Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Grating
Transféré par
Ghanshyam Pandey0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
1K vues8 pagesDIN 1055-5 / A1 DIN 1072 Allowable Nominal Static axial Central Total Total width Uniformly total weight load capacity load trace width width distributed (standard load)
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDIN 1055-5 / A1 DIN 1072 Allowable Nominal Static axial Central Total Total width Uniformly total weight load capacity load trace width width distributed (standard load)
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
1K vues8 pagesGrating
Transféré par
Ghanshyam PandeyDIN 1055-5 / A1 DIN 1072 Allowable Nominal Static axial Central Total Total width Uniformly total weight load capacity load trace width width distributed (standard load)
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 8
Technical data sheet Forge welded gratings
Example SP 330 - 34/38 - 3
Forge-welded grating SP
Bearing bar 30 x 3 mm 330
Pitch 34 x 38 mm -34/38
Banding 30 x 3 mm -3
Type SP 330 -34/38 -3
Type as above, but
Pitch 34 x 50 mm
Type SP 330 -34/50 -3
Serrated type no. 1 and 11
Types of forge-weIded gratings
-34/50
Fabrication widths
Types of forge-welded gratings
Number Number Number
of bars
of bars of bars
2 39 mm 12 382 mm 22 726 mm
3 73 mm 13 417 mm 23 760 mm
4 108 mm 14 451 mm 24 794 mm
5 142 mm 15 485 mm 25 829 mm
6 176 mm 16 520 mm 26 863 mm
7 211 mm 17 554 mm 27 897 mm
8 245 mm 18 588 mm 28 932 mm
9 279 mm 19 623 mm 29 966 mm
10 314 mm 20 657 mm 30 1000 mm
11 348 mm 21 691 mm
All mentioned dimensions are theoretical and include normal production
tolerances
Fabrication widths SP-gratings at bearing bar thickness 3 mm
Pitch of bearing bars 34,33;
panel width= nominal size 1000 mm
Grating
width
Grating
width
Grating
width
1/8
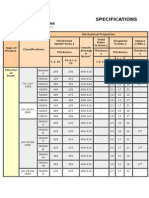
Forge welded gratings Heavy duty gratings
DN 1055-5/A1
DN 1072
Allowable Nominal Static axial Central Total
Total
width
Uniformly
total weight load
capacity
load
trace width width distributed
(standard
load)
Traffic load
P a b I (standard load)
kN kN kN m m m kN/m
25 6 20 0,8 1 2,4 10
35 10 30 0,8 1 2,8 12,5
70 25 65 1 1,2 3,4 15
130 50 120 1,2 1,5 3,6 25
Extract from DIN 1055-5/A1
Fork Iift - standard vehicIe
OsciIIation vaIue Bridge cIass WheeI Ioad Load area
f traffic lane contains construction
parts that are particularly susceptible
to localised brake loading (e.g. parts
of traffic lane crossings, gratings,
etc.), wheel load should be multiplied
by 1,4 to determine brake loading
occurring on single parts
60 100 kN 200 x 600 mm
45 75 kN 200 x 500 mm
30 50 kN 200 x 400 mm
24 40 kN 200 x 300 mm
16 50 kN 200 x 400 mm
12 40 kN 200 x 300 mm
9 30 kN 200 x 260 mm
6 20 kN 200 x 200 mm
3 10 kN 200 x 200 mm
Extract from DIN 1072
Bridge cIass = totaI weight of the vehicIe; Load area = Load contact area
2/8
Forge-welded gratings - serrated
Remarks concerning serration
Reduction of Ioad bearing capacity on gratings
n order to increase levels of slip resistance, bars are serrated by punching out
material from walking surface. Due to this reduction in material, the load values
stated in the load tables for non serrated walking surfaces need to be reduced
proportionately. The load bearing capacity of serrated grating types no. 1, no. 3 und
no. 31 is reduced by approx. 24% for forge-welded gratings and pressure-locked
gratings having 20 x 2 mm bearing bars and by approx. 9% for 60 x 5 mm bearing
bars. At the reduced loading on 20 x 2 mm bearing bars, the deflection is approx.
17% greater and on 60 x 5 mm bearing bars, it is approx. 4% greater.
