Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Revision Questions
Transféré par
Shazia FarheenDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Revision Questions
Transféré par
Shazia FarheenDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
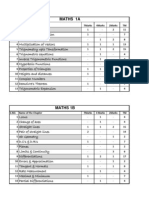
SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY REVISON X1 E AND B 1.
Define a) Law of Conservation of Mass b) Law of Multiple Proportions c) Gay Lussacs Law of Gaseous Volumes d) Avogadro Law e) One atomic mass unit f) mole g) Molar mass and molar volume h) Empirical Formula and molecular formula i) Law of Definite Proportions j) Mole Fraction k) Molarity l) Molality
2. What do you mean Limiting Reagent and excess reagent? 3. How does molarity changes with temperature? 4. Why molality is the best method to express concentration?
5. What is total mole fraction of all the components?
6. A compound contains 4.07 % hydrogen, 24.27 % carbon and 71.65 % chlorine. Its molar mass is 98.96 g. What are its empirical and molecular formulas ? 7. Calculate the amount of water (g) produced by the combustion of 16 g of methane.How many moles of methane are required to produce 22 g CO2 (g) after combustion? 8. 50.0 kg of N2 (g) and 10.0 kg of H2 (g) are mixed to produce NH3 (g). Calculate the NH3 (g) formed. Identify the limiting reagent in the production of NH3 in this 9. A solution is prepared by adding 2 g of a substance A to 18 g of water. Calculate the mass per cent of the solute. 10. Calculate the molarity of NaOH in the solution prepared by dissolving its 4 g in enough water to form 250 mL of the solution. 11. Calculate the mass of sodium acetate (CH3COONa) required to make 500 mL of 0.375 molar aqueous solution. Molar mass of sodium acetate is 82.0245 g mol 1.
12. Calculate the concentration of nitric acid in moles per litre in a sample which
has a density, 1.41 g mL1 and the mass per cent of nitric acid in it being 69%. 13. Dinitrogen and dihydrogen react with each other to produce ammonia according to the following chemical equation: N2 (g) + H2 (g)2NH3 (g) (i) Calculate the mass of ammonia produced if 2.00103 g dinitrogen reacts with 1.00103 g of dihydrogen. (ii) Will any of the two reactants remain un reacted? (iii) If yes, which one and what would be its mass?
ATOMIC STRUCURE
1. Write the configurations of chromium(24) and copper(29) give reason 2. Give Reasons for exceptional configuration of copper(Cu) and Chromium(Cr) 3. What is black body radiation? Explain Plancks quantum theory? 4. What is photoelectric effect? What is work function? 5. Write the expression for the following calculating Kinetic energy of ejected electron during photoelectric effect? 6. Complete the following a) Electrons are ejected from the metal surface ---------- light falls on it. b) The no of electrons ejected is proportional to the --------------------c) The kinetic energy of ejected electron increases by ------------------ on metal surface 7. Define the following terms a) Emission spectra b) Absorption spectra c) Define Quanta or photon 8. Explain hydrogen spectra?
Why atomic spectra is called as finger print of atom 10. What are the Application of Spectroscopy
11. Write the difference between orbit and orbital?
.9
12. Describe Bohrs model of atom? Mention its limitations. 13. What are stark and zeeman effect? 14. What is radial node and spherical node? How many nodded possible for 2 p orbital 15. State the foolowing a) Aufbau principle b) Pauli exclusive principle c) Hunds rule d) n+l rule 16. State the following a. de Broglie dual nature of electron b. Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
17. Show that circumference of the Bhors orbit for hydrogen atom is an
integral multiple of de Broglie wave length . QUANTUM NUMBERS and electronic configuration : 1) Write the electronic configuration of Cu-29 and Cr-24. 2) Write the quantum numbers of the valence electron in Na(z=11) in the ground state.
3) Which of the following orbital has highest energy.(a). n=3 , l=2 ml=+1 (b). n=4
l=0 , ml=0
4) How many unpaired electrons are there in Ni+2?
5. Which atom are indicated by the follwing electronic configuration .
a) [He]2S1 b) [Ne] 3S2 3P3
14. An electron is one of the 3d orbital, Give possible values of n and l. 15. How many electrons in an atom may have the following quantum numbers?
