Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
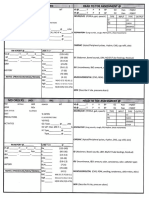
Area Technique Normal Findings Analysis and Interpretation A. Skull
Transféré par
kingawesome21Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Area Technique Normal Findings Analysis and Interpretation A. Skull
Transféré par
kingawesome21Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AREA A. SKULL 1. Size, shape and symmetry of the skull 2. Presence of nodules, masses, and depressions 3.
Facial Features 4. Presence of edema and hollowness in the eye. B. HAIR 1. Evenness of growth, thickness, or thinness of hair 2. Texture and oiliness over the scalp 3. Presence of infection and infestation C. FACE Facial features, symmetry of facial movements
TECHNIQUE Inspection Palpation Palpation Inspection Inspection Palpation Inspection
NORMAL Rounded (normocephalic and symmetrical, with frontal, parietal, and occipital prominences); Smooth skull contour Smooth, uniform consistence; absence of nodules or masses Symmetric or slightly asymmetric facial features; palpebral fissure equal in size; symmetric nasolabial No edema and hollowness
FINDINGS
ANALYSIS and INTERPRETATION
Inspection Palpation Inspection Palpation Inspection Palption Inspection
Evenly distributed and covers the whole scalp; Maybe thick or thin Silky; resilient hair No infection and infestation
Symmetric or slightly asymmetric facial features; palpebral fissures equal in size; symmetric nasolabial folds
IV. EYES A. EYEBROWS Hair distribution, alignment, skin quality and movement B. EYELASHES Evenness of distribution and direction of curl C. EYELIDS Surface characteristics and position (in relation to the cornea, ability to blink, and frequency of blinking) D. CONJUNCTIVA 1. Color, texture, and the presence of lesions in the bulbar conjunctiva 2. Color, texture, and the presence of lesions in the palpebral conjunctiva E. SCLERA Inspection Symmetrical and in line with each other; maybe black, brown or blond depending on race; evenly distributed Evenly distributed; turned outward
Inspection Palpation Inspection
Upper eyelids cover the small portion of the iris, cornea, and sclera when eyes are open; eyelids meet completely when the eyes are closed; symmetrical Pinkish or red in color; with presence of small capillaries; moist; no foreign bodies; no ulcers Pinkish or red in color; with presence of small capillaries; moist; no foreign bodies; no ulcers
Inspection Palapation Inspection Palpation
Color and clarity F. CORNEA Clarity and texture G. IRIS Shape and color H. PUPILS 1. Color, shape, and symmetry of size 2. Light reaction and accommodation I. VISUAL ACUITY 1. Near vision J. LACRIMAL GLAND Palpability and tenderness of the lacrimal gland K. EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES Eye alignment and coordination L. VISUAL FIELDS Peripheral visual fields V. EARS A. AURICLES 1. Color, symmetry of size, and position 2. Texture, elasticity and areas of tenderness C. HEARING ACUITY TESTS 1. Clients response to normal voice tones VI. NOSE 1.Any deviations in shape, size, or color and flaring or discharge from the nares 2. Nasal septum (between the nasal chambers) 3. Patency of both nasal cavities 4. Tenderness, masses, and displacements of bone and cartilage
Inspection
White in color; clear; no yellowish discoloration; some capillaries maybe visible No irregularities on the surface; looks smooth; clear or transparent Anterior chamber is transparent; no noted visible materials; color depends on the persons race
Inspection
Inspection
Inspection Inspection Inspection Palpation
Color depends on the persons race; size ranges from 3-7 mm, and are equal in size; equally round Constrict briskly/sluggishly when light is directed to the eye, both directly and consensual Able to read newsprint or snellen chart No edema or tenderness over lacrimal gland
Inspection Inspection
Both eyes coordinated, move in unison, with parallel alignment When looking straight ahead, client can see objects in the periphery
Inspection Palpation
Color same as facial skin; symmetrical; auricle aligned with outer canthus of eye, about 10 degrees from vertical Mobile, firm, and not tender; pinna recoils after it is folded Normal voice tones audible Symmetric and straight; no discharge or flaring; Uniform color Nasal septum intact and in midline Air moves freely as the client breathes through the nares Not tender; no lesions
Inspection Inspection Inspection Palpation Inspection Palpation