WaIkways' having incIines between 6 and 24
The supply of standard gratings is recommended for walkways to conveyors or
similar installations, when they are inclined up to 6. Walkways inclined from 6 to 10
should be provided with serrated gratings. At an angle of inclination between 10 and
24, metal gratings should be supplied with an anti-slip metal strip securely fixed to
the top surface over the whole length of the grating. For angles of incline in excess of
24, stairs should be used. The pitch of anti-slip strips is to be determined from the
formula used for stair design, which is 600 > g +2h > 660, where g = the stairtread
'going' and h = the height determined from the angle of incline.
3/8
Test resuIts of serration
Gratings and perforated metal planks used as self-supporting floor coverings
Basis of the tests: nstruction sheet ZH 1/571 for flooring in working rooms and
working areas where there is a potential slipping hazard. Tests have been done by
the Berufsgenossenschaftliches nstitut fr Arbeitsschutz BA, St. Augustin
The following table shows the test results of Lichtgitter products.
Type Serration
No.
Surface
treatment
Pitch (mm) Serration
class
Displacement
Gratings out of steeI S235JR
SP 330-34/38-3 ----- galvanized 34x38 mm R 10 V 10
P 330-33-3 ---- galvanized 33x33 mm R 10 V 10
P 230-33/11-3 ---- galvanized 33x11 mm R 9 V 10
XSP 330-34/38-3 1 galvanized 34x38 mm R 10 V 10
XSP 330-34/38-3 11 galvanized 34x38 mm R 11 V 10
XP 230-33-3 2 galvanized 33x33 mm R 12 V 10
XP 230-33/22-3 2 galvanized 33x22 mm R 12 V 10
XP 230-33/11-3 2 galvanized 33x11 mm R 12 V 10
XP 430-33-4 2 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 330-33/22-3 22 galvanized 33x22 mm R 12 V 10
XP 230-33-3 22 galvanized 33x33 mm R 13 V 10
XP 330-33-3 22 galvanized 33x33 mm R 12 V 10
XP 230-33-3 3 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 330-33-3 3 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 230-33-3 31 galvanized 33x33 mm R 12 V 10
XP 330-33-3 31 galvanized 33x33 mm R 12 V 10
XP 430-33-4 31 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 530-33-5 31 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 330-44-3 31 galvanized 44x44 mm R 12 V 10
XP 230-33/11-3 32 galvanized 33x11 mm R 10 V 10
XP 230-33/11-3 4 galvanized 33x11 mm R 11 V 10
XP 230-33-3 4 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 330-33-3 4 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 430-33-4 4 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 530-33-5 4 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
XP 230-33/11-3 42 galvanized 33x11 mm R 10 V 10
XP 230-33-3 42 galvanized 33x33 mm R 11 V 10
Gratings out of stainIess steeI
XP 225-33-3 3 pickled 33x33 mm R 12 V 10
XP 225-33-3 31 pickled 33x33 mm R 13 V 10
XP 325-33-3 31 pickled 33x33 mm R 12 V 10
XP225-25-3 31 pickled 25x25 mm R 13 V 10
XP 325-25-3 31 pickled 25x25 mm R 12 V 10
XP 525-25-5 31 pickled 25x25 mm R 12 V 10
4/8
XP 525-33-5 31 pickled 33x33 mm R 12 V 10
Gratings out of AIuminium AIMg 3G22
XP 225-33-3 3 pickled 33x33 mm R 13 V 10
XP 225-33-3 31 pickled 33x33 mm R 13 V 10
XP 225-33-3 4 pickled 33x33 mm R 13 V 10
Perforated metaI pIanks out of steeI S235JR
BR 50/2 galvanized rhombic R 11 V 10
BP 50/2 galvanized parallel R 11 V 10
BP- 50/2 galvanized parallel
raised
R 12 V 10
BN-G 50/2 galvanized closed R 9
BN-O 50/2 galvanized open R 11 V 10
BZ 50/2 galvanized tooth R 11 V 10
BP 50/2 *see below parallel R 11 V 10
BZ 50/2 * see below tooth R 13 V 10
BN-G 50/2 * see below closed R 9
BN-O * see below open R 11 V 10
BN-G galvanized
sanded with
quartz
closed R 12
* Continuously hot dipped material quality DX51D+Z200 MAC acc. to DN EN 10327
Perforated metaI pIanks out of stainIess steeI
BP 50/2 pickled parallel R 11 V 10
BN-O 50/2 pickled open R 11 V 10
BZ 50/2 pickled tooth R 12 V 10
Perforated metaI pIanks out of AIuminium AIMg 2G22
BP 50/2 pickled parallel R 11 V 10
BN-O 50/2 pickled open R 11 V 10
BZ 50/2 pickled tooth R 13 V 10
GRP-gratings our of UP-GF
GRP-K 630-19-6 concave R 13 V 10
GRP-K 538-38-6 concave R 13 V 10
GRP-gratings out of UP-GF with quartz sand 05-1,0 mm
GFK-K 638-38-6 sanded R 12 V 10
5/8
Forge-weIded stairtreads
Standard stairtreads acc. to DIN 24531-1
Standard stairtreads acc. to DIN 24531-1
Type Bearing bar Dimension b c d e kg/tread
SP 330-34/38-3
Nominal mesh
approx.
