Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Economics
Transféré par
Jerry AntonyDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Economics
Transféré par
Jerry AntonyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
What Is Economics?
Economics is the study of how people choose to use resources. Resources include the time and talent people have available, the land, buildings, equipment, and other tools on hand, and the knowledge of how to combine them to create useful products and services. Important choices involve how much time to devote to work, to school, and to leisure, how many dollars to spend and how many to save, how to combine resources to produce goods and services, and how to vote and shape the level of taxes and the role of government. Often, people appear to use their resources to improve their wellbeing. Well-being includes the satisfaction people gain from the products and services they choose to consume, from their time spent in leisure and with family and community as well as in jobs, and the security and services provided by effective governments. Sometimes, however, people appear to use their resources in ways that don't improve their well-being. In short, economics includes the study of labor, land, and investments, of money, income, and production, and of taxes and government expenditures. Economists seek to measure well-being, to learn how well-being may increase overtime, and to evaluate the well-being of the rich and the poor. The most famous book in economics is the Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of The Wealth of Nations written by Adam Smith, and published in 1776 in Scotland. Although the behavior of individuals is important, economics also addresses the collective behavior of businesses and industries, governments and countries, and the globe as a whole. Microeconomics starts by thinking about how individuals make decisions. Macroeconomics considers aggregate outcomes. The two points of view are essential in understanding most economic phenomena. The list of fields in economics illustrates the scope of economic thought.
Definitions of Economics from Historic Textbooks
"Economics is the study of people in the ordinary business of life." -- Alfred Marshall, Principles of economics; an introductory volume (London: Macmillan, 1890)
"Economics is the science which studies human behavior as a relationship between given ends and scarce means which have alternative uses." -- Lionel Robbins, An Essay on the Nature and Significance of Economic Science (London: MacMillan, 1932) Economics is the "study of how societies use scarce resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people." -- Paul A. Samuelson, Economics (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1948)
About the American Economic Association
The Association has about 18,000 members from all over the world, most of whom are working economists in academia, business, government, international and not-for-profit agencies. It was founded in 1885 to promote the study of economics from all points of view. "The Association as such will take no partisan attitude, nor will it commit its members to any position on practical economic questions." The Association publishes seven journals. About 4,000 libraries subscribe to the journals and individual members receive journals with membership. The Association also produces ECONlit, a database to identify and locate books and articles in economics. The annual meeting of the Association, usually in early January, attracts about eight thousand economists who present their work and discuss current economic issues. The Association recognizes with awards the achievement of a small number of economists who have made outstanding achievements in the advance of economic thought. The Association promotes the market for economists by helping employers find applicants and vice versa. The Association is headquartered in Nashville, Tennessee.
1. Scarcity Scarcity, a concept we already implicitly discussed in the introduction to this tutorial, refers to the tension between our limited resources and our unlimited wants and needs. For an individual, resources include time, money and skill. For a country, limited resources include natural resources, capital, labor force and technology. Because all of our resources are limited in comparison to all of our wants and needs, individuals and nations have to make decisions regarding what goods and services they can buy and which ones they must forgo. For example, if you choose to buy one DVD as opposed to two video tapes, you must give up owning a second movie of inferior technology in exchange for the higher quality of the one DVD. Of course, each individual and nation will have different values, but by having different levels of (scarce) resources, people and nations each form some of these values as a result of the particular scarcities with which they are faced. So, because of scarcity, people and economies must make decisions over how to allocate their resources. Economics, in turn, aims to study why we make these decisions and how we allocate our
resources
most
efficiently.
2. Macro and Microeconomics Macro and microeconomics are the two vantage points from which the economy is observed. Macroeconomics looks at the total output of a nation and the way the nation allocates its limited resources of land, labor and capital in an attempt to maximize production levels and promote trade and growth for future generations. After observing the society as a whole, Adam Smith noted that there was an "invisible hand" turning the wheels of the economy: a market force that keeps the economy functioning. Microeconomics looks into similar issues, but on the level of the individual people and firms within the economy. It tends to be more scientific in its approach, and studies the parts that make up the whole economy. Analyzing certain aspects of human behavior, microeconomics shows us how individuals and firms respond to changes in price and why they demand what they do at particular price levels. Micro and macroeconomics are intertwined; as economists gain understanding of certain phenomena, they can help nations and individuals make more informed decisions when allocating resources. The systems by which nations allocate their resources can be placed on a spectrum where the command economy is on the one end and the market economy is on the other. The market economy advocates forces within a competitive market, which constitute the "invisible hand", to determine how resources should be allocated. The command economic system relies on the government to decide how the country's resources would best be allocated. In both systems, however, scarcity and unlimited wants force governments and individuals to decide how best to manage resources and allocate them in the most efficient way possible. Nevertheless, there are always limits to what the economy and government can do.
Economics Basics: Production Possibility Frontier, Growth, Opportunity Cost and Trade
ProductionPossibilityFrontier(PPF) Under the field of macroeconomics, the production possibility frontier (PPF) represents the point at which an economy is most efficiently producing its goods and services and, therefore, allocating its resources in the best way possible. If the economy is not producing the quantities indicated by the PPF, resources are being managed inefficiently and the production of society will dwindle. The production possibility frontier shows there are limits to production, so an economy, to achieve efficiency, must decide what combination of goods and services can be produced.
Let's turn to the chart below. Imagine an economy that can produce only wine and cotton. According to the PPF, points A, B and C - all appearing on the curve - represent the most efficient use of resources by the economy. Point X represents an inefficient use of resources, while point Y represents the goals that the economy cannot attain with its present levels of resources.
As we can see, in order for this economy to produce more wine, it must give up some of the resources it uses to produce cotton (point A). If the economy starts producing more cotton (represented by points B and C), it would have to divert resources from making wine and, consequently, it will produce less wine than it is producing at point A. As the chart shows, by moving production from point A to B, the economy must decrease wine production by a small amount in comparison to the increase in cotton output. However, if the economy moves from point B to C, wine output will be significantly reduced while the increase in cotton will be quite small. Keep in mind that A, B, and C all represent the most efficient allocation of resources for the economy; the nation must decide how to achieve the PPF and which combination to use. If more wine is in demand, the cost of increasing its output is proportional to the cost of decreasing cotton production. Point X means that the country's resources are not being used efficiently or, more specifically, that the country is not producing enough cotton or wine given the potential of its resources. Point Y, as we mentioned above, represents an output level that is currently unreachable by this economy. However, if there was a change in technology while the level of land, labor and capital remained the same, the time required to pick cotton and grapes would be reduced. Output would increase, and the PPF would be pushed outwards. A new curve, on which Y would appear, would represent the new efficient allocation of resources.