1. n=4 ms=-1/2 2. n=3 , ml=0
16. Arrange the following orbital in the order in which they may get filled. 3d,4S,4P,5S,4f.
17. What are the atomic numbers of the elements whose outer most electrons
are represented by (1). 3S1 (2). 2P3 (3).3P5 18. Using S,P,d,f Notation ,describe the orbital with the following quantum numbers. i. n=2, l=1 ii. n=4, l= 0 iii. n=5, l=3 19. The principle quantum number is n=3. a) Find no of orbital associated with it b) Find no of electrons present in it. 20. 21. Arrange the pair of orbital which experiences the larger effective nuclear charge. (a).2s, 3s (b).4d, 4f The unpaired electron is Al and Si is present in 3p orbital. Which electron will experience more effective nuclear charge? Very important numerical in atomic structure 22. The wavelength range of the visible spectrum extends from violet (400 nm) to red (750 nm). Express these wavelengths in frequencies (Hz). (1nm = 109 m)
Calculate energy of one mole of photons of radiation whose frequency is 5 1014 Hz.
23.
24. What are the frequency and wavelength of a photon emitted during a
transition from n = 5 state to the n = 2 state in the hydrogen atom?
25. Calculate the energy associated with the first orbit of He+. What is the
radius of this orbit?
26. What will be the wavelength of a ball of mass 0.1 kg moving with a velocity
of 10 m s1 ?
27. A microscope using suitable photons is employed to locate an electron in
an involved in the atom within a distance of 0.1 . What is the uncertainty measurement of its velocity?
28. A golf ball has a mass of 40g, and a speed of 45 m/s. If the speed can be measured within accuracy of 2%, calculate the uncertainty in the position.
29. Find energy of each of the photons which (i) Correspond to light of frequency 31015 Hz. (ii) Have wavelength of 0.50 . 30. What is the number of photons of light with a wavelength of 4000 pm that provide 1J of energy?
31. What is the wavelength of light emitted when the electron in a hydrogen
atom undergoes transition from an energy level with n = 4 to an energy level with n = 2?
Classification of elements and periodicity in properties.
1. State the
i) Mendeleev periodic law ii) Mosley modern periodic law 2) Write the IUPAC Name and symbol for the elements with atomic number 120. 110 and 116 3) Why do elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties?
4) Write the general electronic configuration and general properties of
following block of elements. i) s-block elements ii) p-block elements iii) d-block elements iv) f-block element 5) How do atomic radius varies in period and in group? Explain
6) What are iso-electronic species? 7) Explain why cation is smaller and anions larger in radii than parent
atoms. 8) Define following terms a) Ionization enthalpy b) Electron gain enthalpy c) electro negativity
9) account for the following
a) Second electron gain enthalpy of oxygen is positive. b) Cl has more electron gain enthalpy than F.
c) First ionization enthalpy of two isotopes of the same element to be the same. d) Be has higher I.E than Boron. e) N has Higher I.E than O . f) Nobel gas has the highest I.E. g) Group -17 elements ( halogens) have very high negative gain enthalpy. Application type questions
1. An electron belongs to 3rd period of p-block elemts.it has 4 e in
its outer most shell. predict its group. How many unpaired electrons its has?
2. An element has valence shell configuration ns2 np4.Predict the
group and period of the element . 3. Select the element with largest radius. Sate the reason .
(1) O,O-,O-2
4. Which of the following have most negative electron gain enthalpy and least. P, S ,Cl, F.
5. What are iso-electronic species ? arrange the following in the
increasing order of atomic size. Give reason K, K+ 2) Br ,Br- 3) O-2 ,FF-,O-2,Na+Mg
+2
6. In which of the following pairs which species has a larger size.
CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 1. Define octet rule. Write its limitations. 2. What is lattice energy? What is the significance of it?
3. State Fazan's rule?
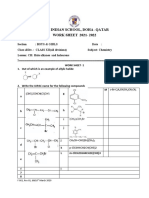
4. Define following bond parameters. a) Bond length. b) Bond energy 5. How do you express the bond strength in terms of bond order? 6. What is the bond order ? what is the bond order of N2 ? Lewis dot structure 1. Draw the Lewis structures for the following molecules and ions : H2S, SiCl4, BeF2, CO2, SO3,SO2, O3 ,NO2- ,HNO3 Resonance 1. What is the resonance? 2. draw the resonance in the following molecules.