30 x 30 mm
30 x 3 mm
600 x 240 mm
600 x 270 mm
600 x 305 mm
800 x 240 mm
800 x 270 mm
800 x 305 mm
1000 x 240 mm
1000 x 270 mm
1000 x 305 mm
55
55
55
55
55
55
55
55
55
70
70
70
70
70
70
70
70
70
120
150
180
120
150
180
120
150
180
85
85
90
85
85
90
85
85
90
6,0
7,5
10,0
8,0
9,0
11,5
9,5
10,5
13,0
SP 340-34/38-3
Nominal mesh
approx.
30 x 30 mm
40 x 3 mm
800 x 240 mm
800 x 270 mm
1000 x 240 mm
1000 x 270 mm
1200 x 240 mm
1200 x 270 mm
1200 x 305 mm
55
55
55
55
55
55
55
70
70
70
70
70
70
70
120
150
120
150
120
150
180
85
85
85
85
85
85
90
8,0
9,0
10,0
11,0
13,0
15,5
18,0
Load instructions
Load instructions acc. to DN EN SO 14122-3
Steps shall resist the following unfactored loadings:
f the width w < 1200 mm, then 1,5 kN shall be distributed over an area of 100 x 100
mm where one boundary is the leading edge of the nosing, applied at the middle of
the stair width. f the width w < 1200 mm, then respectively 1,5 kN shall be
distributed simultaneously over each of the 100 x 100 mm areas applied at the most
unfavourable points, spaced at intervals of 600 mm, where one boundary is the
leading edge of the nosing.
The deflection of the supporting structure and the stairs does not exceed under load
1/300 of the span, maximum 6,0 mm
6/8
Requirements
.
Requirements for stairs made out of steel (DN EN SO 14122-3)
The rise h and going g, shall meet the formula, 600 > g + 2h > 660. The overlap,
r of step or landing shall be < 10 mm. The length of landing l shall be at least 800
mm and in any case < the width of the stair, w.
On the same flight, the rise shall be constant wherever possible. n the case where it
is not possible to maintain the height of the rise between the level of departure and
the lower step, it may be reduced by a maximum of 15%.
H = Climbing height , r = Overlap, g 0 Going, = Angle of pitch, e = Headroom, w =
Width, h = Rise, p = Pitch line, l = Length of landing, t = Height of step, c = Clearance
7/8
Forge-weIded gratings
Surface treatment
Surface treatment for steeI gratings and steeI for construction appIications, in
accordance with to DIN EN 10025
- Galvanizing acc. to DN EN SO 1461 (hot dip galvanized)
- Galvanized followed by bitumen dipping
- Plastic coating *, also on galvanized surfaces (colours according to RAL)
- Baked paint*, also on galvanized surfaces (colours according to RAL)
Gratings and perforated metaI pIanks made of stainIess steeI, materiaI acc. to DIN
17440
- Pickled
- Electrochemically polished
- Glass bead blasting
Gratings and perforated metaI pIanks from aIuminium, materiaI acc. to DIN EN 485 and
DIN EN 573
- Pickled
- Baked paint* (colours according to RAL)
- Anodised
- Plastic coating* (colours according to RAL)
* A coating with epoxy resin powder for outside areas is not recommended. For these
areas, a polyester powder coating should be used.
Gratings and perforated metal planks receive a surface protection to avoid potential
corrosion.
Gratings manufactured from stainless steel and aluminium generally do not need a corrosion
protection. At least one after-treatment by pickling or anodising is recommended.
