Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
MY Bio 12 Photosynthesis Assignment
Transféré par
GSemenkovaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MY Bio 12 Photosynthesis Assignment
Transféré par
GSemenkovaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Biochemistry Unit Photosynthesis Online Assignment Total Mark: 60 Knowledge & Understanding /26 /24 /10 Communication Thinking
& Inquiry
This online assignment is on Photosynthesis. Answer the questions for each section using any online resource as well as the ones provided for each section. State which online sites you used to complete your answers.
Overall Expectations:
C3. demonstrate an understanding of the chemical changes and energy conversions that occur in metabolic process
Specific Expectations:
C3.2 explain the chemical changes and energy conversions associated with the process of photosynthesis (e.g., carbon dioxide and water react with sunlight to produce oxygen and glucose) C3.4 describe, compare, and illustrate (e.g., using flow charts) the matter and energy transformations that occur during the processes of cellular respiration (aerobic and anaerobic) and photosynthesis, including the roles of oxygen and organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts
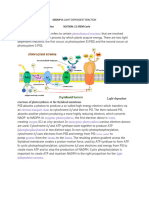
Knowledge and Understanding (26 Marks) Site 1: Photosynthetic Electron Transport and ATP Synthesis
1) What is photophosphorylation? (2 marks) Photosynthesis produces energy (ATP) and reducing power (NADPH). The process of making ATP is called photophosphorylation. There are two types of photophosphorylation: - cyclic in bacterial photosynthesis, when a single photosystem II is involved, and an excited electron returns to the reaction center of Photosystem II;
- noncyclic in plants and cyanobacteria, when two photosystems (II and I) are involved, and an excited electron ejected from the reaction center does not return to that center. 2) What is the role of each of the following in photosynthesis? (4 marks, 1 mark each) NADP Reductase: NADP reductase transfers the electrons to NADP to form NADPH Plastocyanin is a small protein that carries the electrons from the b6-f complex to photosystem I. Plastoquinone is the primary acceptor for the light-energized electrons leaving photosystem II. The reduced plastoquinone passes the excited electrons to b6-f complex. Proton Gradient difference in concentration of protons in stroma and in the thylakoid space. A proton gradient is created by b6-f complex (a proton pump that is embedded in the thylakoid membrane). The proton concentration is more in the thylakoid space, however, the thylakoid memebrane is impermeable to protons. The channels provided by ATP synthase helps the protons to pass in to the stroma where ADP is phosphorylated to ATP using protons. Ferredoxin is the primary acceptor for the light-energized electrons leaving photosystem I.
Site 2: Photosynthesis Movie
http://www.fw.vt.edu/dendro/forestbiology/photosynthesis.swf 3) Sketch a chloroplast (5 marks) Label the: Outer Membrane, Inner Membrane, Stroma, Thylakoid, Granum
4) For each site of interest in the animation movies. Briefly describe what is happening (5 marks each) 1. PSII Photosystem II. A photon of light strikes PS II, the clustered phlorophill, P680 molecule loses electrons, becomes oxidized. Then P680 molecule captures new electrons, becomes reduced by splitting water, which is producing H+ ions and oxygen. 2. Plastoquinone is the primary acceptor for the light-energized electrons leaving photosystem II. The reduced plastoquinone passes the excited electrons to the b6-f complex. Arrival of the energetic electrons causes the b6-f complex to pump protons from the stroma into the lumen. 3. Site #3 Photosystem I. A small protein called plastocyanin carries the electrons from b6-f
complex to photosystem I (PS I). When PS I absorbs a photon of light, the molecule P700 (reaction center) loses an electron and becomes oxidized. The excited electron passes to ferredoxin. 4. Ferredoxin, where the enzyme NADP reductase transfers the electrons to NADP to form NADPH (the reducing power). 5. ATP synthase provides the channel for protons from thylakoid space into the stroma where ADP is phosphorylated to ATP 5. Sketch the membrane shown in the movie. Label with the points of interest (10 marks)
Communication (21 Marks) Site 3: Photosynthesis Movie
6. Label (6 marks)
Questions 7-9: (3 marks) 7. Electrons move from water to the reaction center of Photosystem II, P680 molecule 8. As electrons pass through PQ, cyt b6, and PC, what is created? A proton motive force. 9. What product is created during photosystem II? _ATP
Site 4: Photosynthesis Movie
http://www.johnkyrk.com/photosynthesis.html Complete the fill in the blanks (9 marks) 10. Solar photons take eight minutes to get to earth. 11. When struck by a photon, chlorophyll becomes exited 12. Without a way to trap the energy, what happens to it? It is released in light or heat. 13. The electrons power the synthesis of ATP 14. Re-energized electrons create what substance? NADPH + H + 15. Each photosynthetic event yields 2 ATP and 1 NADPH (numbers) 16. What is a byproduct of these reactions? Oxygen 17. What happens to the energy trapped in the light reactions? The trapped energy powers the biosynthetic phase that followes.
