Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
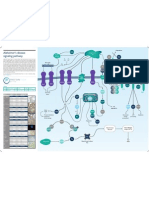
BRCA Signaling Pathway Poster
Transféré par
Proteintech GroupDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
BRCA Signaling Pathway Poster
Transféré par
Proteintech GroupDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ubiquitination DNA repair Mitotic Spindle assembly
Estrogen inducible genes
Transcriptional regulation
Homologus recombination
DNA damage Expression of IFN gene targets
ER- Mismatch repair X-Chromosome silencing
H et er
Homologous recombination
Chromatin remodelling
im od en isa tio n
+P
DNA damage response gene
Nonhomologous end joining
Growth gene transcription / gene transformation
Growth arrest + DNA repair genes
DNA repair/ Homologous recombination
cell cycle
The BRCA pathway is essential for maintaining genome integrity in multicellular organisms; it responds to DNA damage through activation of DNA repair pathways and regulation of cell cycle checkpoint processes. BRCA1 (breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein), the central molecule to the pathway, is a breast and ovarian tumor suppressor; approximately 50% of hereditary breast cancer cases can be attributed to BRCA1. Women carrying heterozygous BRCA1 mutations have an 80% risk of developing cancer over their lifetimes. The majority of BRCA1 exists as a heterodimer with BARD1 (BRCA1associated RING domain protein 1); the two forming an active E3 ubiquitin ligase. The ubiquitination function of BRCA1 associated with BARD1 likely plays an integral role in its tumor suppression. BRCA1 is also implicated in several DNA repair pathways; evidence suggests that the BRCA1/BARD1 heterodimer may play a direct role in DNA repair: it has been observed to interact directly with aberrant DNA structures. The relocation of BRCA1 to these damaged DNA foci coincides with its phosphorylation via ATM, ATR, and chk2 kinases. These kinases phosphorylate several serine sites throughout the length of the protein. Phosphorylated BRCA1 appears to play a role in non-homologous end joining and homology-directed repair as BRCA1 interacts with proteins involved in both pathways. Examples include the Mre11, Rad50, Nbs1 (MRN) complex in non-homologous end-joining and RAD51 and BRCA2 for homologous repair. BRCA1 can also form complexes with
both BACH1 and SWI/SNF to mediate homologous recombination repair and chromatin remodeling. HDACs regulate the access of the SWI/SNFBRCA1 complex to DNA. BRCA1 has also been linked with a number of other DNA repair processes, including mismatch repair (through interactions with the mismatch repair proteins MSH2, MSH6, and MLH1) and inter-strand crosslink repair (through the Fanconi anemia pathway, via the FA complex and FANCD2 (Fanconi Anemia subtype D2) protein). DNA damage activates the monoubiquitylation of FANCD2 which colocalizes with BRCA1 and Rad51; BRCA2 functions both upstream and downstream of this event by promoting FA-complex assembly and transducing signals from FA proteins to Rad51 respectively. BRCA1 also plays a role in gene expression and cell cycle control. BRCA1 can trigger a G1 arrest that is mediated by transcriptional activation of p21. In addition to its association with p21, BRCA1 can bind to several different transcription factors, including p53, Myc, STAT1, and CtIP (CBP-Interacting Protein) promoting the expression of their respective genes. Finally, BRCA1 interacts with Chk1 and PLK1 (PoloLike Kinase-1) to regulate the G2/M and G1/S checkpoints, possibly via GADD45; thereby linking BRCA1 to the regulation of apoptosis. For more information on all the antibodies featured here or to view our extensive catalog, visit www.ptglab.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- BRCA1: Cell Cycle Checkpoint, Genetic Instability, DNA Damage Response and Cancer EvolutionDocument11 pagesBRCA1: Cell Cycle Checkpoint, Genetic Instability, DNA Damage Response and Cancer EvolutionLa Ode Muhammad FitrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Advances in Breast Cancer Research: A Molecular ApproachD'EverandCurrent Advances in Breast Cancer Research: A Molecular ApproachPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of The BRCA1 Tumor Suppressor in DNA Double-Strand Break RepairDocument9 pagesThe Role of The BRCA1 Tumor Suppressor in DNA Double-Strand Break RepairApplePas encore d'évaluation
- Brest CancerDocument7 pagesBrest CancerManish BhattaraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Article: BRCA-Associated Ovarian Cancer: From Molecular Genetics To Risk ManagementDocument12 pagesReview Article: BRCA-Associated Ovarian Cancer: From Molecular Genetics To Risk ManagementSara MagoPas encore d'évaluation
- BRCA1 and BRCA2: Different Roles in A Common Pathway of Genome ProtectionDocument11 pagesBRCA1 and BRCA2: Different Roles in A Common Pathway of Genome Protectionhutten7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brca Funcion NATUREDocument4 pagesBrca Funcion NATUREPaulina SegalottiPas encore d'évaluation
- L9 - Inherited Cancer Susceptibility - Part 1-S23Document18 pagesL9 - Inherited Cancer Susceptibility - Part 1-S23waPas encore d'évaluation