When the PPF shifts outwards, we know there is growth in an economy. Alternatively, when the PPF shifts inwards it indicates that the economy is shrinking as a result of a decline in its most efficient allocation of resources and optimal production capability. A shrinking economy could be a result of a decrease in supplies or a deficiency in technology. An economy can be producing on the PPF curve only in theory. In reality, economies constantly struggle to reach an optimal production capacity. And because scarcity forces an economy to forgo one choice for another, the slope of the PPF will always be negative; if production of product A increases then production of product B will have to decrease accordingly. B. Opportunity Cost Opportunity cost is the value of what is foregone in order to have something else. This value is unique for each individual. You may, for instance, forgo ice cream in order to have an extra helping of mashed potatoes. For you, the mashed potatoes have a greater value than dessert. But you can always change your mind in the future because there may be some instances when the mashed potatoes are just not as attractive as the ice cream. The opportunity cost of an individual's decisions, therefore, is determined by his or her needs, wants, time and resources (income). This is important to the PPF because a country will decide how to best allocate its resources according to its opportunity cost. Therefore, the previous wine/cotton example shows that if the country chooses to produce more wine than cotton, the opportunity cost is equivalent to the cost of giving up the required cotton production. Let's look at another example to demonstrate how opportunity cost ensures that an individual will buy the least expensive of two similar goods when given the choice. For example, assume that an individual has a choice between two telephone services. If he or she were to buy the most expensive service, that individual may have to reduce the number of times he or she goes to the movies each month. Giving up
these opportunities to go to the movies may be a cost that is too high for this person, leading him or her to choose the less expensive service. Remember that opportunity cost is different for each individual and nation. Thus, what is valued more than something else will vary among people and countries when decisions are made about how to allocate resources. C. Trade, Comparative Advantage and Absolute Advantage
Specialization and Comparative Advantage An economy can focus on producing all of the goods and services it needs to function, but this may lead to an inefficient allocation of resources and hinder future growth. By using specialization, a country can concentrate on the production of one thing that it can do best, rather than dividing up its resources. For example, let's look at a hypothetical world that has only two countries (Country A and Country B) and two products (cars and cotton). Each country can make cars and/or cotton. Now suppose that Country A has very little fertile land and an abundance of steel for car production. Country B, on the other hand, has an abundance of fertile land but very little steel. If Country A were to try to produce both cars and cotton, it would need to divide up its resources. Because it requires a lot of effort to produce cotton by irrigating the land, Country A would have to sacrifice producing cars. The opportunity cost of producing both cars and cotton is high for Country A, which will have to give up a lot of capital in order to produce both. Similarly, for Country B, the opportunity cost of producing both products is high because the effort required to produce cars is greater than that of producing cotton. Each country can produce one of the products more efficiently (at a lower cost) than the other. Country A, which has an abundance of steel, would need to give up more cars than Country B would to produce the same amount of cotton. Country B would need to give up more cotton than Country A to produce the same amount of cars. Therefore, County A has a comparative advantage over Country B in the production of cars, and Country B has a comparative advantage over Country A in the production of cotton.
Now let's say that both countries (A and B) specialize in producing the goods with which they have a comparative advantage. If they trade the goods that they produce for other goods in which they don't have a comparative advantage, both countries will be able to enjoy both products at a lower opportunity cost. Furthermore, each country will be exchanging the best product it can make for another good or service that is the best that the other country can produce. Specialization and trade also works when several different countries are involved. For example, if Country C specializes in the production of corn, it can trade its corn for cars from Country A and cotton from Country B.
Determining how countries exchange goods produced by a comparative advantage ("the best for the best") is the backbone of international trade theory. This method of exchange is considered an optimal allocation of resources, whereby economies, in theory, will no longer be lacking anything that they need. Like opportunity cost, specialization and comparative advantage also apply to the way in which individuals interact within an economy. Absolute Advantage Sometimes a country or an individual can produce more than another country, even though countries both have the same amount of inputs. For example, Country A may have a technological advantage that, with the same amount of inputs (arable land, steel, labor), enables the country to manufacture more of both cars and cotton than Country B. A country that can produce more of both goods is said to have an absolute advantage. Better quality resources can give a country an absolute advantage as can a higher level of education and overall technological advancement. It is not possible, however, for a country to have a comparative advantage in everything that it produces, so it will always be able to benefit from trade.
Economics Basics: Demand and Supply
Supply and demand is perhaps one of the most fundamental concepts of economics and it is the backbone of a market economy. Demand refers to how much (quantity) of a product or service is desired by buyers. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product people are willing to buy at a certain price; the relationship between price and quantity demanded is known as the demand relationship. Supply represents how much the market can offer. The quantity supplied refers to the amount of a certain good producers are willing to supply when receiving a certain price. The correlation between price and how much of a good or service is supplied to the market is known as the supply relationship. Price, therefore, is a reflection of supply and demand. The relationship between demand and supply underlie the forces behind the allocation of resources. In market economy theories, demand and supply theory will allocate resources in the most efficient way possible. How? Let us take a closer look at the law of demand and the law of supply. A. The Law of Demand The law of demand states that, if all other factors remain equal, the higher the price of a good, the less people will demand that good. In other words, the higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded. The amount of a good that buyers purchase at a higher price is less because as the price of a good goes up, so does the opportunity cost of buying that good. As a result, people will naturally avoid buying a product that will force them to forgo the consumption of something else they value more. The chart below shows that the curve is a downward slope.
A, B and C are points on the demand curve. Each point on the curve reflects a direct correlation between quantity demanded (Q) and price (P). So, at point A, the quantity demanded will be Q1 and the price will be P1, and so on. The demand relationship curve illustrates the negative relationship between price and quantity demanded. The higher the price of a good the lower the quantity demanded (A), and the lower the price, the more the good will be in demand (C). B. The Law of Supply Like the law of demand, the law of supply demonstrates the quantities that will be sold at a certain price. But unlike the law of demand, the supply relationship shows an upward slope. This means that the higher the price, the higher the quantity supplied. Producers supply more at a higher price because selling a higher quantity at a higher price increases revenue.
