Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Group 8
Transféré par
api-37236120 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues1 pageA condition marked by softening of the bones, with pain, tenderness, muscular weakness, anorexia and loss of weight, resulting from deficiency of vitamin D and calcium. Inflammation of the ear, which may be marked by pain, fever, abnormalities of hearing, hearing loss, tinnitus and vertigo. Infection due to a fungus in the external auditory canal, usually unilateral, with scaling, itching, and pain as the primary symptoms.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentA condition marked by softening of the bones, with pain, tenderness, muscular weakness, anorexia and loss of weight, resulting from deficiency of vitamin D and calcium. Inflammation of the ear, which may be marked by pain, fever, abnormalities of hearing, hearing loss, tinnitus and vertigo. Infection due to a fungus in the external auditory canal, usually unilateral, with scaling, itching, and pain as the primary symptoms.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues1 pageGroup 8
Transféré par
api-3723612A condition marked by softening of the bones, with pain, tenderness, muscular weakness, anorexia and loss of weight, resulting from deficiency of vitamin D and calcium. Inflammation of the ear, which may be marked by pain, fever, abnormalities of hearing, hearing loss, tinnitus and vertigo. Infection due to a fungus in the external auditory canal, usually unilateral, with scaling, itching, and pain as the primary symptoms.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
GROUP 8
Inflammation of a nerve or group of nerves, characterized by pain, loss of
neuritis reflexes, and atrophy of the affected muscles.
Any of various mental or emotional disorders, such as hypochondria or
neurasthenia, arising from no apparent organic lesion or change and
involving symptoms such as insecurity, anxiety, depression, and irrational
fears, but without psychotic symptoms such as delusions or
neurosis hallucinations. No longer in scientific use.
nocturia The excessive urination at night.
oliguria Secretion of a diminished amount of urine in relation to the fluid intake.
oophorectomy The removal of an ovary or ovaries
osteo- prefix for bone
Noninflammatory degenerative joint disease occurring chiefly in older
persons, characterised by degeneration of the articular cartilage,
hypertrophy of bone at the margins and changes in the synovial
membrane. It is accompanied by pain and stiffness, particularly after
osteoarthritis prolonged activity.
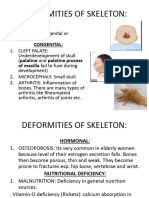
A condition marked by softening of the bones (due to impaired
mineralisation, with excess accumulation of osteoid), with pain,
tenderness, muscular weakness, anorexia and loss of weight, resulting
osteomalacia from deficiency of vitamin D and calcium.
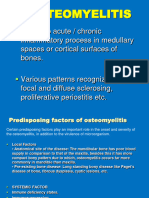
Inflammation of bone caused by a pyogenic organism. It may remain
localised or may spread through the bone to involve the marrow, cortex,
osteomyelitis cancellous tissue and periosteum.
A reduction in the amount of bone mass, leading to fractures after
osteoporosis minimal trauma.
Inflammation of the ear, which may be marked by pain, fever,
otitis abnormalities of hearing, hearing loss, tinnitus and vertigo.
An infection due to a fungus in the external auditory canal, usually
otomycosis unilateral, with scaling, itching, and pain as the primary symptoms.
A pathological condition of the bony labyrinth of the ear, in which there is
formation of spongy bone (otospongiosis), especially in front of and
posterior to the footplate of the stapes, it may cause bony ankylosis of
the stapes, resulting in conductive hearing loss. Cochlear otosclerosis
otosclerosis may also develop, resulting in sensorineural hearing loss.
ototoxicity Toxicity to the auditory nerve (cranial nerve VIII).
Not through the alimentary canal but rather by injection through some
other route, as subcutaneous, intramuscular, intraorbital, intracapsular,
parenteral intraspinal, intrasternal, intravenous, etc.
pathogenesis The origin and development of disease
-penia Deficiency.
