Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Fatigue and weakness assessment
Transféré par
Bob Joyce Dela PeñaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Fatigue and weakness assessment
Transféré par
Bob Joyce Dela PeñaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
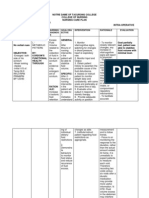
ALTERED NUTRITION: LESS THAN BODY REQUIREMENTS ASSESSMENT S: O: The patient manifested: >poor muscle development >poor muscle
e tone >unable to open mouth wide >weakness The pt. may manifest: >hyperactive bowel sounds >underweight >fecal loss of blood >prone to infections >capillary fragility >pale palpebral conjunctiva >pale mucus membrane NURSING DIAGNOSIS Altered Nutrition: less than body requirement r/t inability to open mouth wide and muscle weakness. SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Acute disease induced by toxin of tetanus bacillus growing anaerobically in wounds and at site of umbilicus among infants. Characterized by muscular contraction. The client manifested weakness due to severe muscle contraction and due to compensator y mechanism of the body like increase in temperature. The client also OBJECTIVES Short Term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will verbalize understanding of causative factors when known and necessary interventions. Patients vital signs will decrease/retu rn to normal rate/ranges. Long Term: After 2 days of NI, the patient will demonstrate behaviors, lifestyle changes to regain and/or maintain appropriate weight and patients vital NURSING RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS > Establish > To gain the rapport trust and cooperation of the pt. and the SO > Monitor and record V/S EXPECTED OUTCOME The patient shall verbalize understanding of causative factors when known and > To gain necessary baseline interventions. data for the Patients vital care and signs shall manageme decrease/retu nt of the rn to normal patient rate/ranges. And the >This will patient shall guide what demonstrate interventions behaviors, to provide lifestyle changes to >To assess regain and/or any maintain abnormalitie appropriate s weight and patients vital signs shall >To maintain to determine normal what rates/ranges. information to provide
>Assess patients condition
>Assess skin turgor and mucous membranes >Ascertain understanding of individual nutritional needs
manifested unable to open mouth wide due to muscle spasm caused by toxins that impaires neurologic functions. Thus, the client is unable to eat resulting to altered nutrition: less than body requirements.
signs will maintain to normal rates/ranges.
>Assess weight, age, body >Provides build, strength, comparativ activity/rest e baseline level, and so forth >Discuss eating >To appeal habits, to clients including food likes/desires preferences, intolerances >Encourage patient to choose foods which are appealing >Emphasize importance of well-balanced, nutritious intake >To stimulate appetite
>To achieve wellness and supply metabolic needs
ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE ASSESSMENT S: O: The patient manifested: > fatigue > weakness > restlessness > increased pulse > abnormal heart rate to activity > low tolerance of activity >with vital signs of: Temperature36.5C Pulse rate104bpm Respiratory rate- 20 cpm The pt. may manifest: > irritability > inability to perform or NURSING DIAGNOSIS Activity Intolerance r/t generalized weakness EXPECTED OUTCOME Short Term: The patient shall Activity After 4 hours of verbalize and intolerance is NI, the patient shall use energy a common will verbalize conservation problem since and will use techniques and physical energy management of activity conservation fatigue with increases the techniques and > Monitor and > To gain increasing demand for management of record V/S baseline data activity level oxygen and for the care and effects of heart rhythm. fatigue with increasing and inactivity shall In tetanus, activity level management have reduced. there is a and effects of of the patient The patients spasm in the inactivity will be vital signs shall muscles due reduced. The > Assess > Provides return to normal to the patients vital temperature, information rates/ranges: spreading of signs will return respirations, about V/S Heart rate in the toxins of and pulse; changes between 60the clostridium to normal rates/ranges: changes in caused by 100bpm. bacteria that Heart rate of 60- behavior hypoxia and causes 100 bpm (irritability, about irritability of lightheadednes behavior synapses of s, short changes the neurons Long Term: attention caused by Long term: making the After 2-3 days of span); if easily reduced The patient shall individuals NI, the patient fatigued, oxygenation demonstrate affected will demonstrate unable to of the brain maintenance of become maintenance of sleep, or weak; energy and physically energy and ability to endurance and weak and endurance tolerate any will be able to SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION OBJECTIVES NURSING RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS > Establish > To gain the rapport trust and cooperation of the pt. and the SO
begin an activity > exertional discomfort or dyspnea
unable to engage in normal physical activity without experiencing profound fatigue. In very advanced cases this may cause parality of muscles and other evidence of heart failure may appear. Patients may experience activity intolerance because of fatigue, weakness, and poor tissue oxygenation and increased heart rate.