A, B and C are points on the supply curve. Each point on the curve reflects a direct correlation between quantity supplied (Q) and price (P). At point B, the quantity supplied will be Q2 and the price will be P2, and so on. (To learn how economic factors are used in currency trading, read Forex Walkthrough: Economics.)
Time and Supply Unlike the demand relationship, however, the supply relationship is a factor of time. Time is important to supply because suppliers must, but cannot always, react quickly to a change in demand or price. So it is important to try and determine whether a price change that is caused by demand will be temporary or permanent. Let's say there's a sudden increase in the demand and price for umbrellas in an unexpected rainy season; suppliers may simply accommodate demand by using their production equipment more intensively. If, however, there is a climate change, and the population will need umbrellas yearround, the change in demand and price will be expected to be long term; suppliers will have to change their equipment and production facilities in order to meet the long-term levels of demand. C. Supply and Demand Relationship Now that we know the laws of supply and demand, let's turn to an example to show how supply and demand affect price. Imagine that a special edition CD of your favorite band is released for $20. Because the record company's previous analysis showed that consumers will not demand CDs at a price higher than $20, only ten CDs were released because the opportunity cost is too high for suppliers to produce more. If, however, the ten CDs are demanded by 20 people, the price will subsequently rise because, according to the demand relationship, as demand increases, so does the price. Consequently, the rise in price should prompt more CDs to be supplied as the supply relationship shows that the higher the price, the higher the quantity supplied. If, however, there are 30 CDs produced and demand is still at 20, the price will not be pushed up because the supply more than accommodates demand. In fact after the 20 consumers have been satisfied with their CD purchases, the price of the leftover CDs may drop as CD producers attempt to sell the remaining ten CDs. The lower price will then make the CD more available to people who had previously decided that the opportunity cost of buying the CD at $20 was too high. D. Equilibrium When supply and demand are equal (i.e. when the supply function and demand function intersect) the economy is said to be at equilibrium. At this point, the allocation of goods is at its most efficient because the amount of goods being supplied is exactly the same as the amount of goods being demanded. Thus, everyone (individuals, firms, or countries) is satisfied with the current economic condition. At the given price, suppliers are selling all the goods that they have produced and consumers are getting all the goods that they are demanding.
As you can see on the chart, equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the demand and supply curve, which indicates no allocative inefficiency. At this point, the price of the goods will be P* and the quantity will be Q*. These figures are referred to as equilibrium price and quantity. In the real market place equilibrium can only ever be reached in theory, so the prices of goods and services are constantly changing in relation to fluctuations in demand and supply. E. Disequilibrium
Disequilibrium occurs whenever the price or quantity is not equal to P* or Q*. 1. Excess Supply If the price is set too high, excess supply will be created within the economy and there will be allocative inefficiency.
At price P1 the quantity of goods that the producers wish to supply is indicated by Q2. At P1, however, the quantity that the consumers want to consume is at Q1, a quantity much less than Q2. Because Q2 is greater than Q1, too much is being produced and too little is being consumed. The suppliers are trying
to produce more goods, which they hope to sell to increase profits, but those consuming the goods will find the product less attractive and purchase less because the price is too high. 2. Excess Demand Excess demand is created when price is set below the equilibrium price. Because the price is so low, too many consumers want the good while producers are not making enough of it.
In this situation, at price P1, the quantity of goods demanded by consumers at this price is Q2. Conversely, the quantity of goods that producers are willing to produce at this price is Q1. Thus, there are too few goods being produced to satisfy the wants (demand) of the consumers. However, as consumers have to compete with one other to buy the good at this price, the demand will push the price up, making suppliers want to supply more and bringing the price closer to its equilibrium.
F. Shifts vs. Movement For economics, the movements and shifts in relation to the supply and demand curves represent very different market phenomena: 1. Movements A movement refers to a change along a curve. On the demand curve, a movement denotes a change in both price and quantity demanded from one point to another on the curve. The movement implies that the demand relationship remains consistent. Therefore, a movement along the demand curve will occur when the price of the good changes and the quantity demanded changes in accordance to the original demand relationship. In other words, a movement occurs when a change in the quantity demanded is caused only by a change in price, and vice versa.
Like a movement along the demand curve, a movement along the supply curve means that the supply relationship remains consistent. Therefore, a movement along the supply curve will occur when the price of the good changes and the quantity supplied changes in accordance to the original supply relationship. In other words, a movement occurs when a change in quantity supplied is caused only by a change in price, and vice versa.
2. Shifts A shift in a demand or supply curve occurs when a good's quantity demanded or supplied changes even though price remains the same. For instance, if the price for a bottle of beer was $2 and the quantity of beer demanded increased from Q1 to Q2, then there would be a shift in the demand for beer. Shifts in the demand curve imply that the original demand relationship has changed, meaning that quantity demand is affected by a factor other than price. A shift in the demand relationship would occur if, for instance, beer suddenly became the only type of alcohol available for consumption.
Conversely, if the price for a bottle of beer was $2 and the quantity supplied decreased from Q1 to Q2, then there would be a shift in the supply of beer. Like a shift in the demand curve, a shift in the supply curve implies that the original supply curve has changed, meaning that the quantity supplied is effected by a factor other than price. A shift in the supply curve would occur if, for instance, a natural disaster caused a mass shortage of hops; beer manufacturers would be forced to supply less beer for the same price.
Economics Basics: Elasticity
The degree to which a demand or supply curve reacts to a change in price is the curve's elasticity. Elasticity varies among products because some products may be more essential to the consumer. Products that are necessities are more insensitive to price changes because consumers would continue buying these products despite price increases. Conversely, a price increase of a good or service that is considered less of a necessity will deter more consumers because the opportunity cost of buying the product will become too high.
A good or service is considered to be highly elastic if a slight change in price leads to a sharp change in the quantity demanded or supplied. Usually these kinds of products are readily available in the market and a person may not necessarily need them in his or her daily life. On the other hand, an inelastic good or service is one in which changes in price witness only modest changes in the quantity demanded or supplied, if any at all. These goods tend to be things that are more of a necessity to the consumer in his or her daily life. To determine the elasticity of the supply or demand curves, we can use this simple equation: Elasticity = (% change in quantity / % change in price) If elasticity is greater than or equal to one, the curve is considered to be elastic. If it is less than one, the curve is said to be inelastic. As we mentioned previously, the demand curve is a negative slope, and if there is a large decrease in the quantity demanded with a small increase in price, the demand curve looks flatter, or more horizontal. This flatter curve means that the good or service in question is elastic.
