Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Paper1 Angle Depressions
Transféré par
idamathsDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Paper1 Angle Depressions
Transféré par
idamathsDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1.
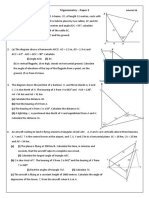
The vertical and horizontal distances of a car from an airborne helicopter is 220 m and 400 m respectively. The angle of depression of the car from the helicopter is A 31.13 B 30 C 28.81 D 25.88
2.
In the diagram above, P, Q and R are three points on the horizontal ground. PS is a vertical pole. The angle of elevation of S from Q is 44. Find the angle of depression of R from S. A 39.31 B 34.61 C 37.08 D 32.3 3. The vertical and horizontal distances of a car from an airborne helicopter is 160 m and 770 m respectively. The angle of depression of the car from the helicopter is A 14.06 B 12.93 C 11.74 D 8.81
4.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of depression of C from A is 15.52. The height of A is 10 m and that of C is 5 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 20 m B 19 m C 17 m D 18 m 5. In the diagram, JK and NL are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. M is a point on NL such that JK = ML.
The angle of depression of J from N is A LJN B NJM C KNM D JLK
6.
The diagram above shows a vertical pole XY on a horizontal plane. The angles of elevation of point X from point A and point B are differ by 6. Given that the angle of elevation of X from A is 38, find the distance of BY. A 15.53 m B 14.06 m C 24.01 m D 25.01 m 7.
In the diagram above, VW is a vertical wall. The angle of depression of U from V is 36. Point U is 7 m from the foot of the wall. Find the height of the wall VW. A 6.32 m B 3.62 m C 5.09 m D 10.63 m 8. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 20 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 20. If the height of tower EF is 70 m, find the height of tower GH. A 65.04 m B 63.91 m
C 61.08 m D 62.72 m 9.
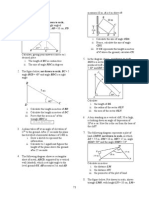
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of depression of S from P is same as A PQS B QSP C RPS D PRQ 10.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of depression of S from P is same as A PQS B QSP C RPS D PRQ
11.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 13 m and 17 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of elevation of V from S. A 13.6 B 11.31 C 21.43 D 7.58 12.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 3 m and 8 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of elevation of V from S. A 23.33 B 21.04 C 31.16 D 17.31
13.
The diagram above shows a vertical pole XY on a horizontal plane. The angles of elevation of point X from point A and point B are differ by 9. Given that the angle of elevation of X from A is 39, find the distance of BY. A 21.94 m B 20.71 m C 39.84 m D 40.84 m 14.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 7 m and the poles are 13 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 40.24. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 20 B 19 C 18 D 16
15.
The diagram above shows a vertical pole XY on a horizontal plane. The angles of elevation of point X from point A and point B are differ by 10. Given that the angle of elevation of X from A is 36, find the distance of BY. A 12.82 m B 10.12 m C 11.59 m D 25.6 m 16. In the diagram, JK and NL are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. M is a point on NL such that JK = ML.
The angle of depression of J from N is A LJN B JNM C NJM D JLK 17. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 50 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 31. If the height of tower EF is 100 m, find the height of tower GH. A 72.28 m
B 71.15 m C 69.96 m D 67.03 m 18. The vertical and horizontal distances of a car from an airborne helicopter is 220 m and 630 m respectively. The angle of depression of the car from the helicopter is A 21.57 B 20.44 C 17.61 D 19.25 19.
In the diagram above, P, Q and R are three points on the horizontal ground. PS is a vertical pole. The angle of elevation of S from Q is 50. Find the angle of depression of R from S. A 42.64 B 40.17 C 47.08 D 37.86 20.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The
value of the angle of depression of S from P is same as A PQS B QSP C RPS D PRQ 21. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 40 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 25. If the height of tower EF is 170 m, find the height of tower GH. A 153.67 m B 152.54 m C 151.35 m D 148.42 m 22.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 3 m and the poles are 18 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 35.84. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 16 B 17 C 15 D 14 23. In the diagram, JK and NL are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. M is a point on NL such that JK = ML.