SO3 ,SO2 NO2- , NO3-2,, HCOOVSERP THEORY:
CO2,
O3 , CO3-2
1. Predict the geometry of following molecules using VSEPR theory. SF4, H3O+, NH4+, CO3-2,H20,CO2, BeF2,BeCl2,NH2-,ClF3, NH3, SO2
2. BeF2 and H2o both are tri-atomic , yet they have different geometries.
Explain?
3. Geometries of NH3 and H20 are distorted tetrahedral. but bond angle in H20
is lesser than that of NH3. Explain . 4. Arrange the following molecules increasing order of bond angle? NH4+, CO3-2,H20,CO2, DI-POLE MOMENT : 1. What is Dipole Moment?
2
,NH2-, NH3, SO2
2. Although both CO2 and H2O are tri atomic molecules, the shape of H2O
molecule is bent while that of CO2 is linear. Explain this on the basis of dipole moment.
3. Explain why BeH2 molecule has a zero dipole moment although the BeH
bonds are polar.
4. Which out of NH3 and NF3 has higher dipole moment and why? 5. Dipole moment of BF3 is zero Explain? 6. Dipole moment of BeCl2is zero Explain?
Valence bond theory. 1. What do you understand by bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons? Illustrate by giving one example of each type. 2. Distinguish between a sigma and a pi bond.
3. Explain the formation of H2 molecule on the basis of valence bond theory.
HYBRIDISATION
1. What is meant by hybridization of atomic orbital? Describe the shapes of
sp, sp2, between carbon atoms in C2H4 and C2H2 molecules. 3. Predict the hybridization in the following molecules. Explain and Draw the shape of the molecules? NH3, NH+4,H2O, PCl5, SF6,BeCl2,BCl3, 4. What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules ? sp3 hybrid orbital. 2. Draw diagrams showing the formation of a double bond and a triple bond
(a) C2H2 ( b) C2H4
(c).C2H6
5. Explain hybridization in following molecules.
(a) C2H2 ( b) C2H4
(c).C2H6 (d).CH4
6. PCl5 is more reactive, explain in terms of shape of the molecule ? 7. Why in PCl5 axial bonds are longer than than equatorial bond ?
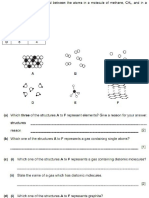
Molecular orbital theory 1. What is Bonding and anti bonding orbital? 2. Calculate Bond Order of following molecules.
H2 , H2 + , H2 O2, O2 +,O2-1, O2-2 B2 , Li2 ,N2,N2+
3. O2, O2 +,O2-1, O2-2 predict the stability order and magnetic behavior. 4. Use molecular orbital theory to explain why Be2 molecule does not exist? 5. What are iso-electronic species? Arrange the following in the
increasing order of atomic size. Give reason F-,O-2,Na+Mg
+2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2022 Puc I Chem Imp QuestionsDocument13 pages2022 Puc I Chem Imp QuestionsCHAKRI BABLUPas encore d'évaluation
- Appsc Junior Lecturer JL Syllabus PDFDocument34 pagesAppsc Junior Lecturer JL Syllabus PDFkandukuru sreenivasuluPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry IPE - Pre Final - JRDocument2 pagesChemistry IPE - Pre Final - JRThe Perfect Human Being100% (2)
- JR. Che. IMP. QDocument10 pagesJR. Che. IMP. QabhichowdarykondaveetiPas encore d'évaluation
- TS JR Chemistry Imp QuestionsDocument6 pagesTS JR Chemistry Imp QuestionsAmair Khan100% (1)
- Snsir JR Chemistry Imp QuestionsDocument4 pagesSnsir JR Chemistry Imp Questionssriram vadrevu100% (1)
- JR. CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesJR. CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsRocky Water0% (1)
- Jr. INTER CHEMISTRY (E.m) PDFDocument12 pagesJr. INTER CHEMISTRY (E.m) PDFkrish100% (1)
- Intermediate1st Year MathsDocument3 pagesIntermediate1st Year MathsksbabuinvestigationPas encore d'évaluation
- JR InterDocument4 pagesJR InterAswani Kumar67% (3)
- Chemistry BBQDocument20 pagesChemistry BBQShaik nabi Farhath banuPas encore d'évaluation
- TS - JR - Maths Ia - Imp Questions PDFDocument7 pagesTS - JR - Maths Ia - Imp Questions PDFPriya BhavanaPas encore d'évaluation
- JR ImpDocument8 pagesJR ImpGovindu PrathapPas encore d'évaluation
- Sr. Che. IMP. Q.Document10 pagesSr. Che. IMP. Q.amruthapingali86100% (1)
- 10-04-21 - Jr. INTER PRE-FINAL IPE - CHEMISTRY - BATCH-II - Q.PaperDocument2 pages10-04-21 - Jr. INTER PRE-FINAL IPE - CHEMISTRY - BATCH-II - Q.PaperrammPas encore d'évaluation
- Inter 2nd Year ChemistryDocument20 pagesInter 2nd Year ChemistryRsp Srinivas50% (4)
