Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
About Public Issues
Transféré par
Avula Pratap KumarDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
About Public Issues
Transféré par
Avula Pratap KumarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
About Public Issues
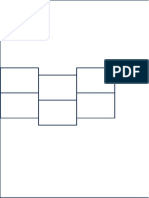
Corporates may raise capital in the primary market by way of an initial public offer, rights issue or private placement. An Initial Public Offer (IPO) is the selling of securities to the public in the primary market. This Initial Public Offering can be made through the fixed price method, book building method or a combination of both. There are two types of Public Issues: ISSUE TYPE
Fixed Price Issues
OFFER PRICE
Price at which the securities are offered and would be allotted is made known in advance to the investors
DEMAND PAYMENT RESERVATIONS
Demand for the securities offered is known only after the closure of the issue 100 % advance payment is required to be made by the investors at the time of application. 50 % of the shares offered are reserved for applications below Rs. 1 lakh and the balance for higher amount applications.
Book BuildingIssues A 20 % price band is offered by the issuer within which investors are allowed to bid and the final price is determined by the issuer only after closure of the bidding.
Demand for the securities offered , and at various prices, is available on a real time basis on the BSE website during the bidding period..
10 % advance payment is required to be made by the QIBs along with the application, while other categories of investors have to pay 100 % advance along with the application.
50 % of shares offered are reserved for QIBS, 35 % for small investors and the balance for all other investors.
More About Book Building Book Building is essentially a process used by companies raising capital through Public Offerings-both Initial Public Offers (IPOs) or Follow-on Public Offers ( FPOs) to aid price and demand discovery. It is a mechanism where, during the period for which the book for the offer is open, the bids are collected from investors at various prices, which are within the price band specified by the issuer. The process is directed towards both the institutional as well as the retail investors. The issue price is determined after the bid closure based on the demand generated in the process. The Process: The Issuer who is planning an offer nominates lead merchant banker(s) as 'book runners'. The Issuer specifies the number of securities to be issued and the price band for the bids. The Issuer also appoints syndicate members with whom orders are to be placed by the investors. The syndicate members input the orders into an 'electronic book'. This process is called 'bidding' and is similar to open auction. The book normally remains open for a period of 5 days. Bids have to be entered within the specified price band. Bids can be revised by the bidders before the book closes. On the close of the book building period, the book runners evaluate the bids on the basis of the demand at various price levels.
The book runners and the Issuer decide the final price at which the securities shall be issued. Generally, the number of shares are fixed, the issue size gets frozen based on the final price per share. Allocation of securities is made to the successful bidders. The rest get refund orders.
Guidelines for Book Building
Rules governing Book building are covered in Chapter XI of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Disclosure and Investor Protection) Guidelines 2000. BSE's Book Building System BSE offers a book building platform through the Book Building software that runs on the BSE Private network. This system is one of the largest electronic book building networks in the world, spanning over 350 Indian cities through over 7000 Trader Work Stations via leased lines, VSATs and Campus LANS. The software is operated by book-runners of the issue and by the syndicate members , for electronically placing the bids on line real-time for the entire bidding period. In order to provide transparency, the system provides visual graphs displaying price v/s quantity on the BSE website as well as all BSE terminals.
About Public Issues Corporates may raise capital in the primary market by way of an initial public offer, rights issue or private placement. An Initial Public Offer (IPO) is the selling of securities to the public in the primary market. This Initial Public Offering can be made through the fixed price method, book building method or a combination of both. There are two types of Public Issues:
ISSUE TYPE
Fixed Price Issues
OFFER PRICE
Price at which the securities are offered and would be allotted is made known in advance to the investors
DEMAND PAYMENT RESERVATIONS
Demand for the securities offered is known only after the closure of the issue 100 % advance payment is required to be made by the investors at the time of application. 50 % of the shares offered are reserved for applications below Rs. 1 lakh and the balance for higher amount applications.
Book BuildingIssues A 20 % price band is offered by the issuer within which investors are allowed to bid and the final price is determined by the issuer only after closure of the bidding.
Demand for the securities offered , and at various prices, is available on a real time basis on the BSE website during the bidding period..