VII. SINUSES Identification of the sinuses and for tenderness VIII. MOUTH A. LIPS Symmetry of contour, color and texture B. BUCCAL MUCOSA Color, moisture, texture, and the presence of lesions C. TEETH Color, number and condition and presence of dentures D. GUMS Color and condition E. TONGUE/FLOOR OF THE MOUTH 1. Color and texture of the mouth floor and frenulum. 2. Position, color and texture, movement and base of the tongue 3. Any nodules, lumps, or excoriated areas F. PALATES and UVULA 1. Color, shape, texture and the presence of bony prominences 2. Position of the uvula and mobility (while examining the palates) Inspection Palpation Inspection Uniform pink color; soft, moist, smooth texture; symmetry of contour; ability to purse lips Uniform pink color; moist, smooth, soft, glistening, and elastic texture Inspection Not tender
Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection Palpation Inspection Inspection Palpation Inspection
32 adult teeth; smooth, white, shiny tooth enamel; smooth, intact dentures Pink gums; no retraction pink color; moist; slightly rough; thin whitish coating; moves freely; no tenderness Central position; pink color; smooth tongue base with prominent veins Smooth with no palpable nodules, lumps, or excoriated areas Light pink, smooth, soft palate; lighter pink hard palate , more irregular texture Positioned in midline of soft palate
G. OROPHARYNX and TONSILS 1. Color and texture 2. Size, color, and discharge of the tonsils 3. Gag reflex X. THORAX A. ANTERIOR THORAX 1. Breathing patterns
Inspection Inspection Inspection
Pink and smooth posterior wall Pink and smooth; no discharge; of normal size Present
Inspection
Quiet, rhythmic, and effortless respirations
2. Temperature, tenderness, masses 3. Anterior thorax auscultation B. POSTERIOR THORAX 1. Shape, symmetry, and comparison of anteroposterior thorax to transverse diameter 2. Spinal alignment 3. Temperature, tenderness, and masses 7. Posterior thorax auscultation XI. CARDIOVASCULAR A. AORTIC and PULMONIC AREAS B. TRICUSPID AREA C. APICAL AREA D. EPIGASTRIC AREA E. CARDIOVASCULAR AREAS AUSCULTATION
Palpation Auscultation Inspection Palpation Inspection Palpation Auscultation
Skin intact; uniform temperature; chest wall intact; no tenderness; no masses Bronchovesicular and vesicular breath sounds Anteroposterior to transverse diameter in ratio 1:2; Chest symmetric Spine vertically aligned Skin intact; uniform temperature; chest wall intact; no tenderness; no masses Vesicular and bronchovesicular breath sounds
Auscultation Auscultation Auscultation Auscultation Auscultation
No pulsations No pulsations; no lift or heave Pulsations visible in 50% of adults and palpable in most PMI in fifth LICS at or medial to MCL Aortic pulsations S1: Usually heard at all sites Usually louder at the apical area S2: Usually heard at all sites Usually louder at the base of heart Systole: silent interval; slightly shorter duration than diastole at normal heart rate (60 to 90 beats/min) Diastole: silent interval; slightly longer duration than systole at normal heart rates S3: in children and young adults S4: in many older adults
XII. CAROTID ARTERIES 1. Carotid artery palpation
Palpation
Symmetric pulse volumes; full pulsations, thrusting quality; quality remains same when the client breathes, turns head, and changes from sitting to supine position; elastic arterial wall No tenderness, masses, or nodules
XIV. AXILLAE 1. Axillary, subclavicular, and supraclavicular lymph nodes XV. ABDOMEN 1. Skin integrity 2. Abdominal contour 3. Enlargement of liver or spleen
Inspection
Inspection Inspection Inspection
Unblemished skin; uniform color Flat, rounded(convex), or scaphoid(concave) No evidence of enlargement of liver or spleen
4.Symmetry of contour 5. Abdominal movements associated with respirations, peristalsis or aortic pulsations 6. Vascular pattern XVI. MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM A. MUSCLES 1. Muscle size and comparison on the other side 2. Fasciculation and tremors in the muscles 3. Muscle tonicity 4. Muscle strength C. JOINTS 1. Joint swelling EXTREMETIES
Inspection Inspection Inspection
Symmetric contour Symmetric movements caused by respiration; visible peristalsis in very lean people; aortic pulsations in thin persons at epigastric area No visible vascular pattern
Inspection Inspection Palpation Palpation Inspection Inspection, Palpation
Proportionate to the body; even in both sides No fasciculation and tremors Even and firm muscle tone Has equal muscular strength on both sides No swelling, no warmth, no redness, no pain, no crepitus No swelling, no warmth, no redness, no pain.
Neurologic Assessment: Category Mental Status Level of Consciousness Orientation Language test Recall Alert Oriented Coherent Able to remember Normal Findings Actual Findings Analysis and interpretation
Cranial Nerves CN 1 Olfactory CN 11 Optic Able to smell and recognize stimuli 20x20 vision, able to read, 3-5 mm [pupil size]
CN III, IV, VI Occulomotor Trochlear Abducens
(+) Extraoccular Movement (EOM); Lateral Upward and downward; pupils reactive to light.
