (3Hrs.) (8Hrs.)
9. Hydraulics and Pneumatics: (a) Introduction to hydraulics and pneumatics systems, comparison of mechanical, hydraulic and pneumatic systems, hydraulic and pneumatic symbols. (3Hrs.) (b) Review of hydraulic pumps, directional control valves: two way valves, solenoid operated valves, three way valves, four way valves, one directional valve, poppet valves, spool valve, pressure relief valve, hydraulic cylinders, hydraulic motors, operation of a hydraulic system. operation of an electro . hydraulic system. (5Hrs.) (c) Pneumatic motors: Sliding vane type, gear type. Air filters, pressure regulators and lubricators, operation of a pneumatic system and electro pneumatic system. (3Hrs.) Term Work A. Performing minimum five experiments term the list of experiments. from Sr.no. 1to8. I. Study of generalized measurement system with a typical instrument 2. Assignment on different static characteristics. 3. Study and demonstration of use of a. Strain Gauge and b. L.V.D.T. 4. Force Measurement a. Load Cell b. Spring balance c. Proving ring 5. Flow measurement: a. Orifice/Venturimeter b. Rotameter c. Pitot tube d. Water meter 6. Pressure measurement: a. U tube manometer. b. Bourdon gauge c. Dead weight pressure gauge. 7. Temperature measurement a. Mercury thermometer b. Resistance thermometer c. Thermocouple. d. Pyrometer 8. Speed Measurement a. Stroboscope b. Tachometer c. Digital Optical Encoder B. Assignment on hydraulic and pneumatic symbols
C. Constructing a hydraulic circuit with the help of hydraulic trainer and drawing of a hydraulic circuit. D. Constructing a pneumatic circuit with the help of pneumatic trainer and drawing of a pneumatic circuit. F. Study and demonstration of working of stepper motor.
Recommended Books I. Introduction to Mechtronics and measurement systems- David G.A1citore and Michael B. Histand, TMH Publication . 2. Mechanical Measurement and Instrumentation-Dhanpat Rai & Sons Publication 3. Mechanical Measurement Beckwith and Buck 4. Measurement System Doeblin Ernest 0, TMH Publication 5. Mechanical Measurement - R.K.Jain 6. Pneumatics and Hydraulics - Harry L Stewart , Audel Series
METROLOGY AND QUALITY CONTROL Teaching scheme Examination scheme Theory lectures / week: 4 Hrs. Theory: 100 marks (3Hrs) Practical/week : 2 Hrs Class test : 20 marks Term work : 25 marks Practical : 25 marks
I. Introduction: Definition & concepts of metrolology, Standardization and standardizing organizations, International system of units, Methods of measurement. (1Hr) 2. Standards of Measurement: Standards, Standards for linear measurement, Line standard including linear standard meter, End standard, Wavelength standard, Classification of standards of traceability . (1Hr) 3. Linear Measurement: Surface plate, angle plate, V block, Bench centers, Combination set, radius gauges, Feeler gauges, Angle gauges, Pitch screw gauge, Principle of verniers, vernier height gauge. Vernier depth gauge, Micrometers, Types of micrometers, slip gauges, wringing of slip gauges, care in case of slip gauges (3Hrs) 4. Limits, Fits & Gauges: a) Limits, tolerances, different ways of expressing tolerances like unilateral & bilateral, tolerance accumulation, relationship between tolerance & cost, maximum & minimum metal conditions, Indian standard (IS 919-1963), Fits: Terminology for limits & fits, types of fits, hole basis system, shaft basis system, selection of fits, types of assemblies like trial & error, interchangeable assembly b) Gauges: Plain gauges, ring gauges, snap gauges, adjustable gap gauges, control & profile gauges, material for gauges. c) Gauge Design: Taylor's principle, gauge makers tolerance, wears allowance, numericals on gauge design. (7 Hrs) 5. Comparators: Introduction, types of Comparators, construction & working of different types of comparators like mechanical, optical, electrical, pneumatic (2 Hrs) 6. Interferometer: Monochromatic lights, principle of interference, optical flat, fringe applications & their interpretations, application of optical flat in flatness testing, surface contour testing, parallelism testing, Interferometers including Nicholson Interferometer, NPL flatness interferometer. (2 Hrs) 7. Angular measurement: Vernier bevel protractor, universal bevel protractor, optical bevel protractor, sine bar, angle gauges, optical instrument like auto collimator, angle dekkor. (2 Hrs) 8. Measurement of surface finish: Definitions, terminology, methods of measuring surface finish. Analysis of surface traces, assessment of surface roughness as per Indian standards. (2 Hrs)
9. Metrology of screw threads: screw threads terminology, errors in threads & their effects, measurement of various elements of threads. (2 Hrs) QUALITY CONTROL I. Introduction: The meaning of quality and quality control, inspection and quality control, quality variables and attributes design, quality conformance, quality of performance, quality assurance, cost of poor quality. (1Hr) 2 Statistical Quality Control: The concept of variation, the normal distribution, central limit theorem, the concept of population (universe).Control charts: Introduction, types of control charts for variables and attributes: Objective, sample size, construction, advantages, limitations, interpretations, applications. Simple numericals on control charts Process capability analysis. 5 Hrs 3. Acceptance Sampling: Introduction, Sampling inspection, objectives, different types of sampling plans, formation of inspection lot, Sampling methods, Operating Characteristic (OC) curve, ideal & realistic OC curve, Producer's risk and consumer's risk, AQL, RQL,IQL,AOQ,AOQL. 5 Hrs 4. Reliability Engineering: Introduction, Reliability and quality, need for a Reliable product, definition of Reliability, product life cycle, failure patterns for complex products, bath tub curve, MTIF, MTBF (only theoretical treatment) 1Hr 5. ISO 9000 Standards: Need for Standardization, overview of ISO series of standards, benefits by becoming an ISO 9000 organization 2 Hrs 6. QUALITY CIRCLE: Philosophy, organization & operation of quality circles, significance, old and new SQC tools, brain storming. 2 Hrs 7. Total Quality Control: Quality policy, total quality control, total quality management 1Hr TERM WORK Term work shall consists of any six experiments from group A and all assignments from B GROUP A : List of experiments: 1. Study and demonstration of measuring Instruments for linear measurements. . 2. Study and demonstration of sine bar, sine centre. 3. Study and demonstration of comparators of different types 4. Study and demonstration of Autocollimator / angle Dekkor. 5. Study and demonstration of Interferometry. 6. Study and demonstration of surface finish measuring instruments. 7. Study and demonstration of screw thread measuring instruments
GROUP B : List of Assignments: I. Assignment on Quality Mindedness and Quality Cost 2. Assignment on Statistical Quality Control 3. Assignment on Acceptance Sampling 4. Assignment on Quality Circle. 5. Drawing of a control chart one each for variables and attributes.
