Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sistem Saraf Pusat
Transféré par
ChristianHendrikDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sistem Saraf Pusat
Transféré par
ChristianHendrikDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
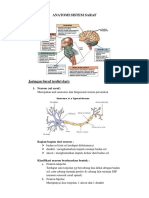
Sistem saraf pusat Dari Wikipedia bahasa Indonesia, ensiklopedia bebas Sistem saraf pusat (SSP) meliputi otak
(Latin: 'ensephalon') dan sumsum tulang belakang (Latin: 'medulla spinalis'). Keduanya merupakan organ yang sangat lunak, dengan fungsi yang sangat penting maka perlu perlindungan. Selain tengkorak dan ruas-ruas tulang belakang, otak juga dilindungi 3 lapisan selaput meninges. Bila membran ini terkena infeksi maka akan terjadi radang yang disebut meningitis. Ketiga lapisan membran meninges dari luar ke dalam adalah sebagai berikut: 1. Durameter; terdiri dari dua lapisan, yang terluar bersatu dengan tengkorak sebagai endostium, dan lapisan lain sebagai duramater yang mudah dilepaskan dari tulang kepala. Diantara tulang kepala dengan duramater terdapat rongga epidural. 2. Arachnoidea mater; disebut demikian karena bentuknya seperti sarang labah-labah. Di dalamnya terdapat cairan yang disebut liquor cerebrospinalis; semacam cairan limfa yang mengisi sela sela membran araknoid. Fungsi selaput arachnoidea adalah sebagai bantalan untuk melindungi otak dari bahaya kerusakan mekanik. 3. Piameter. Lapisan terdalam yang mempunyai bentuk disesuaikan dengan lipatan-lipatan permukaan otak. Otak dan sumsum tulang belakang mempunyai 3 materi esensial yaitu: 1. badan sel yang membentuk bagian materi kelabu (substansi grissea) 2. serabut saraf yang membentuk bagian materi putih (substansi alba) 3. sel-sel neuroglia, yaitu jaringan ikat yang terletak di antara sel-sel saraf di dalam sistem saraf pusat Walaupun otak dan sumsum tulang belakang mempunyai materi sama tetapi susunannya berbeda. Pada otak, materi kelabu terletak di bagian luar atau kulitnya (korteks) dan bagian putih terletak di tengah. Pada sumsum tulang belakang bagian tengah berupa materi kelabu berbentuk kupu-kupu, sedangkan bagian korteks berupa materi putih. [sunting] Otak
Otak mempunyai lima bagian utama, yaitu: otak besar (serebrum), otak tengah (mesensefalon), otak kecil (serebelum), sumsum sambung (medulla oblongata), dan jembatan varol.
Otak besar (serebrum) Otak besar mempunyai fungsi dalam pengaturan semua aktivitas mental, yaitu yang berkaitan dengan kepandaian (intelegensi), ingatan (memori), kesadaran, dan pertimbangan. Otak besar merupakan sumber dari semua kegiatan/gerakan sadar atau sesuai dengan kehendak, walaupun ada juga beberapa gerakan refleks otak. Pada bagian korteks otak besar yang berwarna kelabu terdapat bagian penerima rangsang (area sensor) yang terletak di sebelah belakang area motor yang berfungsi mengatur gerakan sadar atau merespon rangsangan. Selain itu terdapat area asosiasi yang menghubungkan area motor dan sensorik. Area ini berperan dalam proses belajar, menyimpan ingatan, membuat kesimpulan, dan belajar berbagai bahasa. Di sekitar kedua area tersebut dalah bagian yang mengatur kegiatan psikologi yang lebih tinggi. Misalnya bagian depan merupakan pusat proses berfikir (yaitu mengingat, analisis, berbicara, kreativitas) dan emosi. Pusat penglihatan terdapat di bagian belakang.
Otak tengah (mesensefalon) Otak tengah terletak di depan otak kecil dan jembatan varol. Di depan otak tengah terdapat talamus dan kelenjar hipofisis yang mengatur kerja kelenjarkelenjar endokrin. Bagian atas (dorsal) otak tengah merupakan lobus optikus yang mengatur refleks mata seperti penyempitan pupil mata, dan juga merupakan pusat pendengaran.
Otak kecil (serebelum) Serebelum mempunyai fungsi utama dalam koordinasi gerakan otot yang terjadi secara sadar, keseimbangan, dan posisi tubuh. Bila ada rangsangan yang merugikan atau berbahaya maka gerakan sadar yang normal tidak mungkin dilaksanakan.
