Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SCOM - Whats New in OprMgr 2007
Transféré par
Samee ChouguleDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SCOM - Whats New in OprMgr 2007
Transféré par
Samee ChouguleDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Active Directory Integration
Operations Manager 2007 allows you to leverage your investment in AD by enabling you to create AD based rules to assign computers to Management Group, helping to reduce the cost of agent configuration. This is also helpful if your organization uses images to deploy computers. Just add the Operations Management 2007 agent to the SQL Server 2005 image and configure the agent to get its Management Group information from AD. When you bring up a new SQL Server 2005, it's automatically configured to be managed by the specified Management Group. Note: Managed computers do not have to be in an AD domain to be managed by Operations Manager 2007. Operations Manager 2007 uses Active Directory to manage authentication and authorization. AD groups and users can be assigned Operations Manager 2007 roles, leveraging your investment in AD and further helping to reduce the cost of deploying and using Operations Manager 2007.
o o
Manage SNMP Enabled Devices and Non-Windows-Based Computers
With Operations Manager 2007 you can manage SNMP-enabled devices, such as routers, print servers, and non-Windows-based computers, in addition to Windows-based computers. Operations Manager 2007 can obtain a core set of data from SNMP-enabled devices and non-Windows-based computers. A Management Pack for an object type, such as Cisco routers or Linux servers, enables extended management of them by Operations Manager 2007. The Management Pack can be provided by the object's manufacturer, a third party, or developed within your organization.
Service Oriented Monitoring
Operations Manager 2007 shifts the paradigm from managing individual computers to defining and managing the distributed applications you provide, such as email. This enables you to more effectively and efficiently identify, understand, and resolve issues related these applications. Many objects that you can monitor, such as Windows services, are similar to each other. Operations Manager 2007 provides the Distributed Application Designer and templates for similar objects; much like Microsoft Word provides templates for common document types. This makes it easier for you to accurately and quickly define, and subsequently monitor, the distributed applications you are responsible for, such as a web-based application. Synthetic Transactions allow you to emulate your customers' experience with a service, enabling you to better understand their perception of the services you provide them.
Baseline Monitor Feature
The Operations Manager Baseline Monitor feature enables you to monitor the activity of a computer's counter, such as processor utilization. Baseline monitors help to ensure that alerts are raised when there is an issue, while preventing randomized floods of false alerts. Baseline monitors eliminate the need to manually set thresholds for alerts. Baseline monitors also more accurately reflects an organization's use of the IT infrastructure by taking into account normal variations in usage. Operations Manager 2007 creates and continually updates a baseline that represents normal activity for the counter. Operations Manager 2007 uses that baseline to automatically set and adjust thresholds for alerts, taking into account patterns; for example, a spike in processor utilization that might occur when a large number of users log on.
Agentless Exception Monitoring Feature
Operations Manager 2007 Agentless Exception Monitoring (AEM) enables you to monitor operating systems and applications for errors. You can take advantage of the linked knowledge data, as available, to help resolve the issue. AEM configures error reporting clients to redirect error reports to an Operations Manager 2007 Management Server, instead of being reported directly to Microsoft. By staging error reports on a Management Server, AEM is able to leverage Operations Manager 2007 Reporting to generate rich reports that aggregate error data across your organization, providing you insights into the common failures and available solutions. Note: The Windows Error Reporting (WER) client is a feature of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. For Windows 2000, the error reporting client is included in Microsoft programs, such as Office XP and Office 2003 applications, Visio 2002, and Visual Studio .NET. You can determine the frequency an operating system or application experiences an error and the number of affected computers and users. This enables you to target your efforts where they will have the greatest benefit to the organization. When the error reports are anonymously synchronized with Microsoft, per the Microsoft Data Collection Policy, available solutions for the respective errors are provided. You can also use AEM to provide your solutions for issues experienced with your internally developed applications. The solutions enable you to resolve the errors the respective operating systems and applications are experiencing, helping to maintain the productivity of your organization.
Audit Collection Feature
Operations Manager 2007 Audit Collection helps you understand the security of your IT environment by efficiently collecting security events from managed computers and providing reports for analysis. Audit Collection also facilitates the separation of the Security Auditor role from other IT roles, as may be required by your organization's policies. The Audit Collection Forwarder, a component of the Operations Manager 2007 Agent, provides real-time monitoring of the security log on managed computers. The Forwarder encrypts and transmits security events to the Audit Collection Collector, a component of the Operations Manager 2007 Management Server. The Collector makes security events available to WMI subscribers in real-time and persists them in the Audit Collection database. The Security Auditor can use WMI queries to implement custom real-time security analysis and solutions. They can use the Audit Collection reports and SQL queries to perform a historical security analysis of your organization's IT environment, such as account management and privileges, and make recommendations to improve it.