levels and will activity or ADL be able to perform his daily > Assist with activities of life. activities that require exertion and are beyond tolerance and ability > Provide rest periods, plan care and activities around rest/sleep > Provide appropriate quiet activities, and allow interaction with other individuals > Refrain from performing nonessential procedures
perform his daily activities of life. > Minimizes physical exertion, which increases oxygen to tissues > Decreases oxygen expenditure to enhance tissue oxygenation > Promotes diversionary activity and prevents withdrawal
> Patients with limited activity intolerance need to prioritize tasks
> Place patient > To facilitate in semi-Fowler's breathing or sitting position > Replaces blood or blood components depending on type of anemia and need > Provides information to prevent fatigue by minimizing physical activity or exertion, which utilizes more oxygen and less exertion of the heart
> Administer transfusion of blood, packed RBC, platelets as ordered
> Inform patient of measures to take to conserve energy and increase endurance of the client including placing articles within reach, anticipating needs and assisting before client attempts activity, allowing for rest; remain
with patient as needed
> Inform patient to avoid stressful situations > Teach patient to recognize signs of physical overactivity
> Promotes quiet environment for child >This promotes awareness of when to reduce activity
FATIGUE ASSESSMENT
NURSING DIAGNOSIS S: Fatigue r/t muscular O: The weakness and patient spasticity manifested: >decreased performance >weakness >inability to restore energy, even after sleep >tiredness >inability to maintain usual routines >Vital signs taken: Temperature37.5C Pulse rate110 bpm Respiratory rate- 64 cpm The pt. may manifest: >lethargic or listless; drowsy >compromise d
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Decreased The tetanus toxin affects the site of interaction between the nerve and the muscle that it stimulates. This region is called the neuromuscula r junction. The tetanus toxin amplifies the chemical signal from the nerve to the muscle, which causes the muscles to tighten up in a continuous contraction or spasm. This results in either localized or generalized m uscle spasms causing the
EXPECTED OUTCOME Short Term: The patient After 2-3 shall hours of NI, verbalize the patient establishmen will verbalize t of a pattern establishmen of sleep/rest t of a pattern > Monitor and > To gain that of sleep/rest record V/S baseline facilitates that data for the optimal facilitates care and performance optimal managemen of required/ performance t of the desired of required/ >Assess patient activities. desired patients Patients vital activities. condition >This will signs shall Patients vital guide what return to signs will interventions normal return to to provide rates/ranges. normal >Assess current And the rates/ranges. activity level >Fatigue and patient shall exertional achieve Long Term: dyspnea are adequate After 2-3 characteristi activity days of NI, c symptoms tolerance, the patient of anemia AEB ability to will achieve >Assess perform adequate characteristics >Using a activities of activity of fatigue: quantitative daily living tolerance, -severity rating scale and AEB ability to -changes in such as 1 to verbalization perform severity over 10 can help of return to
OBJECTIVES
NURSING RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS > Establish > To gain the rapport trust and cooperation of the pt. and the SO
concentratio n >disinterest in surroundings > increased rest requirements >increased physical complaints
client to be paralyzed and become weakened or fatigued.
activities of daily living and verbalization of return to normal/nearnormal activity levels.
time -aggregating factors -alleviating factors
the patient describe the amount of fatigue experienced. Other rating >Monitor serum scales can electrolytes be and urine developed osmolality and using pictures report or descriptive abnormal words. This values method allows the nurse to compare changes in the patients fatigue level over time. It is important to determine if the patients level of fatigue is constant or if it varies over >Assess time. patients emotional >Anxiety and response to depression fatigue are the more common emotional
normal/nearnormal activity levels.