- Inter Guess PapersDocument13 pagesInter Guess PapersSaiNag100% (1)
- Physics Important Questions 2021Document13 pagesPhysics Important Questions 2021Mythili Ch100% (1)
- 1st Year Chemistry GuessDocument5 pages1st Year Chemistry GuessMuhammad Ishtiaq100% (2)
- Important Questions CHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesImportant Questions CHEMISTRYvijishnu67% (15)
- Important Questions Chemistry 1st YearDocument3 pagesImportant Questions Chemistry 1st YearUmar ZahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Ts SR Chemistry Imp Questions 2023-24Document6 pagesTs SR Chemistry Imp Questions 2023-24pandu2006goudPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaseous StateDocument23 pagesGaseous StateSiddhartha KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Senior Intermediate Chemistry Important Questions - 2022 Long Answer QuestionsDocument9 pagesSenior Intermediate Chemistry Important Questions - 2022 Long Answer QuestionsRam RmPas encore d'évaluation
- EAMCET QR Chemistry JR Chem 3.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 42 71Document25 pagesEAMCET QR Chemistry JR Chem 3.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 42 71pvnchem67% (3)
- MATHS - 1A QUESTION BANK - Chapter Wise Important Questions For IPEDocument36 pagesMATHS - 1A QUESTION BANK - Chapter Wise Important Questions For IPEalphores100% (1)
- Intermediate Public Examination (March - 2014) Maths - IADocument8 pagesIntermediate Public Examination (March - 2014) Maths - IASaiNag92% (13)
- Chemistry II (EM) MQPDocument3 pagesChemistry II (EM) MQPJameelansar AJPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics2-2 Intermediate II Year Model Question PapersDocument3 pagesPhysics2-2 Intermediate II Year Model Question PapersAkshay Pandey100% (3)
- Intermediate First Year AnalysisDocument3 pagesIntermediate First Year AnalysisHemanth Sai54% (41)
- Important Questions Long Answer Types Physics 8 Marks TS&AP Class 11Document3 pagesImportant Questions Long Answer Types Physics 8 Marks TS&AP Class 11Praful VinayakPas encore d'évaluation
- JR Inter MPCDocument7 pagesJR Inter MPCPavankumar Harsha100% (1)
- 09-03-2023 - Jr-Chemistry-Ipe Pre-Final-Iii-Batch-Ii - Q.PDocument2 pages09-03-2023 - Jr-Chemistry-Ipe Pre-Final-Iii-Batch-Ii - Q.PGowri ShankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Board of Intermediate Education (Ap) : Half Yearly Examinations - 2021Document2 pagesBoard of Intermediate Education (Ap) : Half Yearly Examinations - 2021Sriya MalladiPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Year Model Paper-I: Section - A 10 X 2 20Document6 pagesSecond Year Model Paper-I: Section - A 10 X 2 20A.varalaxmi reddy100% (1)
- 137.Jr. Physics Blue PrintDocument1 page137.Jr. Physics Blue Printkannnamreddyeswar83% (41)
- Important Questions Sem1 PhysicsDocument2 pagesImportant Questions Sem1 Physicsprashanth kumar100% (1)
- Sr. Chemistry Important Questions - 2023Document4 pagesSr. Chemistry Important Questions - 2023lohithsoujan4569Pas encore d'évaluation
- JR Zoo EDocument4 pagesJR Zoo Eprem0% (2)
- Juniorinter Physics Questions em 4 PDFDocument13 pagesJuniorinter Physics Questions em 4 PDFnasreenrai7991Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Year Important Questions 2019 - 2020Document3 pages1st Year Important Questions 2019 - 2020Lohith CharyPas encore d'évaluation
- SR Chemistry Final Exam Imp QBDocument6 pagesSR Chemistry Final Exam Imp QBsurya sureshPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths 2a PDFDocument10 pagesMaths 2a PDFVishnu Vardhan RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- JR Inter Chemistry 1Document3 pagesJR Inter Chemistry 1Reddy Gmd100% (5)
- March 2009Document2 pagesMarch 2009forever friends-live freePas encore d'évaluation
- Puc Ii PCMB Board Question Bank PDFDocument439 pagesPuc Ii PCMB Board Question Bank PDFkatti1084154100% (3)
- TS - JR - Physics Imp - Questions 2022-23 PDFDocument5 pagesTS - JR - Physics Imp - Questions 2022-23 PDFpradeep36100% (1)
