Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Medical Instrumentation EE045
Transféré par
Varun ManoharanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bio Medical Instrumentation EE045
Transféré par
Varun ManoharanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
EE045 Bio-Medical Instrumentation (S8 EEE) Two marks Questions and Answers 1.Define a transducer.
. A transducer is a device which when activated by energy in one transmission system,supplies energy in the another form to a second transmission system. This energy transmission may be electrical ,mechanical, chemical , optical(radiant) or thermal. 2.How transducers are classified? Transducers are classified according to their application,method of energy conversions and nature of the output signal. 3. Name the types of Resistance transducers. Potentiometric device,resistance strain gauge,resistance thermometer and photoconductive cell. 4. Name the capacitance transducers. Variable capacitance pressure guage,capacitor microphone and dielectric guage. 5. Name the types of inductance transducers. Magnetic circuit transducer,reluctance pick up,differential transformer,eddy current gage and magnetostriction gage. 6. Mention the various resistance materials used in resistance transducers. Constantan,nichrome,dynaloy,stability and platinum-tungsten alloys. 7. Mention the static characteristics of the transducers. Accuracy,precision,resolution,sensitivity,drift,linearity,saturation ,noise,hysteresis 8. What is meant by resolution of a transducer? It represents the static characteristics of a transducer.It indicates the smallest measurable input increment. 9. Write the important parameter which describes the dynamic performance of a transducer. Response time 10. List some of the characteristics which determines the performance and choice of a transducer input and output impedance,overload range , recovery time after overload, excitation voltage , reliability , size and weight 11. Give an example for a zero-order system transducer. A linear potentiometer used as a displacement transducer is an example for a zeroorder trasducer, since the output is proportional to the input for all frequencies and there is no amplitude or phase distortion. 12. List some of the piezo electric crystals used in piezoelectric transducers. Quartz,tourmaline,ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, Rochelle salt, lithium sulphate ,lead zirconate, barium titanate. 13. Name the application of piezo-electrical transducers in the medical field. They are used in ultrasonic scanners for imaging and blood flow measurements, They are used in the detection of korottkoff sounds in non-invasive blood pressure measurements. They are used in external and internal phonocardiography.
14. How optical transducers are used to measure the position and motion of the organs and tissues of the body? An optical fibre can be used to detect displacement by measuring the transmitted light intensity or phase difference between the measuring beam and a reference beam. Both amplitude and position of the transmitted and reflected light can be used to measure displacement. 15. Static the basic principles of pressure transducers. In the pressure transducers the pressure to be measured is applied to a flexible diaphragm which gets deformed by the action of the pressure exerted on it. This motion of the diaphragm is then measured in terms of an electrical signal. 16. List the various diaphragm materials used in pressure transducers. Stainless steel, phosphor bronze, beryllium copper. 17. Name the commonly employed pressure transducers. Capacitance manometer, differential transformer , strain guage 18. What are linistors? Thermistors which provide a linear change in resistance with a change in temperature are called as linistors. 19. Where pressure transducers are used in medical field? To measure blood pressure 20. To measure body temperature what type of transducers are used. Thermistors,thermocouple 21. State the basic principle of photoelectric transducers. Photoelectric transducers are based on the principle of conversion of light energy into electrical energy.This is done by causing the radiation to fall on a photosensitive element and measuring the electrical current so generated with a sensitive galvanometer directly or after suitable amplification. 22. Name the types of photoelectric cells. Photovoltaic cells (barrier layer cells) and photoemissive cells. 23. Mention the applications of optical fibre transducers in the medical field. This is used to measure physical parameters such as temperature, pressure and displacement .Used in endoscopy .Used as the delivery system for light in LASER surgery. 24. List any 2 advantages of optical fibre sensors. They are non-electrical and hence are free from electrical interference usually associated with electronically based sensors. They do not involve any electrical connection to the patient body,thereby ensuring patient safety. 25. Name the various types of optical fibre transducers. Photometric transducers ,physical transducers and chemical transducers. 26.What is the function of signal conditioner in the biomedical instrumentation system? The signal conditioner converts the output of the electrode into an electrical quantity suitable for operating the writing system in the biomedical instrumentation system. 26. List the important functions performed by the signal conditioners before the signal is given to display or recording device.