Hot dip gaIvanizing (usual corrosion protection for gratings)
The term hot dip galvanizing means the adding of a zinc finish by dipping the pre-treated
parts into a molten zinc dip. The zinc coat adheres firmly to surfaces. n case of normal
mechanical demands such as transportation, pedestrian or vehicle traffic, zinc does not flake
off or develop cracks.
The average weight of the zinc coating is approximately 450 g per sqm of treated surface.
This corresponds to a coating thickness of approximately 65 m. The thickness of the zinc
coating also depends on the thickness of the material. Before galvanizing, parts are pre-
treated to provide a mechanically clean surface in order to achieve a faultless adherence of
zinc.
Bitumen dipping is often requested as an additional treatment for galvanized gratings, and
gives extra surface protection (mainly for chemical use).
PIastic coatings are achieved, e.g. by dipping or electrostatic powder coating. The abrasion
resistance and thickness of finish required, depends upon the application, so this need to be
considered when deciding which procedure and plastic to use.
Painting
Gratings and perforated metal planks can likewise be lacquered in a dipping or spraying
process, preferably after galvanizing.
8/8
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Astm C78Document3 pagesAstm C78avrajan100% (3)
- Zamil Sample CalculationsDocument108 pagesZamil Sample CalculationsAshraf KhalifaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Input Data: Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.1.1Document10 pages1 Input Data: Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.1.1Zaido Al HalabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Base Plate Design SummaryDocument3 pagesBase Plate Design SummarySơn Nguyễn-LêPas encore d'évaluation
- Skylight StructureDocument16 pagesSkylight Structuremsiddiq1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metal Sheet Calculations for 44-195 ProfileDocument29 pagesMetal Sheet Calculations for 44-195 ProfileAnonymous HkX2aE9FxPas encore d'évaluation
- Tower Design SheetDocument41 pagesTower Design Sheet14pcashPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Design Calculations Precast Boundary WallDocument35 pagesStructural Design Calculations Precast Boundary WallrenishkavukattPas encore d'évaluation
- Gantry Girder (B Less Than 0.586l)Document5 pagesGantry Girder (B Less Than 0.586l)abhi arotePas encore d'évaluation
- PurlinDocument10 pagesPurlintheengineersaPas encore d'évaluation
- Larsen & Toubro Limited - Ecc Division: Engineering Design and Research CentreDocument1 pageLarsen & Toubro Limited - Ecc Division: Engineering Design and Research CentreOuseppachan AmbookenPas encore d'évaluation
- Peb BuildingDocument4 pagesPeb BuildingHiren DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- IP4 design reaction summary and analysisDocument8 pagesIP4 design reaction summary and analysisFarhan DanishPas encore d'évaluation
- DOUBLE ANGLE (Rev.2.00)Document4 pagesDOUBLE ANGLE (Rev.2.00)Harjasa AdhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fdocuments - in Insert Plate Design LugsDocument8 pagesFdocuments - in Insert Plate Design Lugsarchetype designPas encore d'évaluation
- Robinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601Document32 pagesRobinair Bombas de Vacío 15401 601MarcWorld100% (1)
- Noise Barriers Supply and Installation For Burfiwala Lane & Gokhale Road Junction FlyoverDocument20 pagesNoise Barriers Supply and Installation For Burfiwala Lane & Gokhale Road Junction FlyoverAvinash JagtapPas encore d'évaluation
- Pile Cap Design - ColumnsDocument7 pagesPile Cap Design - ColumnsJule LobresPas encore d'évaluation
- HILTI RE-500 Rebar ConnectionDocument7 pagesHILTI RE-500 Rebar ConnectionAlma M. LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chequered Plate DesignDocument1 pageChequered Plate DesignAsif AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Beam - Section Classification Is 800-2007Document6 pagesBeam - Section Classification Is 800-2007ranjitPas encore d'évaluation
- A&m BSR-2011Document26 pagesA&m BSR-2011Mukesh Jangid100% (1)
- Tension RodDocument4 pagesTension RodMarkPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhomboidal Steel Wire Rope Net Panels SpecificationDocument5 pagesRhomboidal Steel Wire Rope Net Panels SpecificationSOMNATH JANAPas encore d'évaluation