PRACTICAL EXAMINATION The practical examination shall consist of performing all experiment based on the practical work done during the course and viva voce based on the syllabus and term work. The assessment will be based on a. performing an experiment b. viva voce based on syllabus & record RECOMMENDED BOOKS I . Engineering Metrology by R. K. Jain. 2. Practical Metrology by K.G. Hume 3. Statistical Quality Control, By E. L. Grant and Leavenwai1n (TMH) 4. Quality Planning and Analysis, By Juran (TMH) 5. Taguchi Techniques for Quality Engineering, By Philip J. Rose; 6. Quality Circle Programmes through Participation, By S. R. Upade (TMH) 7. lSO-9000, Terry L. Johnson (Mc Graw Hill Publication.) 8. Total Quality Essentials, By Sarvo Singh Soin (Mc Graw Hill Publication.) 9. Quality Control & Total Quality Management - P.L.Jain (TMH) 10. Production & Operations Management -- S.N. Chary (TMH)
Final Year (Production Engineering) Revised FIRST SEMESTER (PART I) THEORY OF METAL FORMING (One Theory Paper: 100 marks, 3 hrs, Class Test: 20 marks, Term work: 25 marks, Practical Exam: 25 marks) 1. Theory of Metal Forming: Plasticity, Stress-strain curves, true strain, maximum shear stress theory, distortion energy theory, yield criteria, stress and strain in variants, Methods of analysis of bulk forming processes like slip-line, upper bound and lower bound approach. (6 hrs) 2. Fundamentals of Plastic Working of Metals:- Classification of forming processes, effect of temperature and strain rate on forming processes. Structural changes during the process. (3 hrs) 3. Sheet Metal Working: Shear on press tools movement of metal in bending and forming operation, classic spring back Movement of meta! and stresses in drawing, Red drawing limits wall thinning and thickening and ironing theory, defects in deep drawing, deep drawn parts, applications of tensile, cupping wedge and simulative tests. Drawing load calculation. Reverse drawing. (5 hrs) 4. Forging: Application of plastic theory of metal flow under impact pressure, press forging, Designing forged parts, selection of forging metals and heat treating practice, Die design for drop hammer, presses and upset machines. Effect of friction, load calculations, Die block materials and heat treatments, forging plant equipment, Finishing - operations and inspection of forgings, Recent developments in forging: .'" (6hrs) 5 Extrusion: Classification of extrusion processes, equipment:; and dies used in extrusion, Application, plasticity theory to extrusion problem, variables in extrusion, Deformation in extrusion. The influences of speed and temperature upon extrusion pressure, extrusion defects and remedies for minimizing them, metals and alloys available for extrusion, production of seamless pipe and tubing, Hydrostatic extrusion. (6 hrs) 6. Rolling: Types of rolling mills for hot and cold, rolling, forces and geometrical relationship in rolling, Deformation in rolling, Residual stress in rolled products, Theories of cold rolling and hot rolling their applications, calculation of mill-torque, mill horsepower and rolling load, defects in rolled products, roll pass design considerations(6 hrs)
7 Rod Wire and Tube Drawing: Principles involved in the drawing of rod and wire, variables in wire drawing, wire drawing with and without friction, wire drawing machines, Applications of theory of plasticity to drawing. The drawing processes with a stationary and moving materials. Residual stresses in rod wire and tubes, defects in wires and tubes. (5 hrs) 8. Friction and Lubrication in Metal Working: Influence of friction, measurement of coefficient of friction, principles of lubrication, lubricants used in industrial metal working. (3 hrs)
Term Work It shall consists of the record of at least eight assignments on the above syllabus and demonstration of any two forming processes. Practical Examination Practical examination shall consist viva voce based on the syllabus. Recommended Books I) Principles of industrial Metal Working Processes. - G.W. Rowe (Arnold) 2) Engineering Plasticity :- Johnson and Mellor (Reinhold) 3) Metal forming Process & Analysis :- B- Avitzue (Tata McGraw Hill) 4) Principles of Metal Working: S. Kumar (PHI) 5) Manufacturing Science - by Ghosh & Malik 6) Introduction to the Theory of Plasticity for Engineers: Hoffman and Sachs (McGraw Hill) 7) Metal Rolling: R.C. Chaturvedi. 8) Stresses and Strains in Rolling: T selikoy 9) Mechanical Metallurgy: G.E. Dieter, McGraw Hill
PRODUCTION. PLANNING AND CONTROL (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs., 100 Marks, Class Test:20 marks, Term Work:25 marks, Practical Exam. :25 marks) 1 Introduction: Definition of PPC, functions of PPC, Types of production job. Batch. Continuous, production cycle (2 hrs) 2 Product Development and Design: Effect of competition, product analysis, marketing aspects, product characteristics, economic analysis, simplification, standardization. specialization, Break even analysis. (3 hrs.) 3 Forecasting : Importance, time - series analysis, forecasting methods, time series calculation, least squares, simple and moving average, seasonal index, exponential smoothing. co-relation. Co-efficient of co-relation, and determination. Delphi method. Normal group techniques, selection of forecasting methods. (5 hrs.) 4. Plant Layout : Flow system, types of layout: product, process, static product and combination layout, effect of automation on layout, symptoms of bad plan layout. (4 hrs) 5 Evaluation of Materials and Processes: Criteria for rnaterial selection, material utilization of product, selection of process, Design for production. (3 hrs.) 6 Production Order. Formulation of production order, Process charts, activity charts, operation and route sheet. (2 hrs.) 7 Quantities in Batch Production : Stock control, definition of batch size, minimum cost batch size, production range, maximum profit batch size. (3 hrs.) .8 Machine Capacity: .Machine output, Multi machine supervision by one operator, balancing multi product system. (3 hrs.) 9 Scheduling: Basic scheduling problems:- Scheduling for fluctuating demand, assignment problems, sequencing problems, scheduling for orders with random arrivals, master schedule. (4 hrs)
10 Elements of Control Procedure : Stages in control process, Dispatching, Expediting, Evaluating, Recording process: Control tools and techniques like Gantt Charts. ( 3 hrs)
11 Materials Management : Definition, objectives, procurement orders, inventory management : Definition of inventory, need, types inventory models, EOQ, Quantity discounts, ABC analysis, classification and coding of materials, stock. ( 4 hrs) 12 Computer aided PPC: MRP 1, use of computers in scheduling ( 2 hrs) 13 Capacity Planning: Introduction, measurement of capacity, measures of capacity, capacity planning, estimating future capacity needs, factors influencing effective capacity, factors favoring over capacity & under capacity, aggregate planning, master production scheduling. (3 hrs) Term work: 1) It shall consist of at least eight assignment based on the above syllabus 2) Critical analysis of plant lay out of the industry in which student has undergone in plant training Practical Examination: Practical examination shall consist of a Viva. Voce based on the above syllabus. Recommended Books: 1 Elements of Production Planning and Control - Samuel Eilon 2 Production Systems, Planning analysis and control - James L. Riggs 3 Production Planning control and industrial Management - Jain and Agrawal. 4 Modem Production/Operations Managemcnt - Buffa. 5 Industrial Engineering and Managemem - O. P. Khanna.