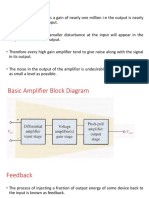
Signal amplification.frequency response ,filtering, isolation , excitation and linearization. 27. Mention the transducers having a non-linear response to changes in the phenomenon being measured? Thermocouple,thermistors 28. State the operating requirement satisfied by the amplifiers in the signal conditioning systems. Input impedance ,gain and frequency response characteristics. 29. What is meant by drift in the amplifier operating characteristics? The drift is a slow change of output having no relation with a input signal applied to the amplifier. 30. What are DC amplifiers? They are generally of the negative feedback type and are used for medium gain applications dowm to about 1mv signal levels for full scale.They are not practical for very low level applications because of dc drift and poor CMRR capabilities.They are usually employed as pen drive amplifiers in direct writing recorders. 31. List the typical examples of signals whose measurement requires the use of differential amplifiers. Heat-generated voltages picked up by means of electrodes on the arms and legs and brain-generated voltages picked up by the electrodes on the scalp are the typical examples of signals. 32. Where differential amplifiers are employed? They are employed when current is necessary to measure the voltage difference between 2 points both of them varying in amplitude at different rates and in different patterns. 33. State the limitations of differential amplifiers in the application of biomedical measurements. The amplifier has a limited input impedance and therefore draws some current from the signal source and loads them to some extent.The CMRR of the amplifier may not exceed 60 db in most of the cases,which is usually inadequate in modern biomedical instrumentation systems. 34. What are the advantages of instrumentation amplifier applied in the biomedical field? Extremely high input impedance,low bias and offset currents,less performance deterioration if source impedance changes possibility of independent reference levels for source and amplifier,very high CMRR, high slew rate and low power consumption. 35. What is meant by an instrumentation amplifier? An instrumentation amplifier is a precision differential voltage gain device that is optimized for operation in an environment hostile to precision measurements.It consists of 3 op-amps and seven resistors. 36. Mention the various methods used in the design of isolation amplifiers. Transformer isolation,opyical isolation and capacitive isolation. 37. What is the use of notch filter in the signal conditioning system? To filter the 50 HZ noise from mains. 38. State the most and commonly used amplifier in biomedical applications.
Differential amplifier. 39.What information is provided by electrocardiograph? ECG provides valuable information about a wide range of cardiac disorders such as the presence of an inactive part (infarction) or an enlargement (cardiac hypertrophy) of the heart muscle. 40 State the sensitivity rate of ECG. 10mm/mv 41. Specify the characteristics of ECG preamplifier. ECG preamplifier is usually a 3 or 4 stage differential amplifier having a large negative current feedback and gives a stabilizing effect. 42. List the important parts of an ECG recorder. Lead selector,ECG electrodes,preamplifier ,power amplifier , frequency selective feedback network, auxiliary circuit and pen motor. 43. Mention the lead configurations used in ECG. Bipolar leads(einthoven leads) , unipolar leads and unipolar precordial leads. 44. Stress ECG helps to diagonise which disease. Cardiac disorders,coronary care units and for routine diagonostic applications in cardiology. 45. What is Einthoven triangle? It is the triangle in which the electric field of the heart is represented diagrammatically.The sides of the triangle represent the lines along which the 3 projections of the ECG vector are measured. 46. What is ECG? ECG is an instrument which records the electrical activity of the heart. 47. Give the range of frequency for ECG signals. 0.05-100hz 48. What are the 2 types of electrodes used for ECG recording? Bipolar and unipolar 49. What is VCG? Vectorcardiography is the technique of analyzing the electrical activity of the heart by obtaining ECGs along the three axes at right angles to one another and displaying any 2 of the ECGs as a vector display on an X-Y oscilloscope.The display is known as a vectorcardiogram. 50. What is PCG? The phonocardiograph is an instrument used for recording the sounds connected with the pumping action of the heart. These sounds provide an indication of the heart rate and its rhythmicity.
51. Define cytoplasm. The protoplasm of a cell exclusive of that of the nucleus is defined as cytoplasm. 52.Define a cell structure. Cell is a small,usually microscopic,mass of protoplasm bounded externally by a semipermeable membrane including one or more nuclei and various nonliving products,capable of performing all the fundamental functions of life.
