Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study
Transféré par
dyprincealbertCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Case Study
Transféré par
dyprincealbertDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
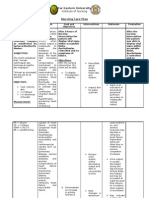
Problem: Difficulty in sleeping Patient: R.
E Date: 11-16-09 ASSESSMENT Subjective: hindi ako makatulog ng maayos dahil nahihirapan akong huminga, as verbalized by the patient. Objective: Use of accessory muscle. Dyspnea Weak looking With contraption s, IVF of D5W x KVO V/S taken as follows: T: 36.7 PR: 57 RR: 25 Bp: DIAGNOSIS Sleep pattern disturbed related to inability to assume usual sleep position due to dyspnea. PLANNING To help the patient be able to have a good sleep within 1-2 hours of Nursing Intervention. INTERVENTION Independent: Provide quiet environmen t RATIONALE this provides a conducive environmen t for the client to relax. this soothes and relaxes the client Caffeine inhibits sleep EVALUATION Goal met. The patient was able to have a good sleep within 1-2 hours of Nursing Intervention .
Provide comfort measures (back rub) Recommend Limiting intake of caffeine and chocolate prior to sleep. Dependent: Administer Oxygen 2-3 LPM as per doctors order
To make patient comfortable and be able to sleep well.
100/80
Problem: Dyspnea
Assessment S> Marigatannak nga umanges as verbalized by the patient. O > uses accessory muscles on breathing with body weakness moaning irritable cold and clammy skin V/S: BP- 120/90 PR- 118 bpm (N= 60-100bpm) RR- 30 breaths/min (12-20 breaths/min) Temp- 35.6 C
Diagnosis Ineffective airway clearance related to decrease energy and increase fatigue with predisposin g factors present
Planning Intervention That the pts: Diagnostics: breathing To monitor pattern vital signs will go back to its normal state after To assess 1-2 hours airway for of nursing patency interventio ns
Rationale As a baseline date for the following interventions that will be done.
Evaluation
Therapeutics: To place the patient in Fowlers or high-Fowlers position. Encourage frequent positions.
Goal partially met. The patient verbalized that his breathing pattern is slightly goes back to its normal state after 1-2 hours of Maintaining airway is the nursing first priority intervention. especially in cases of trauma, acute neurological decompensation , or cardiac arrest. The upright position promotes lung expansion and improves air exchange;
Contraptions: O2 via nasal cannula running at 1-2 Lpm With IVF of D5W 1/2L x KVO
Educative: To explain effects of smoking, including second hand smokes to the patient and to the family members. To tell the family members to provide adequate rest periods for the patient by letting the patient sleep and by not talking to the patient too much. Collaborative: To dminister prescribed medications as ordered, and monitor the effects.
position changes facilitate movement secretions.
the of
Chemical irritants and allergens can increase mucus production and bronchospasm.
Rest reduces metabolic demands, fatigue, and the work of breathing, promoting a more effective breathing pattern.
- If the infecting organism is resistant to the prescribed antibiotic, little improvement may be seen with treatment. Bronchodilators help maintain open airways but may
To administer oxygen as ordered.
have adverse effects such as anxiety and restlessness. > Oxygen therapy increases the alveolar oxygen concentration and facilitates its diffusion across the alveolar-capillary membrane, reducing hypoxia and anxiety
Brand Name Capoten
Generi c Name Captopr il
General Action 25 mg 1 Antihypert tab TID ensive: angiotensi nconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor
Dosage
Contraindicati on Heart block
1. Observe for drop in BP within 3 hrs of initial dose if on diuretic Caution: Dizziness, therapy and low-salt diet. If BP Leukemia, cough, falls rapidly, place supine; have chronic nocturia, saline infusion available. obstructive impotence, 2. Report occurrences of bruising, pulmonary rash, polyuria, petechiae, and/or bleeding. This disease, renal hyperkalemia, may indicate a severe reaction to or thyroid taste an angiotensin antagonist such as disease disturbance captopril 3. Explain to the client that Adverse dizziness and light-headedness Effects: may occur during the first week of captopril therapy. If dizziness Oliguria, persists, the health care provider urticaria, should be notified. severe 4. Inform the client to take hypotension captopril 1 hr before a meal. Food decreases 35% of captopril
Adverse/Side Effects Side Effects:
Nursing Responsibilities
absorption. 5. Inform the client that the taste of food may be diminished during the first month of drug therapy.
Brand Name Lasix
Generic Name Furosemid e
Dosage 40 mg IV
General Action Loop (high ceiling) diuretic
Contraindicati on Presence of severe electrolyte imbalances, hypovolemia, anuria, hypersensitivity to sulfonamides, hepatic coma.