>Assess the patients expectations for fatigue relief, willingness to participate in strategies to reduce fatigue, and level of family and social support >Evaluate the patients sleep patterns for quality, quantity, time taken to fall asleep, and feeling upon awakening >Assist the patient to
responses associated with fatigue. These emotional states can add to the persons fatigue level and create a vicious cycle >Social support will be necessary to help the patient implement changes to reduce fatigue
>This promotes interest in drinking
develop a schedule for daily activity and rest
>Help the patient to set priorities for desired activities and role responsibilities
>A plan that balances periods of activity with periods of rest can help the patient complete desired activities without adding to levels of fatigue >To conserve energy and this can improve the patients mood and sense of emotional well-being >Bright lighting, noise, visitors, frequent distractions, and clutter in the patients physical
>Minimize environmental stimuli, especially during planned times for rest and sleep
>Teach the patient and family task organization techniques
environment can inhibit relaxation, interrupt rest/sleep, and contribute to fatigue
>Organizatio n can help the patient >Help the build patient endurance develop habits for physical to promote activity effective rest/sleep >Promoting patterns relaxation before sleep and providing for several hours of uninterrupted sleep can contribute to >Provide energy diversional restoration activities >Impaired concentratio n can limit ability to
>Encourage the patient to verbalize feelings about the impact of fatigue
block competing stimuli/ distractions >Fatigue can have a profound negative influence on family processes and social interactions
Impaired swallowing ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS S: Impaired swallowing O: The related to patient nueromascul manifested: ar >poor muscle impairment development >poor muscle tone >unable to open mouth wide >weakness >dysphagia >incomplete lip closure The pt. may manifest: >aspiration >coughing >adventitious breath sounds >productive cough >acidic smelling breath >vomiting >dry mucous
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Acute disease induced by toxin of tetanus bacillus growing anaerobically in wounds and at site of umbilicus among infants. Characterized by mascular contraction. Muscle spasm is caused by toxins because it affects impulses that stimulates muscle contration and rigidity. The client manifested dysphagia due to spasm of muscles in
NURSING RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS Short term: > Establish > To gain the After 3-4 hours rapport trust and of nursing cooperation interventions, of the pt. the client will and the SO be able to pass food and > Monitor and > To gain fluid from record V/S baseline mouth to data for the stomach care and safely manageme nt of the Long term: patient After 2-3 days >Assess of nursing patients >This will interventions, condition guide what the client will interventions be able to to provide maintain desired body >Determine >To assess weight ability to for impaired initiate/sustain ability to effective suck swallow
OBJECTIVES
>Note for >It suggests hyperextension inability to of head complete swallowing process
EXPECTED OUTCOME The patient shall verbalize understanding of causative factors when known and necessary interventions. Patients vital signs shall decrease/retu rn to normal rate/ranges. And the patient shall demonstrate behaviors, lifestyle changes to regain and/or maintain appropriate weight and patients vital signs shall maintain to normal rates/ranges.
membrane >poor skin turgor
the oral cavity. Neuromascul ar system is afftected that results to severe contraction of muscles. Thus, results to impaired swallowing.
>Auscultate for >to evaluate breath sounds presence of aspiration >Keep Head of >To reduce Bed risk of regurgitation /aspiration
>Suction oral cavity PRN
>To clear secretions and promotes airway safety
>Encourage a rest period before meals
>To minimize fatigue
Risk for aspiration ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS S: Risk for aspiration O: The related to patient impaired manifested: swallowing >poor muscle development >poor muscle tone >unable to open mouth wide >weakness >dysphagia The pt. may manifest: >coughing >adventitious breath sounds >productive cough
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Acute disease induced by toxin of tetanus bacillus growing anaerobically in wounds and at site of umbilicus among infants. Characterized by mascular contraction. Muscle spasm is caused by toxins because it affects impulses that stimulates muscle contration and rigidity. The client manifested dysphagia due to spasm of muscles in
NURSING RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS Short term: > Establish > To gain the After 1-2 hours rapport trust and of nursing cooperation interventions, of the pt. the client will and the SO be able to identify > Monitor and > To gain causative/risk record V/S baseline factor data for the care and manageme Long term: nt of the After 2-3 days patient of nursing >Assess interventions, patients >This will the client will condition guide what be able to interventions demonstrate to provide techniques to prevent and >Assess clients >To correct ability to determine aspiration swallow and presence/eff strength of ectiveness of gag/cough protective reflex mechanisms >Because of potential for regurgitation and or/
OBJECTIVES
EXPECTED OUTCOME Short term: The client shall have identified causative/risk factor Long term: the client shall have demonstrated techniques to prevent and correct aspiration
>Note for administration of enteral
the oral cavity. Thus, resulting to aspiration that may cause complications like aspiration pneumonia.
feedings
misplaceme nt of tube. >because it affect awareness and muscle of gag/swallow .
