Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pricing Assignment 2
Transféré par
al4423821Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pricing Assignment 2
Transféré par
al4423821Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
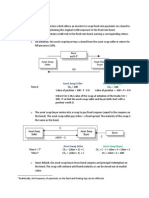
To solve the different scenarios for the Golden Chicken Company we must understand first what is the current
profit and operations of the company, and to perform this we evaluate the structure of the current profits that is as follows: Profit=Revenue-Cost Revenues: The current flow of revenues derives from the sell of eggs to the wholesalers Existing demand is Q=1000 units/day, and the current price is $6/case From this we obtain the following revenue: Revenue(R)=Price(P) * Quantity(Q) R=$6*1,000= $6,000.00 Costs: The costs that Golden chicken company has are related to transportation and raw materials. Raw materials: the cost per case up to 1,000 is $3.00 and as this point, demand is fixed, we will not incur in additional costs to bring eggs from outside suppliers. RMc= 1000 * $3.00 = $3,000.00 Transportation: An agreement with a transportation company allows us to distribute our products, we can transport up to 50 cases per truck at a cost of $50.00 per route.
To transport the 1,000 eggs that we have as current demand we will require 1,000 units/ 50 units/truck = 20 trucks Trc= 20 * $50.00 = $1,000.00 We obtain the total cost by adding the Raw material and transportation cost and we obtain: TC= $3,000.00 + $1,000.00 = $4,000.00 Profit: The initial profit is: P=R-C = $6,000.00 - $4,000.00 = $2,000.00
Case A The wholesale price of a case of eggs increase to $6.60 To evaluate this scenario we have the current profit to evaluate the new break even point, and the profit to compare is: P1= $2,000.00 For this scenario we expect a decrease in the demand as the price increases by 10%, therefore we would expect no need to buy additional eggs. Therefore we calculate the new quantity to be sold to obtain P1 P1= (Price*Quantity) - Transport cost new raw material cost new
$2,000 .00 = $6.6 * Qn (Qn/50)*$50 Qn*$3.00 $2,000.00 = $6.6Qn Qn - $3 Qn $2,000.00 = $2.6 Qn Qn = 770.00 units Case B The wholesale price of a case is reduced to $5.50 For this scenario we will consider the initial profit as our comparison point. Under these circumstances we will assume that demand will be higher than the original 1000 units, therefore there is a possibility to buy additional eggs from external suppliers at a cost of $4.00 per case. To calculate the maximum profit with the existing demand at the new price we perform the following calculation: Cost Tc= (1000/50)*50 = $1,000.00 Rmc= 3*1000= $3,000.00 TC= $4,000 Revenue R=$5.50 * 1000= $5,500.00 Profit = $5,500 - $4,000 = $1,500.00
From this calculation we derive that in order to arrive to a break even point we need to earn additional $500.00 from the external supply to match our initial profit of $2,000.00 We can calculate the additional sales as follows Profit=Revenues-cost $500= $5.5Qn (Qn/50)*$50 - $4.00 Qn $500= $0.5Qn Qn = 1000 units This means that in order to break even in this situation the new quantity to be order is 2,000 units, from which 1,000 will come from external suppliers. Case C How would you answer this if the current sales level is 800 units. To solve this new scenario we require to run the same steps as per the case B Cost Tc= (800/50)*50 = $800.00 Rmc= 3*800= $2,400.00 TC= $3,200 Revenue R=$5.50 * 800= $4,400.00 Profit = $4,400 - $3,200 = $1,200.00
From this calculation we derive that in order to arrive to a break even point we need to earn additional $800.00 from the external supply to match our initial profit of $2,000.00 We can calculate the additional sales as follows Profit=Revenues-cost $800= $5.5Qn (Qn/50)*$50 - $4.00 Qn $800= $0.5Qn Qn = 1600 units This means that in order to break even in this situation the new quantity to be order is 2,400 units, from which 1,600 will come from external suppliers.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsD'EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsPas encore d'évaluation
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)D'EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (9)
- Zerin Tasnim - 03 - MSC301Document14 pagesZerin Tasnim - 03 - MSC301Zerin Tasnim AnannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 011Document5 pagesChap 011dt830280% (5)
- Chapter 2 Q&P Answers SanchezDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Q&P Answers SanchezRobert Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anna Kolos EO-107i - Coursework in MicroeconomicsDocument21 pagesAnna Kolos EO-107i - Coursework in MicroeconomicsRohan Nim0% (1)
- Week 7 - AssignmentDocument11 pagesWeek 7 - AssignmentShakil Reddy BhimavarapuPas encore d'évaluation
- Managerial Economics Michael Baye Chapter 8 AnswersDocument6 pagesManagerial Economics Michael Baye Chapter 8 Answersneeebbbsy8980% (10)