Adverse/Side Effects Side Effects: Nausea, diarrhea, electrolyte imbalances, vertigo, cramping, rash, headache, weakness, ECG changes, blurred vision, photosensitivity Adverse Effects: Severe
Nursing Responsibilities 1. Recognize the furosemide is highly protein-bound and can displace other protein-bound drugs such as Warfarin (Coumadin). 2. Assess vital signs, serum electrolytes, weight, and urine output for baseline levels. 3. Check the half-life of furosemide. With a short halflife, the drug can be repeated or given more than once a day. 4. Check onset of action for furosemide, orally and intravenously (IV). If the drug is
dehydration; marked hypotension
given IV, the urine output should be increase in 5 to 20 minutes. If urine output does not increase, notify the health Life Threatening: care provider. Severe renal Renal failure, disorder may be present. thrombocytopenia 5. Monitor urinary output to , agranulocytosis determine body fluid gain or loss. Urinary output should be at least 25ml/hr or 600ml/24 hrs. 6. Check the clients weight to determine fluid loss or gain. A loss of 2.2 to 2.5 pounds is equivalent to a fluid loss of 1 liter. 7. Monitor vital signs. Be alert of marked decrease in blood pressure. 8. Administer IV furosemide slowly; hearing loss may occur if rapidly injected. 9. Observe for signs and symptoms of hypokalemia (<3.5 mEq/L), such as muscle weakness, abdominal distention, leg cramps, and/or cardiac dysrhythmias. 10. Check serum potassium levels, especially when a client is taking digoxin. Hypokalemia enhances the action of digitalis causing digitalis toxicity. 11. Instruct the client to arise slowly to prevent dizziness resulting from fluid loss.
12. Suggest taking furosemide at mealtime or with food to avoid nausea. 13. If the client tells that he/she only eats pasta and does not eat fruits and vegetables, the nurse may have two options: to encourage the client to eat fruits and vegetables or to contact the health care provider so that an adequate potassium supplement would be prescribed to overcome potassium loss. 14. Emphasize the importance of the client taking a potassium supplement with the potassium-wasting diuretic. In addition, advise the client of consequences and dangers of not taking potassium supplements or lack of appropriate diet while taking potassium-wasting diuretics.
Brand Name Aspirin
Generic Name ASA
Dosage 80mg OD 1 tab
General Action Antipyretic Analgesic (nonopioid) Antiinflammatory Antirheumati c Antiplatelet Salicylate NSAID
Contraindication Contraindicated with allergy to salicylates or NSAIDs (more common with nasal polyps, asthma, chronic urticaria); allergy to tartrazine (cross-sensitivity to aspirin is common); hemophilia, bleeding ulcers, hemorrhagic states, blood coagulation defects, hypoprothrombin emia, vitamin K deficiency (increased risk of bleeding). with impaired renal function
Adverse/Side Effects Acute aspirin toxicity: Respiratory alkalosis, hyperpnea, tachypnea, hemorrhage, excitement, confusion, asterixis, pulmonary edema, seizures, tetany, metabolic acidosis, fever, coma, CV collapse, renal and respiratory failure (dose related, 2025 g in adults, 4 g in children) Aspirin intoleranc e Exacerbation of bronchospasm , rhinitis (with nasal polyps,
Nursing Responsibilit ies Take extra precautio ns to keep this drug out of the reach of children; this drug can be very dangerous for children. Use the drug only as suggeste d; avoid overdose . Avoid the use of other over-thecounter drugs while taking this drug. Many of these drugs contain aspirin,
asthma, rhinitis) GI: Nausea, dyspepsia, heartburn, epigastric discomfort, anorexia, hepatotoxicity
and serious overdose can occur. Take the drug with food or after meals if GI upset occurs. Do not cut, crush, or chew sustained -release products. Over-thecounter aspirins are equivale nt. Price does not reflect effective ness. You may experien ce these side
effects: Nausea, GI upset, heartbur n (take drug with food); easy bruising, gum bleeding (related to aspirin's effects on blood clotting). Report ringing in the ears; dizziness, confusion ; abdomin al pain; rapid or difficult breathing ; nausea, vomiting, bloody stools.
Generic Name Digoxin
Brand Name Lanoxin 200 mg (0.2 mg) twice daily for 4 days.
Action Alone or in combination with other agents / diuretics vasodilators in the treatment of CHF.
Mechanism of Action Initiate the face of myocardial contraction prolongs refractory period of the AV node.
Adverse Effect / Side Effect CNS: fatigue weakness, headache, blurred vision, yellow vision
Nursing Responsibilities BP should be monitored periodically in patients receiving IV digoxin. Monitor ECG throughout IV administration and throughout therapy. Notify physician of bradycardia occur. Assess any sound pulse and BP before administration and during peak administration . Monitor for chest pain. Observe for period bronchospasm .
Salbutamol
Ventolin 1 nebule now then every 8 hours.
Management of reversible due to asthma or COPD.
To prevent or treat bronchospasm in patients with reversible obstructive airway disease
CNS: nervousnes s, insomnia, headache GI: nauseas, vomiting
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Mental Health Case StudyDocument15 pagesMental Health Case Studyapi-653708698Pas encore d'évaluation
- Emotion Code-Body Code Consent AgreementDocument1 pageEmotion Code-Body Code Consent Agreementapi-75991446100% (1)
- Institute of Nursing: Far Eastern UniversityDocument3 pagesInstitute of Nursing: Far Eastern UniversityaleccespirituPas encore d'évaluation
- Ankyloglossia in The Infant and Young Child: Clinical Suggestions For Diagnosis and ManagementDocument8 pagesAnkyloglossia in The Infant and Young Child: Clinical Suggestions For Diagnosis and ManagementZita AprilliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Techniques Client ManualDocument42 pagesQuantum Techniques Client ManualVeres Beatrix100% (4)
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument12 pagesCommon Medical AbbreviationsShania Kate Ledesma ManabatPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Grafts PDFDocument112 pagesSkin Grafts PDFalinutza_childPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013-11-20 Metlit Meta-Analysis Critical Appraisal Partini P. TrihonoDocument64 pages2013-11-20 Metlit Meta-Analysis Critical Appraisal Partini P. TrihonoHanumPas encore d'évaluation
- School Health ProgrammeDocument40 pagesSchool Health ProgrammezulfitrieeePas encore d'évaluation
- Health Flow ChartDocument1 pageHealth Flow ChartAlex Cainoy JrPas encore d'évaluation
- Eblr Formal Paper KropkoDocument10 pagesEblr Formal Paper Kropkoapi-586815209Pas encore d'évaluation
- Glaucoma: by Tekia BuntynDocument18 pagesGlaucoma: by Tekia BuntynTekia BuntynPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Role of Ultrasound in The Evaluation of Acute Pelvic PainDocument11 pages1 Role of Ultrasound in The Evaluation of Acute Pelvic PainGhofran Ibrahim HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Antithrombotic DrugsDocument11 pagesAntithrombotic DrugsKatyBrnPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study RopivacaineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ropivacainerica sebabillonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Physiotherapy in Antenatal and Post-Natal Care: Dr. Venus Pagare (PT)Document74 pagesRole of Physiotherapy in Antenatal and Post-Natal Care: Dr. Venus Pagare (PT)Haneen Jehad Um Malek100% (1)
- Esophageal Perforation: Diagnostic Work-Up and Clinical Decision-Making in The First 24 HoursDocument7 pagesEsophageal Perforation: Diagnostic Work-Up and Clinical Decision-Making in The First 24 HourssyaifularisPas encore d'évaluation
- ABCDEFGHI Systematic Approach To Wound Assessment and ManagementDocument36 pagesABCDEFGHI Systematic Approach To Wound Assessment and ManagementsaerodinPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Talk TopicsDocument3 pagesHealth Talk Topicsvarshasharma0562% (13)
- Events and Affairs Request Ms Gay BarakoDocument2 pagesEvents and Affairs Request Ms Gay Barako잔돈Pas encore d'évaluation
- Injectable Anesthesia and Analgesia of Birds 5-Aug PDFDocument15 pagesInjectable Anesthesia and Analgesia of Birds 5-Aug PDFYaserAbbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of A Case of Ventricular Bigeminy UsingDocument2 pagesManagement of A Case of Ventricular Bigeminy UsingAlfian AlfianPas encore d'évaluation
- Actinomycetes Staining MethodsDocument14 pagesActinomycetes Staining MethodsvikasPas encore d'évaluation
- b2 CoolDocument2 pagesb2 CoolGanesh kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- BCS Guidance On Workload For Cardiologists - Final March 2010Document9 pagesBCS Guidance On Workload For Cardiologists - Final March 2010Narendra KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.OA 533 01 18 Comparative Efficacy of Isometric Exercises and Active Range of MotionDocument5 pages10.OA 533 01 18 Comparative Efficacy of Isometric Exercises and Active Range of MotionAbdul Mateen TahirPas encore d'évaluation
- Decision Making: Managing Risk: Summary of An Isop Workshop, Berlin, 2004Document22 pagesDecision Making: Managing Risk: Summary of An Isop Workshop, Berlin, 2004Dipendra Ghimire100% (1)
- Form 2 Reporting Form Revision 1Document1 pageForm 2 Reporting Form Revision 1Cha Tuban DianaPas encore d'évaluation
- PaediatricTuina Elisa RossiDocument7 pagesPaediatricTuina Elisa Rossideemoney3100% (1)
- Why Worry About: High Blood Pressure?Document8 pagesWhy Worry About: High Blood Pressure?mattvestrandPas encore d'évaluation