The angle of depression of J from N is A LJN B JNM C KNM D NJM 24. The vertical and horizontal distances of a car from an airborne helicopter is 440 m and 220 m respectively. The angle of depression of the car from the helicopter is A 63.43 B 64.62 C 61.79 D 60.5 25.
In the diagram above, VW is a vertical wall. The angle of depression of U from V is 37. Point U is 23 m from the foot of the wall. Find the height of the wall VW. A 18.56 m B 15.86 m C 30.52 m D 17.33 m
26.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of elevation of C from A is 34.38. The height of A is 5 m and that of C is 18 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 21 m B 19 m C 18 m D 17 m 27.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of elevation of C from A is 11.89. The height of A is 14 m and that of C is 18 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 21 m B 20 m C 18 m D 19 m
28.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 11 m and 7 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of depression of V from S. A 11.89 B 9.23 C 22.01 D 8.16 29. In the diagram, PQ is a vertical flag pole. QR is horizontal.
The angle of elevation of P from R is 38. The height, in m, of the flag pole is A 18.47 B 23.64 C 38.4 D 23.44 30. In the diagram, PQ is a vertical flag pole. QR is horizontal.
The angle of elevation of P from R is 40. The height, in m, of the flag pole is A 23.14 B 27.58 C 30.21 D 36 31. In the diagram, PQ is a vertical flag pole. QR is horizontal.
The angle of elevation of P from R is 38. The height, in m, of the flag pole is A 21.55 B 27.34 C 44.8 D 35
32.
The diagram above shows two vertical lamp posts, PQ and RS, that are of equal heights. The angle of elevation of P and R from point V, on the horizontal ground, are 2122' and 1515' respectively. V is 23 m from the base of the lamp post PQ. Find the distance between the lamp posts. A 12 m B 10 m C 9m D 8m 33. In the diagram, PQ is a vertical flag pole. QR is horizontal.
The angle of elevation of P from R is 43. The height, in m, of the flag pole is A 41.03 B 32.18 C 47.18 D 44
34.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 8 m and the poles are 17 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 22.38. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 17 B 16 C 14 D 15 35.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 9 m and the poles are 18 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 9.46. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 14 B 13 C 11 D 12 36. The vertical and horizontal distances of a car from an airborne helicopter is 530 m and 220 m respectively. The angle of depression of the car from the helicopter is A 69.78 B 68.65
C 65.82 D 67.46 37.
The diagram above shows two vertical lamp posts, PQ and RS, that are of equal heights. The angle of elevation of P and R from point V, on the horizontal ground, are 1248' and 947' respectively. V is 44 m from the base of the lamp post PQ. Find the distance between the lamp posts. A 16 m B 15 m C 13 m D 14 m 38.
In the diagram above, P, Q and R are three points on the horizontal ground. PS is a vertical pole. The angle of elevation of S from Q is 49. Find the angle of depression of R from S. A 46.46 B 41.76 C 44.23 D 39.45
39.
The diagram above shows two vertical lamp posts, PQ and RS, that are of equal heights. The angle of elevation of P and R from point V, on the horizontal ground, are 2634' and 1652' respectively. V is 20 m from the base of the lamp post PQ. Find the distance between the lamp posts. A 13 m B 14 m C 12 m D 11 m 40.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 13 m and 14 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of elevation of V from S. A 4.09 B 1.43 C 14.21 D 0.36
41.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of elevation of C from A is 19.44. The height of A is 3 m and that of C is 9 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 17 m B 18 m C 16 m D 15 m 42.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 9 m and 5 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of depression of V from S. A 19.39 B 14.44 C 27.22 D 17.1
43.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of depression of S from P is same as A QSP B SPQ C RPS D PRQ 44.
In the diagram above, VW is a vertical wall. The angle of depression of U from V is 40. Point U is 8 m from the foot of the wall. Find the height of the wall VW. A 7.94 m B 5.24 m C 6.71 m D 10.53 m
45.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of elevation of C from A is 14.04. The height of A is 14 m and that of C is 18 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 16 m B 17 m C 15 m D 14 m 46.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of elevation of P from S is same as A PSQ B SPQ C RPS D PRQ
47.