- Chemistry II (EM) MQPDocument3 pagesChemistry II (EM) MQPRamya GokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermediate 1st Year Physics Blueprint 2013Document1 pageIntermediate 1st Year Physics Blueprint 2013Lakshmi Sony60% (5)
- TS - SR - Physics - Imp - Questions 2022-23Document5 pagesTS - SR - Physics - Imp - Questions 2022-23Kota ๖ۣۜRαkͥesͣhͫ0% (1)
- CVT 2marks - 21Document23 pagesCVT 2marks - 21Pasupuleti Venkata RamanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsDocument17 pagesProposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsAbhiram muddanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Maths Important Questions PDFDocument5 pages11 Maths Important Questions PDFJEGANATHAN KPas encore d'évaluation
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IID'EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- 1ST Year Physics Guess PaperDocument8 pages1ST Year Physics Guess Papermubashar khokharPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Class 11 Important QuestionDocument2 pagesPhysics Class 11 Important QuestionBanna Mohit Singh TanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Inter 2nd Year BotanyDocument9 pagesInter 2nd Year BotanyRsp Srinivas100% (2)
- 1st Year Physics ImportantDocument8 pages1st Year Physics ImportantMuhammad AdreesPas encore d'évaluation
- 16Document4 pages16Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar WORK SHEET 2021-2022Document12 pagesM.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar WORK SHEET 2021-2022Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- ElementDocument1 pageElementShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank Class Xii ChemistryDocument75 pagesQuestion Bank Class Xii ChemistryArvindNarayanPas encore d'évaluation
- P - Block Reasoning 16, 17, 18 Very Simplified - (1) FDocument9 pagesP - Block Reasoning 16, 17, 18 Very Simplified - (1) FShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Dps Indian School Uae: - Million 100 ThousandDocument5 pagesDps Indian School Uae: - Million 100 ThousandShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Board Class XII Worksheet KineticsDocument3 pagesBoard Class XII Worksheet KineticsShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Group-18 ElementsDocument19 pagesGroup-18 ElementsShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Check List of Group 18Document2 pagesCheck List of Group 18Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 17Document36 pagesGroup 17Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 17Document36 pagesGroup 17Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Crystal LatticeDocument9 pagesCrystal LatticeShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- P Block 18th Group PDFDocument4 pagesP Block 18th Group PDFShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Board-D and FDocument4 pagesBoard-D and FShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument2 pagesChemistry in Everyday LifeShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- EXERCISESDocument1 pageEXERCISESShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Define The Following TermsDocument8 pagesDefine The Following TermsShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Bonding - NewDocument2 pagesBonding - NewShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Numericals 1Document7 pagesNumericals 1Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Basic - NewDocument2 pagesSome Basic - NewShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- P Block Elements Notes For Entrance ExaminationDocument13 pagesP Block Elements Notes For Entrance ExaminationSrijan ChakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet Ch1Document36 pagesWorksheet Ch1Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Basic - NewDocument2 pagesSome Basic - NewShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 Science Handwritten Notes Chapter 4 PDFDocument32 pagesClass 10 Science Handwritten Notes Chapter 4 PDFShazia Farheen56% (16)
- M.E.S. Indian School, Doha - QatarDocument1 pageM.E.S. Indian School, Doha - QatarShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- BondingDocument52 pagesBondingArian CoenPas encore d'évaluation