Meanwhile, inelastic demand is represented with a much more upright curve as quantity changes little with a large movement in price.
Elasticity of supply works similarly. If a change in price results in a big change in the amount supplied, the supply curve appears flatter and is considered elastic. Elasticity in this case would be greater than or equal to one.
On the other hand, if a big change in price only results in a minor change in the quantity supplied, the supply curve is steeper and its elasticity would be less than one.
A. Factors Affecting Demand Elasticity There are three main factors that influence a demand's price elasticity: 1. The availability of substitutes - This is probably the most important factor influencing the elasticity of a good or service. In general, the more substitutes, the more elastic the demand will be. For example, if the price of a cup of coffee went up by $0.25, consumers could replace their morning caffeine with a cup of tea. This means that coffee is an elastic good because a raise in price will cause a large decrease in demand as consumers start buying more tea instead of coffee. However, if the price of caffeine were to go up as a whole, we would probably see little change in the consumption of coffee or tea because there are few substitutes for caffeine. Most people are not willing to give up their morning cup of caffeine no matter what the price. We would say, therefore, that caffeine is an inelastic product because of its lack of substitutes. Thus, while a product within an industry is elastic due to the availability of substitutes, the industry itself tends to be inelastic. Usually, unique goods such as diamonds are inelastic because they have few if any substitutes. 2. Amount of income available to spend on the good - This factor affecting demand elasticity refers to the total a person can spend on a particular good or service. Thus, if the price of a can of Coke goes up from $0.50 to $1 and income stays the same, the income that is available to spend on coke, which is $2, is now enough for only two rather than four cans of Coke. In other words, the consumer is forced to reduce his or her demand of Coke. Thus if there is an increase in price and no change in the amount of income available to spend on the good, there will be an elastic reaction in demand; demand will be sensitive to a change in price if there is no change in income. 3. Time - The third influential factor is time. If the price of cigarettes goes up $2 per pack, a smoker with very few available substitutes will most likely continue buying his or her daily cigarettes. This means that tobacco is inelastic because the change in price will not have a significant influence on the quantity demanded. However, if that smoker finds that he or she
cannot afford to spend the extra $2 per day and begins to kick the habit over a period of time, the price elasticity of cigarettes for that consumer becomes elastic in the long run.
B. Income Elasticity of Demand In the second factor outlined above, we saw that if price increases while income stays the same, demand will decrease. It follows, then, that if there is an increase in income, demand tends to increase as well. The degree to which an increase in income will cause an increase in demand is called income elasticity of demand, which can be expressed in the following equation:
If EDy is greater than one, demand for the item is considered to have a high income elasticity. If however EDy is less than one, demand is considered to be income inelastic. Luxury items usually have higher income elasticity because when people have a higher income, they don't have to forfeit as much to buy these luxury items. Let's look at an example of a luxury good: air travel. Bob has just received a $10,000 increase in his salary, giving him a total of $80,000 per annum. With this higher purchasing power, he decides that he can now afford air travel twice a year instead of his previous once a year. With the following equation we can calculate income demand elasticity:
Income
elasticity
of
demand
for
Bob's
air
travel
is
seven
- highly
elastic.
With some goods and services, we may actually notice a decrease in demand as income increases. These are considered goods and services of inferior quality that will be dropped by a consumer who receives a salary increase. An example may be the increase in the demand of
DVDs as opposed to video cassettes, which are generally considered to be of lower quality. Products for which the demand decreases as income increases have an income elasticity of less than zero. Products that witness no change in demand despite a change in income usually have an income elasticity of zero - these goods and services are considered necessities.
Economics Basics: Utility
We have already seen that the focus of economics is to understand the problem of scarcity: the problem of fulfilling the unlimited wants of humankind with limited and/or scarce resources. Because of scarcity, economies need to allocate their resources efficiently. Underlying the laws of demand and supply is the concept of utility, which represents the advantage or fulfillment a person receives from consuming a good or service. Utility, then, explains how individuals and economies aim to gain optimal satisfaction in dealing with scarcity.
Utility is an abstract concept rather than a concrete, observable quantity. The units to which we assign an amount of utility, therefore, are arbitrary, representing a relative value. Total utility is the aggregate sum of satisfaction or benefit that an individual gains from consuming a given amount of goods or services in an economy. The amount of a person's total utility corresponds to the person's level of consumption. Usually, the more the person consumes, the larger his or her total utility will be. Marginal utility is the additional satisfaction, or amount of utility, gained from each extra unit of consumption. Although total utility usually increases as more of a good is consumed, marginal utility usually decreases with each additional increase in the consumption of a good. This decrease demonstrates the law of diminishing marginal utility. Because there is a certain threshold of satisfaction, the consumer will no longer receive the same pleasure from consumption once that threshold is crossed. In other words, total utility will increase at a slower pace as an individual increases the quantity consumed. Take, for example, a chocolate bar. Let's say that after eating one chocolate bar your sweet tooth has been satisfied. Your marginal utility (and total utility) after eating one chocolate bar will be quite high. But if you eat more chocolate bars, the pleasure of each additional chocolate bar will be less than the pleasure you received from eating the one before - probably because you are starting to feel full or you have had too many sweets for one day.
This table shows that total utility will increase at a much slower rate as marginal utility diminishes with each additional bar. Notice how the first chocolate bar gives a total utility of 70 but the next three chocolate bars together increase total utility by only 18 additional units. The law of diminishing marginal utility helps economists understand the law of demand and the negative sloping demand curve. The less of something you have, the more satisfaction you gain from each additional unit you consume; the marginal utility you gain from that product is therefore higher, giving you a higher willingness to pay more for it. Prices are lower at a higher quantity demanded because your additional satisfaction diminishes as you demand more. In order to determine what a consumer's utility and total utility are, economists turn to consumer demand theory, which studies consumer behavior and satisfaction. Economists assume the consumer is rational and will thus maximize his or her total utility by purchasing a combination of different products rather than more of one particular product. Thus, instead of spending all of your money on three chocolate bars, which has a total utility of 85, you should instead purchase the one chocolate bar, which has a utility of 70, and perhaps a glass of milk, which has a utility of 50. This combination will give you a maximized total utility of 120 but at the same cost as the three chocolate bars.
Economics Basics: Monopolies, Oligopolies and Perfect Competition
Economists assume that there are a number of different buyers and sellers in the marketplace. This means that we have competition in the market, which allows price to change in response to changes in supply and demand. Furthermore, for almost every product there are substitutes, so if one product becomes too expensive, a buyer can choose a cheaper substitute instead. In a market with many buyers and sellers, both the consumer and the supplier have equal ability to influence price.