- Bs5950 Calculation Decking SheetDocument6 pagesBs5950 Calculation Decking SheetKho C Ahl100% (1)
- Anchor Bolt Types A and B SpecificationsDocument1 pageAnchor Bolt Types A and B SpecificationsmodarthPas encore d'évaluation
- 06-Mx, My, N MemberDocument2 pages06-Mx, My, N MemberMazenMowafyPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation LoadingsDocument1 pageFoundation Loadingsmanish318Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wind LoadDocument5 pagesWind LoadPATEL JIGARPas encore d'évaluation
- SPECIFICATIONS FOR STRUCTURAL STEEL AND SHEET PILEDocument9 pagesSPECIFICATIONS FOR STRUCTURAL STEEL AND SHEET PILEAbdul Syukur ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Base Plate and Anchor BoltsDocument7 pagesDesign of Base Plate and Anchor BoltsShaikh Muhammad AteeqPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensional Solutions Mat3DDocument69 pagesDimensional Solutions Mat3DTimothy HancockPas encore d'évaluation
- Corbel and NibDocument17 pagesCorbel and NibCatherine Mohanji GeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Steel Contractor Alternate Beam Proposal CalculationDocument1 pageStructural Steel Contractor Alternate Beam Proposal CalculationJeff cadavaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Catalogue VOL1Document330 pagesGeneral Catalogue VOL1lifib23970Pas encore d'évaluation
- GRC Design and LoadsDocument4 pagesGRC Design and Loadsmohamed rafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Section A-A: Wall Cheq'D PlateDocument1 pageSection A-A: Wall Cheq'D PlateAL BASTAKI CONTRACTING L.L.C.50% (2)
- SC348-ME-FDN-006 - RE - Foundation DrawingDocument6 pagesSC348-ME-FDN-006 - RE - Foundation DrawingsajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Staircase Design DetailsDocument1 pageStaircase Design DetailsBry RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- BoqDocument24 pagesBoqDilshad AhemadPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Self-Supported Steel Chimney With The Effects of Geometrical ParametersDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Self-Supported Steel Chimney With The Effects of Geometrical Parametersvikram413Pas encore d'évaluation
- Annex-3 Vetogrout CG518Document2 pagesAnnex-3 Vetogrout CG518MdShahbazAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Combination For Steel Design Per BS en 1990 EditionDocument2 pagesLoad Combination For Steel Design Per BS en 1990 EditionAsaru Deen100% (1)
- Z Purlin Design Span 12 SL 0.3Document1 pageZ Purlin Design Span 12 SL 0.3arman malikPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Case, Load Combination, Modal Case Options. Choose The Load Case To Be DisplayedDocument5 pagesLoad Case, Load Combination, Modal Case Options. Choose The Load Case To Be DisplayedLivia15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design Parameters For Corbel:1: B D D D 450Document3 pagesDesign Parameters For Corbel:1: B D D D 450Living LifePas encore d'évaluation
- Load Combination Is 800-2007Document5 pagesLoad Combination Is 800-2007Jitendra PPas encore d'évaluation
- Insert Plate CheckDocument6 pagesInsert Plate CheckSatish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic design loads and combinationsDocument15 pagesSeismic design loads and combinationsAmey Gudigar100% (1)
- Calculation - Loading PlatformDocument6 pagesCalculation - Loading PlatformDaniel SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of angle and ISMC section splicesDocument2 pagesDesign of angle and ISMC section splicesPartha GangopadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-Design of Grade Slab - As Per TR-34Document42 pages02-Design of Grade Slab - As Per TR-34Anonymous Clm40C1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Z Purlins ReportDocument18 pagesDesign of Z Purlins ReportAgarwal MittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Binder 1Document68 pagesBinder 1Anh KyPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Aids of Flexural Members and Beam Columns Based On Limit State Method PDFDocument16 pagesDesign Aids of Flexural Members and Beam Columns Based On Limit State Method PDFscshekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Name: Item Description Quantity Unit Rate TotalDocument23 pagesProject Name: Item Description Quantity Unit Rate TotalAlexandruDanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Consistent determination of flexural and lateral buckling resistanceDocument106 pagesConsistent determination of flexural and lateral buckling resistanceAnonymous hprsT3WlPPas encore d'évaluation
