Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
First Line TB Drugs
Transféré par
Catherine Jane UlpindoDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
First Line TB Drugs
Transféré par
Catherine Jane UlpindoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
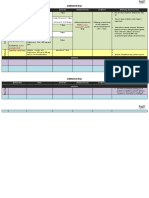
Table 5.
First-Line Anti-TB Medications
Dose in mg/kg (Maximum Dose) Drug Route Children
INH PO or IM 10 - 20 (300 mg)
Daily Adults
5 (300 mg)
2 Times/Week* Children
20 - 40 (900 mg)
3 Times/Week* Children
20 - 40 (900 mg)
Adverse Reactions
Monitoring
Comments
Adults
15 (900 mg)
Adults
15 (900 mg) Rash Hepatic enzyme elevation Hepatitis Peripheral neuropathy Mild CNS effects Drug interactions resulting in increased phenytoin (Dilantin) or disulfiram (Antabuse) levels Baseline measurements of hepatic enzymes for adults Repeat measurements if - baseline results are abnormal - patient is at high risk for adverse reactions - patient has symptoms of adverse reactions Baseline measurements of CBC, platelets, and hepatic enzymes Repeat measurements if - baseline results are abnormal - patient has symptoms of adverse reactions Hepatitis risk increases with age and alcohol consumption Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) may prevent peripheral neuropathy and CNS effects 10-15 mg/kg should be used for children when treating for latent TB infection
RIF
PO or IV
10 - 20 (600 mg)
10 (600 mg)
10 - 20 (600 mg)
10 (600 mg)
10 - 20 (600 mg)
10 (600 mg)
GI upset Drug interactions Hepatitis Bleeding problems Flu-like symptoms Rash Renal failure Fever
Significant interactions with methadone, birth control hormones, and many other drugs Contraindicated or should be used with caution when administered with PIs and NNRTIs Colors body fluids orange May permanently discolor soft contact lenses
RFB
PO or IV
10-20 (300 mg) or (150 mg) or (450 mg)
5 (300 mg) or (150 mg) or
10 - 20 (300 mg) or 10 - 20 (300 mg) or
5 (300 mg) or 5 (300 mg) or (450 mg)
Not Known
Not Known
Rash Hepatitis Fever Thrombocytopenia
Baseline measurements of CBC, platelets, and hepatic enzymes Repeat measurements if - baseline results are abnormal - patient has symptoms of adverse reactions Use adjusted daily dose of RFB, and monitor for decreased antiretroviral activity and for RFB toxicity if RFB taken concurrently with PIs or NNRTIs Baseline measurements of uric acid and hepatic enzymes Repeat measurements if - baseline results are abnormal - patient has symptoms of adverse reactions Baseline and monthly tests of visual acuity and color vision
Reduces levels of many drugs (e.g., PIs, NNRTIs, methadone, dapsone, ketoconazole, hormonal contraceptives, etc.) Colors body fluids orange May permanently discolor soft contact lenses
Not Known
Not Known With increased levels of RFB: - Severe arthralgias - Uveitis - Leukopenia
(450 mg)
(450 mg)
Not Known
Not Known
PZA
PO
15 - 20 (2 g)
15 - 30 (2 g)
50 - 70 (4 g)
50 - 70 (4 g)
50 - 70 (3 g)
50 - 70 (3 g)
Hepatitis Rash GI upset Joint aches Hyperuricemia Gout (rare)
Treat hyperuricemia only if patient has symptoms May make glucose control more difficult in diabetics
EMB#
PO
15 - 25
15 - 25
50
50
25 - 30
25 - 30
Optic neuritis Rash
Not recommended for children too young to be monitored for changes in vision unless TB is drug resistant Optic neuritis may be unilateral, check each eye separately
SM
IM or IV
20 - 40 (1 g)
15 (1 g)
25 - 30 (1.5 g)
25 - 30 (1.5 g)
25 - 30 (1.5 g)
25 - 30 (1.5 g)
Ototoxicity (hearing loss or vestibular dysfunction) Renal toxicity
Baseline and repeat as needed of hearing and renal function tests
Ultrasound and warm compresses to injection site may reduce pain Avoid or reduce dose in adults 60 years old
INH - isoniazid, RIF - rifampin, RFB - rifabutin, PZA - pyrazinamide, EMB - ethambutol, SM - streptomycin, PIs - Protease Inhibitors, NNRTIs - nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors PO - by mouth, IM - intramuscular, IV - intravenous, CNS - central nervous system Notes: Consult product insert for detailed information. Children 12 years old. Adjust weight-based dosages as weight changes.