Machine Tool Technology (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test: 20 marks, Term-work: 25 marks) 1. Introduction: Trend in designing machine tools. Classification of various machine tools. General purpose, Special purpose, NC-CNC on the basis of kinematics, force & power required for various metal cutting operations & machine tools used. (3 hrs) 2. Drives: Consideration in designing drives, based on continuous or intermittent requirement of power. Type and selection of motor for the drive, Regulation and range of speed based on preferred number / series / geometric progression. Design of head stock gear box for spindle drive using ray diagram, structure diagram, nodal optimization while designing compact gearbox, Harmonic drive, Recirculating Ball Screw. - - - (12 hrs) 3. Step less Regulation: Electromechanical System of regulation, friction, pressure and ball variators, P.I. V. drive (Kopp.Variator) Epicyclic drive etc. (3 hrs) 4. Element of Machine Tools: Design of beds, slide ways, carriage, tables of lathes, milling machines based on force, Frictional behaviour and - different types of lubrication system. Design of Power Screws - sliding as well as rolling friction, spindle units, supports for spindles, bearings, Preloaded supports, Rigidity and vibration analysis including stick slip sliding.(8 hrs) 5. Control System: Electrical Control: Push button control, directional control relays, thermal relays, electrical brakes: automation in feed mechanism. Hydraulic Control in machine tool, positional movement. Power pack for lubrication system in hydrostatic drive. Control systems for Gear sliding and feed mechanism (open loop or closed loop) for NC/CNC machine using stepper motor or DC motor. (5 hrs) 6. Flexible Manufacturing System: Definition, Types - Classification, equipment, application - Auto Tool Changer - types, functional details, Machine tool - features and constructional details. (3 hrs) 7. Static and Dynamic testing of Machines as per Schlesinger's test and Tobias stability envelopes,Performance criteria of Machine Tools. (3 hrs)
8. Recent Trends: A review of recent practices used in Machine Tool Technology effect of development in manufacturing process, modular design concepts. (2 hrs) Term Work The term work shall consist of record of assignments on following topics. Design & Working drawing of speed gear and feed gear box. Design & Working drawing of four machine tool mechanisms. Design of bed or column. Design of sideways or power screws. Preparation of standard test chart for General Purpose Machine (Anyone)
Recommended Books: " 1. Mehta, N.K. : Machine Tool Design, Tata McGraw Hill. 2. Pal D.K. and Basu, S.K.: Design of Machine Tools (4th Revised Ed) Oxford-IBH. 3. Acherkan, N.S. et al: Machine Tools Vol. I to Vol. IV, MIR Publications. 4. Bhattacharya, A. and Sen, G.C.: Principles of Machine Tools, New Central Book Agency, Calcutta. 5. T. Kundra, Rao, P.M. Tiwari, N.K.: Numerical Control and Computer Aided Manufacturing, Tata McGraw Hill. 6. Martin, S.J : NC Machine Tools, ELBS.
TOOL ENGINEERING (One Theory Paper: 100 marks, 4 hrs, Class Test: 20 marks, Term Work: 25 marks, Practical Exam: 25 marks) 1. Introduction: Definition of tool, classification of tools, tool materials and their properties. (2 hrs) 2. Elements Of Machining Process: Basic requirements of machining process, single point cutting tool, tool signature, machines and geometry of chip formation, types of chips, effect of tool geometry and cutting conditions on machining processes, tool wear, tool life, forces on cutting tool, machine force circle, power requirement, design and construction details of single point cutting tool for turning, boring and shaping operations, economics based on tool life, cutting fluids, - types. Properties required, application, heat treatment of cutting tools. (l0 hrs) 3. Multipoint Cutting Tools: Drills - Classification and nomenclature, drill point geometry, selection of drills for various operation. Reamers - Classification and nomenclature, milling Cutter - Classification and nomenclature of end mill, plain milling clutter, force acting on milling cutter, Taps- Classification and nomenclature, Broaches Classification and nomenclature, Hob- Nomenclature. (4hrs) 4. Jigs and Fixtures: Principle of location, twelve degree of freedom, 3-2-1 method of location, 4-2-1 method of location, locating devices. Drill Jig - Types of jig bushes, types of drill jigs, design and development procedure of jig for different components. Fixtures Setting block, tennon, clamping of fixtures, types of fixtures, design and development of milling, turning fixtures for different components. (l0hrs) 5. Design of Dies. : Power presses types and construction details, die cutting operation, cutting action in die and punch, center of pressure, clearance and its significance, cutting forces, methods of reducing cutting forces, methods of punch support, strippers, stock stops, Guide pilots, knockout, design of blanking and piercing dies. (6 hrs) 6. Drawing Dies: Metal flow and factors affecting drawing, blank size calculations, drawing force, single and double acting drawing dies, design and development of drawing dies for different components. (4 hrs) 7. Process Planning: Product Engineering, Process Engineering, Contents of a Process plan, Process operations, Steps of process planning, Planning and tooling for low cost processing. (4 hrs) Term Work a. Prepare a single point cutting tool in workshop made of a soft material. b. Demonstration of formation of various types of chips. Effect of tool geometry and cutting condition on Machining process. c. Handling and study of various types of multipoint cutting tools. d Handling and study of various types of locating & clamping devices.
e. Measurement of cutting forces in turning, killing & drilling operation using lathe, dril1, milling dynamometers. f. One sheet on multipoint cutting tools. g. One sheet on locating and clamping devices. h. One sheet on Jig design. Practical Examination. Practical examination shall consists of designing a Jig / Fixture / die for a given component and Vivavoce based on the syllabus. Recommended Books I) Production Technology.- HMT 2) Tool Design- Donaldson. 3) Jigs & Fixtures- Kempster 4) Design of Jigs and Fixtures- P.R Joshi 5) Jigs and Fixture design manual -Harirkson 6) Tool Design- Pollack RD 7) Production Engineering- P.C.Sharma Term work One sheet on Fixture design. One sheet on die design.
Mechatronics - II (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test: 20 marks) 1. Analog Signal Processing using op-amp : Introduction, Block-diagram of opamp IC ideal model of opamp. Study of opamp parameters. Application of opamp : inverting amplifier non-inverting amplifier, summing amp, scaling & avg. amp. Voltage follower. Voltage to current & current to voltage converter. Integrator, differentiator, instrumentation amplifier, sample & Hold circuit. (6 hrs) 2. Active filters : Transfer function, Buffer worth filter, low pass filter, high pass filter, band pass filter & band stop filter. (3 hrs) 3. Digital Circuits: Number system, Binary number system. Gates - Or, AND, NOR, XOR NAND, NOT, Flip-Flops SR, JK & D-type fI (3 hrs) 4. Microprocessor 8085 : Architecture, addressing. modes. instruction, set. Assembly language. programming. simple Arithmetic programs, counters, delays, stock & subroutine. Concept of memory & I/O interfacing, Interfacing of 8255 PPI, its initialization & programming. interfacing of LEDS, Keys, Seven-segment LEDS, opto isolators, electromechanical, relays, A to D and D to A conversion interfacing of ADC 0808 & DAC 08. (10 hrs) 5. Micro Controllers, programming & interfacing - introduction of 8051 family. Architecture of 8051, instruction set, programming, system, overview, I/O memory mapped. I/O interfacing, stepper motor, interfacing. (12 hrs) 6. Micro controller based mechanical systems - Boiler temperature, Controller- Speed Controller - Pressure Controller - Case studies: Coin counter - Robotic walking M/c. (6hrs) Recommended Books 1) Linear Integrated circuits & Op2.1I1p - R.G. Gaigwad. 2) Modem Digital Electronics - R..P. Jain. 3) Microprocessor Architecture Programming & Application - Ramesh Gaonkcr 4) The 8085 Micro controller Architecture, Programming And Application." - Kenneth Ayala 5) Introduction to Mechatronics &, Measurement system - David G. Alciatore, Michael B. Histand, Tata McGraw Hill.