Sumsum sambung (medulla oblongata) Sumsum sambung berfungsi menghantar impuls yang datang dari medula spinalis menuju ke otak. Sumsum sambung juga mempengaruhi jembatan,
refleks fisiologi seperti detak jantung, tekanan darah, volume dan kecepatan respirasi, gerak alat pencernaan, dan sekresi kelenjar pencernaan. Selain itu, sumsum sambung juga mengatur gerak refleks yang lain seperti bersin, batuk, dan berkedip.
Jembatan varol (pons varoli) Jembatan varol berisi serabut saraf yang menghubungkan otak kecil bagian kiri dan kanan, juga menghubungkan otak besar dan sumsum tulang belakang.
Sumsum tulang belakang (medula spinalis) Pada penampang melintang sumsum tulang belakang tampak bagian luar berwarna putih, sedangkan bagian dalam berbentuk kupu-kupu dan berwarna kelabu. Pada penampang melintang sumsum tulang belakang ada bagian seperti sayap yang terbagi atas sayap atas disebut tanduk dorsal dan sayap bawah disebut tanduk ventral. Impuls sensori dari reseptor dihantar masuk ke sumsum tulang belakang melalui tanduk dorsal dan impuls motor keluar dari sumsum tulang belakang melalui tanduk ventral menuju efektor. Pada tanduk dorsal terdapat badan sel saraf penghubung (asosiasi konektor) yang akan menerima impuls dari sel saraf sensori dan akan menghantarkannya ke saraf motor Central Nervous System Overview The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord (see Multimedia File 1).
The brain plays a central role in the control of most bodily functions, including awareness, movements, sensations, thoughts, speech, and memory. Some reflex movements can occur via spinal cord pathways without the participation of brain structures.
The spinal cord is connected to a section of the brain called the brainstem and runs through the spinal canal. Cranial nerves exit the brainstem. Nerve roots exit the spinal cord to both sides of the body. The spinal cord carries signals (messages) back and forth between the brain and the peripheral nerves.
Cerebrospinal fluid surrounds the brain and the spinal cord and also circulates within the cavities (called ventricles) of the central nervous system. The leptomeninges surround the brain and the spinal cord. The cerebrospinal fluid circulates between 2 meningeal layers called the pia matter and the arachnoid (or pia-arachnoid membranes). The outer, thicker layer serves the role of a protective shield and is called the dura matter. The basic unit of the central nervous system is the neuron (nerve cell). Billions of neurons allow the different parts of the body to communicate with each other via the brain and the spinal cord. A fatty material called myelin coats nerve cells to insulate them and to allow nerves to communicate quickly. The Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and controls voluntary actions, speech, senses, thought, and memory. The surface of the cerebral cortex has grooves or infoldings (called sulci), the largest of which are termed fissures. Some fissures separate lobes. The convolutions of the cortex give it a wormy appearance. Each convolution is delimited by two sulci and is also called a gyrus (gyri in plural). The cerebrum is divided into two halves, known as the right and left hemispheres. A mass of fibers called the corpus callosum links the hemispheres. The right hemisphere controls voluntary limb movements on the left side of the body, and the left hemisphere controls voluntary limb movements on the right side of the body. Almost every person has one dominant hemisphere. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes, or areas, which are interconnected.
The frontal lobes are located in the front of the brain and are responsible for voluntary movement and, via their connections with other lobes, participate in the execution of sequential tasks; speech output; organizational skills; and certain aspects of behavior, mood, and memory. The parietal lobes are located behind the frontal lobes and in front of the occipital lobes. They process sensory information such as temperature, pain, taste, and touch. In addition, the processing includes information about numbers, attentiveness to the position of ones body parts, the space around ones body, and one's relationship to this space.
The temporal lobes are located on each side of the brain. They process memory and auditory (hearing) information and speech and language functions.
The occipital lobes are located at the back of the brain. They receive and process visual information.