>Ascertain lifestyle habits such as use of alcohol, tobacco, and other CNS
>Keep wire cutter/scissors with client at all times when jaws are wired/banded >Suction as needed
>To facilitate clearing airway in emergency situations >To clear secretions while reducing potential for aspiration of secretions >To decrease potential risk for aspiration.
>Avoid keeping client in supine position when enteral feedings.
C. diet Type of Diet Date ordered, performed,changed Description Indication/Purpose Specific foods taken Clients response/reaction
DAT with SAP
8/14/11
This type of diet is usually ordered for patients with respiratory problems.
The patient manifests difficulty of swallowing and unable to open mouth wide
Soft foods such as porridge, kamote, mashed potato, soup.
The client has not experienced aspiration. The patient is compliant with regards to the diet ordered.
Before Explain to the patient and the patients relatives the need of the diet. Encourage deep breathing exercises
During Instruct patient to be on high fowlers position while eating or drinking . Instruct patient to eat food that are easy to chew and swallow. Instruct patient to avoid
after Instruct patient to drink water to flush down food Instruct patient to maintain high fowlers position for 10 minutes after eating
certain foods (eg, caffeine, fatty meals, carbonated beverages, peppermint, citrus)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Summary of Herbert Benson, M.D. & Miriam Z. Klipper's The Relaxation ResponseD'EverandSummary of Herbert Benson, M.D. & Miriam Z. Klipper's The Relaxation ResponsePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlansDocument14 pagesNursing Care PlansTels Dela PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPKrizelle Abadesco Libo-on50% (2)
- NCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyDocument3 pagesNCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyGidget de Leon100% (7)
- Advanced Clinical Therapies in Cardiovascular Chinese MedicineD'EverandAdvanced Clinical Therapies in Cardiovascular Chinese MedicinePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Reflexology: The Definitive Practitioner's Manual: Recommended by the International Therapy Examination Council for Students and PractitonersD'EverandReflexology: The Definitive Practitioner's Manual: Recommended by the International Therapy Examination Council for Students and PractitonersÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Nursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDanica Salinas100% (1)
- Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationApol Pen67% (3)
- 5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansDocument19 pages5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansRoanna Alyssa Sy Jimenez75% (4)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitFrances Anne Pasiliao100% (3)
- NCP (Fatigue)Document1 pageNCP (Fatigue)student_019100% (1)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 03Document6 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 03AgronaSlaughterPas encore d'évaluation
- Deficient Fluid Volume Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume Nursing Care PlansThessabelles Ebuen-PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLean Ashly Tuddao Macarubbo0% (1)
- 4 NCP's FinalDocument9 pages4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument13 pagesNCPLee Da HaePas encore d'évaluation
- MI Chest Pain AssessmentDocument5 pagesMI Chest Pain AssessmentDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP HeadDocument11 pagesNCP Headann-lisel-manahan-7670100% (2)
- NCP TahbsoDocument18 pagesNCP TahbsoKe EjiePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP CaseDocument35 pagesNCP Caselicservernoida100% (1)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPBeverLyPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageNCP Activity IntoleranceBen David100% (2)
- Painful Abdominal ContractionsDocument4 pagesPainful Abdominal ContractionsKarizza Mae Celis100% (2)
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPjfgnzls182892% (12)
- NCP MiDocument8 pagesNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesNCP Rheumatic Heart DiseaseAdrian Mallar71% (28)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlansTwobee Kriz LeghidPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic patient wound careDocument7 pagesDiabetic patient wound careMichael Anthony Cardenas Macaballug67% (3)
- DM Care PlanDocument9 pagesDM Care PlanHarish Kumar KumawatPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP FatigueDocument2 pagesNCP FatigueJon Eric G. Co100% (4)
- Reducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresDocument10 pagesReducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresKier Jucar de GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Coronary Artery Disease Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pages5 Coronary Artery Disease Nursing Care PlansMichelle Danica Vicente PaswickPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument12 pagesNCPJonathan Liscano100% (3)