- 60 453 PDFDocument13 pages60 453 PDFVictor Hugo OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- BRCA Genes Review 2018Document5 pagesBRCA Genes Review 2018JonasMarçaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Suppressor GenesDocument21 pagesTumor Suppressor GenesPrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Balderas, Jaira E. ArticleDocument14 pagesBalderas, Jaira E. ArticleJaira E. BalderasPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Suppressor GeneDocument21 pagesTumor Suppressor GeneDayananda SalamPas encore d'évaluation
- BRCA - Inadequate DNA Damage Repair Promotes Mammary Transdifferentiation, Leading To BRCA1 Breast Cancer PDFDocument37 pagesBRCA - Inadequate DNA Damage Repair Promotes Mammary Transdifferentiation, Leading To BRCA1 Breast Cancer PDFVilla Sekar citaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioinformatics Assignment: Medha Banerjee 1660091 IMTH-7 (A)Document11 pagesBioinformatics Assignment: Medha Banerjee 1660091 IMTH-7 (A)Medha BanerjeePas encore d'évaluation
- BRCA1Document10 pagesBRCA1lee jennyPas encore d'évaluation
- Balmus Et Al. - 2019 - ATM Orchestrates The DNA-damage Response To Counter Toxic Non-Homologous End-Joining at Broken Replication Forks-AnnotatedDocument18 pagesBalmus Et Al. - 2019 - ATM Orchestrates The DNA-damage Response To Counter Toxic Non-Homologous End-Joining at Broken Replication Forks-AnnotatedThaís MesequePas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Suppressor Gene & Proto-OncogeneDocument61 pagesTumor Suppressor Gene & Proto-OncogeneKartthik ShanmugamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarDocument42 pagesCancer: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarM.PRASAD NAIDUPas encore d'évaluation
- Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Susceptibility Genes (Review) PDFDocument11 pagesHereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Susceptibility Genes (Review) PDFVilla Sekar citaPas encore d'évaluation
- BRCA1 Gene Mutations in Breast Cancer Patients From Kerman Province, IranDocument6 pagesBRCA1 Gene Mutations in Breast Cancer Patients From Kerman Province, IranMohammed AladhraeiPas encore d'évaluation
- დნმ-ის დაზიანების მექანიზმები კანცეროგენეზისა და კიბოს მკურნალობის დროსDocument1 pageდნმ-ის დაზიანების მექანიზმები კანცეროგენეზისა და კიბოს მკურნალობის დროსEMD GROUPPas encore d'évaluation
- TUMORDocument11 pagesTUMORPraveen ChandarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer BDocument14 pagesCancer BDiego SoteloPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 GMppt-chapter16-2019 (Ok)Document17 pages13 GMppt-chapter16-2019 (Ok)Kw ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - PDFsam - Ijms 17 00310 v2Document1 page1 - PDFsam - Ijms 17 00310 v2rodblochonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ash Sap 2010Document614 pagesAsh Sap 2010starandom100% (2)
- tmp95F9 TMPDocument14 pagestmp95F9 TMPFrontiersPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Suppressor Gene TherapyDocument10 pagesTumor Suppressor Gene TherapyMuhammad Ikram RabbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 TSGDocument21 pages4 TSGErics EfranyPas encore d'évaluation
- PARP Inhibitors: Synthetic Lethality in The Clinic: ReviewDocument7 pagesPARP Inhibitors: Synthetic Lethality in The Clinic: ReviewZhe YuPas encore d'évaluation
- BRCA1 Promoter Methylation in Peripheral Blood DNA of MutationDocument8 pagesBRCA1 Promoter Methylation in Peripheral Blood DNA of MutationOded KushnirPas encore d'évaluation
- Ovarian CancerDocument24 pagesOvarian CancerIulia HolbanPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecules 26 00375Document18 pagesMolecules 26 00375Hello diraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Review: Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics: Two Sides of The Same Coin?Document12 pagesReview: Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics: Two Sides of The Same Coin?Fernando Castro EchavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol-2010-Lee-a003236Document20 pagesCold Spring Harb Perspect Biol-2010-Lee-a003236lauranachefPas encore d'évaluation
- Epigenetic Regulation of Cancer-Associated Gene ProductsDocument27 pagesEpigenetic Regulation of Cancer-Associated Gene ProductsPace RaditPas encore d'évaluation
- BRCA 12-Mutation Related and Sporadic Breast and ODocument15 pagesBRCA 12-Mutation Related and Sporadic Breast and OWojtek JanotaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2663 Full PDFDocument6 pages2663 Full PDFleilalargate_3780929Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Genes Growth FactorsDocument4 pagesTumor Genes Growth FactorsM PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Epigenetic and Cancer Therapy, 2019Document12 pagesEpigenetic and Cancer Therapy, 2019AbsjeyPas encore d'évaluation
- PHD Credit Seminar 2 Punjab Agricultural University, LudhianaDocument141 pagesPHD Credit Seminar 2 Punjab Agricultural University, LudhianaSUSHANT DHARPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Article: Hereditary Breast Cancer: The Era of New Susceptibility GenesDocument12 pagesReview Article: Hereditary Breast Cancer: The Era of New Susceptibility GenesSara MagoPas encore d'évaluation