Site 5: Photosynthesis Animation
Questions 18 and 19 (3 marks) 18. How many protons does it take to reduce PQ? ____________________ 19. What donates electrons to the P680 complex? Water What donates electrons to the P700 complex? Electrons from Photosystem II comes via the electron carriers
Thinking and Inquiry (10 Marks) Site 6: Photosynthesis Animation
http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/metabolism/photosynthesis.swf 20. For each of the following, write a long name and a brief description of its role in the process (3 marks, 1 mark each) PQ, Plastoquinone is the primary acceptor for the light-energized electrons leaving photosystem II. The reduced plastoquinone passes the excited electrons to the b6-f complex. Pc, Plastocyanin is a small protein that carries the electrons from b6-f complex to photosystem I Fd, Ferredoxin is the electron acceptor for the light-energized electrons leaving photosystem I
Site 7: Photosynthesis Animation
http://www.cix.co.uk/~argus/Dreambio/photosynthesis/photosynthsis%20animation.htm *This one goes pretty fast! 21. Identify each by color (4 marks) Light Purple blob ____________________ Green blobs _______________________ Red blob __________________________. Blue blob _________________________
Site 8: Calvin Cycle
http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/calvin.html 22. What are the three stages of the Calvin Cycle as illustrated in the animation? (3 marks) 23. How is RuBP regenerated? (2 marks)
24. What is the purpose of RUBISCO? (1 mark)
Literature cited (3 marks, added to communication section) (websites and online resources used for the assignment)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pearson Science TextbookDocument50 pagesPearson Science TextbookRick100% (2)
- SodaPDF-converted-Science-9 - Q1 - Module-5 - PHOTOSYNTHESIS-RESPIRATION EDITEDDocument30 pagesSodaPDF-converted-Science-9 - Q1 - Module-5 - PHOTOSYNTHESIS-RESPIRATION EDITEDMA SOLEDAD LEDESMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration-0Document49 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration-0Zulhanif IdrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Lab ManualDocument32 pagesBiology Lab ManualDũng Nguyễn100% (1)
- General Biology 1 (Light-Dependent Reactions)Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Light-Dependent Reactions)Jean DaclesPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.3.1 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pages4.3.1 PhotosynthesisMariam AymanPas encore d'évaluation
- U4 PhotosynthesisDocument14 pagesU4 PhotosynthesisjanaPas encore d'évaluation
- CAPE Biology 2004 U2 P1 MSDocument12 pagesCAPE Biology 2004 U2 P1 MSYagna LallPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis Short ConceptsDocument51 pagesPhotosynthesis Short Conceptsauguste noe100% (2)
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument12 pagesPhotosynthesis NotesSulthan Ramiz100% (1)
- Biology Unit 4 - The Natural Environment and Species SurvivalDocument20 pagesBiology Unit 4 - The Natural Environment and Species SurvivalnsinadaPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM BIOLOGY PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Photosynthesiswkwhui100% (6)
- Photosystems I&iiDocument49 pagesPhotosystems I&iiObiajulu Crystal OnyinyechiPas encore d'évaluation
- Green Plants Their Origin and Diversity Peter R Bell Alan R Hemsley (001 100)Document100 pagesGreen Plants Their Origin and Diversity Peter R Bell Alan R Hemsley (001 100)Andra febriona PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 3 PhotosynthesisDocument84 pagesChap 3 Photosynthesissarah575Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureDocument11 pagesPhotosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureMatthew BetinolPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 21 PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 21 Photosynthesis楊畯凱Pas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Biology Past Year QuestionDocument8 pagesSTPM Biology Past Year QuestionMc Donalds Ohl Ohlsen100% (2)
- FY B.Sc. Photosynthetic Electron TransportDocument4 pagesFY B.Sc. Photosynthetic Electron TransportVijendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Competency:: Marjoriechiong001@deped - Gov.phDocument9 pagesLearning Competency:: Marjoriechiong001@deped - Gov.phAnnejhel Mae PoralanPas encore d'évaluation
- Light DependentDocument46 pagesLight DependentMadame Ursula100% (1)
- Photosynthesis COMPLETEDocument44 pagesPhotosynthesis COMPLETEsantoshnairsPas encore d'évaluation