In the diagram above, VW is a vertical wall. The angle of depression of U from V is 34. Point U is 23 m from the foot of the wall. Find the height of the wall VW. A 16.74 m B 14.04 m C 34.1 m D 15.51 m 48.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of elevation of P from S is same as A PQS B SPQ C PSQ D PRQ
49.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 7 m and 3 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of depression of V from S. A 17.22 B 12.27 C 25.05 D 14.93 50.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 3 m and the poles are 12 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 47.29. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 18 B 17 C 15 D 16
51.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of depression of Q from R is same as A QRS B SQR C PQS D PQR 52.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 9 m and the poles are 18 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 23.96. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 19 B 18 C 17 D 15
53.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 4 m and the poles are 14 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 35.54. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 14 B 15 C 13 D 12 54. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 40 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 35. If the height of tower EF is 110 m, find the height of tower GH. A 81.99 m B 83.18 m C 80.35 m D 79.06 m 55.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of elevation of C from A is 34.51. The height of A is 5 m and that of C is 16 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 16 m
B 17 m C 15 m D 14 m 56.
In the diagram above, P, Q and R are three points on the horizontal ground. PS is a vertical pole. The angle of elevation of S from Q is 49. Find the angle of depression of R from S. A 42.25 B 39.78 C 46.69 D 37.47 57.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 8 m and 13 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of elevation of V from S. A 16.39 B 13.73 C 26.51 D 12.66
58.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 6 m and 18 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of elevation of V from S. A 42.89 B 37.94 C 40.6 D 36.87 59. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 30 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 35. If the height of tower EF is 100 m, find the height of tower GH. A 81.31 m B 80.18 m C 77.35 m D 78.99 m 60.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of elevation of C from A is 22.62. The height of A is 9 m and that of C is 14 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 14 m B 12 m
C 11 m D 10 m 61.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 7 m and 13 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of elevation of V from S. A 27.07 B 24.78 C 34.9 D 21.05 62.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of depression of C from A is 18.43. The height of A is 15 m and that of C is 9 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 18 m B 19 m C 17 m D 16 m
63.
In the diagram above, VW is a vertical wall. The angle of depression of U from V is 34. Point U is 9 m from the foot of the wall. Find the height of the wall VW. A 7.3 m B 4.6 m C 13.34 m D 6.07 m 64.
In the diagram above, P, Q and R are three points on the horizontal ground. PS is a vertical pole. The angle of elevation of S from Q is 48. Find the angle of depression of R from S. A 44.12 B 39.42 C 41.89 D 37.11
65.
The diagram above shows a vertical pole XY on a horizontal plane. The angles of elevation of point X from point A and point B are differ by 6. Given that the angle of elevation of X from A is 40, find the distance of BY. A 9.92 m B 7.22 m C 13.34 m D 8.69 m 66.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of elevation of R from Q is same as A RQS B QSR C PQS D PQR
67.
In the diagram above, P, Q and R are three points on the horizontal ground. PS is a vertical pole. The angle of elevation of S from Q is 49. Find the angle of depression of R from S. A 39.72 B 37.25 C 44.16 D 34.94 68.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 4 m and the poles are 12 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 36.87. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 15 B 13 C 12 D 11
69. In the diagram, JK and LM are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. The height of LM is twice the height of JK. The angle of depression of J from vertex L is 51.
Calculate the height, in m, of LM. A 25.91 B 19.76 C 39.52 D 24.87 70. The vertical and horizontal distances of a car from an airborne helicopter is 430 m and 210 m respectively. The angle of depression of the car from the helicopter is A 66.29 B 65.16 C 62.33 D 63.97 71.
In the diagram above, VW is a vertical wall. The angle of depression of U from V is 35. Point U is 5 m from the foot of the wall. Find the height of the wall VW. A 4.73 m B 2.03 m C 7.14 m
D 3.5 m 72.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of depression of C from A is 14.04. The height of A is 15 m and that of C is 12 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 14 m B 13 m C 11 m D 12 m 73.
In the diagram above, ST and VU are two vertical poles of heights 6 m and 12 m respectively on the horizontal ground. Calculate the angle of elevation of V from S. A 20.72 B 15.77 C 28.55 D 18.43 74. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 50 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 31. If the height of tower EF is 120 m, find the height of tower GH.