- IS 14817 (Part 2) 2004 - MECHANICAL VIBRATION - EVALUATION OF MACHINE VIBRATION - PART 2 LARGE LADocument11 pagesIS 14817 (Part 2) 2004 - MECHANICAL VIBRATION - EVALUATION OF MACHINE VIBRATION - PART 2 LARGE LAAbinashBeheraPas encore d'évaluation
- Exhibition Stand - REV 0Document12 pagesExhibition Stand - REV 0shibu4321Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Face Mounted BracketDocument4 pagesDesign of Face Mounted Bracketvishal tomarPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Loko Pabrik UD - MajuDocument28 pagesMaterial Loko Pabrik UD - MajuIlma FaidahPas encore d'évaluation
- IMI TRUFLO RONA Fully Welded Ball ValvesDocument12 pagesIMI TRUFLO RONA Fully Welded Ball ValvesAlexandra HarperPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioplastic: Sustainable Green Plastic: December 2015Document3 pagesBioplastic: Sustainable Green Plastic: December 2015Lakshmipriya GopinathPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Composite Materials (Laminated Composite Materials)Document60 pagesIntroduction To Composite Materials (Laminated Composite Materials)soma_durga6606Pas encore d'évaluation
- MSDS of Methyl PalmitateDocument8 pagesMSDS of Methyl PalmitateAmm MarakataPas encore d'évaluation
- Request Tools and Materials for Electrical InstallationDocument8 pagesRequest Tools and Materials for Electrical InstallationJake AngoluanPas encore d'évaluation
- Beam Design ReportDocument22 pagesBeam Design Reportkwoshaba pidsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Batteries 05 00034 PDFDocument11 pagesBatteries 05 00034 PDFguschinPas encore d'évaluation
- STEEL DESIGN (PDF - Io)Document24 pagesSTEEL DESIGN (PDF - Io)Maher AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Calabano Clinical Bacteriology Activity 1 (Lab)Document6 pagesCalabano Clinical Bacteriology Activity 1 (Lab)MarkJasperCalabanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For ForDocument22 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For ForYashPas encore d'évaluation
- 3) Dynamic Properties and Influence of Clay Mineralogy Types On The Cyclic Strength of Mine Tailings PDFDocument13 pages3) Dynamic Properties and Influence of Clay Mineralogy Types On The Cyclic Strength of Mine Tailings PDFVgkBharadwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic Salt Analysis Record WritingDocument20 pagesInorganic Salt Analysis Record WritingDineshPas encore d'évaluation
- Masterseal 380 TDSDocument2 pagesMasterseal 380 TDSArasu DonPas encore d'évaluation
- Aalco Metals LTD Copper Brass Bronze CW712R Naval Brass CZ112Document2 pagesAalco Metals LTD Copper Brass Bronze CW712R Naval Brass CZ112kriskee13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Utopia Eat and Drink 2018Document452 pagesUtopia Eat and Drink 2018Anonymous AjRMVNwPas encore d'évaluation
- Niclal 38, Cumn10Ni4: (Shunt Grade)Document2 pagesNiclal 38, Cumn10Ni4: (Shunt Grade)Marcel KuhnePas encore d'évaluation
- Astm F-568M - 98Document8 pagesAstm F-568M - 98awesome_600Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mandi Gobindgarh Hazardous Waste Report NGT April2021Document7 pagesMandi Gobindgarh Hazardous Waste Report NGT April2021arbaz khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Visco Elastic DamperDocument4 pagesVisco Elastic DampergauravPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactive & Functional Polymers: Li Liu, Jun Zhang, Ren-Cheng TangDocument8 pagesReactive & Functional Polymers: Li Liu, Jun Zhang, Ren-Cheng TangAnonymous bkXWlFidPas encore d'évaluation
- D375 PDFDocument4 pagesD375 PDFArnold RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ilovepdf Merged RemovedDocument19 pagesIlovepdf Merged RemovedNeet AspirantPas encore d'évaluation
- 0620 - 0971 - Ext - OTG - Marking FeedbackDocument15 pages0620 - 0971 - Ext - OTG - Marking FeedbackEffPas encore d'évaluation
- A Course in General ChemistryDocument590 pagesA Course in General Chemistryd010060002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Polymer Processing Assignment-2 (11,20,25,45,51)Document2 pagesPolymer Processing Assignment-2 (11,20,25,45,51)Eshan BhatPas encore d'évaluation
- M&MSDocument2 pagesM&MSASIST MechPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas and Oil - ExploitationDocument12 pagesGas and Oil - ExploitationAnonymous puv25NQenPas encore d'évaluation