Manufacturing Systems (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test: 20 marks) I. Introduction & Fundamentals of Manufacturing System: fundamental of Manufacturing, input / output of manufacturing, manufacturing system definition, system design, mold building, structural, transformational and procedural aspects of manufacturing system, integrated manufacturing system (lMS), integrated Manufacturing and Management System (IMMS), basic structure, framework of IMMS, production, types of production, types of manufacturing systems. (8 hrs) 2. High-volume Manufacturing System: Transfer line, Detroit type automation, design and fabric consideration, Analysis of automated flow lines: Technology, analysis of transfer line without shortage, practical automation, automated flow lines with storage buffers, computer simulation of automated flow lines. (6 hrs) 3. Computer Integrated Manufacturing: Introduction, Need, Computer application in manufacturing, automation and robotics, , computer integral production inventory systems. (4 hrs) 4.Group Technology: Introduction, review of part families part classification and coding, production flow analysis machine cell design. (4 hrs) 5. Cellular Manufacturing system: !introduction, need, cell formation, multiskill operator, man machine, chart, inter and intra sell movement of material, maintenance of equipment. Flexible Manufacturing System: Introduction, concept, components of FMS, FMS planning, automated workplace handling, layout, cost feasibility, typical application, advanced areas: automated factory remote control. (6 hrs) 7. Manufacturing System: Lean manufactming system, Toyota production system, 6 sigma Introduction its culture, implementation process, direct on line system, concept of zero inventory. (6 hrs) Recommended Books 1 Manufacturing System Engineering by Rastasndo Hitom, Viva Books Pvt. Ltd. 2. CIM by Harrington, 1. Krieger. 3. Computer Integrated Design and Manufacturing by David Bedworth, McGraw Hill. 4. - C.c. Naw
5 Automation. Production Systems and CIM by M.P. Grooves Pearson Education. NewDelhi. 6. Toyato Production Systems by Taguchi Ohno, Productivity Press 7. Combining six sigma Quality with Lean speed by Michael L. George, TMH
Advanced Materials & Manufacturing Techniques (One Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test: 20 marks) A) Advanced Materials 1. Ferrous Materials: Mechanical properties, chemical composition, microstructures, heat treatment and applications, stainless steel and heat resisting steels, precipitation harden able steels, valve steels, high s1rength low alloy steel (HSLA), micro alloyed steels, ball bearing steel, tool steels; high nitrogen steels, alloy cast iron. (4hrs) 2. Nonferrous Materials: Mechanical properties, chemical composition, microstructures, heat treatment and applications, copper alloys (Brasses and Bronzes), Ai-alloys (AiMgSi, Al-Cu, Ai-Si), designation system in Ai-alloys, nickel and its alloys, lead and its alloys, tin and its alloys, tita11ium and its alloys, and zinc and its alloys. (4 hrs) 3. Composites: Classifications, properties, application of composites, polymer matrix materials, metal matrix materials, ceramic matrix materials, carbon materials, glass materials, fiber reinforcements, types of fibers, whiskers, laminar composite, filled composites, particulate reinforced composites, design of composites material hybrid composites, angle plied composites, mechanism of composites. calculation of properties, unidirectional fiber composites, critical volume :&action, discontinuous fiber composites, rule of mixtures equation, critical angle (8 hrs) 4. Organic Materials: Classification, properties, applications of polymers, plastics and elastomers. (2hrs) 5. Ceramics: Classifications, properties, structures of refractories, abrasive materials, electronic ceramics, cement and concrete. (2 hrs) 6. Miscellaneous Materials: Classification, applications and properties of cutting tool materials, semi conducting materials, dielectric materials, magnetic materials, ferroelectric materials. (2 hrs) B) Advanced Manufacturing Techniques : 7. Advances In Casting Processes : Sheet moulding casting V-Process, flask less moulding, evaporative casting, plaster mould casting design for plaster mould casting qualityaccuracy uniformity & other considerations in casting and moulding. (5 hrs) 8. Chip!ess Metal Removal Process: Magneto abrasive finishing, Abrasive flow machining,
Wire EDM, Water jet machining, Micro dril1ing by different processes like laser beam, ion beam, electro Jet, etc, electro stream drilling. Non traditional Deburring processes. (6 hrs) 9. Metallic Coating: Importance, principle, applications of: Chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition, thermal spray coating, Electro plating, Electro less coating. (3 hrs) 10Rapid Prototyping (RP) . Principle and elements of RP. Advantages and applications of RP, Introduction to regenerative manufacturing processes like SLS, LOM, FDM (4hrs) Term Work Term work shall consist of the record of at least eight assignments based on the above syllabus.
Recommended Books 1. The Nature and Properties of Engineering Materials by Z-D. Jastrezebski. 2. Introduction to Physical Metallurgy by S.H. Avner. 3. Composites Materials by S.C. Sharma. 4. Materials and Processes in Manufacturing by E.P. DeGarmo, J.T. Black, R.A. Kosher. 5. Materials Science and Engineering by R.K. Rajput. 6. Composites Materials by Iele Chawla. 7. The Metals Data Book by Alok Nayar. 8. Polymer Science and Technology by Joel R. Fried. 9. ASM Handbook - Vol 10 10. ASM Handbook - Vol.2 Properties and Selection: Nonferrous alloys and special purpose materials. 11. Modern Manufacturing process Engineering by - Benjamin W. Niebel, Allen B. Draper, Richard A Wysk. - McGraw Hill 12. Non Traditional Manufacturing processes. By - Gany F. Benedict Marcel 13. Production Technology Hand Hook.- H.M.T. Tata McGraw Hill. 14. Metal Casting by - HaY&I1e and Rosenthal. 15. Non Traditional Machining Processes. By - E.J. Weller Society of Manufacturing Engineers, Dearban Michigan. 16. Manufacturing Processes: B.H. Amsted. Philip F. Oswald and Myron L. . Begeman, John Wiley Sc Sons, eighth edition. 17. ASM "Metals Hand Book", ASM Publications. 18. Non-conventional Machining Processes- P.K. Mishra, Narosa Publication.
Computer Aided Engineering (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test: 20 marks.) 1) Introduction:- Need, Applications, Advantages and disadvantages of CAE. (01 hrs) 2) Finite Element Modeling (FEM) : Introduction, steps in Finite Element Analysis, Finite element formulation, variational methods, (Raleigh - Ritz method), weighted residual method (Gelerkin method) . (06 hrs) 3) FEM: One Dimensional Modeling : Element division, numbering scheme. co-ordinate and shape function, Disp1a.cement, strain and stress relational ship, element stiffness matrix by potential energy approach. Penalty Approach, Thermal effects in one dimensional Elements,. Analysis of trusses, Thermal effect in trusses, Boundary conditions.. (08 hrs) 4) FEM - Two dimensional modeling : Constant strain Triangular element - Stiffness matrix, const Triangular element - shape function application to heat transfer, fluid mechanics, plane elasticity. . (08 hrs) 5) Trusses: Introduction, plane truss, real and Globa1 co-ordinate systems, calculation of l and m, element stiffness matrix, stress ca1cu1ation. Temp. effects. (05 hrs) 6) Dynamic considerations : Introduction, formulation - solid body with distributed mass, element mass matrices, evaluation of eigen values and eigen vectors, properties of eigen vectors, eigen value, eigen vector evaluation, generalized Jacobin method, Tri diagonalization. . (06 hrs) 7) Preprocessing and Post-processing: Introduction, mesh generation, determed configuration and mode shape, contour plotting. Nodal values from known constant element. values for a triangle, least squares fit for a four nodal quadrilateral (04 hrs) 8) Collaborative engineering : Introduction & need, Web based design, extended enterprises, enterprise wide product visualization. (02 hrs)
Recommended Books 1) The Finite Element Methods in Engg. - by S.S. Rao 2) The Finite Element Methods in Engg - Reddy, Tata McGraw Hill. 3) The finite Element method - 3td Edition - O.c. Zienkiewicz. Tata McGraw Hill.
