Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Question of Digital Electronics
Transféré par
Santosh BanDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Question of Digital Electronics
Transféré par
Santosh BanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
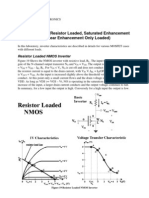
Digital Electronics (BEX III/II) Group 1 1.
Write the Eber-Moll equation on normal operation and inverted operating using superposition of two currents. 2. Define saturated, non-saturated, and uni-polar logic family and give examples of it. 3. Why monostable multivibrator is called as on shot multivibrator? 4. Analyze the Diode Transistor Logic (DTL) circuit with input low. 5. Draws the two inputs DTL AND-OR-INVERT gates circuits and DTL NOR gate circuit. 6. Determine the one input is low for TTL circuit model. 7. Discuss the NMOS inverter with resister load at cut off and non-saturation region. 8. Discuss the NMOS inverter with resister load at non-saturation and transition region. 9. Show that, n-channel MOSFET with depletion load is differing from others. 10. Explain the driver transistor curve and load curve of the NMOS. 11. Analyze the CMOS inverter for VI is just greater than VTN when both transistors are enhancement mode devices. 12. Give complete voltage transfer characteristics of the CMOS inverter when both transistors are enhancement mode devices. 13. Construct the two inputs CMOS NAND gate with its truth table. 14. How ROM is differs from RAM? Give its importance and examples also. 15. Write down the importance of photolithography process in IC fabrication. 16. Realize the PLA and make PLA tables for the following logic expressions: F0 = m (0, 8, 15, 12, 5, 7, 3) F1 = m (2, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 15) F3 = m (1, 4, 5, 7, 9, 12, 15) F4 = m (5, 6, 8, 10, 11) 17. Write short notes. a. Charge Coupled Devices b. SDRAM c. Bistable multivibrator d. Power dissipation in CMOS inverter e. NMOS transmission gate Group 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Why the Eber-Moll model is called T model? Describe charge distribution in the base. What are the parameters to characterize digital ICs, how can you compare performance of it. Write operation procedures for monostable multivibrator when it is in stable state. Calculate maximum low input voltage for DTL circuit, when supply voltage is 5 volts and take the appropriate values of resisters. Explain the operation of DTL logic circuit. Explain the operation of TTL logic circuit when all inputs high. Write down the three formulae used in n-channel MOSFET. What are the basic properties of logic gates? Write down, MOSFET inverters with resistive load. Justify all possible cases for voltage input and output characteristics for NMOS inverter with depletion load. What are the differences in the concept of effective width to length ratios of NMOS logic circuit? Analyze the CMOS inverter for VI = VDD when both transistors are enhancement mode devices. Give the possible logics for CMOS inverter design consideration. Write FAN-IN and FAN-OUT of CMOS inverter. Write operation procedures for SRAM. Realize the PLA and make PLA tables for the following logic expressions: F0 = m (0, 8, 15, 12, 5, 7, 3) F1 = m (2, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 15) F3 = m (1, 4, 5, 7, 9, 12, 15) 1
F4 = m (5, 6, 8, 10, 11) 16. What are the main steps follow during IC fabrication? 17. Write short notes. a. Noise Margin b. Charge Coupled Devices c. Power dissipation in CMOS inverter d. NMOS transmission gate e. Comparison between BJT and MOS Group 3 1. Write the Eber-Moll equation on normal operation and inverted operating using superposition of the four currents. 2. What is multivibrator? Explain the Bistable multivibrator briefly. 3. Write operation procedures for monostable multivibrator when it is triggered. 4. Describe the operation procedures when Resister Transistor Logic input high with circuit diagram. 5. How Transistor Transistor Logic (TTL) is differing from DTL? 6. Explain the operation of ECL logic circuit. 7. How NMOS is replaced by CMOS? Justify. 8. Explain input and output voltage characteristics curve for NMOS inverter with resister load. 9. What will happen when i) VI < VTND, ii) VI is just greater than VTND, iii) transition point for the driver, NMOS inverter with depletion load? 10. Define NMOS NOR logic gate with depletion load and realize the all possible combinations for two inputs. 11. Analyze the CMOS inverter for VI = 0 when both transistors are enhancement mode devices. 12. Generalized CMOS inverter current when NMOS inverter biased in the saturation region. 13. What are the most important parameters for evaluating and comparing logic families? 