Performed through the skin, as injection of radiopacque material in
radiological examination or the removal of tissue for biopsy accomplished
percutaneous by a needle.
pericarditis Inflammation of the pericardium
Inflammation of the tissues surrounding a bladder, especially the urinary
pericystitis bladder.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Osteomyelitis of The JawsDocument70 pagesOsteomyelitis of The JawsMONIKAPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomyelitisofjaw 131117034448 Phpapp02Document35 pagesOsteomyelitisofjaw 131117034448 Phpapp02D YasIr MussaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of BonesDocument94 pagesDiseases of BonesAngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomyelitis 130708212636 Phpapp01Document107 pagesOsteomyelitis 130708212636 Phpapp01merikasorPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Lecture 5Document10 pagesSpecial Lecture 5HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteomyelitisofjawDocument35 pagesOsteomyelitisofjawOded KantzukerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pemicu 4 "Mengapa Telingaku Tak Dapat Mendengar?": Adrian - 405100018 - Blok PenginderaanDocument71 pagesPemicu 4 "Mengapa Telingaku Tak Dapat Mendengar?": Adrian - 405100018 - Blok PenginderaanRilianda SimbolonPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Bone II-2Document59 pagesDisorders of Bone II-2Guhan DergPas encore d'évaluation
- OSTEOARTHRITISDocument36 pagesOSTEOARTHRITISHzm Mus83% (12)
- Screenshot 2022-11-12 at 7.36.53 AMDocument62 pagesScreenshot 2022-11-12 at 7.36.53 AMeman.ta3labPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammatory Lesions of The JAW: Bhavika Pol Vhatkar 1 Yr PGDocument132 pagesInflammatory Lesions of The JAW: Bhavika Pol Vhatkar 1 Yr PGArpita SankhwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 4 (Bone Pathology)Document206 pagesSheet 4 (Bone Pathology)ardesh abdillePas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Curs Osteomielita Engl BunDocument41 pages4 Curs Osteomielita Engl BunCatalin PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- OSTEOMYELITISDocument5 pagesOSTEOMYELITISArafat Masud Niloy100% (1)
- 5 Inflammation of Bone NewDocument15 pages5 Inflammation of Bone Newnightfury200313Pas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomyelitis of Jaws: Presented By: Anuradha B.D.S Final YearDocument11 pagesOsteomyelitis of Jaws: Presented By: Anuradha B.D.S Final YearGujjar VishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammatory Diseases of BoneDocument20 pagesInflammatory Diseases of BonesiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomyelitis: ClassificationDocument5 pagesOsteomyelitis: Classificationthanuja mathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomyelitis Metabolic Bone DisordersDocument36 pagesOsteomyelitis Metabolic Bone DisordersVishesh JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammatory Disorder of BoneDocument13 pagesInflammatory Disorder of Bonedentist07801644159Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 OsteomyelitisDocument29 pages6 OsteomyelitisMohammed AshrefPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomyelitis: Oral Pathology 4 Stage DR - Hemn M.Sharif (B.D.S, MSC, O.Medicine) 2-4-2020Document18 pagesOsteomyelitis: Oral Pathology 4 Stage DR - Hemn M.Sharif (B.D.S, MSC, O.Medicine) 2-4-2020محمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلPas encore d'évaluation
- Bones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasDocument34 pagesBones and Joints: Bone Is A Specialised Connective Tissue Which HasvaishnaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology of Bone and Soft Tissue-LectureDocument52 pagesPathology of Bone and Soft Tissue-Lecturejohnwickshopping79Pas encore d'évaluation
- Due To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryDocument6 pagesDue To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryBashar EbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteomyelitisDocument17 pagesOsteomyelitisBindu BinduPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of BonesDocument3 pagesDisorders of BonesAnonymous 0pSLjJYPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiologic PathologyDocument11 pagesRadiologic PathologyElaiza IcazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Remota 170426124830Document34 pagesRemota 170426124830Lolo TotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 10 NCM 112 - (Osteonecrosis)Document8 pagesGroup 10 NCM 112 - (Osteonecrosis)Jezreel BonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0006.Document14 pagesWa0006.mldmddhPas encore d'évaluation
- Infection of The JawDocument51 pagesInfection of The JawMutia Safitri0% (1)
- Patho (Osteomyelitis)Document2 pagesPatho (Osteomyelitis)sidavePas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic OsteomylitisqDocument5 pagesChronic Osteomylitisqdrahmed1028Pas encore d'évaluation