- Chapter 8: Answers To Questions and Problems: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 5eDocument5 pagesChapter 8: Answers To Questions and Problems: Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 5eadityaintouch100% (1)
- Chap 002 SDocument8 pagesChap 002 SAashima GroverPas encore d'évaluation
- f5 Mock SolDocument16 pagesf5 Mock SolSalome farrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Work Sheet (1) Chapter - 1Document10 pagesMaths Work Sheet (1) Chapter - 1ibsaashekaPas encore d'évaluation
- IMT Ghaziabad Lectures 19 and 20Document30 pagesIMT Ghaziabad Lectures 19 and 20Arun AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Complete SolutionsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Complete SolutionsVictor64% (14)
- Hw2-Nguyễn Thị Tâm Thanh-ielsiu19263Document11 pagesHw2-Nguyễn Thị Tâm Thanh-ielsiu19263Nguyễn Thị Tâm ThanhPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic CH 3 & CH4Document4 pagesEconomic CH 3 & CH4m habiburrahman55Pas encore d'évaluation
- ExtraDocument6 pagesExtrajunaidzia0% (1)
- Just Baked - SambhuSankarDocument10 pagesJust Baked - SambhuSankarSambhu Sankar100% (1)
- Module 4 Math in The Modern WorldDocument11 pagesModule 4 Math in The Modern WorldJerusa May CabinganPas encore d'évaluation
- MGMT 3100 CH 4 ExerciseDocument2 pagesMGMT 3100 CH 4 ExerciseJames Riley CasePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - 2 With Answer-1Document7 pagesAssignment - 2 With Answer-1rawan APas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Asg3Document12 pagesCost Asg3Shahzȝb KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Break Even Analysis and Short Term Profit PlanningDocument35 pagesBreak Even Analysis and Short Term Profit PlanningArnab BhattacharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA 500 Managerial Economics-AssignmentDocument23 pagesMBA 500 Managerial Economics-AssignmentHarris LuiPas encore d'évaluation
- Consignment Sums ExampleDocument9 pagesConsignment Sums ExampleDale 08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Imp Numerical Perfect CompetitionDocument27 pagesImp Numerical Perfect CompetitionSachin SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- APM Pricing-Decision-Nov2020Document31 pagesAPM Pricing-Decision-Nov2020Bijay AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Pricing Decision Nov2020Document31 pagesChapter 7 Pricing Decision Nov2020PratyushPas encore d'évaluation
- Maranan, A2A - Break Even Point AnalysisDocument6 pagesMaranan, A2A - Break Even Point AnalysisJere Mae Maranan100% (1)
- LogisticDocument7 pagesLogisticМаша Сабір'яноваPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics NumericalsDocument9 pagesEconomics NumericalsIshaan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Written Assignment Week 4Document5 pagesWritten Assignment Week 4Shiraz ShafqatPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice: 1. Suppose There Is A Perfectly Competitive Industry Where All The Firms AreDocument10 pagesPractice: 1. Suppose There Is A Perfectly Competitive Industry Where All The Firms Aremaddie isnt realPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 AssignmentDocument13 pagesChapter 16 Assignmentshoaiba1Pas encore d'évaluation
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Assignment 1Document23 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Assignment 1BRAMANTYO CIPTA ADI100% (1)
- CalculusDocument18 pagesCalculusShahrukh Abdur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Problems On Quantitative Techniques in BusinessDocument16 pagesSome Problems On Quantitative Techniques in BusinessChao khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Break Even AnalysisDocument4 pagesBreak Even AnalysisOwen Hudson0% (1)
- 4.6 Optimization: Day 2: Problems Involving Revenue or ProfitDocument5 pages4.6 Optimization: Day 2: Problems Involving Revenue or ProfitAnne Nicole GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 9 Suggested Solutions To Class QuestionsDocument8 pagesWeek 9 Suggested Solutions To Class QuestionspartyycrasherPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledBipin Kumar JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- PPP - Homework 5Document17 pagesPPP - Homework 5Wiratha Nungrat67% (9)
- Add or Drop Product DecisionsDocument6 pagesAdd or Drop Product DecisionsksnsatishPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions & AnswerDocument5 pagesPractice Questions & AnswerAreej Fatima 29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Break EvenDocument46 pagesBreak EvenRaj TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesModule 2 SolutionsNeha Wadhwani AhujaPas encore d'évaluation
- $70) ÷ $150 53.33%) - This May Suggest That D. LawranceDocument1 page$70) ÷ $150 53.33%) - This May Suggest That D. LawrancejppjelPas encore d'évaluation