In some industries, there are no substitutes and there is no competition. In a market that has only one or few suppliers of a good or service, the producer(s) can control price, meaning that a consumer does not have choice, cannot maximize his or her total utility and has have very little influence over the price of goods.
A monopoly is a market structure in which there is only one producer/seller for a product. In other words, the single business is the industry. Entry into such a market is restricted due to high costs or other impediments, which may be economic, social or political. For instance, a government can create a monopoly over an industry that it wants to control, such as electricity. Another reason for the barriers against entry into a monopolistic industry is that oftentimes, one entity has the exclusive rights to a natural resource. For example, in Saudi Arabia the government has sole control over the oil industry. A monopoly may also form when a company has a copyright or patent that prevents others from entering the market. Pfizer, for instance, had a patent on Viagra. In an oligopoly, there are only a few firms that make up an industry. This select group of firms has control over the price and, like a monopoly, an oligopoly has high barriers to entry. The products that the oligopolistic firms produce are often nearly identical and, therefore, the companies, which are competing for market share, are interdependent as a result of market forces. Assume, for example, that an economy needs only 100 widgets. Company X produces 50 widgets and its competitor, Company Y, produces the other 50. The prices of the two brands will be interdependent and, therefore, similar. So, if Company X starts selling the widgets at a lower price, it will get a greater market share, thereby forcing Company Y to lower its prices as well. There are two extreme forms of market structure: monopoly and, its opposite, perfect competition. Perfect competition is characterized by many buyers and sellers, many products that are similar in nature and, as a result, many substitutes. Perfect competition means there are few, if any, barriers to entry for new companies, and prices are determined by supply and demand. Thus, producers in a perfectly competitive market are subject to the prices determined by the market and do not have any leverage. For example, in a perfectly competitive market, should a single firm decide to increase its selling price of a good, the consumers can just turn to the nearest competitor for a better price, causing any firm that increases its prices to lose market share and profits.
Economics Basics: Conclusion
We hope that this has given you some insight to the market and, in turn, your investment strategies. Let's recap what we've learned in this tutorial:
y y
Economics is best described as the study of humans behaving in response to having only limited resources to fulfill unlimited wants and needs. Scarcity refers to the limited resources in an economy. Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole. Microeconomics analyzes the individual people and companies that make up the greater economy. The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) allows us to determine how an economy can allocate its resources in order to achieve optimal output. Knowing this will lead countries to specialize and trade products amongst each other rather than each producing all the products it needs.
Demand and supply refer to the relationship price has with the quantity consumers demand and the quantity supplied by producers. As price increases, quantity demanded decreases and quantity supplied increases. Elasticity tells us how much quantity demanded or supplied changes when there is a change in price. The more the quantity changes, the more elastic the good or service. Products whose quantity supplied or demanded does not change much with a change in price are considered inelastic. Utility is the amount of benefit a consumer receives from a given good or service. Economists use utility to determine how an individual can get the most satisfaction out of his or her available resources. Market economies are assumed to have many buyers and sellers, high competition and many substitutes. Monopolies characterize industries in which the supplier determines prices and high barriers prevent any competitors from entering the market. Oligopolies are industries with a few interdependent companies. Perfect competition represents an economy with many businesses competing with one another for consumer interest and profits.
NOTES:Dismal Science
What Does Dismal Science Mean? A term coined by Scottish writer, essayist and historian Thomas Carlyle to describe the discipline of economics. The term dismal science was inspired by T. R. Malthus' gloomy prediction that population would always grow faster than food, dooming mankind to unending poverty and hardship.
Investopedia explains Dismal Science Exactly what inspired the term has been a subject of debate. Those who doubt the story say that Carlyle was reacting not to Malthus but economists such as John Stuart Mill, who argued that institutions, not race, explained why some nations were rich and others poor. Carlyle attacked Mill, not for supporting Malthus' predictions about the dire consequences of population growth, but for supporting the emancipation of slaves. It was the discipline's assumption that people are basically all the same and thus entitled to liberty that led Carlyle to label the study of economics "the dismal science". The connection was so well known throughout the 19th century, that even cartoonists would refer to it knowing that their audience would understand the reference. What Does Scarcity Mean? The basic economic problem that arises because people have unlimited wants but resources are limited. Because of scarcity, various economic decisions must be made to allocate resources efficiently.
Investopedia explains Scarcity When we talk of scarcity within an economic context, it refers to limited resources, not a lack of riches. These resources are the inputs of production: land, labor and capital. People must make choices between different items because the resources necessary to fulfill their wants are limited. These decisions are made by giving up (trading off) one want to satisfy another.
Microeconomics
What Does Microeconomics Mean? The branch of economics that analyzes the market behavior of individual consumers and firms in an attempt to understand the decision-making process of firms and households. It is concerned with the interaction between individual buyers and sellers and the factors that influence the choices made by buyers and sellers. In particular, microeconomics focuses on patterns of supply and demand and the determination of price and output in individual markets (e.g. coffee industry).
Investopedia explains Microeconomics The field of economics is broken down into two distinct areas of study: microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics looks at the smaller picture and focuses more on basic theories of supply and demand and how individual businesses decide how much of something to produce and how much to charge for it. People who have any desire to start their own business or
who want to learn the rationale behind the pricing of particular products and services would be more interested in this area. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, looks at the big picture (hence "macro"). It focuses on the national economy as a whole and provides a basic knowledge of how things work in the business world. For example, people who study this branch of economics would be able to interpret the latest Gross Domestic Product figures or explain why a 6% rate of unemployment is not necessarily a bad thing. Thus, for an overall perspective of how the entire economy works, you need to have an understanding of economics at both the micro and macro levels.
Macroeconomics
What Does Macroeconomics Mean? The field of economics that studies the behavior of the aggregate economy. Macroeconomics examines economy-wide phenomena such as changes in unemployment, national income, rate of growth, gross domestic product, inflation and price levels.
Investopedia explains Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is focused on the movement and trends in the economy as a whole, while in microeconomics the focus is placed on factors that affect the decisions made by firms and individuals. The factors that are studied by macro and micro will often influence each other, such as the current level of unemployment in the economy as a whole will affect the supply of workers which an oil company can hire from, for example.