- Meniere's Disease & OtosclerosisDocument44 pagesMeniere's Disease & OtosclerosisNadzirah Ahmad JailaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Compare Pyogenic and Tuberculous OsteomyelitisDocument3 pagesCompare Pyogenic and Tuberculous OsteomyelitisMOHAMED AMINPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Muskulo SkletalDocument68 pagesPathology Muskulo SkletalwilliamPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteomyelitisDocument32 pagesOsteomyelitisyogeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Deformities of SkeletonDocument11 pagesDeformities of SkeletonHasnain AsifPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomyelitis of The JawsDocument73 pagesOsteomyelitis of The JawsArshu Shaik812Pas encore d'évaluation
- OsteomyelitisDocument147 pagesOsteomyelitisAnkit Agur100% (1)
- Osteonecrosis: Avascular NecrosisDocument8 pagesOsteonecrosis: Avascular NecrosisJezreel BonaPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteoarthritisDocument39 pagesOsteoarthritisRohit RajeevPas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal Infection: Nor Aida, Jessica, Nivasini, Sarah, SyarifahDocument87 pagesMusculoskeletal Infection: Nor Aida, Jessica, Nivasini, Sarah, SyarifahShalltear BloodfallenPas encore d'évaluation
- Otosclerosis Content PDFDocument12 pagesOtosclerosis Content PDFAhmed MorsyPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthopaedic and PaediatricDocument25 pagesOrthopaedic and PaediatricHari Prasad KPas encore d'évaluation
- Pemicu 4 Eko Blok PenginderaanDocument59 pagesPemicu 4 Eko Blok PenginderaanEko SiswantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fraktur Patologis EngDocument11 pagesFraktur Patologis EngAisya IndiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Paget's DiseaseDocument13 pagesPaget's DiseasePooja PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteomyelitisDocument41 pagesOsteomyelitisArumpaavai PugazhiniPas encore d'évaluation
- K32 - Pathology of Bone (Dr. Dody)Document60 pagesK32 - Pathology of Bone (Dr. Dody)faris100% (1)
- OsteomylitisDocument28 pagesOsteomylitisHiba V.APas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of Bone: Brig Shahid Jamal MBBS, Fcps (Pak), Frcpath (Uk) Professor of Histopathology Am College RawalpindiDocument27 pagesDiseases of Bone: Brig Shahid Jamal MBBS, Fcps (Pak), Frcpath (Uk) Professor of Histopathology Am College RawalpindiMuhammad IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- 34 OsteomyelitisDocument3 pages34 OsteomyelitisDurga VoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lo MSK 5-1Document8 pagesLo MSK 5-1FirmanHidayatPas encore d'évaluation
- Staphyllococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli (Chronic Osteomyelitis)Document4 pagesStaphyllococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli (Chronic Osteomyelitis)wasak123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 14. COURSE TASK - Classification of OsteomyelitisDocument3 pagesWeek 14. COURSE TASK - Classification of OsteomyelitisSOPHIA PILLENAPas encore d'évaluation
- Oesteomyelitis: By: Llana, Arnold Jay Jumarang, Kim Enrico MDocument5 pagesOesteomyelitis: By: Llana, Arnold Jay Jumarang, Kim Enrico MKim Enrico JumarangPas encore d'évaluation
- Spring 2008 Assessment 2Document6 pagesSpring 2008 Assessment 2api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group Assing 7Document3 pagesGroup Assing 7api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assing 6Document5 pagesAssing 6api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Excier 2Document4 pagesExcier 2api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 2 ADocument6 pagesExam 2 Aapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group ExerciseDocument3 pagesGroup Exerciseapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- SummmmmmaryDocument8 pagesSummmmmmaryapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Econ Final NotesDocument13 pagesEcon Final Notesapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam 2000 For ReviewDocument7 pagesFinal Exam 2000 For Reviewapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Sources of Economic DataDocument45 pages11 Sources of Economic Dataapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assing 4Document3 pagesAssing 4api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Stats ReviewDocument51 pages12 Stats Reviewapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- AssingDocument4 pagesAssingapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Compounding & DiscountingDocument19 pages9 Compounding & Discountingapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Decision Analysis Part 2Document18 pages4 Decision Analysis Part 2api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Net Present ValueDocument13 pages10 Net Present Valueapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Costs and PerspectivesDocument28 pages8 Costs and Perspectivesapi-37236120% (1)