4) Concept and Application at finite Element Analysis - R.D. Cook, John Wiley publication 5) CAD/CAM and Autornation by Farazdak Maiden, Nirali Prakashan, Pune. 6) CAD/CAM By . Radhakrishnan, S. Subrarnaniam,
SEMINAR AND INPLANT TRAINING SEMINAR (Term work 25 marks) Seminar: .. Every student either individually or jointly with other students shall work on a topic selected/assigned from any Engineering /allied fields for the seminar of academic and or/industrial interest. He/she should deliver a seminar talk based on the work done by him. His guide will judge his performance and another teacher appointed by the Principal. He/she should submit a seminar report as per the instructions and the format given below: [AI Instructions: 1. Seminar Report shall be typed on A-4 size white bond paper. 2. Typing shall be with spacing of 1.5 or 2.0 using black ribbon or carbon on one side of the Paper . 3. Margins:- (i) Left 37.5 mm. (ii) Right, top and bottom 25 mm. 4. Binding:- Hard with golden embossing on the front cover of blue colour or soft comb binding with transparent front cover and non transparent plastic blue /black cover. 5. Front cover in case of hard bound report: It should be identical to first title page. 6. Format for title page (First Page) Seminar Report On Title of Seminar by Name of student Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Engineering (Production) Department of Production Engineering Name of the college 7. Format for Certification page (i.e. Second page) CERTIFICA TE This is to certify that the Seminar report entitled "Title of Seminar" Submitted by Name of Student is completed as per the requirements of the Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University in partial fulfillment of degree of B.E.(Production) for the Academic Year---------Guide Head of Department Principal 8. The third page would be for acknowledgements which would be followed by index page 9. The mathematical symbol should be typed or neatly written so as to match darkness of the text.
10. The last item on the index should be references.
[B] In plant Training: Every student will submit his training report in the format mentioned in the T.E.(Production) syllabus and will deliver a talk on his in plant training activities. His performance will be judged by his guide and another teacher appointed by the Principal of the institution.
Final Year (Production Engineering) Revised SECOND SEMESTER (PART II) AUTOMATIC CONIROL SYSTEMS (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs. 100 marks. Class Test: 25 marks. Term Work: 25 marks. Practical Exam: 25 marks) 1. Introduction: Basic concepts of Control Systems. Classification- Open Loop and Closed Loop Control Systems. Review of various types of measuring instruments and transducers. important components of a Control System, Definition of Transfer Function.(3 hrs) 2. Representation of Control System Components : Study of various types of Control System Components and their mathematical representations used in systems like Mechanical Systems. Electrical Systems. Thermal Systems, Analogies, fluid Systems, grounded chair representation.(6 hrs) 3. Block Diagram Algebra : Basics, rules for solving block diagrams. solving block diagrams for Liquid Level System, Temperature Control System, Speed Control System,etc (3hrs) 4. Signal Flow Diagram : Concept, masons gain formula, generating a signal flow diagram for a system, solving signal flow diagram to find transfer function. (3hrs) 5. Electrical System: Detail Study of various types of Electrical Motors like DC Servomotors, AC Servomotors, control methods, servo mechanisms, position control systems. (3 hrs) 6. Types of Control Actions. : Introduction to various types of output characteristics and their analysis, Basic types Control Actions like ON/OFF, Proportional, integral, Derivative type and their combinations. Viz., Proportional plus integral. proportional plus Derivative, Proportional plus integral plus derivative type of control actions. (4hrs) .7. Industrial Controllers : Mechanica1, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Controllers of Proportional Plus integral, Proportional Plus Derivative, Proportional plus integral Plus Derivative type of control actions, Mathematical treatment of above controllers. (.4hrs) 8. Response Characteristics : Introduction of various types of Standard input signals commonly Used, Definition of Transient and Steady State Response, Characteristics of First Order Systems when subjected to standard input signals, Transient and Steady state Response.
Characteristics of Second Order Systems, Specifications etc. (6 hrs) 9. Analysis of Frequency Response : Characteristics of Frequency Response of different functions (limited up to Second Order Systems only), Graphical Analysis. Bode Plots, Nyquist (polar) criterion of stability. Rouths Stability Criterion, use of Matlab software. (6 hrs) Term Work 1) Study of Control System Components (at leasr 10 component) 2) .An experiment on Speed Control of a DC Motor. 3) An experiment on Speed Control of an AC Motor. 4) An experiment on Speed Control of a Stepper Motor. 5) An experiment on a Level Control System 6) An experiment on a Temperature Control System. 7) Study of Controller of a one each NC Machine. 8) At least six assignments on chapter no. 2.3,6,7,8 &9.
Practical Examination The Practical examination shall be consist of performing experiment based on the practical work done during the course and Viva - voice based on the syllabus.
Recommended Books 1) Automatic Control Systems - by Nagrath Gopal. 2) Control System Engineering - by Ogatta, PHI 3) Automatic Control Systems - by Francis Raven, McGraw Hill. 4) Feedback Control Systems - S. Bhide, JaIgoankar, TechnovaPublications
Operations Research (One Theory Paper, 3 hrs., marks :100, Class Test: 25 marks, Term Work: 25 marks) 1. Introduction Operations Research: Development, history, definitions, objectives, characteristics, limitations, phases and applications. Optimization models and their classifications. (2 hrs.) 2. Linear Programming: Formulation of LP problem. Basic Solution. Theorems of LP. Graphical method. Simplex method(minimization I maximization cases). Degeneracy in LP. Duality in LP. Sensitivity analysis, Introduction to integer programming, Dynamic Programming and Non- linear programming.(8 hrs) 3. Transportation Problem: Introduction, Methods for finding initial solution, Test of toptimality, Maximization Transportation problem, Transshipment problem, Degeneracy. (4 hrs) 4. Assignment Problem: Introduction. Solution methods, Variations of the assignment problem, Traveling salesman problem.(3 hrs) 5. Sequencing Models: Scheduling and sequencing, Assumptions in sequencing models, Processing 'n' jobs on 'm' machines,Proce3sing of two jobs on machines with each having different processing order.(3 hrs) 6. inventory Control System (Quantitative Approach) : Introduction, Meaning of Inventory Control, Functional classifications of Inventories. Advantages of Inventory Control, Costs associated with Inventories. Advantages of Inventory Control, Deterministic Inventory Models; economic lot size with instantaneous replenishment with and without shortage costs, economic lot size with finite replenishment with and without shortage, economic lot size models with quantity discount. (3 hrs) 7. Replacement Analysis: Displacement Vs Replacement, Methods of replacement analysis, Uniform gradient serious unacost method. (3 hrs) 8. Queuing Theory: Queuing Systems: Introduction, cost associated with characteristics, operating characteristics and probability distribution, Classification of queuing models. Kendalls notations. Models : (M/M/I),Minimum cost service rate. (3 hrs) 9. Theory of Games:
Introduction, two-person zero-sum game, Minimum and Maximum principle, Saddle point, Methods for solving game problems with mixed strategies, Introduction to graphical and iterative models for solving problems. (3 hrs) 10. Network Models: Introduction to PERT/CPM and its importance in project management. Concepts and construction of network diagrams. Critical path and project duration, floats, network crashing, optimum project duration and cost, PERT activity, time estimates:. probability of completion of a project on or before specified time. Updating of project, Resource allocation and load smoothen ing. (6 hrs) 11. Simulation: Simulation: Monte-Carlo Method. (2 hrs)
Term Work Term Work shall consist of at least eight assignments based on the above syllabus. Recommended Books 1. Gupta P.K. and Hira D.S. : Operational Research. S. Chand & Co. Ltd. 2. Gupta P.K. and Hira D.S. : Introduction to Optimization, Jain Brothers. 3. Askhedkar R.D. and Kulkarni R.V. : Operations Research, Dhanpat Raj & Sons. 4. Patel R.C., Dave N.R. & Manglani A.K.: Operations Research, C. Jamnadas & Co. 5. Sharma J.K : Mathematical Models in Operations Research, Tata McGraw - HilI Publishing Co. Ltd. 6. Sharma S.D., KedarNath: Operations Research, Ram Nath & Co. 7. Taha H.A. : Operations Research: An Introduction, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd. 8. Wagner H.N. : Principles of Operations Research with applications to Managerial Decisions, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd. 9. Wiest J.D. & Levy F.K. : Managerial Guide to PERT/CPM, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.