Management Pack Enhancements
Management Packs for Operations Manager 2007 focus on discovering and monitoring applications, components and devices. These are collectively referred to as objects. Once objects are discovered, each is monitored according to the health model defined in the management pack. The Operations Manager 2007 Console displays the discovery and health information for the discovered objects. Once an object is discovered it can be used to define a distributed application, such as messaging, using the Distributed Application Designer. Monitoring the health of an application or device can include monitoring for significant events from a particular source, such as the Windows Event log, as well as scheduled testing of an application or device using synthetic transactions.
Management packs can contain diagnostic and recovery actions that can run automatically or on demand. Data can be collected and stored exclusively for reporting purposes, bypassing the Operations Manager database. When a significant event is detected an alert is raised for the Operations Manager operator. The alert will contain actionable knowledge, with views and tasks embedded in the text, that walk the operator through the steps to resolve the issue. Management packs can also contain common administrative tasks that can be launched from the Operations Manager 2007 console. To help the operator take in relevant information, data collected by the management pack is presented using views and reports that are part of the management pack. Views types include: alert, dashboard, diagram, event, performance and URL. Dashboard views are used to provide a summary of the health of a particular application or device. Operations Manager 2007 introduces the concept of sealed management packs. Management packs from Microsoft and other vendors are sealed, versioned and signed with a certificate. Once a management pack is imported you can customize it, saving the changes separately. When you import a new version of the management pack, the original management pack is replaced, but your customizations are retained. Operations Manager 2007 also includes the ability to delete a management pack. Deleting a management pack will remove all management pack objects and discovered data from the database.
Reporting Enhancements
o o o o o
The Reporting feature of Operations Manager 2007 is newly engineered for this release and focuses on customer scenarios, performance, and usability. Data does not have to go through the Operations Manager 2007 database to the Reporting database. Data can be sent directly to either the Operations Manager 2007 or Reporting databases, or both. Reporting data is available in virtually no latency. Reports are displayed in the Operations Manager 2007 Console, not a separate one. Data is pre-aggregated, summarized, and indexed. Even reports for long time periods display quickly.
Console Enhancements
o o o o o o
Administration, Reporting, and Authoring are unified in a single console, with views based on roles, making your Operations Manager 2007 team more efficient. Personalize the Operations Console with My Workspace; quickly get to the information that matters most to you. Overview pages provide easy to understand summaries, and the integrated search makes it easy to delve into the details. You can create Dashboard views that contain multiple view types, such as performance and state, helping to make you more efficient at managing your environment. Knowledge data can be used in more helpful ways, such as launching inline linked tasks, making it easier and faster to investigate and resolve alerts. Tight integration between alerts and other views, enabling you to switch from an alert to a corresponding event or performance view, for example.
o o
Performance views are easier to use, helping you perform your work more effectively. Highly extensible with PowerShell scripting, helping to ensure that it meets your organization's needs.
Task Functionality
Operations Manager 2007 provides consistent and real-time task status regardless of the target, helping you efficiently run and monitor tasks. There is also greater granularity of control over who can run which task and on what objects, and anyone can run a runtime task. Operations Manager 2007 also provides a Run As option that enables you to launch a task with the necessary permissions without going through the laborious process of logging out and logging back into the system.
Command Shell Feature
Based on the Windows PowerShell technology, this command-line environment provides administrators with a set of composable and extensible commands for automating Operations Manager 2007 administration without using the Operations Manager Console user interface. Within the shell, you can use the get-momcommand to get a list of Operations Manager 2007 cmdlets and the get-Help cmdlet to display help for each Operations Manager 2007 cmdlet.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Microsoft Cluster Server BasicsDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Cluster Server BasicsSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- Wins Tech - FaqDocument34 pagesWins Tech - FaqSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- Remote Access TECH - FAQDocument90 pagesRemote Access TECH - FAQSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- Server Cluster Best PracticesDocument6 pagesServer Cluster Best PracticesSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- How DNS Query WorksDocument13 pagesHow DNS Query WorksSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- Ipsec Tech - FaqDocument52 pagesIpsec Tech - FaqSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- DHCP Tech - FaqDocument59 pagesDHCP Tech - FaqSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- File and Folder Per MissionsDocument8 pagesFile and Folder Per MissionsSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- Iis Tech - FaqDocument133 pagesIis Tech - FaqSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- DNS Tech - FaqDocument97 pagesDNS Tech - FaqSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- Failover Cluster StepDocument22 pagesFailover Cluster StepSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- IT Service ManagementDocument3 pagesIT Service ManagementSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- SQL BasicsDocument68 pagesSQL BasicsSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- SQL Basics PDFDocument28 pagesSQL Basics PDFArjun SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- SCOM - The Cumulative Update 5Document19 pagesSCOM - The Cumulative Update 5Samee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- SQL BasicsDocument18 pagesSQL BasicsSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- SCOM - Understanding How Active Directory Integration Feature Works in OpsMgr 2007Document3 pagesSCOM - Understanding How Active Directory Integration Feature Works in OpsMgr 2007Samee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- SCOM - GATEWAY SessionDocument30 pagesSCOM - GATEWAY SessionSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- SCOM - Understanding and Modifying Data Warehouse Retention and GroomingDocument7 pagesSCOM - Understanding and Modifying Data Warehouse Retention and GroomingSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
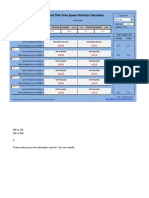
- SCOM - Logical Disk Space Monitor CalculatorDocument2 pagesSCOM - Logical Disk Space Monitor CalculatorSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- Microsoft Cluster Server BasicsDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Cluster Server BasicsSamee ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- 32.2.3.4 Wireless - PD - 4 ZXSDR B8200 Product DescriptionDocument32 pages32.2.3.4 Wireless - PD - 4 ZXSDR B8200 Product DescriptionRajesh PorwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 - Describing Logic CircuitsDocument25 pagesLecture 2 - Describing Logic CircuitsMichele OconnorPas encore d'évaluation
- Tech Note 478 - Industrial Application Server Platform Deployment ChecklistDocument7 pagesTech Note 478 - Industrial Application Server Platform Deployment ChecklistteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clientop A.vst29.01bDocument14 pagesClientop A.vst29.01baaa bbbPas encore d'évaluation
- CIC 2018 Art00035 Sungjin-KimDocument6 pagesCIC 2018 Art00035 Sungjin-KimHafid Lutfan IhwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Catalyst 2955 Series Switches: Data SheetDocument16 pagesCisco Catalyst 2955 Series Switches: Data Sheetsardarji1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Remedy Applicatin PermissionsDocument75 pagesRemedy Applicatin PermissionsVenkat SPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Notes: Topic 1: Computer OverviewDocument12 pagesIT Notes: Topic 1: Computer OverviewJayaMadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Sequence Control - LC64Document34 pagesSequence Control - LC64said_rahmansyah4750Pas encore d'évaluation
- CMSV6 Operation Manual V1.1 PDFDocument25 pagesCMSV6 Operation Manual V1.1 PDFIsmaelPas encore d'évaluation
- QMS250 IDocument2 pagesQMS250 IVenugopal Venu100% (1)
- Motorola SEMV12 SmartStream, Encryptor ModulatorDocument2 pagesMotorola SEMV12 SmartStream, Encryptor Modulatorjuanlasserre9444Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1Altaf KondakamaralaPas encore d'évaluation
- AWS Account: Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)Document3 pagesAWS Account: Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)soumendra.chandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practicedump: Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of Practice ExamDocument4 pagesPracticedump: Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of Practice ExamVetrivel SPas encore d'évaluation
- About The HART ProtocolDocument13 pagesAbout The HART ProtocolChanakya KatyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap8 HCI NotesDocument3 pagesChap8 HCI Notesrboy1993Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Information and Communication Technology and Its Applications PDFDocument821 pagesDigital Information and Communication Technology and Its Applications PDFnganapathysPas encore d'évaluation
- AWS Administration - The Definitive Guide - Sample ChapterDocument39 pagesAWS Administration - The Definitive Guide - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing100% (1)
- ProductSheet N7700 04032013Document2 pagesProductSheet N7700 04032013Jose Ramirez LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Bus Reservartion - Team 1 - Sec - B PDFDocument27 pagesOnline Bus Reservartion - Team 1 - Sec - B PDFDimo OfficialPas encore d'évaluation
- Operational Qualification TemplateDocument9 pagesOperational Qualification TemplateBhuvana RamananPas encore d'évaluation
- GNURadio Tutorials ReportDocument2 pagesGNURadio Tutorials Reportvignesh126Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7934-Bwidth-Consume Inglés PDFDocument8 pages7934-Bwidth-Consume Inglés PDFSergio OssaPas encore d'évaluation
- System Bus in Computer Architecture: Goran Wnis Hama AliDocument34 pagesSystem Bus in Computer Architecture: Goran Wnis Hama AliGoran WnisPas encore d'évaluation
- ALC650 Datasheet PDFDocument46 pagesALC650 Datasheet PDFPedro Ruiz GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer AwarenessDocument64 pagesComputer Awarenessgauravgupta_pusa365Pas encore d'évaluation
- Smex 10.2 IugDocument182 pagesSmex 10.2 Iugfirdous_soberPas encore d'évaluation
- CTEU-PN 2017-03a 8067836g1Document2 pagesCTEU-PN 2017-03a 8067836g1Mahadzir Bin Mat Rabi'Pas encore d'évaluation
- HE Mini-Pak 6 ManualDocument100 pagesHE Mini-Pak 6 ManualJavier Alejandro QuingaPas encore d'évaluation