- 11Document6 pages11Shazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryRavi Kumar50% (4)
- Covalent Bonding QDocument14 pagesCovalent Bonding QShazia FarheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Step FlowDocument11 pagesReverse Step FlowRupesh BhusalPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Design - 2Document31 pagesAC Design - 2Linh GiaPas encore d'évaluation
- KeplarDocument10 pagesKeplarprashant94Pas encore d'évaluation
- HW 5Document8 pagesHW 5Anonymous AjrDxGPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidation Test - 023Document11 pagesConsolidation Test - 023nepster620533% (3)
- Cheng2021 Article TheTheoreticalPerformanceAnaly1Document16 pagesCheng2021 Article TheTheoreticalPerformanceAnaly1Rishikesh MorePas encore d'évaluation
- 1-D, WB-2Document1 page1-D, WB-2Monal KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment: Assignment On Center of Gravity and CentroidDocument3 pagesAssignment: Assignment On Center of Gravity and CentroidSolomon MehariPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Material Science & Engineering: Processing Structure Properties PerformanceDocument40 pagesIntroduction of Material Science & Engineering: Processing Structure Properties PerformanceGladi RosinPas encore d'évaluation
- MycvDocument3 pagesMycvapi-400068002Pas encore d'évaluation
- L2C1 MEC420 1D Kinematics of Particle FS2 PDFDocument30 pagesL2C1 MEC420 1D Kinematics of Particle FS2 PDFMuhammad Danial Hakim Bin JohariPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Design of A Semi-Submersible Platform With Water-Entrapment Plates Based On A Time-Domain Hydrodynamic Algorithm Coupled With Finite-ElementsDocument8 pagesStructural Design of A Semi-Submersible Platform With Water-Entrapment Plates Based On A Time-Domain Hydrodynamic Algorithm Coupled With Finite-Elementssaeed-21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert ch7 Physics Class 11Document42 pagesNcert ch7 Physics Class 11Karan ManglaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4) Statement of Purpose/introduction/objectiveDocument4 pages4) Statement of Purpose/introduction/objectiveMuhd AdamPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet Week 5Document4 pagesWorksheet Week 5Jaybie TejadaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Engin 1Document444 pages(Engin 1Esmael AdemPas encore d'évaluation
- A Level PhysicsDocument157 pagesA Level Physicsvinod_kumarranPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Science Week 4Document4 pagesPhysical Science Week 4Alona Cello ParagesPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Duct CalculatorDocument1 pageAir Duct CalculatorEngFaisal AlraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Hydraulic &water Resource Engineering: Open Channel Hydraulics Chapter 1,2 and 3 Work SheetDocument5 pagesDepartment of Hydraulic &water Resource Engineering: Open Channel Hydraulics Chapter 1,2 and 3 Work SheetLemi100% (3)
- Other Canal Structures: Regulation WorksDocument56 pagesOther Canal Structures: Regulation WorkskkodgePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-Flow RatesDocument8 pagesChapter 1-Flow RatesJeisther Timothy GalanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Yield Line TheoryDocument7 pagesYield Line TheoryasdPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.0 Thermal PhysicsDocument38 pages4.0 Thermal Physicsmuhd hafizzudinPas encore d'évaluation
- M. Tech Engineering DesignDocument24 pagesM. Tech Engineering DesignKKPas encore d'évaluation
- Assiment PDFDocument4 pagesAssiment PDFRedaEbidPas encore d'évaluation
- Prijslijst Eletta MarcolinDocument4 pagesPrijslijst Eletta MarcolinTenakhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Deber Capitulo 2Document1 pageDeber Capitulo 2carloss antonio acosta lopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Octahedral Stress TheoryDocument18 pagesOctahedral Stress TheoryAsad Khan100% (1)
- CE199 2L 1Q1819 HGE 1st Take PDFDocument8 pagesCE199 2L 1Q1819 HGE 1st Take PDFCristal Haze VictoriaPas encore d'évaluation