- Prochlorophytes), Also Generates Oxygen. The: Photosynthesis Occurs On Thylakoid MembranesDocument6 pagesProchlorophytes), Also Generates Oxygen. The: Photosynthesis Occurs On Thylakoid MembranesPearl Jean FrueldaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit III BSWDocument37 pagesUnit III BSWAshwinPas encore d'évaluation
- Nbio1 FionnahDocument2 pagesNbio1 FionnahlyravixxPas encore d'évaluation
- In PlantDocument2 pagesIn PlantSeiha LimPas encore d'évaluation
- ELS GovindjeeEtAl (2010)Document184 pagesELS GovindjeeEtAl (2010)38551351Pas encore d'évaluation
- Light ReactionDocument2 pagesLight Reactionfelina.duran001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis Study GuideDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis Study GuideJunhee KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis: Lecture 3 - 4 What Is The Moral of This Cartoon?Document6 pagesPhotosynthesis: Lecture 3 - 4 What Is The Moral of This Cartoon?Muhammad IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetChelsea MansuetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Quarter 2 PPT 2 - Dark and Light ReactionDocument29 pagesQuarter 2 PPT 2 - Dark and Light ReactionKarl Patrick PachecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis and Photorespiration 02Document15 pagesPhotosynthesis and Photorespiration 02simamkelemqina4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-13: Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument8 pagesChapter-13: Photosynthesis in Higher PlantssujushPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials of The Living World 5th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manual 1Document4 pagesEssentials of The Living World 5th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manual 1ronald100% (37)
- Essentials of The Living World 5th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manual 1Document35 pagesEssentials of The Living World 5th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manual 1michellespencekapnfwqzbd100% (27)
- Essentials of The Living World 5Th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument25 pagesEssentials of The Living World 5Th Edition George Johnson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmary.williams422100% (11)
- Light Reactions of PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesLight Reactions of PhotosynthesisRajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 28: Photosynthesis & GlycolysisDocument6 pagesLecture 28: Photosynthesis & Glycolysislongdi18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis Part 1Document27 pagesPhotosynthesis Part 1m4h1rstPas encore d'évaluation
- Photo SystemsDocument8 pagesPhoto SystemsTinna Devi ArmasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Bio ReviewerhahatdogPas encore d'évaluation
- Esci 2Document3 pagesEsci 2Victor Gojo CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis 9700 CieDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis 9700 CietrinhcloverPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3 PhotosynthesisDocument32 pagesWeek 3 PhotosynthesisGerald BajadoPas encore d'évaluation
- BFE Unit 3Document22 pagesBFE Unit 3tanvichalke17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On Light Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesNotes On Light Reaction of Photosynthesisxdobby260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis PDFDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis PDFHayamMohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis (Handouts)Document5 pagesPhotosynthesis (Handouts)Jelea MagallanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsAjay JamwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Tutorial 8Document3 pagesBio Tutorial 8Viyasinei KumaramoneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Dependent ReactionsDocument23 pagesLight Dependent ReactionsEriPas encore d'évaluation
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisMarc Vincent CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Print - Short, Potrait, For Pics.Document8 pagesPrint - Short, Potrait, For Pics.Jc IcaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2006 PhotoDocument8 pages2006 PhotodeaqthPas encore d'évaluation
- Unveiling The Light Reaction Event in PhotosynthesisDocument18 pagesUnveiling The Light Reaction Event in Photosynthesiszbplayer8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Component 1 GuidanceDocument14 pagesComponent 1 GuidanceJasmin StoyanovaPas encore d'évaluation
- L10 2023 - Photosynthesis IDocument10 pagesL10 2023 - Photosynthesis Imaddie.jngPas encore d'évaluation