Invisible Hand
What Does Invisible Hand Mean? A term coined by economist Adam Smith in his 1776 book "An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations". In his book he states: "Every individual necessarily labours to render the annual revenue of the society as great as he can. He generally neither intends to promote the public interest, nor knows how much he is promoting it ... He intends only his own gain, and he is in this, as in many other cases, led by an invisible hand to promote an end which was no part of his intention. Nor is it always the worse for society that it was no part of his intention. By pursuing his own interest he frequently promotes that of the society more effectually than when he really intends to promote it. I have never known much good done by those who affected to trade for the public good."
Thus, the invisible hand is essentially a natural phenomenon that guides free markets and capitalism through competition for scarce resources.
Investopedia explains Invisible Hand Smith assumed that individuals try to maximize their own good (and become wealthier), and by doing so, through trade and entrepreneurship, society as a whole is better off. Furthermore, any government intervention in the economy isn't needed because the invisible hand is the best guide for the econom
Market Economy
What Does Market Economy Mean? An economic system in which economic decisions and the pricing of goods and services are guided solely by the aggregate interactions of a country's citizens and businesses and there is little government intervention or central planning. This is the opposite of a centrally planned economy, in which government decisions drive most aspects of a country's economic activity.
Investopedia explains Market Economy Market economies work on the assumption that market forces, such as supply and demand, are the best determinants of what is right for a nation's well-being. These economies rarely engage in government interventions such as price fixing, license quotas and industry subsidizations. While most developed nations today could be classified as having mixed economies, they are often said to have market economies because they allow market forces to drive most of their activities, typically engaging in government intervention only to the extent that it is needed to provide stability. Although the market economy is clearly the system of choice in today's global marketplace, there is significant debate regarding the amount of government intervention considered optimal for efficient economic operations.
Demand
What Does Demand Mean? An economic principle that describes a consumers desire and willingness to pay a price for a specific good or service. Holding all other factors constant, the price of a good or service increases as its demand increases and vice versa.
Investopedia explains Demand Think of demand as your willingness to go out and buy a certain product. For example, market demand is the total of what everybody in the market wants. Businesses often spend a considerable amount of money in order to determine the amount of demand that the public has for its products and services. Incorrect estimations will either result in money left on the table if its underestimated or losses if its overestimated.
Supply
What Does Supply Mean? A fundamental economic concept that describes the total amount of a specific good or service that is available to consumers. Supply can relate to the amount available at a specific price or the amount available across a range of prices if displayed on a graph. This relates closely to the demand for a good or service at a specific price; all else being equal, the supply provided by producers will rise if the price rises because all firms look to maximize profits.
Investopedia explains Supply Supply and demand trends form the basis of the modern economy. Each specific good or service will have its own supply and demand patterns based on price, utility and personal preference. If people demand a good and are willing to pay more for it, producers will add to the supply. As the supply increases, the price will fall given the same level of demand. Ideally, markets will reach a point of equilibrium where the supply equals the demand (no excess supply and no shortages) for a given price point; at this point ,consumer utility and producer profits are maximized.
Elasticity
What Does Elasticity Mean? A measure of a variable's sensitivity to a change in another variable. In economics, elasticity refers the degree to which individuals (consumers/producers) change their demand/amount supplied in response to price or income changes. Calculated as:
Investopedia explains Elasticity Elasticity is used to assess the change in consumer demand as a result of a change in the good's price. When the value is greater than 1, this suggests that the demand for the good/service is affected by the price, whereas a value that is less than 1 suggest that the demand is insensitive to price. Businesses often strive to sell/market products or services that are or seem inelastic in demand because doing so can mean that few customers will be lost as a result of price increase
Monopoly
What Does Monopoly Mean? A situation in which a single company or group owns all or nearly all of the market for a given type of product or service. By definition, monopoly is characterized by an absence of competition, which often results in high prices and inferior products. According to a strict academic definition, a monopoly is a market containing a single firm.
Investopedia explains Monopoly Monopoly is the extreme case in capitalism. Most believe that, with few exceptions, the system just doesn't work when there is only one provider of a good or service because there is no incentive to improve it to meet the demands of consumers. Governments attempt to prevent monopolies from arising through the use of antitrust laws. Of course, there are gray areas; take for example the granting of patents on new inventions. These give, in effect, a monopoly on a product for a set period of time. The reasoning behind patents is to give innovators some time to recoup what are often large research and development costs. In theory, they are a way of using monopolies to promote innovation. Another example are public monopolies set up by governments to provide essential services. Some believe that utilities should offer public goods and services such as water and electricity at a price that is affordable to everyone.
Oligopoly
What Does Oligopoly Mean? A situation in which a particular market is controlled by a small group of firms. An oligopoly is much like a monopoly, in which only one company exerts control over most of a market. In an oligopoly, there are at least two firms controlling the market.
Investopedia explains Oligopoly The retail gas market is a good example of an oligopoly because a small number of firms control a large majority of the market
Perfect Competition
What Does Perfect Competition Mean? A market structure in which the following five criteria are met: 1. All firms sell an identical product. 2. All firms are price takers. 3. All firms have a relatively small market share. 4. Buyers know the nature of the product being sold and the prices charged by each firm. 5. The industry is characterized by freedom of entry and exit. Sometimes referred to as "pure competition".
Investopedia explains Perfect Competition Perfect competition is a theoretical market structure. It is primarily used as a benchmark against which other market structures are compared. The industry that best reflects perfect competition in real life is the agricultural industry
Leverage
What Does Leverage Mean? 1. The use of various financial instruments or borrowed capital, such as margin, to increase the potential return of an investment. 2. The amount of debt used to finance a firm's assets. A firm with significantly more debt than equity is considered to be highly leveraged.
Leverage is most commonly used in real estate transactions through the use of mortgages to purchase a home.
Investopedia explains Leverage 1. Leverage can be created through options, futures, margin and other financial instruments. For example, say you have $1,000 to invest. This amount could be invested in 10 shares of Microsoft stock, but to increase leverage, you could invest the $1,000 in five options contracts. You would then control 500 shares instead of just 10. 2. Most companies use debt to finance operations. By doing so, a company increases its leverage because it can invest in business operations without increasing its equity. For example, if a company formed with an investment of $5 million from investors, the equity in the company is $5 million - this is the money the company uses to operate. If the company uses debt financing by borrowing $20 million, the company now has $25 million to invest in business operations and more opportunity to increase value for shareholders. Leverage helps both the investor and the firm to invest or operate. However, it comes with greater risk. If an investor uses leverage to make an investment and the investment moves against the investor, his or her loss is much greater than it would've been if the investment had not been leveraged - leverage magnifies both gains and losses. In the business world, a company can use leverage to try to generate shareholder wealth, but if it fails to do so, the interest expense and credit risk of default destroys shareholder value. al, such as margin, to increase the potential return of an investment. 2. The amount of debt used to finance a firm's assets. A firm with significantly more debt than equity is considered to be highly leveraged. Leverage is most commonly used in real estate transactions through the use of mortgages to purchase a home.