10 % advance payment is required to be made by the QIBs along with the application, while other categories of investors have to pay 100 % advance along with the application.
50 % of shares offered are reserved for QIBS, 35 % for small investors and the balance for all other investors.
More About Book Building Book Building is essentially a process used by companies raising capital through Public Offeringsboth Initial Public Offers (IPOs) or Follow-on Public Offers ( FPOs) to aid price and demand discovery. It is a mechanism where, during the period for which the book for the offer is open, the bids are collected from investors at various prices, which are within the price band specified by the issuer. The process is directed towards both the institutional as well as the retail investors. The issue price is determined after the bid closure based on the demand generated in the process. The Process:
The Issuer who is planning an offer nominates lead merchant banker(s) as 'book runners'. The Issuer specifies the number of securities to be issued and the price band for the bids. The Issuer also appoints syndicate members with whom orders are to be placed by the investors. The syndicate members input the orders into an
'electronic book'. This process is called 'bidding' and is similar to open auction. The book normally remains open for a period of 5 days. Bids have to be entered within the specified price band. Bids can be revised by the bidders before the book closes. On the close of the book building period, the book runners evaluate the bids on the basis of the demand at various price levels. The book runners and the Issuer decide the final price at which the securities shall be issued. Generally, the number of shares are fixed, the issue size gets frozen based on the final price per share. Allocation of securities is made to the successful bidders. The rest get refund orders. Guidelines for Book Building
Rules governing Book building are covered in Chapter XI of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Disclosure and Investor Protection) Guidelines 2000. BSE's Book Building System
BSE offers a book building platform through the Book Building software that runs on the BSE Private network. This system is one of the largest electronic book building networks in the world, spanning over
350 Indian cities through over 7000 Trader Work Stations via leased lines, VSATs and Campus LANS. The software is operated by book-runners of the issue and by the syndicate members , for electronically placing the bids on line real-time for the entire bidding period. In order to provide transparency, the system provides visual graphs displaying price v/s quantity on the BSE website as well as all BSE terminals.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- IpoDocument3 pagesIpoVinod GudimaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Float at IonDocument2 pagesFloat at IonDivyya PritwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Bombay Stock ExchangeDocument10 pagesBombay Stock Exchangeaddy9760Pas encore d'évaluation
- About Public Issues: More About Book BuildingDocument6 pagesAbout Public Issues: More About Book BuildingBalaji RavigopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary MArketsDocument45 pagesPrimary MArketssaufin29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis On Public IssueDocument21 pagesAnalysis On Public IssueSaurabh BandekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report: Public Issue (Book Building Method)Document21 pagesProject Report: Public Issue (Book Building Method)Saurabh BandekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building Process: By: Gaurav DawarDocument7 pagesBook Building Process: By: Gaurav DawarSharang ParuthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building of Equity SharesDocument20 pagesBook Building of Equity Sharessneha_rulz157757Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building of Equity SharesDocument15 pagesBook Building of Equity Sharesbackspace11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building of Equity SharesDocument15 pagesBook Building of Equity Sharesmayank0963Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ipo & The Book Building Process: Kanika GuptaDocument10 pagesIpo & The Book Building Process: Kanika GuptaKanika GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building: By: Rafeh Jamal Hafiz Inaam Jahazeb AmirDocument16 pagesBook Building: By: Rafeh Jamal Hafiz Inaam Jahazeb AmirXaIb NazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building of Equity SharesDocument20 pagesBook Building of Equity Sharesdhiman.saurabhPas encore d'évaluation
- 1136pm11.Mr. Ravindra & Dr. B.M KanahalliDocument8 pages1136pm11.Mr. Ravindra & Dr. B.M KanahalliHimanshiPas encore d'évaluation