14. What are the differences between SRAM and DRAM? Give its symbolic representation. 15. How can you say that 555 Timer IC is most popular commercially available integrate-circuit packages? Give the internal function diagram of the 555IC. 16. Realize the PLA and make PLA tables for the following logic expressions: F0 = m (0, 8, 15, 12, 5, 7, 3) F1 = m (2, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 15) F3 = m (1, 4, 5, 7, 9, 12, 15) F4 = m (5, 6, 8, 10, 11) 17, Write short notes. a. A 3-bit CCD shift register b. Basic steps of IC fabrication c. Enhanced DRAM d. Difference between NMOS and PMOS e. CMOS transmission gate Group 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What are the delay, rise, storage, and fall time for BJT switching? Explain each with neat diagrams. Why astable multivibrator is called as free running multivibrator? Justify. What are the advantages and limitations of resister transistor logic? Analyze the Diode Transistor Logic (DTL) circuit with all input high. Calculate the maximum load current. Explain the operation of TTL logic circuit. What are the merits, demerits, and uses of ECL? How merge transistor logic is differing from other logic family? Write down the current voltage relationship for NMOS inverter with resister load. What is the advantage of depletion load inverter over the enhancement load inverter? 2
10. Define NMOS NAND logic gate with depletion load and realize the all possible combinations for two inputs. 11. Write down the CMOS properties, and draw cross section view of CMOS logic. 12. Generalized CMOS inverter current when PMOS inverter biased in the saturation region. 13. Analyze the CMOS transmission gate when i. input high condition, ii. Input low condition, iii. Remains in dynamic condition. 14. Give the RAM family chart. How main memory differ from the mass storage memory. 15. Design a programmable logic array (PLA) using AND matrix and OR matrix, which should realize the following logic expressions: Y0 = mno + mno + mno + mno Y1 = mno + mno + mno Y2 = mno + mno + mno Y3 = mno + mno + mno 16. What are the ten basic steps of photolithography process during semiconductor fabrication process? 17, Write short notes. a. Difference between NMOS and PMOS b. Power dissipation in CMOS inverter c. NMOS transmission gate d. Enhanced DRAMs e. Comparison between BJT and MOS Group 5 1. How can you improve BJT time? Give circuit diagram and corresponding wave form. 2. Write operation procedures for astable multivibrator. 3. Derive the operation procedures when Resister Transistor Logic input both low to both transistor with circuit diagram. 4. Draw the two input DTL AND gate circuits and DTL OR gate circuit. 5. Determine the maximum low input current for TTL circuit model. 6. Explain the operation of ECL 10K series with circuit diagram. 7. What are the important features of Integrated Injection Logic (IIL)? Draw the circuit diagram of 2 input IIL circuit. 8. What are the major differences between NMOS inverter with resister load and enhancement load? Which NMOS inverter is greater in size and how? 9. What are the difference between NMOS and PMOS? 10. How can you say that rise time is relatively longer than fall time of an NMOS inverter with depletion load? Justify. 11. What are the merits of CMOS logic? Explain the operations of this logic. 12. Construct the two inputs CMOS NOR gate with its truth table. 13. How can you design CMOS NOR symmetrical gate? 14. Explain the semiconductor memories with its basic properties. 15. Design a programmable logic array (PLA) using NMOS, which should realize the following logic expressions: F0 = m (0, 8, 15, 12, 5, 7, 3) F1 = m (2, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 15) F3 = m (1, 4, 5, 7, 9, 12, 15) F4 = m (5, 6, 8, 10, 11) 16. What are the ten basic steps of photolithography process during semiconductor fabrication process? 17. Write short notes. 1. Propagation Delay Time 2. Charge Coupled Devices 3. Enhanced DRAM 4. Difference between NMOS and PMOS 5. Comparison between BJT and MOS 3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- A Handbook/manual On How To Search Courses/universities AbroadDocument43 pagesA Handbook/manual On How To Search Courses/universities AbroadDeepakKaduwalPas encore d'évaluation
- DSP1Document6 pagesDSP1Santosh BanPas encore d'évaluation
- GMSKDocument20 pagesGMSKSantosh Ban100% (1)
- Section SchedulingDocument23 pagesSection SchedulingAJ ToledoPas encore d'évaluation
- CompArchCh06L01PipeLine PDFDocument39 pagesCompArchCh06L01PipeLine PDFparinaz2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Communication StandardsDocument52 pagesMobile Communication StandardsSantosh BanPas encore d'évaluation