A B C D 75.
89.96 m 91.15 m 88.32 m 87.03 m
In the diagram above, P, Q and R are three points on the horizontal ground. PS is a vertical pole. The angle of elevation of S from Q is 47. Find the angle of depression of R from S. A 39.35 B 36.88 C 43.79 D 34.57 76. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 20 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 29. If the height of tower EF is 180 m, find the height of tower GH. A 171.23 m B 168.91 m C 167.27 m D 165.98 m 77. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 50 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 23. If the height of tower EF is 160 m, find the height of tower GH. A 141.1 m B 139.97 m C 137.14 m D 138.78 m
78.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 11 m and the poles are 13 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 28.3. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 18 B 19 C 17 D 16 79.
The diagram above shows two vertical lamp posts, PQ and RS, that are of equal heights. The angle of elevation of P and R from point V, on the horizontal ground, are 3341' and 1623' respectively. V is 15 m from the base of the lamp post PQ. Find the distance between the lamp posts. A 21 m B 19 m C 18 m D 17 m
80.
The diagram above shows a vertical pole XY on a horizontal plane. The angles of elevation of point X from point A and point B are differ by 13. Given that the angle of elevation of X from A is 38, find the distance of BY. A 7.71 m B 5.01 m C 6.48 m D 18.16 m 81. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 20 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 39. If the height of tower EF is 180 m, find the height of tower GH. A 166.12 m B 164.99 m C 162.16 m D 163.8 m 82.
The diagram above shows a vertical pole XY on a horizontal plane. The angles of elevation of point X from point A and point B are differ by 13. Given that the angle of elevation of X from A is 36, find the distance of BY. A 12.17 m
B 10.7 m C 32.98 m D 33.98 m 83. In the diagram, PQ is a vertical flag pole. QR is horizontal.
The angle of elevation of P from R is 42. The height, in m, of the flag pole is A 28.77 B 31.96 C 38.72 D 43 84. In the diagram, JK and NL are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. M is a point on NL such that JK = ML.
The angle of depression of J from N is A LJN B NJM C KNM D JLK 85. The vertical and horizontal distances of a car from an airborne helicopter is 580 m and
100 m respectively. The angle of depression of the car from the helicopter is A 82.54 B 81.41 C 78.58 D 80.22 86.
In the diagram above, P, Q and R are three points on the horizontal ground. PS is a vertical pole. The angle of elevation of S from Q is 41. Find the angle of depression of R from S. A 36.77 B 32.07 C 34.54 D 29.76 87. Two vertical towers, EF and GH, are on the horizontal ground. The horizontal distance between the base of towers E and G is 40 m. The angle of depression of point H from point F is 22. If the height of tower EF is 170 m, find the height of tower GH. A 153.84 m B 155.03 m C 152.2 m D 150.91 m
88.
The diagram above shows two vertical lamp posts, PQ and RS, that are of equal heights. The angle of elevation of P and R from point V, on the horizontal ground, are 142' and 95' respectively. V is 32 m from the base of the lamp post PQ. Find the distance between the lamp posts. A 20 m B 18 m C 17 m D 16 m 89. In the diagram, JK and LM are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. The height of LM is twice the height of JK. The angle of depression of J from vertex L is 45.
Calculate the height, in m, of LM. A 50 B 50 C 25 D 35.36
90.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of elevation of R from Q is same as A RQS B QSR C PQS D PQR 91. In the diagram, JK and LM are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. The height of LM is twice the height of JK. The angle of depression of J from vertex L is 46.
Calculate the height, in m, of LM. A 40.56 B 21.75 C 43.49 D 30.21
92.
In the diagram above, AB and CD are two vertical poles on the horizontal ground. The angle of depression of C from A is 6.71. The height of A is 6 m and that of C is 4 m. Calculate the horizontal distance of BD. A 19 m B 17 m C 16 m D 15 m 93.
The diagram above shows a vertical pole XY on a horizontal plane. The angles of elevation of point X from point A and point B are differ by 12. Given that the angle of elevation of X from A is 34, find the distance of BY. A 28 m B 26.53 m C 71.78 m D 72.78 m
94. In the diagram, JK and LM are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. The height of LM is twice the height of JK. The angle of depression of J from vertex L is 53.