- Light and Dark Reaction - 1Document15 pagesLight and Dark Reaction - 1Louie Joice MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology I Activity SheetDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology I Activity SheetAldous Pax ArcangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 9 - GenBio1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesWeek 9 - GenBio1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINAPas encore d'évaluation
- Redox and Photosynthesis: Redox Reactions Electron Transport Chains Light ReactionsDocument34 pagesRedox and Photosynthesis: Redox Reactions Electron Transport Chains Light ReactionsshiyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis, Process by Which Green Plants and Certain Other OrganismsDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis, Process by Which Green Plants and Certain Other OrganismsAbhinavPas encore d'évaluation
- Relate Chloroplast Structure To Its Function:: Photosynthesis Summary NotesDocument7 pagesRelate Chloroplast Structure To Its Function:: Photosynthesis Summary NotesJonathan Wee Cheng YangPas encore d'évaluation
- It's Not That Easy Bein' Green But It Is Essential For Life On Earth!Document36 pagesIt's Not That Easy Bein' Green But It Is Essential For Life On Earth!Fathmath JameelPas encore d'évaluation
- Compare and Contrast Light and Dark Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesCompare and Contrast Light and Dark Reaction of PhotosynthesisSari Mae R. AragonPas encore d'évaluation
- Downloaded For Personal Use Only: Column-I Column-IIDocument7 pagesDownloaded For Personal Use Only: Column-I Column-IIMohit SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Physiology Plant ReproductionDocument23 pagesAnatomy Physiology Plant ReproductionAndrea Nicole BalaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Std09 I SSS EM 1 PDFDocument114 pagesStd09 I SSS EM 1 PDFSindhu GunaPas encore d'évaluation
- (L) Nagarajan2016. BiohydrogenDocument48 pages(L) Nagarajan2016. BiohydrogenSacra PsyntergiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis Misconceptions Quiz - With AnswersDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Misconceptions Quiz - With AnswersJohn Kevin NochePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell As A Factory PDFDocument17 pagesCell As A Factory PDFJonathan WongPas encore d'évaluation
- 8th Full Science-2Document201 pages8th Full Science-2great kashmirPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 5 (Part-2) PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 5 (Part-2) PhotosynthesisAnubis GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- DPS Revision Offline Test - 1: Based On DPS 1 To DPS 30Document16 pagesDPS Revision Offline Test - 1: Based On DPS 1 To DPS 30Savitri HegdePas encore d'évaluation
- Q1 Science 9 Module 5Document28 pagesQ1 Science 9 Module 5Shiena Lou Tucasan CudadaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Chequered History of The Development and Use of Simultaneous Equations For The Accurate Determination of Chlorophylls A and BDocument8 pagesThe Chequered History of The Development and Use of Simultaneous Equations For The Accurate Determination of Chlorophylls A and BFitri SukmawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental Unit of Life NotesDocument17 pagesFundamental Unit of Life Notesbabushamewara.mstPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocument24 pagesChapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesVassalyn Su ThatPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Class 9 Kerala Notes Part 1 (English Medium) by OdakkalDocument13 pagesBiology Class 9 Kerala Notes Part 1 (English Medium) by Odakkalmariyu palakkot tms100% (5)
- Photosynthesis Basics, History and ModellingDocument27 pagesPhotosynthesis Basics, History and ModellingDario DiosPas encore d'évaluation
- @arbts20 CSS1 PDFDocument25 pages@arbts20 CSS1 PDFAbhishek Kumar Singh100% (2)
- Intensive Program For Neet-2021: Complete Syllabus of NEETDocument18 pagesIntensive Program For Neet-2021: Complete Syllabus of NEETRohan SikdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience ReviewerHanna TizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation of Chloroplast and Its ActivityDocument6 pagesIsolation of Chloroplast and Its ActivityEsen Nur ÖzlükPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell and Cytology Resonance PDFDocument79 pagesCell and Cytology Resonance PDFEkta Manglani100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 1: Energy TransformationDocument37 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 1: Energy TransformationNikki AlquinoPas encore d'évaluation