Industrial Engineering (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test :25 marks, Term Work: 25 marks, Practical Exam: 25 marks) I. Introduction: Productivity, definitions of work study, scope, applications, relationship, between productivity & standard of living, basic work content, excess work content, Management, techniques to reduce excess work content due to product process and ineffective time in control of workers and Management- (3 hrs) 2. Work Study: Definition, concept, relation with Productivity, human factors, good relations, work study versus Management, supervisor, work study man, qualities of work study man, working conditions, prevention accidents and hazards. (3 hrs) 3. Method Study: Definition, objectives procedure factors affecting selection of work, recording techniques such as outline process short, flow process chart, factory layout, flow diagrams, developing new layout materials handling its principles and equipment, movement of workers and materials in working area, string diagram and its significance, travel chart, multiple activity chart and their significance Micro motion study, two handed process chart, principles, therbligs, simo chart, cycle graph, and use of limits in method study, MOST (7 hrs) ,4. Work Measurement: Techniques, Pm-pose, use & basic procedure time study equipment selection of jobs for time study, approach to workers, steps in time study, data collection about jobs, operator & surroundings breaking down jobs into elements, types of elements, selection and measurement of each element. (4 hrs) 5. job Evaluation And Merit Rating: Introduction, Different techniques of job evaluation; Merits, Demerits, Techniques of Merit rating, Significance of Job evaluation / merit rating with work measurement. (3 hrs) 6. Time Study Rating And Allowances: Definition of rating, system of rating, wasting house system of rating skill & effort, synthetic rating & objective rating, use of rating factor, rating the job, normalizing observations, types of allowances, applying the allowances. (3 hrs) 7. Other Works Measurement Techniques: Work sampling - need, establishing confidence levels, determination of sample size, ra:1dom observation, conduct of study, use of work sampling. General study of standard data & PMTS. Methods of Improving Materials Productivity, factors affecting materials productivity. Introduction to Business Process Reengineering. (4 hrs)
8. Kaizen : Continuous method improvement, Kaizan concept, Kaizen umbrella for quality improvement. Kaizen and management, implications of QC for Kaizen, kaizen and TQC, Kaizen and suggestion systems, Kaizen and competition, process oriented Management versus result oriented Management, Kaizen and innovation, Kaizen and measurement, PDCA cycle, Kaizen Management. (3 hrs) 9. Single Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED) : Aspects of setup activities, internal and external setup. Fundamentals of SMED, setup improvement, conceptual stages. Techniques for ,streamlining the aspect of set up, effects of SMED. one minute exchange of die (OTED) (5hrs) ,10 Just in Time: Concept, scope, objectives, push & pull system, reduced inventories and improved set up times, source of profit in manufacturing process, TOYOTA production system, basic assumptions of TOYOTA production system, leveling, smoothing out the production system, JIT and automation, workplace control through - the Kaizen system. Customizationofmanufacturing. (5hrs)
Term Work Minimum Eight assignments based on the above syllabus and minimum two experiments based one each on method study and time study. Practical Examination It shall consist of oral based on the term work and the above syllabus.
Recommended Books 1. Introduction to work study - ILO 2 Motion & Time study Design & Measurement of Work - Ralph Barnes (Wiley Eastern) 3 Work Study - R.M. Currie & J. Faraday. (ELBS Pitman) 4 Hand Book of Industrial Engineering - Irson & Grant. 5 Just In Time: David Hukins 6 Kaizen : Shyam. Talwadekar 7 Kaizen : Masaki Imai 8 SMED : Shino Shingo.
Simulation & Mathematical Modeling (One theory paper 100 marks, 3 hrs, Class Test 25 marks, Term 'Work: 25 M3rks) 1. Introduction to Simulation: System and System environment, Components of system, Type of systems, Type of models, Steps in simulation. Study, Advantages and Disadvantages of simulation. Simulation Examples: Simulation of Queuing systems (06 hrs) 2. General Principles: Concepts of discrete event simulation, Time-Advance Mechanisms, Component and Organization of a Discrete-Event Simulation Model (4hrs) 3. Statistical models in Simulation: Useful statistical model, Discrete distribution, Continuous distribution, Poisson process, Empirical distribution. (4hrs) 4. Queuing Models: Characteristics of Queuing systems, Queuing notations, Long run measures of performance of Queuing systems, Steady state behavior of infinite population Markovian models, Steady state behavior finite population model. [04 hrs] 5. Random Number Generation: Properties of random numbers, Generation of pseudo random numbers, Techniques for generating random numbers, Tests for random numbers.[02 hrs] 6. Random Variate Generation: Inverse transform technique, Conv0lution method, Acceptance rejection techniques. [02 hrs] 7. Input Modeling: Data Collection, Identifying the Distribution of data, Parameter estimation, Goodness-of-fit tests, Selection input model without data, Multivariate and Time series input model. [04 hrs] 8. Verification and Validation of Simulation Model: Length of simulation runs, validation [03 hrs] 9.Output Analysis for a Single Model: Types of simulations with respect to output analysis, stochastic nature of output data, Measure of performance and their estimation. Output analysis of terminating simulators, Output analysis for steady state simulation. [06 hrs] 10. Case Studies: Simulation of manufacturing systems, Simulation of inventory control systems, Simulation of pert network. [04 hrs] 11. Simulation Software: GPSS [01hr] TERM WORK Term work should consist of at least 10 Practical experiments and two assignments covering the topics of the syllabus.