53.What is biometrics? The branch of science that includes the measurement of physiological variables and parameters is known as biometrics. 54.Name the factors specified in designing a bio-medical instrumentation system. Range,sensitivity,linearity,hysteresis,frequency response, accuracy, signal-to-noise ratio , stability, simplicity and isolation. 55.Define sensitivity of an instrument. It determines how small a variation of variable or parameter can be reliably measured.The sensitivity determines the resolution of the device which is the minimum variation that can accurately be read. 56.What are the different types of electrodes used in recording of muscle activity? Needle electrode made of stainless steel consisting monopolar and bipolar systems. Multi element needle electrodes 57.Define action potential. The positive potential of the cell membrane during excitation is called as action potential. 58.What is meant by sodium pump? It is an active process by which the sodium ions are quickly transported to the outside of the cell and the cell becomes polarized. 59.Define depolarization of a cell. The process of changing of a cell from the resting state to the action potential. 60.What are called electrodes? Devices that convert ionic potentials into electronic potentials are called electrodes. 61.Define an electrode potential. The interface of metallic ions in a solution with their associated metals results in an electric potential called as electrode potential. 62.State the Nernst equation with an explanation. The equation relating the potential across the membrane and the two concentrations of the ions are called the Nernst equation. E=RT ln c1f1 ----------------Nf C2F2 63.Mention the biosignal frequency range from various sections of the human body. 0 to few khz 64.Mention the ranges of frequency and voltage related to EEG. 0.5 hz to 100 hz and 10microvolt to 100 microvolt. 65.What is called motor unit? The bundle of muscle fibres in a muscle supplied by a single motor nerve fibre is called motor unit. 66.Mention the most abundant negative ions in our body. Chlorides 67.Mention the electrode having high input impedance. Micro electrodes 68.In which type of biomedical recorders loud speakers are used? EMG recorder
69.By using which type of electrode the hydrogen ion concentration of the blood is easily determined? Glass electrode 70.What is meant by ventricular fibrillation? The convulsive non synchronized activity of the ventricles of the heart is called as ventricular fibrillation. 71.Define a ventricle. A ventricle is defined as a chamber of the heart which receives blood from a corresponding atrium and from which blood is forced into the arteries. 72.What is called as tricuspid valve? The valve connecting the right atrium to the right ventricle. 73.Define a tissue in the body organ. It is defined as an aggregation of specialized cells united in the performance of a particular function. 74.What is tidal volume? The volume of gas inspired or expired during each quiet respiration cycle. 75.Define systole. The contraction or period of contraction of the heart especially that of the ventricles.It coincides with the interval between the first and second heart sound,during which the blood is forced into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. 76.What is meant by stroke volume? The amount of blood pumped during each heart beat. 77.Define residual volume. The air left in the lungs after deep exhale.(about 1.2 litres) 78.What is CAT? Computerised axial tomography is a technique combining X-rays and computer technology for visualization of internal organs and body structures 79. What information is provided by PCG? PCG provides information regarding effectiveness of blood pumping and valve action. 80. Mention the types of microphones for PCG? Crystal microphone and dynamic microphone 81. What is EEG? Electroencephalograph is an instrument for recording the electrical activity of the brain,by placing surface electrodes on the scalp. 82. Stress EEG helps to diagonise which disease. Epilepsy,tumour, cerebrovascular lesions,ischemis and problems associated with trauma. 83. What type of electrodes are used to record EEG? Peel and stick electrodes, Silver plated cup electrodes and Needle electrodes. 84. Give the name of a new non invasive imaging method utilizing the measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance. Zeugmatography. 85. What is meant by CAT scanner?