- p53 in Leukernogenesis of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Francesco Lanza, A?' SucaiDocument8 pagesp53 in Leukernogenesis of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Francesco Lanza, A?' SucaiEduardo Martín Ramírez López.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Genetics - 2011 - Kanwal - Epigenetic Modifications in CancerDocument9 pagesClinical Genetics - 2011 - Kanwal - Epigenetic Modifications in Cancerpharm.ajbashirPas encore d'évaluation
- Brca2: 1 FunctionDocument9 pagesBrca2: 1 FunctionZiedTrikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cubillos Ruiz2017Document15 pagesCubillos Ruiz2017Alina LenghelPas encore d'évaluation
- The DNA Damage Response Pathways - at The Crossroad of Protein ModificationsDocument9 pagesThe DNA Damage Response Pathways - at The Crossroad of Protein Modificationsshaheena ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Principlesoftargeted Therapyformelanoma: James Sun,, Michael J. Carr,, Nikhil I. KhushalaniDocument14 pagesPrinciplesoftargeted Therapyformelanoma: James Sun,, Michael J. Carr,, Nikhil I. KhushalaniAhmad TaufikPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ProposalDocument8 pagesProject ProposalArnab ChakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- p53 (Tumor Suppressor Gene) : Presented By: Saeed Rashid Presented To: Sir YasirDocument25 pagesp53 (Tumor Suppressor Gene) : Presented By: Saeed Rashid Presented To: Sir YasirSaeed RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Oncogene EtcDocument48 pagesOncogene EtcInsyirah JohariPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S1934590920300059 Main PDFDocument22 pages1 s2.0 S1934590920300059 Main PDFStem EducationPas encore d'évaluation
- Both Cell Autonomous and Non Autonomous Processes Modulate The Association Between Replication Timing and Mutation RateDocument14 pagesBoth Cell Autonomous and Non Autonomous Processes Modulate The Association Between Replication Timing and Mutation Ratevajal79932Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle and Cancer - Unit I IV/IDocument6 pagesCell Cycle and Cancer - Unit I IV/IManoj GourojuPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecularmarkersfor Colorectalcancer: Moriah Wright,, Jenifer S. Beaty,, Charles A. TernentDocument19 pagesMolecularmarkersfor Colorectalcancer: Moriah Wright,, Jenifer S. Beaty,, Charles A. TernentFernando Castro EchavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal 4Document7 pagesJurnal 4dicky wahyudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Alterations and DNA Repair in Human Carcinogenesis: Kathleen Dixon, Elizabeth KoprasDocument8 pagesGenetic Alterations and DNA Repair in Human Carcinogenesis: Kathleen Dixon, Elizabeth Kopras1205lorenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oncogene Function: Specific Transcript - Ion Factors or Components of Growth Stimulating Signal PathwaysDocument8 pagesOncogene Function: Specific Transcript - Ion Factors or Components of Growth Stimulating Signal PathwaysRitwik ChakradharPas encore d'évaluation
- VEGF Signaling PosterDocument1 pageVEGF Signaling PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- WNT Pathway PosterDocument1 pageWNT Pathway PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterDocument1 pageNeurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- p53 Signaling Pathway PosterDocument1 pagep53 Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterDocument1 pageNeurotrophin Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- mTOR Signaling Pathway PosterDocument1 pagemTOR Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer's Disease Signaling Pthway PosterDocument1 pageAlzheimer's Disease Signaling Pthway PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Apoptosis Signaling Pathway PosterDocument1 pageApoptosis Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia Signaling Pathway PosterDocument1 pageAcute Myeloid Leukemia Signaling Pathway PosterProteintech GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- A-Level: Biology (7402/1)Document24 pagesA-Level: Biology (7402/1)Ronald WalburnPas encore d'évaluation
- Amino Acids Reference Chart Sigma AldrichDocument3 pagesAmino Acids Reference Chart Sigma AldrichcfmonarquiaPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Forgettables - What You Need To Review Few Days Before The Exam - USMLE ForumsDocument1 pageList of Forgettables - What You Need To Review Few Days Before The Exam - USMLE ForumsJahanzeb AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Cure of Hiv Using Crispr - Adlene Jenitta, Vikrant Thokchom, W. Jasmine Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, CoimbatoreDocument2 pagesFunctional Cure of Hiv Using Crispr - Adlene Jenitta, Vikrant Thokchom, W. Jasmine Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences, CoimbatoreRaj WillseePas encore d'évaluation
- Enzimologia KanekoDocument28 pagesEnzimologia KanekoKatty Urbano OrdoñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells R UsDocument2 pagesCells R Usapi-264011999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formative Assessment BiologyDocument2 pagesFormative Assessment Biologyroosita damayantiPas encore d'évaluation
- AGR514 Chapter 3Document60 pagesAGR514 Chapter 3Muhamad Afif Abdul FatahPas encore d'évaluation