Recommended Books 1. Donald W. Body, "System Analysis and Modeling", Academic Press Harcourt India 2. David Kelton, Randall Sadowski, Deborah Sadowski, "Simulation With Arena", McGraw Hill 3. Jerry Banks, John Carson, Barry Nelson, David Nicol, "Discrete Event System Simulation"
Costing And Financial Management (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test: 25 marks, Term-Work: 25 marks) 1. Introduction: Cost, elements of cost, selling price, costing, cost and financial accounting, cost estimate, types,functions, applications, cost unit and cost centers. (3 hrs) 2. Overheads: Definition, types, allocation, depreciation, methods of depreciations, calculations of machine hour rates, indirect labor and organizational size. (4 hrs) 3. Tooling cost: Elements of tooling cost, comparison of different toolings, selection of best tooling, shop orders.NC tapes as tooling. (3 hrs) 4. Equivalence and cost comparison: Time valve of money, unacost, capitalized cost; cost comparison with equal duration, unequal duration by present worth, unacost and capitalized cost method. (5 hrs) 5. Break Even Analysis: Break even point, Economic production. chart, Economic production chart above 100 % capacity, Economic production chart with dumping, Nonlinear break even chart, contribution to sales ratio, Profit path chart, margin of safety. (5hrs) 6. Displacement analysis: Displacement Vs Replacement, uniform gradient series, Best policy with uniform Gradient series Unacost method, burden, unburden. (3 hrs) 7. Cost estimate and review: Parts Explosion diagram, estimating material cost, estimating labor cost, making an Initial cost estimate, cost sheet, cost review grid, cost estimate sheet. (5 hrs) 8. Cost control: Cost control. cost reduction, capital cost control, elements of cost control programme, project planning and scheduling, cost reporting corrective action. Operating cost control: Repetitive nature, standard cost, cost reporting and corrective action. (4 hrs) 9. Budgeting: Budget, definition, importance, types of budgets, fixed, variable, sales, production, capital expenditure. materials and purchase, direct labor, cash master, introduction to budgetary control.(5 hrs) 10 Finance management: Investment capital, types, sources of finance. financial accounting. Introduction to profit loss account, balance sheet, financial rations. (3 hrs)
Term Work Term work will consist of at least eight assignments based on the above syllabus. Recommended Books 1.Cost And Optimization Engineering - F. C. Jelen (McGraw Hill). 2. Manufacturing cost Engineering Hand book - Edited by E. M. Malstrom, Mare! Dekkan Inc. 3. Accounting and Financial Management - A.M. Pandey. 4 IndustrialEngineering and Management - O.P. Khanna. 5. Cost & Management Accounting by S. N. Inamdar, Everest Pubishing House.
DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTATION (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test: 25 marks, Term work: 25 marks) 1. Introduction: Quality: eight dimensions of quality, Customer satisfaction and Quality concept of TQM, TQM axioms, consequences, Key elements of TQC, Two dimensional of quality, TQM Philosophies of Deming, Juran, P. Crosby, lmai, Ishikawa, Conway. (3 hrs) 2. Tools for Quality Improvement: Alternate Process Control: Cusum control chart, chart for drifting process, multi-vari charts, precontrol. tools, Benchmarking. Quality Circles, The PDCA cycle, Hoshin kanri Plan. (4 hrs) 3. Quality Function Development: Concept and defining QFD, product deployment system, QFD process, QFD matrix concept. Deployment- part, process. T -type matrix. (3 hrs) 4. ISO 9000 : Concepts, methods and implementation. Quality management practices world wide, Quality, Customers and ISO 9000, Company quality policy, interpretation of Key ISO 9000 clauses, Implementing ISO 9000, Indian equivalent for ISO 9000. The ISO 9001 :2000, standard steps for certification under IS0900 1: 2000.(4 hrs) 5. Introduction to design of experimentation: Taguchi loss function, desire for low loss, factory tolerance, other loss functions.(3 hrs) 6. Analysis of Variance: Variation, No-way, One-way, Two-way, three way analysis of Variances. (ANOVA)(5 hrs) 7. Orthogonal Array Design: Meaning;, necessity, one factor experiment, several factors one at a time, several factors all at the same time, Test strategies. Better test strategies, efficient test strategies step in designing, conducting and analyzing an experiment. (6 hrs) 8. Multi level Experiment: Introduction, necessity, conversion from two to four levels, ANOVA for four level factors, polynomial decomposition, multiple level factor interactions, dummy treatment for three level factors, ANOVA for dummy treatment. (4 hrs) 9. Interpretation of Experimental Results: Interpretation Methods : Present Contribution, estimating the mean, confidence interval around the estimation mean, Omega transformation of data. (4 hrs) 10. Parameters & Tolerance Design:
lntroduction, control and noise factor. Signa1 to Noise ratio Parameters design strategy, Analysis of inner /outer array experiment, Tolerance design, quality Counter measures, steps in experimentation (4hrs)
Term Work: Term work shall consist of at least eight assignments based on the above syllabus. Recommended Books: 1.Quali!y Planning and Analysis J.M, Juran, Frank M, Gryna. 2 Total Quality Management Logothetis 3. Total Quality Management- Banks 4. Total Quality Control Essentials- Sarv singh Soin 5. Taguchi Techniques for Quality Engg.- Phillip J. Ross, Mc Graw Hill Ltd.
Non Conventional Machining Processes (One Theory Paper: 3 hrs, 100 marks, Class Test: 25 marks, Term Work: 25 marks) I. Tool Technology: - Tool wear and failure: Mechanism of tool wear, measurement of tool wear, tool failure criterion, effect of process parameters on tool life, tool life tests, and tool life improvement by various coatings. New development in tool materials. (3 hrs) 2. Introduction: - Need for non-conventional machining processes, process selection, classification,comparative study of different processes. (2 hrs) 3. Mechanical Processes: - Ultrasonic machining: - Definition, mechanism of metal removal, elements of the processes, tool feed mechanism, theories of mechanism of cutting, effect of parameters, applications and numericals. (4 hrs) 4. Abrasive Jet Machining: - Principle, parameters of the process, applications, advantages ,disadvantages, numericals. (4 hrs) 5. Thermal metal removal processes: - Electric Discharge Machining - principle of operation, mechanism of metal removal, basic EDM circuitry, spark erosion generators, analysis of relaxation type circuit, material removal rate in relaxation circuit, critical resistance parameters in Ro circuits, dielectric fluids, application and numericals. (8 hrs) 6. Electrochemical and chemical processes: - Electrochemical Machining (ECM), classification of ECM process, principle of ECM process, chemistry of the ECM processes, Parameters of the process, determination of the metal removal rate, dynamics of EC~ process, polarization, tool design, advantages and disadvantages, application, electrochemical grinding, Electrochemical honing, Electrochemical deburing. Chemical machining:- Introduction, fundamental principle, types of chemical machining, maskants, etchants, advantages, disadvantages, applications. (6 hrs) 7. Plasma Arc Machining:-Introduction, plasma, general .ion of plasma and equipments, mechanism of metal removal, PAM Parameters, process characteristics, types of torches, applications.(3hrs) 8. Electro Beam Machining (EBM):- Introduction, equipment for production of Electron Beam, theory of EBM, thermal and non-thermal type, process characteristics, applications. (4 hrs) 9. LASER Beam Machining (LBM):- Introduction principle of generation of LASER, equipment and machining procedure, types of lasers, process characteristics, advantages and limitations,applications. (4 hrs) 10. Ion Beam Machining:- Introduction, Mechanism of metal removal and associated equipments,process characteristics and applications. (2 hrs)
Term Work. The Term work shall consist of at least eight assignments based on above syllabus and demonstration of AJM / ECM / LBM /EDM at least any two types of the processes.