Computerised axial tomography scanners combines X-ray imaging with computer techniques permits visualization of internal organs and body structures with reater definition and clarity that could not be attained accurately by conventional methods. 86.Name the imaging system having more non-invasive character. Ultrasonic imaging systems 87. What is the use of superconducting magnets in the MRI systems? To give high magnetic field strength 88. Why a.c magnetic fields are used in electromagnetic blood flow meters? To avoid electrode polarization and bio-potential artifacts. 89. State the normal PH value of the blood. 7.4 90. Name the medical name of low blood pressure. Hypotension 91. What is stasis? The obstruction of blood flow is known as stasis. 92. Mention the body organ having the highest attenuation of ultrasound. Bone 93. What is meant by 10-20 system/ EEG electrodes are arranged on the scalp of the brain according to a standard known as 10/20 system.There are 21 electrode locations in the 10/20 system. This system involves placement of electrodes at distances of 10% and 20% of measured coronal,sagittal and circumferential arcs between landmarks on the cranium. 94. What is EMG? Electromyograph is an instrument used for recording the electrical activity of the muscles to determine whether the muscle is contracting or not. 95. Mention the clinical uses of EMG instrument? EMG instrument is useful for several aspects of neuromuscular function,neuromuscular condition,extent of nerve lesion,reflex responses etc. 96. Mention the typical EMG signal range values. 0.1 to 0.5 mv 97. What is the full form of LASER? Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation 98. Which machine is used to find epilepsy? EEG machine 99. What is cardiac pacemaker? An electronic instrument which gives external stimulation impulses to the heart muscle to regulate the heart rate. 100. Mention the basic NMR components. Magnet, transmitter, gradient system, detection system and an imager system.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- All AssignmentDocument12 pagesAll AssignmentChala GetaPas encore d'évaluation
- EI8073 BMI QN BankDocument8 pagesEI8073 BMI QN BankKeerthana SahadevanPas encore d'évaluation
- Clin. Eng. LabsDocument67 pagesClin. Eng. Labsप्रथमेश क्षीरसागरPas encore d'évaluation
- U20ecst09 Mi Unit IIDocument20 pagesU20ecst09 Mi Unit IIDr.M.Nagarajan biherPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit V Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems TransducersDocument13 pagesUnit V Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems TransducersViswanathan ASPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Electronics Semester: 5 Paper Title: Electronic Instrumentation Unit IV: Transducers Topic:Electrical Transducers and Their SelectionDocument2 pagesSubject: Electronics Semester: 5 Paper Title: Electronic Instrumentation Unit IV: Transducers Topic:Electrical Transducers and Their SelectionDespicari PiratesPas encore d'évaluation
- Sicx1003 Unit 2Document66 pagesSicx1003 Unit 2mosadik26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Temperature and Pressure. Photo-Conductive and Photo-Voltaic Cells. 06 HoursDocument50 pagesMeasurement of Temperature and Pressure. Photo-Conductive and Photo-Voltaic Cells. 06 HoursKarthik VPas encore d'évaluation
- Emi Unit 5Document28 pagesEmi Unit 5neha yarrapothuPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Instrumentation: ECG, EEG, EMG, Cardiovascular Measurements & Venous PressureDocument11 pagesBio Instrumentation: ECG, EEG, EMG, Cardiovascular Measurements & Venous PressureSaeed Ali ShahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee 308Document52 pagesEee 308Samuel SamsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Sensors and ActuatorsDocument115 pagesPresentation On Sensors and ActuatorschibuikePas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6Document15 pagesModule 6syamalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro to Biomedical Engineering TransducersDocument37 pagesIntro to Biomedical Engineering TransducersZhafir Naufal0% (1)
- ECE QuestionsDocument7 pagesECE QuestionsMadhulikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. H. S. Kalsi Dept. of Physics Guru Nanak Khalsa College Matunga, MumbaiDocument100 pagesDr. H. S. Kalsi Dept. of Physics Guru Nanak Khalsa College Matunga, MumbaiGAURI AGROTECH100% (1)
- Transducer Notes Vtu (Electrical and Electronics Measurement and Instrumentation)Document50 pagesTransducer Notes Vtu (Electrical and Electronics Measurement and Instrumentation)Narayan S. Burbure50% (4)
- Transducers and Data Aquisition SystemsDocument176 pagesTransducers and Data Aquisition SystemsSHINYPas encore d'évaluation