- Fatigue Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesFatigue Nursing Care PlanNeil AlviarPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceKryza Dale Bunado Batican0% (1)
- NCP For CipDocument22 pagesNCP For CipBing DayaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Improve Activity Tolerance Through Rest and RelaxationDocument7 pagesImprove Activity Tolerance Through Rest and RelaxationKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- GERONTOLOGY Focuses On The Care of Older Adults and Addresses The PhysilogicalDocument7 pagesGERONTOLOGY Focuses On The Care of Older Adults and Addresses The PhysilogicalMhee FaustinaPas encore d'évaluation
- R: This Provides Baseline Measurement For Future Evaluation and Guides TherapyDocument4 pagesR: This Provides Baseline Measurement For Future Evaluation and Guides TherapyTyron ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cva NCPDocument1 pageCva NCPxiang jinPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plans for Acute Pain, Hyperthermia, Activity Intolerance, and Infection RiskDocument20 pagesNursing Care Plans for Acute Pain, Hyperthermia, Activity Intolerance, and Infection RiskNursidar Pascual Mukattil80% (5)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesNursing Care PlanjmichaelaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Risk For FallDocument20 pagesNCP Risk For FallRen Ren Determinado86% (7)
- GastroenteritisDocument8 pagesGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan (CASE STUDY DENGUE)Document10 pagesNursing Care Plan (CASE STUDY DENGUE)NioolePas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Diabetes and RisksDocument8 pagesManaging Diabetes and RisksChristopher LontocPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument17 pagesNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument18 pagesNCPChristian Karl B. LlanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Nsg. Research Betty NeumannDocument9 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN For Nsg. Research Betty NeumannFlor SabaysabayPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Diagnosis Fatigue related to Hyper metabolic stateDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Fatigue related to Hyper metabolic stateJohn CenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mrs. MM Nursing Care PlanDocument34 pagesMrs. MM Nursing Care PlanIsobel Mae JacelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The BronchiDocument9 pagesChronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchiinamaliit100% (1)
- DengueDocument14 pagesDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubrePas encore d'évaluation
- Tuberculosis: Angeles University FoundationDocument10 pagesTuberculosis: Angeles University FoundationBob Joyce Dela PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scan 0001Document3 pagesScan 0001Bob Joyce Dela PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tuberculosis: Angeles University FoundationDocument10 pagesTuberculosis: Angeles University FoundationBob Joyce Dela PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abruption of the Placenta Risk Factors, Signs, and ManagementDocument4 pagesAbruption of the Placenta Risk Factors, Signs, and ManagementBob Joyce Dela Peña100% (1)
- Muscle Building Diet Plan For MenDocument2 pagesMuscle Building Diet Plan For MenZora IdealePas encore d'évaluation
- Smoothie Recipes For Optimum HealthDocument202 pagesSmoothie Recipes For Optimum HealthObiezePas encore d'évaluation
- Sweetpotato Community Recipe Book OptimizedDocument30 pagesSweetpotato Community Recipe Book OptimizedKelemua ZebenePas encore d'évaluation
- Diverticulosis Diverticulitis Case StudyDocument3 pagesDiverticulosis Diverticulitis Case StudyDoolyPas encore d'évaluation
- Baked Goods 15-06-2007Document11 pagesBaked Goods 15-06-2007Lucía CassaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Worry About Disease Again with Advanced Healing TechniquesDocument51 pagesNever Worry About Disease Again with Advanced Healing TechniquesVictorFaucheret100% (2)
- Bangladesh Soybean AssociationDocument33 pagesBangladesh Soybean AssociationAbu ShamimPas encore d'évaluation
- Weight Management 1st Chapter 1Document33 pagesWeight Management 1st Chapter 1Rabisha AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Entry 3 Center For Discovery With Theresa CarmichaelDocument9 pagesJournal Entry 3 Center For Discovery With Theresa Carmichaelapi-489592025Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry of Lipids: Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, Mls (Ascpi) - April, 2023Document4 pagesBiochemistry of Lipids: Prof. Fritdey Jad Doctolero, RMT, Mls (Ascpi) - April, 2023May Ann EnoserioPas encore d'évaluation
- The Lockdown On Linoleic Acid Exposing The Damaging Effects of ThisDocument32 pagesThe Lockdown On Linoleic Acid Exposing The Damaging Effects of ThisPatricia PopescuPas encore d'évaluation