- 8 Clinical TrialsDocument24 pages8 Clinical Trialsapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Cost Utility AnalysisDocument29 pages2 Cost Utility Analysisapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Community and Managed CareDocument28 pages9 Community and Managed Careapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Pharmacoeconomic GuidelinesDocument21 pages6 Pharmacoeconomic Guidelinesapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Decision Analysis Part 1Document26 pages3 Decision Analysis Part 1api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Sensitivity Analysis and HRQOLDocument39 pages5 Sensitivity Analysis and HRQOLapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3.13.08 - COI Cost MinimizationDocument16 pages3.13.08 - COI Cost Minimizationapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- MC II Test 1Document9 pagesMC II Test 1api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2003 Exam 3Document9 pages2003 Exam 3api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam 2000 For ReviewDocument7 pagesFinal Exam 2000 For Reviewapi-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Cost Effective AnalysisDocument32 pages1 Cost Effective Analysisapi-3723612100% (1)
- 2006 Exam 1Document8 pages2006 Exam 1api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2006 Exam 2.5Document5 pages2006 Exam 2.5api-3723612Pas encore d'évaluation
- AsdasDocument7 pagesAsdasDwi Nugroho JuandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce HAPDocument8 pagesCe HAPSajid IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteoporosis GuidelinesDocument10 pagesOsteoporosis GuidelinesMia DangaPas encore d'évaluation
- Correlation of Dental Implants Surface Texture and Osseointegration  " A Review ArticleDocument5 pagesCorrelation of Dental Implants Surface Texture and Osseointegration  " A Review ArticleIJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By: Ogrimen, Jovilyn L. Pagayanan Aira Mae CDocument22 pagesPresented By: Ogrimen, Jovilyn L. Pagayanan Aira Mae CMonette Abalos MendovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Aneurysmal Bone Cyst in Fibrous Dysplasia of The Proximal FemurDocument5 pagesSecondary Aneurysmal Bone Cyst in Fibrous Dysplasia of The Proximal FemurdamdamienaPas encore d'évaluation
- DAPUSDocument8 pagesDAPUSagasatriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Osseointegration and Bone BiologyDocument29 pagesOsseointegration and Bone BiologyHarini PadmanabhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Type of Joints: Group MembersDocument21 pagesType of Joints: Group MembersBeni Ram RawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammatory Jaw LesionsDocument3 pagesInflammatory Jaw LesionsDeen MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- CB Catalog 4thedition B PDFDocument192 pagesCB Catalog 4thedition B PDFDifermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis 3rd Ed. - R. Rizzoli (CMG, 2010) WWDocument127 pagesAtlas of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis 3rd Ed. - R. Rizzoli (CMG, 2010) WWBrankoSalvariPas encore d'évaluation
- EJMCM - Volume 7 - Issue 7 - Pages 1738-1743Document6 pagesEJMCM - Volume 7 - Issue 7 - Pages 1738-1743Alejandro FereñoPas encore d'évaluation
- RAP - Yaffe1994Document5 pagesRAP - Yaffe1994Srishti SyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteochondroma of The Mandibular Condyle: About A CaseDocument3 pagesOsteochondroma of The Mandibular Condyle: About A CaseasclepiuspdfsPas encore d'évaluation
- AO Classification of FractureDocument15 pagesAO Classification of FractureNanda Perdana100% (1)
- Implant SurfaceDocument6 pagesImplant SurfaceAshaAgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition AssignmentDocument11 pagesNutrition AssignmentAngela MorPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- Epiphysis - WikipediaDocument3 pagesEpiphysis - WikipediaABHINABA GUPTAPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effectiveness of Red Ginger Compress Therapy (Zingiber Officinale Rosc. Var. Rubrum) On Elders With Joint PainDocument7 pagesThe Effectiveness of Red Ginger Compress Therapy (Zingiber Officinale Rosc. Var. Rubrum) On Elders With Joint PainlunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Etiology and PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesEtiology and PathophysiologyRomneck RoveroPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Terminology TermsDocument28 pagesMedical Terminology TermsNikka Moreen DagdagPas encore d'évaluation
- Science of Bone CementDocument12 pagesScience of Bone CementajinkyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Myofascial Release/ Therapeutic Massage TechniquesDocument21 pagesMyofascial Release/ Therapeutic Massage TechniquesadeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Advancing Dental Implant Surface Technology - From Micron To NanotopographyDocument14 pagesAdvancing Dental Implant Surface Technology - From Micron To NanotopographyVictor NederiţăPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Endodontics and Operative Dentistry PDFDocument246 pagesReview of Endodontics and Operative Dentistry PDFMuaiyed Buzayan Akremy100% (2)
- Intraosseous GanglionDocument10 pagesIntraosseous GanglionNasir MuzaffarPas encore d'évaluation
- Stretching Exercises For Seniors Over 60Document134 pagesStretching Exercises For Seniors Over 60Sal OtPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 05 Skeletal SystemDocument78 pagesChapter 05 Skeletal SystemLiam MaghanoyPas encore d'évaluation