Recommended Books 1. HMT "Production technology" 2. Bhattacharya:- "New technology Institution Of Engineers 3. Ghosh. MaIlik:- '"Manufacturing Science"- Everest Publications 4. P.C. Pandey and HS. Shah: - "Modern Machining Processes~" Tata McGraw Hill 5 V. K. Jain Advanced Machining Processes-;. Allied Publishers
Project (Term work 50 marks, Practical Examination 100 marks) Every student or group of students should undertake a project work under the guidance of a teacher. The project work could be a theoretical work on trouble shooting, design development and fabrication of prototype /model (wherever necessary). THE STUDENT/S SHOULD GET HIS/THEIR TOPIC OF THE PROJECT APPROVED FROM THE PRINCIPAL IN THE FIRST TERM ONLY. The report of the project, in duplicate, should be submitted by every student as per the instructions and in the format given below: Instructions: 1. The project report shall be typed on A-4 size white bond paper. 2. Typing shall be with spacing of 1.5 or 2.0 using black ribbon or carbon on one side of the paper. 3. Margins:- (i) Left 37.5 mm. (ii) Right, top and bottom 25 mm. 4. Binding:- Hard with golden embossing on the front cover of blue colour or soft comb binding with transp8.rent front cover and non transparent plastic blue/black cover. 5. From: cover in case of hard bound report: It should be identical to first title page. 6. Format for title page (First Page) Report of the project on (Title of Project) by (Name of student) Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Engineering (Production) Department of Production Engineering (Name of the college) 7. Format for Certification page (i.e. Second page) CERTIFICATE This is to certify that the project entitled "Title of Project" Submitted by (Name of Student/s) . is completed as per the requirements of the Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University in partial fulfillment of degree of B.E.(Production) For the academic year-------Guide Head of Department Principal 16. The last item on the index should be references 8. The third page would be for acknowledgements which would be followed by index page/so 13. Sketches should be drawn on separate sheet (minimum A4 size) and be inserted at proper places. The sketches should be drawn in black ink and be numbered.
14. Tables should preferably typed in the text only. 15. The mathematical symbol should be typed or neatly written so as to match darkness of the text. 16. The last item on the index should be references
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Introduction To Convective Heat Transfer Analysis Chapter 8 PDFDocument84 pagesIntroduction To Convective Heat Transfer Analysis Chapter 8 PDFhenrengPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-4 Lesson 2 Key Concept Builder #35 and 37 Ws 2Document3 pagesCh-4 Lesson 2 Key Concept Builder #35 and 37 Ws 2Kevin Farfan0% (1)
- Ch13 Rigid BodiesDocument23 pagesCh13 Rigid Bodiesakshaybj4396Pas encore d'évaluation
- FoodDocument33 pagesFoodakshaybj43960% (1)
- AutomobileDocument33 pagesAutomobilemarinerajesh3022Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 15Document7 pagesCH 15akshaybj4396Pas encore d'évaluation
- GearboxDocument5 pagesGearboxakshaybj4396100% (1)
- Solar Energy Storage MethodsDocument3 pagesSolar Energy Storage Methodsakshaybj4396Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tube Bending MachineDocument1 pageTube Bending Machineakshaybj4396Pas encore d'évaluation
- B.E Mechnical2009Document64 pagesB.E Mechnical2009akshaybj4396Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pie ChartDocument1 pagePie Chartakshaybj4396Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pie ChartDocument1 pagePie Chartakshaybj4396Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vilter Refrigeration Piping Data Manual en US 5419418 02Document89 pagesVilter Refrigeration Piping Data Manual en US 5419418 02AmmoniaR717Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Week 2Document4 pagesAssignment Week 2Victor LoongPas encore d'évaluation
- Fork Oil PDFDocument12 pagesFork Oil PDFGabor SzollosiPas encore d'évaluation
- Vertical Inline Centrifugal Pump Troubleshooting GuideDocument4 pagesVertical Inline Centrifugal Pump Troubleshooting Guideadepp8642Pas encore d'évaluation
- EGN 3353C Fluid Mechanics: P P P GHDocument7 pagesEGN 3353C Fluid Mechanics: P P P GHSumantri HatmokoPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Seminar PPT-3 3Document26 pagesFM Seminar PPT-3 3Sharafat MushtaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Ingeniería de Mantenimiento: Roberto Carlos Rojas Molina, PHDDocument39 pagesIngeniería de Mantenimiento: Roberto Carlos Rojas Molina, PHDRichard PucaPas encore d'évaluation
- SE Lecture 6Document8 pagesSE Lecture 6666667Pas encore d'évaluation
- Backup of FLOW COMPUTATION FORMULASDocument17 pagesBackup of FLOW COMPUTATION FORMULASRefisa JiruPas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Actuated Flaps For Passive Flow Separation ControlDocument5 pagesSelf-Actuated Flaps For Passive Flow Separation ControlInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 17Document57 pagesChap 17Saeed ullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Nozzles and Jet PropulsionDocument25 pagesNozzles and Jet PropulsionPierce Hardin100% (1)
- Numerical Solutions of Viscous Flow Through A Pipe Orifice Al Low Reynolds NumbersDocument8 pagesNumerical Solutions of Viscous Flow Through A Pipe Orifice Al Low Reynolds NumbersozkenePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid-Mechanics SyllabusDocument8 pagesFluid-Mechanics SyllabusMarky SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Side Channel Pumps /: Data Sheet Data SheetDocument4 pagesSide Channel Pumps /: Data Sheet Data SheetJason Wei Han LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Efficient Selection of Agitators: Sulzer PumpsDocument2 pagesEfficient Selection of Agitators: Sulzer PumpsjokishPas encore d'évaluation
- Waterous Manual FireDocument268 pagesWaterous Manual FireChristian NkomayombiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pump IntakeDocument6 pagesPump IntakeAnonymous CMS3dL1T100% (1)
- CatalogDocument129 pagesCatalogdvarsastryPas encore d'évaluation
- VOF Methods PDFDocument6 pagesVOF Methods PDFentertainpurpPas encore d'évaluation
- Highlights in The History of Hydraulics ROUSEDocument16 pagesHighlights in The History of Hydraulics ROUSEAlberto Polo CuetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Investigations of The Convective Heat Transfer From Turbulent Flow Over Staggered Tube BankDocument11 pagesNumerical Investigations of The Convective Heat Transfer From Turbulent Flow Over Staggered Tube BankYasser AlrifaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Teddy Ardiansyah - Study On Sodium Cavitation For Fast Reactors (III) Analysis of Cavitation With FLUENT and Erosion ExperimentDocument20 pagesTeddy Ardiansyah - Study On Sodium Cavitation For Fast Reactors (III) Analysis of Cavitation With FLUENT and Erosion ExperimentmedianuklirPas encore d'évaluation
- The Integral Forms of The Fundamental Laws - 2Document24 pagesThe Integral Forms of The Fundamental Laws - 2Jenille C. VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pagesFluid MechanicsAnthony MacalindongPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic-Wise GATE1Document32 pagesTopic-Wise GATE1CHHAVI AGARWAL0% (1)
- Tutorial: Turbulent Flow in A Compact Heat Exchanger: C ANSYS, Inc. March 6, 2012Document15 pagesTutorial: Turbulent Flow in A Compact Heat Exchanger: C ANSYS, Inc. March 6, 2012wasemPas encore d'évaluation
- Generalized Water Hammer Algorithm For Piping Systems With Unsteady Friction PDFDocument115 pagesGeneralized Water Hammer Algorithm For Piping Systems With Unsteady Friction PDFHugo RuizPas encore d'évaluation