Investopedia explains Leverage 1. Leverage can be created through options, futures, margin and other financial instruments. For example, say you have $1,000 to invest. This amount could be invested in 10 shares of Microsoft stock, but to increase leverage, you could invest the $1,000 in five options contracts. You would then control 500 shares instead of just 10. 2. Most companies use debt to finance operations. By doing so, a company increases its leverage because it can invest in business operations without increasing its equity. For example, if a company formed with an investment of $5 million from investors, the equity in the company is $5 million - this is the money the company uses to operate. If the company uses debt financing by borrowing $20 million, the company now has $25 million to invest in business operations and more opportunity to increase value for shareholders.
Leverage helps both the investor and the firm to invest or operate. However, it comes with greater risk. If an investor uses leverage to make an investment and the investment moves against the investor, his or her loss is much greater than it would've been if the investment had not been leveraged - leverage magnifies both gains and losses. In the business world, a company can use leverage to try to generate shareholder wealth, but if it fails to do so, the interest expense and credit risk of default destroys shareholder value.
ECONOMIES OF SCALE
When more units of a good or a service can be produced on a larger scale, yet with (on average) less input costs, economies of scale (ES) are said to be achieved. Alternatively, this means that as a company grows and production units increase, a company will have a better chance to decrease its costs. According to theory, economic growth may be achieved when economies of scale are realized. Adam Smith identified the division of labor and specialization as the two key means to achieve a larger return on production. Through these two techniques, employees would not only be able to concentrate on a specific task, but with time, improve the skills necessary to perform their jobs. The tasks could then be performed better and faster. Hence, through such efficiency, time and money could be saved while production levels increased. Just like there are economies of scale, diseconomies of scale (DS) also exist. This occurs when production is less than in proportion to inputs. What this means is that there are inefficiencies within the firm or industry resulting in rising average costs. Internal and External Economies of Scale Alfred Marshall made a distinction between internal and external economies of scale. When a company reduces costs and increases production, internal economies of scale have been achieved. External economies of scale occur outside of a firm, within an industry. Thus, when an industry's scope of operations expands due to, for example, the creation of a better transportation network, resulting in a subsequent decrease in cost for a company working within that industry, external economies of scale are said to have been achieved. With external ES, all firms within the industry will benefit. Where Are Economies of Scale? In addition to specialization and the division of labor, within any company there are various inputs that may result in the production of a good and/or service.
y
Lower input costs: When a company buys inputs in bulk - for example, potatoes used to make French fries at a fast food chain - it can take advantage of volume discounts. (In turn, the farmer who sold the potatoes could also be achieving ES if the farm has lowered its average input costs through, for example, buying fertilizer in bulk at a volume discount.)
Costly inputs: Some inputs, such as research and development, advertising, managerial expertise and skilled labor are expensive, but because of the possibility of increased efficiency with such inputs, they can lead to a decrease in the average cost of production and selling. If a company is able to spread the cost of such inputs over an increase in its production units, ES can be realized. Thus, if the fast food chain chooses to spend more money on technology to eventually increase efficiency by lowering the average cost of hamburger assembly, it would also have to increase the number of hamburgers it produces a year in order to cover the increased technology expenditure. Specialized inputs: As the scale of production of a company increases, a company can employ the use of specialized labor and machinery resulting in greater efficiency. This is because workers would be better qualified for a specific job - for example, someone who only makes French fries - and would no longer be spending extra time learning to do work not within their specialization (making hamburgers or taking a customer's order). Machinery, such as a dedicated French fry maker, would also have a longer life as it would not have to be over and/or improperly used. Techniques and Organizational inputs: With a larger scale of production, a company may also apply better organizational skills to its resources, such as a clear-cut chain of command, while improving its techniques for production and distribution. Thus, behind the counter employees at the fast food chain may be organized according to those taking in-house orders and those dedicated to drive-thru customers. Learning inputs: Similar to improved organization and technique, with time, the learning processes related to production, selling and distribution can result in improved efficiency practice makes perfect!
External economies of scale can also be realized from the above-mentioned inputs as a result of the company's geographical location. Thus all fast food chains located in the same area of a certain city could benefit from lower transportation costs and a skilled labor force. Moreover, support industries may then begin to develop, such as dedicated fast food potato and/or cattle breeding farms. External economies of scale can also be reaped if the industry lessens the burdens of costly inputs, by sharing technology or managerial expertise, for example. This spillover effect can lead to the creation of standards within an industry. But Diseconomies Can Also Occur As we mentioned before, diseconomies may also occur. They could stem from inefficient managerial or labor policies, over-hiring or deteriorating transportation networks (external DS). Furthermore, as a company's scope increases, it may have to distribute its goods and services in progressively more dispersed areas. This can actually increase average costs resulting in diseconomies of scale. Some efficiencies and inefficiencies are more location specific, while others are not affected by area. If a company has many plants throughout the country, they can all benefit from costly inputs such as advertising. However, efficiencies and inefficiencies can alternatively stem from a particular location,
such as a good or bad climate for farming. When ES or DS are location specific, trade is used in order to gain access to the efficiencies. Is Bigger Really Better? There is a worldwide debate about the effects of expanded business seeking economies of scale, and consequently, international trade and the globalization of the economy. Those who oppose this globalization, as seen in the demonstrations held outside World Trade Organization (WTO) meetings, have claimed that not only will small business become extinct with the advent of the transnational corporation, the environment will be negatively affected, developing nations will not grow and the consumer and workforce will become increasingly less visible. As businesses get bigger, the balance of power between demand and supply could become weaker, thus putting the company out of touch with the needs of its consumers. Moreover, it is feared that competition could virtually disappear as large companies begin to integrate and the monopolies created focus on making a buck rather than thinking of the consumer when determining price. The debate and protests continue. Conclusion The key to understanding ES and DS is that the sources vary. A company needs to determine the net effect of its decisions affecting its efficiency, and not just focus on one particular source. Thus, while a decision to increase its scale of operations may result in decreasing the average cost of inputs (volume discounts), it could also give rise to diseconomies of scale if its subsequently widened distribution network is inefficient because not enough transport trucks were invested in as well. Thus, when making a strategic decision to expand, companies need to balance the effects of different sources of ES and DS so that the average cost of all decisions made is lower, resulting in greater efficiency all around.