- Esa QbankDocument15 pagesEsa QbankB.yaduveer KaruppasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- تقرير قياساتDocument13 pagesتقرير قياساتAreej AdeebPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensor Technologies: Syed Khawar Hussain ShahDocument26 pagesSensor Technologies: Syed Khawar Hussain ShahM. RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1982 National AN301 Conditioning ElectronicsDocument13 pages1982 National AN301 Conditioning ElectronicsTelemetroPas encore d'évaluation
- Transducers and Data Acquisition SystemsDocument176 pagesTransducers and Data Acquisition SystemsBenson Mansingh P MPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ElectronicsDocument62 pagesBasic Electronicsvivek sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- TransducerDocument70 pagesTransducersmcoolguy68100% (1)
- 18EC36 - Module5 - Transducer, Programmable Logic ControllerDocument33 pages18EC36 - Module5 - Transducer, Programmable Logic ControllerINDIAN LEGENDSPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document46 pagesChapter 2kidanemariam tesera100% (1)
- Introduction To Robotics M3 L1Document28 pagesIntroduction To Robotics M3 L1Nithya ShreePas encore d'évaluation
- Transducers: Historical BackgroundDocument40 pagesTransducers: Historical BackgroundTheCycleboYPas encore d'évaluation
- Q@ 9 TransducersDocument39 pagesQ@ 9 TransducersKhayyam HusnainPas encore d'évaluation
- Mount Zoin Engineering Medical Electronics Test IIDocument11 pagesMount Zoin Engineering Medical Electronics Test IIbhagyampPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Types of Transducers - Characteristics, Classification, Applications PDFDocument18 pagesDifferent Types of Transducers - Characteristics, Classification, Applications PDFAAKASHPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank - Unit VDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - Unit Vjames RPas encore d'évaluation
- SA QB Solved Unit 1-2Document26 pagesSA QB Solved Unit 1-2Kundan PednekarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 CO4 Inst Sys Till Cap TransDocument78 pages1 CO4 Inst Sys Till Cap TransRashmika MurugeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Sensor / Transducers Review of Sensor / TransducersDocument21 pagesReview of Sensor / Transducers Review of Sensor / TransducersdhineshpPas encore d'évaluation
- Tranducers 2Document10 pagesTranducers 2Preston JerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Medical Instrumentation EI004Document6 pagesBio Medical Instrumentation EI004Sundaravadivel ArumugamPas encore d'évaluation
- BMI 2marksDocument8 pagesBMI 2marksPradheep RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Sensors and Transducers Term PaperDocument14 pagesIndustrial Sensors and Transducers Term PaperKumater TerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Voltage: Chapter Review QuestionsDocument16 pagesPressure Voltage: Chapter Review QuestionsPrakash Chandran CPas encore d'évaluation
- Transducer: Mechanical and Electrical TransducersDocument4 pagesTransducer: Mechanical and Electrical TransducersKhaled RabeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transducer and Their ResponseDocument53 pagesTransducer and Their Responseabuki bekriPas encore d'évaluation
- Transducer Instrumentation & ControlDocument8 pagesTransducer Instrumentation & Control401-Arsh AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Transducers and Signal ConditionersDocument157 pagesTransducers and Signal Conditionersrohit pooniaPas encore d'évaluation
- TransducerDocument87 pagesTransducerBobeth TubigPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Transducers ExplainedDocument3 pagesElectrical Transducers ExplainedhavejsnjPas encore d'évaluation
- AutomationDocument2 pagesAutomationTaanzPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumentation and Measurement Chapter on Transducers and Measuring InstrumentsDocument30 pagesInstrumentation and Measurement Chapter on Transducers and Measuring InstrumentsYab TadPas encore d'évaluation
- Transductores AF1 LopezGarcia 1908570Document3 pagesTransductores AF1 LopezGarcia 1908570n35708lopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Oa1-Two MarksDocument28 pagesOa1-Two MarksMEIVELJ 19EE025Pas encore d'évaluation
- Speed Measurement Trainer GuideDocument16 pagesSpeed Measurement Trainer Guidehydromec_indiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 2: Sensors and TransducersDocument66 pagesUnit - 2: Sensors and TransducersAkhil VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics in Biomedical ApplicationsDocument4 pagesPower Electronics in Biomedical Applicationselpatotas22Pas encore d'évaluation