- An OverviewDocument34 pagesAn Overviewvanarp2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Session 6 Long Term+raising CapitalDocument35 pagesSession 6 Long Term+raising CapitalSakshi VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Book BuildingDocument2 pagesBook BuildinghmgamitPas encore d'évaluation
- Bookbuilding 1Document7 pagesBookbuilding 1Shibu AbrahamPas encore d'évaluation
- Book BuildingDocument40 pagesBook Buildingvineet ranjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital Market - Part-6 - Book Building and Buy-BackDocument7 pagesCapital Market - Part-6 - Book Building and Buy-Backenvim66Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building: Presented By: Rajni Sharma MBA, Final YearDocument23 pagesBook Building: Presented By: Rajni Sharma MBA, Final YearRixim86% (7)
- Issue Type Offer Price Demand Payment ReservationsDocument14 pagesIssue Type Offer Price Demand Payment ReservationssmileysashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipo Book BuildingDocument12 pagesIpo Book BuildingGaurav DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- Book-Building Presentation (Read-Only)Document20 pagesBook-Building Presentation (Read-Only)Sauban AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview and Executive SummaryDocument61 pagesOverview and Executive SummaryAkshay SablePas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building MechanismDocument18 pagesBook Building MechanismMohan Bedrodi100% (1)
- Concepts and Process of Book BuildingDocument4 pagesConcepts and Process of Book BuildingGopalsamy SelvaduraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Initial Public OfferDocument29 pagesInitial Public OfferAjay MadaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Book BuildingDocument19 pagesBook Buildingmonilsonaiya_91Pas encore d'évaluation
- Initial Public OfferDocument29 pagesInitial Public OfferWashim SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Book BuildingDocument3 pagesBook Buildingrupika_borntowin2Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is It Book BuildingDocument5 pagesWhat Is It Book BuildingPratik N. PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Book BuildingDocument24 pagesBook Buildingmariam_abbasi5100% (2)
- Q-What Are The Steps Taken by SEBI To Protect Investors in The Primary Market?Document4 pagesQ-What Are The Steps Taken by SEBI To Protect Investors in The Primary Market?bhargavi mishraPas encore d'évaluation
- ABC of Primary MarketDocument34 pagesABC of Primary MarketNaveen RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- FinalDocument29 pagesFinalapi-3732797Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ipo Book Bldg.Document32 pagesIpo Book Bldg.Akanksha RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Book Building?Document15 pagesWhat Is Book Building?Rishi KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipo ProcessDocument3 pagesIpo ProcessDrApurva ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Shares and DebenturesDocument45 pagesShares and DebenturesAkshit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Equity Share Public IssuesDocument9 pagesEquity Share Public IssuesmyselfmeriPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building IPODocument2 pagesBook Building IPOSarada NagPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Book BuildingDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Book BuildingMehul J VachhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Book BuildingDocument2 pagesBook Buildingpriyesh04Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book BuildingDocument3 pagesBook BuildingrvgrockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building ProcessDocument9 pagesBook Building ProcessLin Jian Hui EricPas encore d'évaluation
- Security Analysis and Portfolio Management: Presented By, Saitha MeeranDocument8 pagesSecurity Analysis and Portfolio Management: Presented By, Saitha Meeransaidha meeranPas encore d'évaluation