*All intermittent dosing should be used with directly observed therapy. The concurrent administration of rifabutin is contraindicated with hard-gel saquinavir and delavirdine. An alternative is the use of rifabutin with indinavir, nelfinavir, amprenavir, ritonavir, efavirenz, and possibly soft-gel saquinavir and nevirapine. Caution is advised when using
rifabutin with soft-gel saquinavir and nevirapine, because data regarding the use of rifabutin with soft-gel saquinavir and nevirapine are limited. If nelfinavir, indinavir, amprenavir, or ritonavir is administered with RFB, blood concentrations of the PIs decrease. Thus, when RFB is used concurrently with any of these drugs, the daily dose of RFB is reduced from 300 mg to 150 mg when used with nelfinavir, indinavir, or amprenavir; and to 150 mg two or three times a week when used with ritonavir. If efavirenz is administered with RFB, blood concentrations of RFB decrease. Thus, when RFB is used with efavirenz, the daily dose of RFB should be increased from 300 mg to 450 mg or 600 mg. # No maximum dosages for EMB but in obese patients dosage should be calculated on lean body weight.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- My Father Goes To Court by Carlos BulosanDocument5 pagesMy Father Goes To Court by Carlos BulosanCatherine Jane Ulpindo80% (5)
- New Yorker in TondoDocument18 pagesNew Yorker in TondoJoanne Zuniga67% (9)
- Harvest by Loreto Paras SulitDocument6 pagesHarvest by Loreto Paras SulitMaureen Aira PastorPas encore d'évaluation
- Sonnets To A GardenerDocument1 pageSonnets To A GardenerChristine Esguerra Orozco67% (3)
- Children of The City by Amadis GuererroDocument10 pagesChildren of The City by Amadis GuererroCatherine Jane Ulpindo100% (2)
- Set B Phil LitDocument27 pagesSet B Phil LitCatherine Jane UlpindoPas encore d'évaluation
- NVM Gonzales - Bread of SaltDocument8 pagesNVM Gonzales - Bread of SaltHiro Jemmima Renoud100% (1)
- Magnificence ScriptDocument2 pagesMagnificence ScriptCatherine Jane Ulpindo100% (2)
- Sociology Report Article 17Document17 pagesSociology Report Article 17Catherine Jane UlpindoPas encore d'évaluation
- PamphletDocument2 pagesPamphletCatherine Jane UlpindoPas encore d'évaluation
- Human SexualityDocument50 pagesHuman SexualityCatherine Jane Ulpindo100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- ALERGIDocument3 pagesALERGIdyahPas encore d'évaluation
- FarmakokinetikDocument48 pagesFarmakokinetikYopi JuliantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Aus Pi TargocidDocument5 pagesAus Pi TargocidAsto Ata InteristiPas encore d'évaluation
- FDA-approved List of BiosimilarsDocument2 pagesFDA-approved List of BiosimilarsYoo AnPas encore d'évaluation
- Bodega - Id Casa - ID Articulo - Id Textbox6 ExistenciaDocument48 pagesBodega - Id Casa - ID Articulo - Id Textbox6 ExistenciaAshley TerrazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Forcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyDocument12 pagesForcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Update On The Management of Symptoms in Schizophrenia: Focus On AmisulprideDocument11 pagesUpdate On The Management of Symptoms in Schizophrenia: Focus On AmisulpridepaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Ah Fs Classification With DrugsDocument30 pagesAh Fs Classification With DrugsIndah Dian Perdana PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Isi Ebook Ujian ApotekerDocument2 pagesDaftar Isi Ebook Ujian ApotekerFiqua Nurul Rafiqua SimsPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 8th Edition DownloadDocument2 pagesHandbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 8th Edition DownloadPipe Rodriguez33% (3)
- Indications Dose Duration Administration Stability Warning & PrecautionsDocument2 pagesIndications Dose Duration Administration Stability Warning & PrecautionsFatma HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cns Stimulants: (MOA and Uses)Document39 pagesCns Stimulants: (MOA and Uses)Mirza Shaharyar BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Sustained Release Suppositories of Metoclopramide HCL Formulation and in Vitro EvaluationDocument7 pagesSustained Release Suppositories of Metoclopramide HCL Formulation and in Vitro EvaluationveniPas encore d'évaluation
- Us Bactroban OintmentDocument4 pagesUs Bactroban OintmentJayCee AriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Pharmacology DefinitionDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology DefinitionMaicha PestañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Dosage Practice Problem PacketDocument14 pagesDrug Dosage Practice Problem PacketAlex Gildea100% (1)
- CDM Antibio1 DosageGuidelines Adults enDocument2 pagesCDM Antibio1 DosageGuidelines Adults endwiPas encore d'évaluation
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Postoperative Pain Control: Veerabhadram Garimella, MD, MRCS Christina Cellini, MDDocument6 pagesPostoperative Pain Control: Veerabhadram Garimella, MD, MRCS Christina Cellini, MDBani ZakiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevalensi Tardive Dyskinesia Pada Pasien Skizofrenia Yang Mendapat Terapi Antipsikotik Di RSJ HB Saanin Padang Wenny Sagita Dita HasniDocument7 pagesPrevalensi Tardive Dyskinesia Pada Pasien Skizofrenia Yang Mendapat Terapi Antipsikotik Di RSJ HB Saanin Padang Wenny Sagita Dita HasniArif IrpanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyemmanuelmyagokayePas encore d'évaluation
- DR Siraj AhmadDocument20 pagesDR Siraj AhmadswethaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Therapy Assessment Worksheet (Dtaw)Document5 pagesDrug Therapy Assessment Worksheet (Dtaw)Mica Charish VillaluzPas encore d'évaluation
- Draft European Union Herbal Monograph Silybum Marianum L Gaertn Fructus - en 0Document7 pagesDraft European Union Herbal Monograph Silybum Marianum L Gaertn Fructus - en 0Venerable DezzyPas encore d'évaluation
- Calauan - Bangyas - Inventory of Vaccinated Population For The Month of December 2022Document30 pagesCalauan - Bangyas - Inventory of Vaccinated Population For The Month of December 2022Barangay MabacanPas encore d'évaluation
- 175 Anaesthesia and Psychiatric Drugs Part 2 Mood Stabilisers and Antipsychotics PDFDocument6 pages175 Anaesthesia and Psychiatric Drugs Part 2 Mood Stabilisers and Antipsychotics PDFWahyu Permata LisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metformin A Review of Its Use in The Treatment Typ-DikonversiDocument30 pagesMetformin A Review of Its Use in The Treatment Typ-DikonversiAida H.djamhuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Mi v20n3p244 enDocument11 pagesJournal Mi v20n3p244 enMina MohammadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study-MethyldopaDocument4 pagesDrug Study-MethyldopaJinnijinniPas encore d'évaluation