- Modulation MethodsDocument41 pagesModulation MethodsMuhammad Hammad TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec08 DSPDocument42 pagesLec08 DSPSantosh BanPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating System KERNELDocument2 pagesOperating System KERNELSantosh BanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cache Memory CADDocument16 pagesCache Memory CADSantosh BanPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadmeDocument2 pagesReadmeMuhamad Tuah AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- LM35 Temperature SensorDocument13 pagesLM35 Temperature Sensorapi-3799604100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Cmos Vlsi DesignDocument359 pagesCmos Vlsi Designashish100% (1)
- Expt 4 Truth Table Verification of Logic GatesDocument5 pagesExpt 4 Truth Table Verification of Logic GatesSwapnil Babele100% (1)
- Feedback Control System CharacteristicsDocument29 pagesFeedback Control System CharacteristicsGafry MahmoudPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC Controlling Program of An ElevatorDocument64 pagesPLC Controlling Program of An ElevatorRohit BarmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Logic GatesDocument12 pagesFundamentals of Logic Gatesquickrelease_32100% (2)
- Bi CMOSDocument6 pagesBi CMOSlachuns123Pas encore d'évaluation
- NMOS InverterDocument6 pagesNMOS Inverterrohindeep-singh-6605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cristobal, Rowela - Research Work #4Document17 pagesCristobal, Rowela - Research Work #4rowela cristobalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 10Document9 pagesLab 10amngreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Microwind User Manual v1Document126 pagesMicrowind User Manual v1Jamal HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Elad Alon Homework #4 EECS141Document2 pagesUniversity of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Elad Alon Homework #4 EECS141Vidhya DsPas encore d'évaluation
- VlsiDocument79 pagesVlsimdhuq1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nirma University Institute of Technology: B. Tech. in Electronics and Communication Engineering Semester - VDocument15 pagesNirma University Institute of Technology: B. Tech. in Electronics and Communication Engineering Semester - VPragya jhalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Logic Design - Switch Logic & Basic GatesDocument27 pagesDigital Logic Design - Switch Logic & Basic GatesTroon SoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Logic Gates: Truth TablesDocument7 pagesLogic Gates: Truth TablesMichael JalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Work 3 - CMOS + Rubric PDFDocument25 pagesPractical Work 3 - CMOS + Rubric PDFRiki SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- 9.4 Logic GatesDocument12 pages9.4 Logic GatesEric TohPas encore d'évaluation
- Embedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software IntroductionDocument29 pagesEmbedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software Introductionmanibcaa78Pas encore d'évaluation
- CMOS Inverter: DC Analysis: Courtesy: Prof Andrew MasonDocument8 pagesCMOS Inverter: DC Analysis: Courtesy: Prof Andrew MasonvmspraneethPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Digital Electronics: Microelectronic Circuit DesignDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Digital Electronics: Microelectronic Circuit DesignramibotrosPas encore d'évaluation
- DLD CEL 120 Lab Manual PDFDocument65 pagesDLD CEL 120 Lab Manual PDFBurhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Electronics Lab Worksheet: The Various Logical Gates AreDocument80 pagesDigital Electronics Lab Worksheet: The Various Logical Gates AreSAURAVPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report ElectronicDocument41 pagesLab Report Electronichyebibie0% (1)
- Lec 06Document24 pagesLec 06bivaye4887Pas encore d'évaluation
- CS 202 - Digital Design Lecture 1Document25 pagesCS 202 - Digital Design Lecture 1cleofe caloPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Logic GatesDocument5 pagesBasic Logic GatesVasu ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Hamza Hanif DLD Lab #2Document6 pagesHamza Hanif DLD Lab #2Hamza KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3.1 Logic Gates WorkbookDocument44 pages1.3.1 Logic Gates WorkbookTakudzwa MajongisiPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital CMOS Logic CircuitsDocument84 pagesDigital CMOS Logic CircuitsPulkit AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- VLSI Design SoC CH 6Document125 pagesVLSI Design SoC CH 6Arqam Ali KhanPas encore d'évaluation