Economies Of Scale
What Does Economies Of Scale Mean? The increase in efficiency of production as the number of goods being produced increases. Typically, a company that achieves economies of scale lowers the average cost per unit through increased production since fixed costs are shared over an increased number of goods. There are two types of economies of scale: -External economies - the cost per unit depends on the size of the industry, not the firm. -Internal economies - the cost per unit depends on size of the individual firm.
Investopedia explains Economies Of Scale Economies of scale gives big companies access to a larger market by allowing them to operate
with greater geographical reach. For the more traditional (small to medium) companies, however, size does have its limits. After a point, an increase in size (output) actually causes an increase in production costs. This is called "diseconomies of scale"
Economies of Scope
What Does Economies of Scope Mean? An economic theory stating that the average total cost of production decreases as a result of increasing the number of different goods produced.
Investopedia explains Economies of Scope For example, McDonalds can produce both hamburgers and French fries at a lower average cost than what it would cost two separate firms to produce the same goods. This is because McDonalds hamburgers and French fries share the use of food storage, preparation facilities, and so forth during production. Another example is a company such as Proctor & Gamble, which produces hundreds of products from razors to toothpaste. They can afford to hire expensive graphic designers and marketing experts who will use their skills across the product lines. Because the costs are spread out, this lowers the average total cost of production for each product.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Progress On E-Waste Management-2009-05 - Bcrc-China - May 09Document14 pagesProgress On E-Waste Management-2009-05 - Bcrc-China - May 09Lakshmi Narayanan MahalingamPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- SCB - K & NDocument7 pagesSCB - K & NJerry AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Basel CommitteeDocument4 pagesBasel CommitteeJerry AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- CBDocument3 pagesCBJerry AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
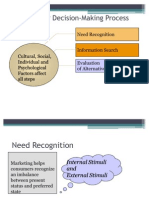
- Buying Decisions SohamDocument8 pagesBuying Decisions SohamJerry AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- HRM AssignmentDocument10 pagesHRM AssignmentrenneyPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Assignment No. 3 (Decision Making)Document2 pagesAssignment No. 3 (Decision Making)April Lyn SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- UTHM Assignment BFC 34303 - Civil Engineering Statistics Sem I 2017/2018Document6 pagesUTHM Assignment BFC 34303 - Civil Engineering Statistics Sem I 2017/2018WeyWeyEnne0% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- How To Choose Your Life PartnerDocument11 pagesHow To Choose Your Life PartnerAref Daneshzad100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Studies in Human-Thing Entanglement Ian Hodder 2016Document178 pagesStudies in Human-Thing Entanglement Ian Hodder 2016Carolina SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions: Activity 1: Checking Out Local Art MaterialsDocument2 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions: Activity 1: Checking Out Local Art MaterialsZharina Villanueva100% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Hussian Matrix Economic Applications PDFDocument51 pagesHussian Matrix Economic Applications PDFSiddi RamuluPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Grade 10 Test QuestionsDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Test QuestionsMAUREEN GARCIAPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Summary Diffusion TheoryDocument9 pagesSummary Diffusion Theoryhaliermarek100% (2)
- p1 Visual Analysis HybridDocument3 pagesp1 Visual Analysis Hybridapi-437844434Pas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Spirituality, What It IsDocument141 pagesSpirituality, What It IsSant MatPas encore d'évaluation
- Section OneDocument14 pagesSection Onecam spiderPas encore d'évaluation
- BASC9001 Essay RubricsDocument1 pageBASC9001 Essay RubricsnpriscillaswPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Big Five Model of Personality - Assignment 1Document13 pagesBig Five Model of Personality - Assignment 1Rohitakshi SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- 11 - Surah HudDocument65 pages11 - Surah HudmostromPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Human Geography Chapter 1 Basic Concepts VocabularyDocument3 pagesAP Human Geography Chapter 1 Basic Concepts VocabularyElizabethPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Rasa Theory ShakuntalaDocument11 pagesRasa Theory ShakuntalaShivam Aggarwal100% (1)
- DIGC102: Ethnography Guest LectureDocument27 pagesDIGC102: Ethnography Guest LectureKatie FreundPas encore d'évaluation
- A Visit To Royal Food (Case)Document13 pagesA Visit To Royal Food (Case)Delawar BarekzaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis Matematis Peserta Didik Kelas VIII SMP Negeri 3 Payakumbuh MenggunakanDocument7 pagesAnalisis Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis Matematis Peserta Didik Kelas VIII SMP Negeri 3 Payakumbuh MenggunakanIstiqomahPas encore d'évaluation
- First Aid DLPDocument2 pagesFirst Aid DLPGavinKarl Mianabanatao67% (3)
- Chapter4 SULLIVAN, Graeme Art As Practice ResearchDocument26 pagesChapter4 SULLIVAN, Graeme Art As Practice ResearchkarithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Seven Lots of Vice and VirtueDocument7 pagesSeven Lots of Vice and Virtueshadowgraph100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Bcs Higher Education Qualifications BCS Level 5 Diploma in ITDocument6 pagesBcs Higher Education Qualifications BCS Level 5 Diploma in ITOzioma IhekwoabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Historicity of The Resurrection of Jesus ChristDocument13 pagesHistoricity of The Resurrection of Jesus ChristServant Of Truth100% (2)
- 1 Peter Student's GuideDocument25 pages1 Peter Student's GuideAnonymous J4Yf8FPas encore d'évaluation
- CRIMINOLOGY, Textbook, 12th Ed.: January 2015Document9 pagesCRIMINOLOGY, Textbook, 12th Ed.: January 2015Adonai Jireh Dionne BalitePas encore d'évaluation
- History of Human Resource ManagementDocument19 pagesHistory of Human Resource ManagementNaila MehboobPas encore d'évaluation
- EPC Assignment 2 3Document3 pagesEPC Assignment 2 3TiongJingYinPas encore d'évaluation
- Sense of Control Under Uncertainty Depends On People's Childhood Environment: A Life History Theory ApproachDocument17 pagesSense of Control Under Uncertainty Depends On People's Childhood Environment: A Life History Theory ApproachRiazboniPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)