The cortex, also called gray matter, is the most external layer of the brain and predominantly contains neuronal bodies (the part of the neurons where the DNAcontaining cell nucleus is located). The gray matter participates actively in the storage and processing of information. An isolated clump of nerve cell bodies in the gray matter is termed a nucleus (to be differentiated from a cell nucleus). The cells in the gray matter extend their projections, called axons, to other areas of the brain. Fibers that leave the cortex to conduct impulses toward other areas are termed efferent fibers, and fibers that approach the cortex from other areas of the nervous system are termed afferent (nerves or pathways). Fibers that go from the motor cortex to the brainstem (for example, the pons) or the spinal cord receive a name that generally reflects the connections (that is, corticopontine tract for the former and corticospinal tract for the latter). Axons are surrounded in their course outside the gray matter by myelin, which has a glistening whitish appearance and thus gives rise to the term white matter. Cortical areas receive their names according to their general function or lobe name. If in charge of motor function, the area is called the motor cortex. If in charge of sensory function, the area is called a sensory or somesthetic cortex. The calcarine or visual cortex is located in the occipital lobe (also termed occipital cortex) and receives visual input. The auditory cortex, localized in the temporal lobe, processes sounds or verbal input. Knowledge of the anatomical projection of fibers of the different tracts and the relative representation of body regions in the cortex often enables doctors to correctly locate an injury and its relative size, sometimes with great precision. Central Structures of the Brain The central structures of the brain include the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland. The hippocampus is located in the temporal lobe but participates in the processing of memory and emotions and is interconnected with central
structures. Other structures are the basal ganglia, which are made up of gray matter and include the amygdala (localized in the temporal lobe), the caudate nucleus, and the lenticular nucleus (putamen and globus pallidus). Because the caudate and putamen are structurally similar, neuropathologists have coined for them the collective term striatum.
The thalamus integrates and relays sensory information to the cortex of the parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes. The thalamus is located in the lower central part of the brain (that is, upper part of the brainstem) and is located medially to the basal ganglia. The brain hemispheres lie on the thalamus. Other roles of the thalamus include motor and memory control.
The hypothalamus, located below the thalamus, regulates automatic functions such as appetite, thirst, and body temperature. It also secretes hormones that stimulate or suppress the release of hormones (for example, growth hormones) in the pituitary gland.
The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland produces hormones that control many functions of other endocrine glands. It regulates the production of many hormones that have a role in growth, metabolism, sexual response, fluid and mineral balance, and the stress response.
The ventricles are cerebrospinal fluid-filled cavities in the interior of the cerebral hemispheres.
For more information, see Anatomy of the Endocrine System.
The Base of the Brain The base of the brain contains the cerebellum and the brainstem. These structures serve complex functions. Below is a simplified version of these roles:
Traditionally, the cerebellum has been known to control equilibrium and coordination and contributes to the generation of muscle tone. It has more recently become evident, however, that the cerebellum plays more diverse roles such as participating in some types of memory and exerting a complex influence on musical and mathematical skills.
The brainstem connects the brain with the spinal cord. It includes the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. It is a compact structure in which multiple pathways traverse from the brain to the spinal cord and vice versa. For instance, nerves that arise from cranial nerve nuclei are involved with eye movements and exit the brainstem at several levels. Damage to the brainstem can therefore affect a number of bodily functions. For instance, if the corticospinal tract is injured, a loss of motor function (paralysis) occurs, and it may be accompanied by other neurologic deficits, such as eye movement abnormalities, which are reflective of injury to cranial nerves or their pathways in the brainstem.
o
The midbrain is located below the hypothalamus. Some cranial nerves that are also responsible for eye muscle control exit the midbrain.
The pons serves as a bridge between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. The pons also contains the nuclei and fibers of nerves that serve eye muscle control, facial muscle strength, and other functions.
The medulla oblongata is the lowest part of the brainstem and is interconnected with the cervical spinal cord. The medulla oblongata also helps control involuntary actions, including vital processes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration, and it carries the corticospinal (that is, motor function) tract toward the spinal cord.
The Spinal Cord The spinal cord is an extension of the brain and is surrounded by the vertebral bodies that form the spinal column (see Multimedia File 3). The central structures
of the spinal cord are made up of gray matter (nerve cell bodies), and the external or surrounding tissues are made up of white matter. Within the spinal cord are 30 segments that belong to 4 sections (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral), based on their location:
Eight cervical segments: These transmit signals from or to areas of the head, neck, shoulders, arms, and hands.
Twelve thoracic segments: These transmit signals from or to part of the arms and the anterior and posterior chest and abdominal areas.
Five lumbar segments: These transmit signals from or to the legs and feet and some pelvic organs.
Five sacral segments: These transmit signals from or to the lower back and buttocks, pelvic organs and genital areas, and some areas in the legs and feet.
A coccygeal remnant is located at the bottom of the spinal cord.