Calculate the height, in m, of LM. A 28.64 B 50.43 C 14.32 D 30.35 95.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, PQ and RS, on a horizontal ground. The value of the angle of elevation of R from Q is same as A QRS B RQS C PQS D PQR 96. In the diagram, JK and NL are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. M is a point on NL such that JK = ML.
The angle of depression of J from N is A NJM B JNM C KNM D JLK 97.
The diagram above shows two vertical poles, ST and VU on the horizontal ground. The height of pole ST is 11 m and the poles are 14 m apart. The angle of depression of S from V is 26.57. The height, in m, of pole VU is A 20 B 18 C 17 D 16
98.
In the diagram above, VW is a vertical wall. The angle of depression of U from V is 37. Point U is 8 m from the foot of the wall. Find the height of the wall VW. A 6.03 m B 4.56 m C 10.62 m D 11.62 m 99. In the diagram, JK and LM are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. The height of LM is twice the height of JK. The angle of depression of J from vertex L is 59.
Calculate the height, in m, of LM. A 22.83 B 31.62 C 11.42 D 63.24 100. The vertical and horizontal distances of a car from an airborne helicopter is 590 m and 120 m respectively. The angle of depression of the car from the helicopter is A 80.82 B 79.69 C 76.86
D 78.5
Answers: 1. C 2. C 3. C 4. D 5. B 6. A 7. C 8. D 9. B 10. B 11. B 12. B 13. B 14. C 15. C 16. C 17. C 18. D 19. A 20. B 21. C 22. A 23. D 24. A 25. D 26. B 27. D 28. A 29. D 30. C 31. B 32. B 33. A 34. D 35. D 36. D 37. D 38. C 39. A 40. A 41. A 42. D
43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88.
A C A A D C D D B C A A A A A C D B B A D C D A A B C D D D D A A B D A B C D A C B D C A B
89. B 90. A 91. C 92. B 93. A 94. B 95. B 96. A 97. B 98. A 99. D 100. D
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 28-Trigonometry Paper 2Document6 pages28-Trigonometry Paper 2iyaad MubarakPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigo (E) Worksheet 2Document8 pagesTrigo (E) Worksheet 2Sohail Merchant100% (1)
- TrigonometryDocument4 pagesTrigonometryRosemary Reynolds100% (1)
- Chapter1-Nature of StatisticsDocument10 pagesChapter1-Nature of StatisticsNelia Olaso InsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 I Circles ENRICHDocument16 pagesChapter 14 I Circles ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahim100% (1)
- MCQ in Plane Trigonometry Part 3 ECE Board Exam PDFDocument8 pagesMCQ in Plane Trigonometry Part 3 ECE Board Exam PDFJed LavuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingSiamHashan100% (1)
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersD'EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersPas encore d'évaluation
- 3D Angles QuestionsDocument4 pages3D Angles QuestionsyddapPas encore d'évaluation
- Handouts - Trigonometry and GeometryDocument5 pagesHandouts - Trigonometry and GeometryTrisha Rañada100% (1)
- Ornament & Crime 1.3.0 User ManualDocument49 pagesOrnament & Crime 1.3.0 User ManualGiona VintiPas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Engineers Competency Matrix - Society of Petroleum EngineersDocument5 pagesReservoir Engineers Competency Matrix - Society of Petroleum Engineersbillal_m_aslamPas encore d'évaluation
- BearingsDocument15 pagesBearingsJoann NgPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Paper of SurveyingDocument11 pagesTest Paper of Surveyingjhacademyhyd100% (2)
- How To Play Sci DamathsDocument9 pagesHow To Play Sci DamathsJoeisa JoeisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Angles of Elevation and Depression ProblemsDocument8 pagesAngles of Elevation and Depression ProblemsNasir Rahman100% (1)
- Spherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesD'EverandSpherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.0 TrigonometryDocument16 pages2.0 TrigonometryMae TadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Review ExercisesDocument68 pagesReview ExercisesDream Cafe0% (1)
- Problem Sets - Simple, Compound, Reverse Curved PDFDocument4 pagesProblem Sets - Simple, Compound, Reverse Curved PDFBeerRide50% (6)