- ME2143 Sensors and Transducers GuideDocument30 pagesME2143 Sensors and Transducers GuideClarence TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Opical Tranducer MaualDocument40 pagesOpical Tranducer MaualhemantecPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageD'EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StoragePas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumentation and Measurements: Engr. Muhammad Usman Sardar Lecturer, EEDocument29 pagesInstrumentation and Measurements: Engr. Muhammad Usman Sardar Lecturer, EEMuhammad HarisPas encore d'évaluation
- Project For ElectronicDocument26 pagesProject For ElectronicGanesh GaradPas encore d'évaluation
- Software Testers Find Errors Where Others FailDocument3 pagesSoftware Testers Find Errors Where Others FailVarun ManoharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 1001Document7 pagesEe 1001youngmoonPas encore d'évaluation
- EI1351 Bio Medical Instrumentation Nov Dec 2007Document2 pagesEI1351 Bio Medical Instrumentation Nov Dec 2007Varun ManoharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee Sem Vi - Viii 2010Document46 pagesEee Sem Vi - Viii 2010maheedarPas encore d'évaluation
- 6811 BserDocument118 pages6811 BserVijay AmbPas encore d'évaluation
- Feedback AmplifiersDocument45 pagesFeedback Amplifiersحافظ حمزہ اعوانPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Signal Conditioning CircuitsDocument5 pages3-Signal Conditioning Circuitsudhai170819Pas encore d'évaluation
- 66 Simplex Dual Rs - 232 If Card NullDocument12 pages66 Simplex Dual Rs - 232 If Card NullJulian Ernesto Martinez OlivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital To Analog ConverterDocument7 pagesDigital To Analog ConverterDeepakNathPas encore d'évaluation
- P 6900 ARE DatasheetDocument2 pagesP 6900 ARE DatasheetManualSearcher_5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Max 8798Document31 pagesMax 8798Reynaldo PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Casio AT 1 Service ManualDocument28 pagesCasio AT 1 Service ManualMario Gabriel MoralliPas encore d'évaluation
- Audisankara College of EngineeringDocument2 pagesAudisankara College of EngineeringkiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Law of AmplificationDocument7 pagesLaw of Amplificationapi-341751579Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of ElectronicsDocument2 pagesFundamentals of ElectronicsatulzendePas encore d'évaluation
- APX7000 Detailed SMDocument444 pagesAPX7000 Detailed SMHelen Helenopoulos100% (2)
- Topik 4 - Field Effect Transistors (Fet)Document39 pagesTopik 4 - Field Effect Transistors (Fet)faizahPas encore d'évaluation
- Question BankDocument10 pagesQuestion BankAres DavajPas encore d'évaluation
- Removal of DC Offset in Current Waveforms Using Digital Mimic FilteringDocument10 pagesRemoval of DC Offset in Current Waveforms Using Digital Mimic FilteringOscar Cabrera ChirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Summer Training Report On Central Electronics Limited (AXEL COUNTER)Document50 pagesSummer Training Report On Central Electronics Limited (AXEL COUNTER)mundalsandeep50% (2)
- 704MRF de PDFDocument92 pages704MRF de PDFPetros TsenesPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Feed Back So Far - Norman H. Crowhurst (Radio-Electronics, Sep 1953)Document2 pagesWhy Feed Back So Far - Norman H. Crowhurst (Radio-Electronics, Sep 1953)jimmy67musicPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog & Digital Electronics: Course Instructor: Course InstructorDocument9 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics: Course Instructor: Course InstructorPriyesh PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Demodulation: Eng .Dr./Ahmed HarmalDocument14 pagesFM Demodulation: Eng .Dr./Ahmed HarmalhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 321 Prelim Exam Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesECE 321 Prelim Exam Multiple ChoiceLoryliza M DeiparinePas encore d'évaluation
- 06-158 VESDA HLI Rev 5Document48 pages06-158 VESDA HLI Rev 5Marcos Vinicius Salvador TeixeiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Topaz AM1 User Manual EnglishDocument8 pagesTopaz AM1 User Manual English106trPas encore d'évaluation
- RFIC Agr Dai All PowerDocument181 pagesRFIC Agr Dai All PowernidhilmpPas encore d'évaluation
- PDS S-Series Electronic MarshallingDocument42 pagesPDS S-Series Electronic MarshallingisraelalmaguerPas encore d'évaluation
- Open 16f8 ECDocument62 pagesOpen 16f8 ECRitik TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- The Zl2bmi DSB Transceiver Introduction 2Document9 pagesThe Zl2bmi DSB Transceiver Introduction 2jlnlimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec II Lab ManualDocument60 pagesEc II Lab ManualRam Kumar100% (3)
- Emissary v1.0.0 User ManualDocument9 pagesEmissary v1.0.0 User ManualmarcusolivusPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultra-wideband radar motion sensor detects objects through wallsDocument24 pagesUltra-wideband radar motion sensor detects objects through wallsGauravRajputPas encore d'évaluation