Gerak Sadar Impuls>reseptor>saraf sensorik>otak>saraf motorik>efektor Gerak Refleks Impuls> reseptor>saraf sensorik>s>saraf motorik>efektor
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pengantar psikologi emosi: Dari Darwin hingga ilmu saraf, apa itu emosi dan bagaimana cara kerjanyaD'EverandPengantar psikologi emosi: Dari Darwin hingga ilmu saraf, apa itu emosi dan bagaimana cara kerjanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kesadaran: Menemukan tahapan-tahapan pikiran: dari yang sadar ke yang tidak sadar, dari pengaruh ritme biologis hingga tidur dan mimpiD'EverandKesadaran: Menemukan tahapan-tahapan pikiran: dari yang sadar ke yang tidak sadar, dari pengaruh ritme biologis hingga tidur dan mimpiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sejarah psikologi ilmiah: Dari kelahiran psikologi hingga neuropsikologi dan bidang aplikasi terkiniD'EverandSejarah psikologi ilmiah: Dari kelahiran psikologi hingga neuropsikologi dan bidang aplikasi terkiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem SarafDocument13 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem SarafFeby Zenistiya100% (3)
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem-SarafDocument13 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem-SarafranudienPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah Sistem Saraf Pusat OtakDocument18 pagesMakalah Sistem Saraf Pusat Otakaryani100% (1)
- Dosis Letal, Dosis Efektif Dan Penentuan Sigmoid CurveDocument13 pagesDosis Letal, Dosis Efektif Dan Penentuan Sigmoid CurveChristianHendrik100% (3)
- Sistem Saraf PusatDocument10 pagesSistem Saraf PusatdelamanasonPas encore d'évaluation
- PENGELOLAAN LIMBAH CAIR DI RSDocument13 pagesPENGELOLAAN LIMBAH CAIR DI RSChristianHendrikPas encore d'évaluation
- NEUROANATOMIDocument14 pagesNEUROANATOMIBalqis Basbeth100% (1)
- Pedoman Hepatitis OK PDFDocument50 pagesPedoman Hepatitis OK PDFAhmad SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf PusatDocument3 pagesSistem Saraf PusatpuadisragenPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf PusatDocument3 pagesSistem Saraf PusatYoudhystira Putra Asmara TanusasmitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf PusatDocument4 pagesSistem Saraf PusatnadiyaregitaPas encore d'évaluation
- SISTEM REGULASI BIOLOGIDocument15 pagesSISTEM REGULASI BIOLOGIStefanPas encore d'évaluation
- Embriologi CNSDocument44 pagesEmbriologi CNSOkky AndreraztaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf PusatDocument5 pagesSistem Saraf PusatArgun WidarsaPas encore d'évaluation
- sistem saraf kranialDocument14 pagessistem saraf kranialidhasePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomi Fisiologi Untuk Mahasiswa Kedokteran Dan KeperawatanDocument11 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Untuk Mahasiswa Kedokteran Dan Keperawatanjuli harsonoPas encore d'évaluation
- ANATOMI SISTEM SARAFDocument9 pagesANATOMI SISTEM SARAFSyafrizalDoankPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf Pada ManusiaDocument5 pagesSistem Saraf Pada ManusiaH Putra HasibuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem SarafDocument14 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem Sarafida ayu kade trisnayanthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Regulasi Pada ManusiaDocument25 pagesSistem Regulasi Pada ManusiaIyan GiftianPas encore d'évaluation
- KEJANG DEMAMDocument34 pagesKEJANG DEMAMphilemonPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh LP Kanker OtakDocument16 pagesContoh LP Kanker OtakDresti RF100% (2)
- Ruang AnakDocument41 pagesRuang AnakIyar YadraPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Pendahuluan IchDocument24 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan IchDesy MeldawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- SARAFDocument13 pagesSARAFGeby OrlancePas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem SarafDocument17 pagesSistem SarafandiniPas encore d'évaluation
- NyeriDocument16 pagesNyeriAfriyaldy100% (1)
- LP Epilepsi AnakDocument25 pagesLP Epilepsi Anakyvs552kcfqPas encore d'évaluation
- ANATOMISARAFDocument7 pagesANATOMISARAFTania ManusamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf PusatDocument13 pagesSistem Saraf PusatErika Nopauli SitindaonPas encore d'évaluation
- Penatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Kasus StrokeDocument16 pagesPenatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Kasus StrokeMuhammad Ridha Al JinaniPas encore d'évaluation
- LP SHDocument28 pagesLP SHPika RahayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf PusatDocument7 pagesSistem Saraf PusatNmn dolphinPas encore d'évaluation
- Praktikum Sistem Saraf PtintDocument25 pagesPraktikum Sistem Saraf PtintMaulina ManurungPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomedik Sistem SarafDocument27 pagesBiomedik Sistem SarafNeskleng PunkPas encore d'évaluation
- Klasifikasi Sistem SarafDocument36 pagesKlasifikasi Sistem SarafObyndaPas encore d'évaluation
- SNH RSKDocument22 pagesSNH RSKmaey yap ViaPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah Sistem Saraf Kelompok 2Document19 pagesMakalah Sistem Saraf Kelompok 2Hany SyahiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Epilepsi LaporanDocument24 pagesEpilepsi LaporanFetinuhan97Pas encore d'évaluation
- EPILEPSI ANATOMIDocument23 pagesEPILEPSI ANATOMINazilaPas encore d'évaluation
- SistemSarafDocument17 pagesSistemSarafDewa Sagitha87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf PusatDocument14 pagesSistem Saraf Pusatmaghfirah jailaniPas encore d'évaluation
- SISTEM SARAF MANUSIADocument46 pagesSISTEM SARAF MANUSIARenny Jho83% (6)
- EPIDEMIOLOGI SISTEM SARAF PUSAT DAN SARAF TEPI Violita Mellania 6411418124Document35 pagesEPIDEMIOLOGI SISTEM SARAF PUSAT DAN SARAF TEPI Violita Mellania 6411418124Violita MellaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem SarafDocument20 pagesSistem Sarafsakinatuz zakiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf BiopsikologiDocument10 pagesSistem Saraf BiopsikologiUchi FzhPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Saraf SensorikDocument7 pagesSistem Saraf SensorikAngga Punggawa KoedoeboenPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem SarafDocument3 pagesSistem Sarafkartika utamiPas encore d'évaluation
- OtakDocument4 pagesOtakSumarlik Dewi FitriawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- LAPSUS PRE KLINIK Hemiparese Dextra Post Op Craniotomy Et Causa Subdural Mi-2Document26 pagesLAPSUS PRE KLINIK Hemiparese Dextra Post Op Craniotomy Et Causa Subdural Mi-2Musyahidatun anisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bagian Bagian OtakDocument6 pagesBagian Bagian OtakNunung MardiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah Sistem Saraf PusatDocument8 pagesMakalah Sistem Saraf Pusatabu rasyid67% (3)
- LP TetrapareseDocument21 pagesLP TetrapareseFahmi BulPas encore d'évaluation
- Rahmatika R. - Anatomi Fisiologi EpilepsiDocument17 pagesRahmatika R. - Anatomi Fisiologi EpilepsiRahmatika RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem SarafDocument10 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem SarafNur BudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Otak Merupakan Pusat Computer Dari Semua Alat Tubuh, Yang Terletak Di Dalam Rongga Tengkorak (Cranium) Yang Dibungkus Oleh Selaput Otak Yang KuatDocument4 pagesOtak Merupakan Pusat Computer Dari Semua Alat Tubuh, Yang Terletak Di Dalam Rongga Tengkorak (Cranium) Yang Dibungkus Oleh Selaput Otak Yang KuatbellaPas encore d'évaluation
- SSPDocument7 pagesSSPNurul UlfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumbuhan Herbal Tradisional Untuk Pengobatan Penyakit Mental Spiritual Dari Hutan Pegunungan NusantaraD'EverandTumbuhan Herbal Tradisional Untuk Pengobatan Penyakit Mental Spiritual Dari Hutan Pegunungan NusantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1 Anemia Defisiensi Fe Dan MegaloblastikDocument15 pagesTutorial 1 Anemia Defisiensi Fe Dan MegaloblastikChristianHendrikPas encore d'évaluation
- HipertensiDocument5 pagesHipertensiChristianHendrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Keseimbangan Cairan TubuhDocument5 pagesKeseimbangan Cairan TubuhChristianHendrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Egg and AcneDocument5 pagesEgg and AcneChristianHendrikPas encore d'évaluation
- PatogenesisGoutSingkatDocument1 pagePatogenesisGoutSingkatChristianHendrikPas encore d'évaluation
- TandaGejalaDBDDocument2 pagesTandaGejalaDBDChristianHendrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Tanda Dan GejalaDocument2 pagesTanda Dan GejalaChristianHendrikPas encore d'évaluation