- CVP BEP Analysis. Assignments, (In Class) : RequiredDocument3 pagesCVP BEP Analysis. Assignments, (In Class) : Requiredmuhammed shadPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdul Basit BUS-17S-085 Subject: Cost Accouting Assignment 3Document8 pagesAbdul Basit BUS-17S-085 Subject: Cost Accouting Assignment 3Shahzȝb KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- ĐÁP ÁN PHIẾU ÔN TẬP TOÁN CAO CẤPDocument62 pagesĐÁP ÁN PHIẾU ÔN TẬP TOÁN CAO CẤPTrường XuânPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand For The Two Is CalculatedDocument3 pagesThe Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand For The Two Is CalculatedhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Managerial Economics - Lecture 3Document18 pagesManagerial Economics - Lecture 3Fizza MasroorPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic CalculationDocument7 pagesEconomic CalculationsingsaranPas encore d'évaluation
- ME Answer Keys (Problem Set-5) - 2020Document5 pagesME Answer Keys (Problem Set-5) - 2020aksPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Problems 100202064251 Phpapp01Document27 pagesEconomics Problems 100202064251 Phpapp01Hashma KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Ariel ProjectDocument36 pagesFinal Ariel ProjectAkshit JhingranPas encore d'évaluation
- Convertible and Non Convertible DebenturesDocument2 pagesConvertible and Non Convertible Debenturesvenkatrao_100Pas encore d'évaluation
- M.a.part - I - Macro Economics (Eng)Document341 pagesM.a.part - I - Macro Economics (Eng)Divyesh DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- Macroeconomics International 5th Edition Williamson Solutions ManualDocument6 pagesMacroeconomics International 5th Edition Williamson Solutions Manualchristinamerrittqgdopicfxt100% (11)
- Micro-U4L2A44-How Many Workers Should Be HiredDocument2 pagesMicro-U4L2A44-How Many Workers Should Be HiredAdvika PunjePas encore d'évaluation
- 8270 IOMS Chap1Document12 pages8270 IOMS Chap1Rafa SambeatPas encore d'évaluation
- Asset SwapsDocument5 pagesAsset Swaps15dumplings100% (1)
- AddonsDocument11 pagesAddonsShreyas Marulkar100% (1)
- Economics Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesDocument6 pagesEconomics Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesAndres Krauss100% (1)
- 3-3. How Do Porter's Competitive Forces Model, The Value Chain Model, Synergies, Core Competencies, and Network Economics Help Companies Develop Competitive Strategies Using Information Systems?Document4 pages3-3. How Do Porter's Competitive Forces Model, The Value Chain Model, Synergies, Core Competencies, and Network Economics Help Companies Develop Competitive Strategies Using Information Systems?Phú Nguyễn Văn HoàngPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital MarketsDocument12 pagesCapital MarketsSanoj Kumar YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 7 Price EscalationDocument16 pagesModule 7 Price EscalationkatherinePas encore d'évaluation
- Titan Raga: Contemporary Elegance in Ethnic Design "For" Contemporary WomenDocument4 pagesTitan Raga: Contemporary Elegance in Ethnic Design "For" Contemporary WomenArpit KasturePas encore d'évaluation
- Brand Marketing Project Manager in NYC Resume Colleen CollierDocument2 pagesBrand Marketing Project Manager in NYC Resume Colleen CollierColleenCollierPas encore d'évaluation
- Promotion and Pricing Strategies: Learn Ing G OalsDocument42 pagesPromotion and Pricing Strategies: Learn Ing G OalsCristine SaludoPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics 2006 Postume TestDocument16 pagesEconomics 2006 Postume Testvaluba01Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Rebranding Brief - TemplateDocument8 pagesThe Rebranding Brief - TemplateRushiraj Patel100% (1)
- Advantage For Online ShoppingDocument1 pageAdvantage For Online ShoppingPrateek MathurPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8BDocument41 pagesChapter 8Bbrandon reileyPas encore d'évaluation
- MIDTERM FinMar 1Document11 pagesMIDTERM FinMar 1Aira ArabitPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 AssignmentDocument2 pagesChapter 3 AssignmentLeo GuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- Bodie10ce SM Ch01Document5 pagesBodie10ce SM Ch01beadand1Pas encore d'évaluation
- SUNSILK Company ObjectivesDocument8 pagesSUNSILK Company ObjectivesTasslim Shaikh50% (4)
- Mark Up Mark Down QuizDocument6 pagesMark Up Mark Down QuizEfrelyn Grethel Baraya AlejandroPas encore d'évaluation
- ElasticitypracticeDocument3 pagesElasticitypracticeapi-2605125630% (1)
- Problems Stocks ValuationDocument3 pagesProblems Stocks Valuationmimi96Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Photonis ProjectDocument26 pagesThe Photonis ProjectchandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Function and Role of Financial SystemsDocument33 pagesFunction and Role of Financial Systemsaamirjewani100% (1)
- Gary Smith - MomentumDocument17 pagesGary Smith - MomentumbrentPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Derivative Markets 1. Forward Contracts 2. Future Contracts 3. Options Example of Forward ContractsDocument3 pagesTypes of Derivative Markets 1. Forward Contracts 2. Future Contracts 3. Options Example of Forward ContractsJoseph NarizPas encore d'évaluation