- About Public Issues: Issue Type Offer Price Demand Payment ReservationsDocument18 pagesAbout Public Issues: Issue Type Offer Price Demand Payment ReservationsJinesh BagadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Issue: What Is Book Building?Document9 pagesPrimary Issue: What Is Book Building?mitalptPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building ProcessDocument2 pagesBook Building ProcessSneha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Initial Public Offering (IPO)Document22 pagesInitial Public Offering (IPO)P.h. ModiPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Building Process: Presented By: GouravDocument10 pagesBook Building Process: Presented By: Gouravviv1612Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Meant by Book BuildingDocument2 pagesWhat Is Meant by Book BuildingParul PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Market: Prepared By: Rajesh KiriDocument30 pagesPrimary Market: Prepared By: Rajesh Kirinilampatel_mbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Initial Public Offering (IPO)Document12 pagesInitial Public Offering (IPO)Jinesh BagadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Philip J. Romero & Tucker Balch's What Hedge Funds Really DoD'EverandSummary of Philip J. Romero & Tucker Balch's What Hedge Funds Really DoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2D'EverandFixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principle of Law ContractDocument38 pagesPrinciple of Law ContractMuhammad ZaimmuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Order No. 227 by The People's Commissar of Defence of The USSRDocument4 pagesOrder No. 227 by The People's Commissar of Defence of The USSRsigne.soderstrom1785Pas encore d'évaluation
- Invoice 8gaus 1634323553717 PDFDocument2 pagesInvoice 8gaus 1634323553717 PDFHarsh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- FASM - 2011 Faisal Spinning Mills LimitedDocument57 pagesFASM - 2011 Faisal Spinning Mills Limitedsome_one372Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sociology Weekly ReportDocument1 pageSociology Weekly ReportRan DomPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrating Peace Education in Teacher Education: A Teaching GuideDocument282 pagesIntegrating Peace Education in Teacher Education: A Teaching GuideversmajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 (A) Water Supply EngineeringDocument2 pagesUnit 2 (A) Water Supply EngineeringAkshit GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- RA 6655. Free Public Secondary Education Act. 1988Document2 pagesRA 6655. Free Public Secondary Education Act. 1988Jemaica TumulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Katarungang PambarangayDocument58 pagesKatarungang PambarangayVinvin Esoen100% (1)
- Bpi V Cir DigestDocument3 pagesBpi V Cir DigestkathrynmaydevezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 3 - Lesson 12 - 13 - Leadership - Working in Diverse TeamsDocument36 pagesSession 3 - Lesson 12 - 13 - Leadership - Working in Diverse TeamsNam NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Case No. 34Document3 pagesCase No. 34Khristienne BernabePas encore d'évaluation
- A Decentralized, Uniswap-And Pancakeswap-Based, Algorithmic Margin Trading ProtocolDocument10 pagesA Decentralized, Uniswap-And Pancakeswap-Based, Algorithmic Margin Trading ProtocolRakesh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kitagawa2021 Article TheOriginOfTheBernoulliNumbersDocument11 pagesKitagawa2021 Article TheOriginOfTheBernoulliNumbersjeremia yusPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel Election TemplateDocument2 pagesExcel Election TemplateZaskia Mehrunisha Arizani100% (2)
- Conceptual Framework in AccountingDocument4 pagesConceptual Framework in AccountingKrizchan Deyb De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- III. Fam Code (Arts 26-39)Document49 pagesIII. Fam Code (Arts 26-39)Ellen DebutonPas encore d'évaluation
- AROGYA RAKSHAK-one PagerDocument1 pageAROGYA RAKSHAK-one PagerRaktim PujariPas encore d'évaluation
- Balochistan Assembly Rules of Procedure 5 April 2018Document137 pagesBalochistan Assembly Rules of Procedure 5 April 2018bilalmpddPas encore d'évaluation
- IICLE Employment Discrimination 2012 PDFDocument72 pagesIICLE Employment Discrimination 2012 PDFAndy Williams Jr.100% (1)
- M&A Task 1 (Issues List Template)Document2 pagesM&A Task 1 (Issues List Template)ShauryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Execution PetitionDocument2 pagesExecution PetitionBharath S Nadig50% (2)
- Us Bank Bus RRDocument10 pagesUs Bank Bus RRMadison Black100% (4)
- Reverse DCFDocument6 pagesReverse DCFErvin Khouw0% (1)
- Cambridge Primary Mathematics Games Book 4 With CD-ROM - PublicDocument19 pagesCambridge Primary Mathematics Games Book 4 With CD-ROM - PubliclilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ramavtar v. Asst. Sales TAx, AkolaDocument4 pagesRamavtar v. Asst. Sales TAx, AkolaAnkitaPas encore d'évaluation
- TaxssdakcnsaDocument164 pagesTaxssdakcnsaLouisse Marie CatipayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelagio - Fs Module Lesson 1 2Document10 pagesPelagio - Fs Module Lesson 1 2api-613019400Pas encore d'évaluation
- Complainant Vs Vs Respondent: First DivisionDocument7 pagesComplainant Vs Vs Respondent: First DivisionMaureen AntallanPas encore d'évaluation
- 27 AmendmentsDocument6 pages27 AmendmentsnamePas encore d'évaluation