- Membran SelDocument62 pagesMembran SelLena EnjelinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene TherapyDocument210 pagesGene Therapypriyankanth192861100% (1)
- Test Bank For Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Thomas M Devlin DownloadDocument23 pagesTest Bank For Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Thomas M Devlin DownloadMeganGomezpizb100% (17)
- GST Gene Fusion System HandbookDocument132 pagesGST Gene Fusion System HandbookDaniela Gonzalez CaceresPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Sequencing by Capillary Electrophoresis Chemistry GuideDocument310 pagesDNA Sequencing by Capillary Electrophoresis Chemistry GuidepicapenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Biology Chapter I4Document13 pagesNcert Biology Chapter I4sai arunPas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal System 03 Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular TransmissionDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal System 03 Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Transmissionvkpremiyahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LColeenPas encore d'évaluation
- MYP Unit Plan 4Document5 pagesMYP Unit Plan 4ashokPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 Embl Genericposter ScreenDocument1 page2023 Embl Genericposter ScreenItzel GonzálezPas encore d'évaluation
- GEN. ZOO (Midterms)Document4 pagesGEN. ZOO (Midterms)mimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Gene MappingDocument7 pagesTypes of Gene MappingJay MenonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ono Et Al 2021 Frontiers in NeuroscienceDocument8 pagesOno Et Al 2021 Frontiers in NeuroscienceDaisuke OnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Molecules: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument66 pagesBiological Molecules: The Building Blocks of Life:Y FrankPas encore d'évaluation
- ALK ManualDocument16 pagesALK ManualRanvir RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- GeneDx Variant Classification Process June 2021Document4 pagesGeneDx Variant Classification Process June 2021Liza HavengaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cinnamaldehyde Suppresses NLRP3 Derived IL-1β via Activating SuccinatDocument7 pagesCinnamaldehyde Suppresses NLRP3 Derived IL-1β via Activating SuccinatOmar AlghulamiPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 SYNTHESIS OF ADRENALINEADRENERGIC RECEPTORS by COL AZMAT ALIDocument53 pages19 SYNTHESIS OF ADRENALINEADRENERGIC RECEPTORS by COL AZMAT ALIAhmed YTPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem QuestionsDocument10 pagesStem QuestionslouPas encore d'évaluation
- Campylobacter Spp. and Related Organisms in PoultryDocument212 pagesCampylobacter Spp. and Related Organisms in PoultryNicku MalanceaPas encore d'évaluation
- Name Designation Department Faculty E-Mail AddressDocument3 pagesName Designation Department Faculty E-Mail AddressMuhammad Adnan LaghariPas encore d'évaluation
- Sars-Cov-2 Can Recruit A Haem Metabolite To Evade Antibody ImmunityDocument19 pagesSars-Cov-2 Can Recruit A Haem Metabolite To Evade Antibody ImmunityShreyasri SainPas encore d'évaluation
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceD'EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (516)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceD'EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (18)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseD'EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (69)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerD'EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (392)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessD'EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessPas encore d'évaluation
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)D'EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (378)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincD'EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (137)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldD'EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsD'EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainD'EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (65)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperD'EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (15)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeD'EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifePas encore d'évaluation
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouD'EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (62)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedD'EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessD'Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionD'EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (811)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationD'EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (37)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsD'EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (223)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightD'EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveD'EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (66)