- TV Chefs' Food Portion SizesDocument2 pagesTV Chefs' Food Portion SizesJuliane GuedesPas encore d'évaluation
- Valorization of Spent Brewers Yeast For The ProduDocument18 pagesValorization of Spent Brewers Yeast For The ProduHarshad Vinay SavantPas encore d'évaluation
- Sedentary BehaviourDocument2 pagesSedentary BehaviourRiyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Low CarbDocument28 pagesLow CarbAttila TamasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lingsat Integrated SchoolDocument5 pagesLingsat Integrated SchoolDana Michele Rivera CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- SgfsDocument1 pageSgfsjoycechicagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Nutrition Monitoring AND Nutrition Surveillance: StructureDocument14 pagesUnit Nutrition Monitoring AND Nutrition Surveillance: StructureShubhendu ChattopadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Santol Siopao - 1Document6 pagesChapter 1 - Santol Siopao - 1GilbertGacisPas encore d'évaluation
- Benefits and Drawbacks of OMAD DietingDocument4 pagesBenefits and Drawbacks of OMAD DietingDal Makhani100% (3)
- Unilever Pakistan Sustainability Report 2012 - tcm96-355078Document35 pagesUnilever Pakistan Sustainability Report 2012 - tcm96-355078Akmal Gondal100% (1)
- Mayo Package Program penurunan berat badan dengan konsep mengurangi garam berlebih dalam tubuhDocument4 pagesMayo Package Program penurunan berat badan dengan konsep mengurangi garam berlebih dalam tubuhLala LalianiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Simple Nutrition Principles To Power Up Your Simple & Sinister Training - Steve KoDocument8 pages3 Simple Nutrition Principles To Power Up Your Simple & Sinister Training - Steve KoIacopoMariaFilippoBarni0% (1)
- Click Here - : EnzymesDocument4 pagesClick Here - : EnzymesAmit GodaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolisme Kolesterol, Lipoprotein Dan ApolipoproteinDocument32 pagesMetabolisme Kolesterol, Lipoprotein Dan ApolipoproteinAlmira Ulfa Utari NasutionPas encore d'évaluation
- Gorilla Mode Premium Stimulant Pre-Workout - Gorilla MindDocument1 pageGorilla Mode Premium Stimulant Pre-Workout - Gorilla MindRuda PortugalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Supplements You Need by Roger MasonDocument45 pagesThe Supplements You Need by Roger MasonRonald MarstonPas encore d'évaluation
- Vitabiotics Jointace Max Capsules OcadoDocument1 pageVitabiotics Jointace Max Capsules OcadoShafay Jawed ZakariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Presenting Meat DishesDocument14 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Presenting Meat DishesConstancia PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- THE VERNE CODE: The Secret of the Anunnaki, Atlantis and the true shape of the Earth unveiledD'EverandTHE VERNE CODE: The Secret of the Anunnaki, Atlantis and the true shape of the Earth unveiledÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (20)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceD'EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (51)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyD'EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (31)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingD'EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingD'EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (31)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorD'EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (137)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (41)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisD'EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (8)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeD'EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifePas encore d'évaluation
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlD'EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (57)
- Highest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersD'EverandHighest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersPas encore d'évaluation
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondD'EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonD'EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (103)
- Brain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolD'EverandBrain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (702)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldD'EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (57)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldD'EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (18)
- Lessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”D'EverandLessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingD'EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Mother Earth Spirituality: Native American Paths to Healing OurselvesD'EverandMother Earth Spirituality: Native American Paths to Healing OurselvesÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (11)