- Nav Test For CPL CandidatesDocument8 pagesNav Test For CPL CandidatesVivek BaskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Algorithmic and High Frequency TradingDocument16 pagesAlgorithmic and High Frequency TradingAdi MPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 I Angles of Ele & Depression ENRICHDocument14 pagesChapter 16 I Angles of Ele & Depression ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 I Angles of Elevation & Depressions ENHANCEDocument21 pagesChapter 16 I Angles of Elevation & Depressions ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Angles of Elevation and Depression MCQs and Word ProblemsDocument7 pagesAngles of Elevation and Depression MCQs and Word ProblemsyusainiKasiron69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry and Trigonometry Word Problems (40 QuestionsDocument16 pagesGeometry and Trigonometry Word Problems (40 QuestionsBoyImanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mine Survey Ass 1Document3 pagesMine Survey Ass 1Leroy MundaPas encore d'évaluation
- Directions: Answer The Following Questions. Write Your SOLUTION and BOX Your Final Answer in Your NotebookDocument6 pagesDirections: Answer The Following Questions. Write Your SOLUTION and BOX Your Final Answer in Your NotebookKevin Abenojar NamayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Problem SetDocument2 pagesMidterm Problem SetJoylene Dayrit KIMPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Cebu (UC) : College of Engineering (COE)Document1 pageUniversity of Cebu (UC) : College of Engineering (COE)Edenjade MacawiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigo PreboardDocument26 pagesTrigo PreboardMichael Beltran100% (1)
- Cartography 5 - Intervisibility and Map NamingDocument2 pagesCartography 5 - Intervisibility and Map NamingGie Marie GuarinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Form 2 Exam P3Document5 pagesMaths Form 2 Exam P3JKPas encore d'évaluation
- Lines & Planes in 3DDocument41 pagesLines & Planes in 3Djuriah binti ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Triangle Solved QuestionsDocument38 pagesProperties of Triangle Solved QuestionsKaran DoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter10 - Angle of Elevation and DepressionDocument4 pagesChapter10 - Angle of Elevation and DepressionHayati Aini AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Surveying IIDocument7 pagesQuestion Surveying IIahzamshadabPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision QuestionDocument3 pagesRevision QuestionKasyage AbubakaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Exercise 21 Objective)Document11 pagesReview Exercise 21 Objective)Vimalraj MoghanPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1Danzyl VillatemaPas encore d'évaluation
- CircleDocument20 pagesCirclesabummathewPas encore d'évaluation
- CircleDocument20 pagesCirclejuriah binti ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023-24 - X - CBSE - (C.W-120) - 31.01.2024 (Geometry)Document5 pages2023-24 - X - CBSE - (C.W-120) - 31.01.2024 (Geometry)shivaPas encore d'évaluation
- HeightdistanceJEEMAINSPYQs2022 21qDocument2 pagesHeightdistanceJEEMAINSPYQs2022 21qsureshserious7226Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trigo and Anal GeomDocument37 pagesTrigo and Anal GeomxaiiPas encore d'évaluation
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: OME Pplications OF RigonometryDocument11 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: OME Pplications OF RigonometryAkshit MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Applications of TrigonometryDocument11 pagesSome Applications of TrigonometryArshdeep KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- TheodoliteDocument26 pagesTheodoliteRajiv KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- TrigDocument5 pagesTrigDaniel KwokPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 601 Trigonometry Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument2 pagesME 601 Trigonometry Practice Problems and Solutionslance galorportPas encore d'évaluation
- FOURTH QUARTER-Mth9Document6 pagesFOURTH QUARTER-Mth9Christ IanPas encore d'évaluation
- 10- App of Trig--MCQ- Ques 2023Document6 pages10- App of Trig--MCQ- Ques 2023Partha sarathyPas encore d'évaluation
- 10- App of Trig--MCQ- Ques and Ans 2023Document6 pages10- App of Trig--MCQ- Ques and Ans 2023Partha sarathyPas encore d'évaluation