CN V Trigeminal
Able to feel and clearly identify stimulus, with bilateral facial sensation. With active corneal reflex. (+) Corneal reflex , Facial asymmetry
CN VII Facial CN VIII Vestibulocochlear Able to hear clearly, can maintain balance
CN IX, X Glossopharyngeal Vagus CN XI Accessory (Spinal)
(+) gag reflex, uvula at the center, soft palate rises Able to shrug shoulders against resistance and able to turn the head side and against resistance. Able to move tongue from side to side
CN XII Hypoglossal
Muscle Strength Left Arm
MNT Grading System: (+5) Active motion against full resistance (+5) Active motion against full resistance (+5) Active motion against full resistance (+5) Active motion against full resistance
Right Arm Left Leg Right Leg
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Reducing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Jails: Recommendations For Local PracticeDocument64 pagesReducing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Jails: Recommendations For Local PracticeThe Brennan Center for JusticePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP & FdarDocument3 pagesNCP & Fdarkingawesome21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Buddhist Concept of HappinessDocument11 pagesBuddhist Concept of HappinessTharaka Nadeeshan100% (1)
- Complete Assessment Script UpdatedDocument5 pagesComplete Assessment Script UpdatedMichael-Ethel LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Head To Toe BrainDocument1 pageHead To Toe BrainDean WinchesterPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes on Nursing - What It Is, and What It Is Not: With a Chapter From 'Beneath the Banner, Being Narratives of Noble Lives and Brave Deeds' by F. J. CrossD'EverandNotes on Nursing - What It Is, and What It Is Not: With a Chapter From 'Beneath the Banner, Being Narratives of Noble Lives and Brave Deeds' by F. J. CrossPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts To Be Assessed Technique Normal Findings Actual Findings Remarks Interpretation General AppearanceDocument8 pagesParts To Be Assessed Technique Normal Findings Actual Findings Remarks Interpretation General AppearanceJulius Balingit100% (1)
- Physical Assessment: Assessment Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal FindingsDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment: Assessment Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal FindingsJosal SinonPas encore d'évaluation
- Conduct of Physical Examination: I. General SurveyDocument10 pagesConduct of Physical Examination: I. General SurveyWeng RamojalPas encore d'évaluation
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument3 pagesHead To Toe Assessmentjeraldine marceraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical AssessmentDocument29 pagesPhysical AssessmentTheSweetpea501100% (1)
- Physical Examination Evaluation Format: Patient's ProfileDocument6 pagesPhysical Examination Evaluation Format: Patient's Profileyangi dokaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Appearance: Ital SignDocument4 pagesGeneral Appearance: Ital SignLiza Estrabo100% (1)
- FDARDocument17 pagesFDARLylibette Anne CalimlimPas encore d'évaluation
- (Murag Ga Tinan - Away Ra Ta Ani Na Part From # 1-4) : Appearance and BehaviourDocument3 pages(Murag Ga Tinan - Away Ra Ta Ani Na Part From # 1-4) : Appearance and BehaviourKaissa GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Skill ScriptDocument12 pagesClinical Skill Scriptannoying fuckerPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Assessing Female and Male Genitourinary SystemDocument7 pagesFinal Assessing Female and Male Genitourinary SystemJo Marchianne PigarPas encore d'évaluation
- Gordons Case Pres 1Document5 pagesGordons Case Pres 1JM Asentista0% (1)
- Downtime Daily Nursing Assessment & Care Plan: 1 of 5 Date: TimeDocument5 pagesDowntime Daily Nursing Assessment & Care Plan: 1 of 5 Date: TimerupaliPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM112 LP1 Transes - RosalesDocument4 pagesNCM112 LP1 Transes - RosalesChristine CalleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessing Neurologic FunctionsDocument10 pagesAssessing Neurologic FunctionsDenise DizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular (CVS) Examination: Procedure StepsDocument15 pagesCardiovascular (CVS) Examination: Procedure StepsGeorich NarcisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gordon S Functional Health Pattern Assessment ToolDocument10 pagesGordon S Functional Health Pattern Assessment ToolMiguel VicentePas encore d'évaluation
- Current Medical Treatment On BPHDocument33 pagesCurrent Medical Treatment On BPHDeviruchi GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Pead 3 - Abdominal Pain and VommitingDocument22 pagesPead 3 - Abdominal Pain and Vommitingbbyes100% (1)
- Ostomias PDFDocument17 pagesOstomias PDFRicardo Uzcategui Arregui100% (1)
- Review 2Document12 pagesReview 2Christine Rubio100% (1)
- Abdominal Examination ProcedureDocument5 pagesAbdominal Examination ProcedureAnamul hossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Catherization Insertion and Removal of An Indwelling Catheter DateDocument2 pagesCatherization Insertion and Removal of An Indwelling Catheter DatecarlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical AssessmentDocument90 pagesPhysical AssessmentReann LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Sample of Medical and Surirgical NursingDocument8 pagesSample of Medical and Surirgical NursingMounir ChadliPas encore d'évaluation
- Bedside Nurse: Name of Student: Jela Mae V. Pates Score: - /25Document8 pagesBedside Nurse: Name of Student: Jela Mae V. Pates Score: - /25janna mae patriarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Assessment ChecklistDocument3 pagesPhysical Assessment ChecklistIsang ButaPas encore d'évaluation
- Head To Toe Assessment WorksheetDocument7 pagesHead To Toe Assessment WorksheetNina Klairea PaduaPas encore d'évaluation
- History and Physical Exam Skills List: Opening VisitDocument7 pagesHistory and Physical Exam Skills List: Opening VisitAnonymous Sfcml4GvZPas encore d'évaluation
- ASSESSMENT FORM: Spring 2006 Client's Number: InstructionsDocument6 pagesASSESSMENT FORM: Spring 2006 Client's Number: Instructionsdenisemw88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sree Vasantham Hospital, Salem: 1. Er Protocol For Acute Intoxication (Poisoning)Document7 pagesSree Vasantham Hospital, Salem: 1. Er Protocol For Acute Intoxication (Poisoning)Elango MuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Vital Signs 1Document2 pagesVital Signs 1carlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Adult Assessment Tool 2014 (GOOD)Document4 pagesAdult Assessment Tool 2014 (GOOD)Basinga Okinam100% (1)
- Abdomenal Exam HandoutDocument5 pagesAbdomenal Exam HandoutNesma AdelPas encore d'évaluation
- Weebly Head To Toe AssessmentDocument3 pagesWeebly Head To Toe Assessmentapi-608265381Pas encore d'évaluation
- Newborn Assessment, Apgar & Ballard Scoring NotesDocument3 pagesNewborn Assessment, Apgar & Ballard Scoring NotesAshitakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genitourinary Assessment: Jan Bazner-Chandler RN, MSN, CNS, CPNPDocument27 pagesGenitourinary Assessment: Jan Bazner-Chandler RN, MSN, CNS, CPNPJason Nisky100% (1)
- Complete Normal Physical Exam PDFDocument3 pagesComplete Normal Physical Exam PDFFrancisco Casio MataPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 116 - Nursing Care of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionDocument11 pagesNCM 116 - Nursing Care of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionRigel Kent C. TobiasPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are Febrile Convulsions?Document16 pagesWhat Are Febrile Convulsions?Redgina CalimlimPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurses Note DONEDocument1 pageNurses Note DONEjhenssinePas encore d'évaluation
- Physical ExamDocument3 pagesPhysical Examinah krizia laguePas encore d'évaluation
- Sampleresponseletters PDFDocument4 pagesSampleresponseletters PDFlevanah87369Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MapDocument6 pagesConcept Mapapi-499028250Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Examination Techniques and ManueversDocument160 pagesPhysical Examination Techniques and ManueversMa-anJaneDiamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessing Female Genitourinary SystemDocument6 pagesAssessing Female Genitourinary SystemJo Marchianne PigarPas encore d'évaluation
- Charting Terminology 2Document11 pagesCharting Terminology 2Danielle ShullPas encore d'évaluation
- An Easy Guide To Head To Toe Assessment Vrtis 12 2008 WebsiteDocument6 pagesAn Easy Guide To Head To Toe Assessment Vrtis 12 2008 WebsiteGary Cochran100% (1)
- NURS 225V Principles III Data Collection ToolDocument2 pagesNURS 225V Principles III Data Collection ToolKrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Case PresentationDocument30 pagesCase PresentationAmira HelayelPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Dummy ChartDocument4 pagesNursing Dummy Chartis_aradanasPas encore d'évaluation
- Head-To-Toe Checklist: Beautiful Nursing LLCDocument4 pagesHead-To-Toe Checklist: Beautiful Nursing LLCcarlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bates Physical Exam Video NotesDocument3 pagesBates Physical Exam Video Notesdulcedeleche12359Pas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Review of Systems: General, Constitutional Heart and Cardiovascular Hematologic/LymphaticDocument1 pageMedical Review of Systems: General, Constitutional Heart and Cardiovascular Hematologic/LymphaticBola S-SPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing TheoriesDocument5 pagesNursing TheoriesThuganamix100% (19)
- Instruction: Indicate The Appropriate Numerical Rating Using The Label BelowDocument10 pagesInstruction: Indicate The Appropriate Numerical Rating Using The Label Belowkingawesome21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aaa SN PsycDocument2 pagesAaa SN Psyckingawesome21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stroke: Brain Attack and Acute Ischemic Cerebrovascular Syndrome (Modeled AfterDocument15 pagesStroke: Brain Attack and Acute Ischemic Cerebrovascular Syndrome (Modeled Afterkingawesome21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ownership Data: InstallationDocument2 pagesOwnership Data: InstallationRoshin99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) Faqs: Why Is TKN Important?Document4 pagesTotal Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) Faqs: Why Is TKN Important?dsbishtPas encore d'évaluation
- Metrel D.D. - Class A Power Quality AnalysersDocument7 pagesMetrel D.D. - Class A Power Quality AnalysersMonster LifePas encore d'évaluation
- Nuñez Survey InstrumentDocument3 pagesNuñez Survey InstrumentAnna Carmela NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Unidajump2019,+6 +djunaediDocument10 pagesUnidajump2019,+6 +djunaeditri septianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuji FCR 5000Document435 pagesFuji FCR 5000Lion Micheal OtitolaiyePas encore d'évaluation
- Form 1 Nutrition in Animals A Teacher - Co .KeDocument6 pagesForm 1 Nutrition in Animals A Teacher - Co .Kelydiaciru01Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Neurovascular Bundle of The Anterior Compartment ofDocument30 pagesThe Neurovascular Bundle of The Anterior Compartment ofAnnapurna Bose100% (2)
- 5 - DystociaDocument43 pages5 - DystociaMara Medina - BorleoPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Ethics ANSWERSDocument3 pagesBusiness Ethics ANSWERSMỹ HàPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Waste Management in SchoolsDocument32 pagesSolid Waste Management in SchoolsRusty TorioPas encore d'évaluation
- C1 - C7 General Requirements For Equipment ErectionDocument24 pagesC1 - C7 General Requirements For Equipment ErectionephPas encore d'évaluation
- O Feci : (BL (ElDocument107 pagesO Feci : (BL (ElKaren Elsy Gonzales CamachoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ayurvedic and Naturopathic Way of Life by Manthena Sathyanarayana RajuDocument7 pagesAyurvedic and Naturopathic Way of Life by Manthena Sathyanarayana RajuvishnuprakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Detector Bump Test Record Log Sheet: Bump Test Result Test Date Time Pass Fail Retest Pass Retest Fail Tester NameDocument2 pagesGas Detector Bump Test Record Log Sheet: Bump Test Result Test Date Time Pass Fail Retest Pass Retest Fail Tester NameAndry Kurnia100% (2)
- KM Ebook 15FatLossStrategiesDocument18 pagesKM Ebook 15FatLossStrategiesfoof faafPas encore d'évaluation
- LeRoy v. United States of America - Document No. 3Document5 pagesLeRoy v. United States of America - Document No. 3Justia.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Cutting Data For Plain Surface: DegrosareDocument4 pagesSummary of Cutting Data For Plain Surface: DegrosareAndrei MihaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Levels of The Psyche and Archetypes of JungDocument2 pagesLevels of The Psyche and Archetypes of JungPeperonii100% (1)
- Starbucks - Strategic ManagementDocument31 pagesStarbucks - Strategic ManagementharshmarooPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Building Construction Types - Firefighter Nation PDFDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Building Construction Types - Firefighter Nation PDFRakeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Cast Metal RestorationDocument48 pagesCast Metal RestorationRosa Faraon EspeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrolyte & Acid Base Disturbances in Diabetes MellitusDocument12 pagesElectrolyte & Acid Base Disturbances in Diabetes MellitusAla SoroceanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategies From Functional AnalyticDocument7 pagesStrategies From Functional AnalyticSantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide in Filling Up The Competency Assessment FormDocument5 pagesGuide in Filling Up The Competency Assessment FormJOSEPH CAJOTEPas encore d'évaluation
- July 16, 2016Document12 pagesJuly 16, 2016The Delphos HeraldPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Advances in Natural Polymer-Based Drug Delivery SystemsDocument18 pagesRecent Advances in Natural Polymer-Based Drug Delivery SystemsTelmoPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Banks Retail Forex DealersDocument7 pagesCentral Banks Retail Forex DealersBCom HonsPas encore d'évaluation