- CEST PRELIM LT 9 2019-2020 SurveyingDocument4 pagesCEST PRELIM LT 9 2019-2020 SurveyingHarold Fritz GumawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Course On 3-DDocument66 pagesSimple Course On 3-DCartmanTaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Revision 19 20 21Document6 pagesForm 4 Revision 19 20 21Noor Fazliati SulaimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Circles II: Properties of Circles and Angles in CirclesDocument11 pagesCircles II: Properties of Circles and Angles in Circlessims363Pas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Trigonometry 1Document19 pagesApplication of Trigonometry 1Albert RusliPas encore d'évaluation
- 10th SA2 I QDocument29 pages10th SA2 I QKarthik NishanthPas encore d'évaluation
- TrigandBearings ExercisesDocument2 pagesTrigandBearings ExercisesCoolman PoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Surveying PDFDocument3 pagesSurveying PDFMariah Kathleen LacsinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Surveying ReviewerDocument2 pagesSurveying ReviewerAndre NispÉrosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17 I Lines & Planes in 3D ENRICHDocument18 pagesChapter 17 I Lines & Planes in 3D ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Gypsum-Anhydrite Equilibria in Systems Gaso - H, O and Ga@N-Nacl-H, ODocument9 pagesGypsum-Anhydrite Equilibria in Systems Gaso - H, O and Ga@N-Nacl-H, OFarzad sadeghzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Series Forecasting ANNDocument8 pagesTime Series Forecasting ANNTika PsbPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus B Tech 1 Year PDFDocument36 pagesSyllabus B Tech 1 Year PDFPcm Aryan AnkitPas encore d'évaluation
- MAC 1147 Exam 3 PaperDocument5 pagesMAC 1147 Exam 3 PaperNeil BreenPas encore d'évaluation
- GTU BE Semester III Circuits and Networks Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesGTU BE Semester III Circuits and Networks Exam QuestionsPanktiPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Quiz PermutationsDocument76 pagesGroup Quiz PermutationsMr. Rhumer LanojanPas encore d'évaluation
- Che 312 Notebook DistillationDocument19 pagesChe 312 Notebook DistillationUGWU MARYANNPas encore d'évaluation
- คำอธิบายกระบวนวิชาDocument12 pagesคำอธิบายกระบวนวิชาCuga SaharathPas encore d'évaluation
- Math-6 Demo-LPDocument4 pagesMath-6 Demo-LPREZAPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 12-53: A T A V TDocument57 pagesProblem 12-53: A T A V Tadam johnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers TheDocument13 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers TheaaxdhpPas encore d'évaluation
- Java Course Notes CS3114 - 09212011Document344 pagesJava Course Notes CS3114 - 09212011Manuel SosaetaPas encore d'évaluation
- FFJM Semi-Finals March 21st 2015 rankingsDocument2 pagesFFJM Semi-Finals March 21st 2015 rankingsTapas HiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1: Introduction To Numerical Analysis QuestionsDocument2 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Numerical Analysis QuestionsNinoMay Suazo RoblePas encore d'évaluation
- Population Growth: Flows O N The LineDocument6 pagesPopulation Growth: Flows O N The LineRaúl Baigorri MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1: Nature of StatisticsDocument47 pagesModule 1: Nature of StatisticsHannah Bea LindoPas encore d'évaluation
- D 2718 - 00 Rdi3mtgtmda - PDFDocument6 pagesD 2718 - 00 Rdi3mtgtmda - PDFRufo CascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes on Linear Regression ModelsDocument46 pagesNotes on Linear Regression Modelsken_ng333Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Induction Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Induction Lesson PlanRenz CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Odd Numbers and SeriesDocument9 pagesOdd Numbers and SeriesOmer Ali100% (1)
- 5DOF Manipulator Simulation Based On MATLAB-Simulink MethodologyDocument7 pages5DOF Manipulator Simulation Based On MATLAB-Simulink MethodologySasha NarvaezPas encore d'évaluation
- Robust Collaborative Object Transportation Using Multiple MavsDocument25 pagesRobust Collaborative Object Transportation Using Multiple MavsMegan RileyPas encore d'évaluation
- LQGDocument64 pagesLQGstephenPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrostaticsDocument79 pagesElectrostaticsHead Department of PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation