Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Mould
Transféré par
Cheng YeeDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Types of Mould
Transféré par
Cheng YeeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
TYPES OF MOULD
There are two major types of molds: 1. 2. Two plate mold Three plate mold
1. Two Plate Mold
A two plate mold is the simplest type of mold. It is called a two plate mold because there is one parting plane, and the mold splits into two halves. The runner system must be located on this parting plane; thus the part can only be gated on its perimeter.
1.1 Direct Gate Method:
Figure 1 shows a simplest structure only for a single impression (parts) mould.
Figure 1: Direct Gate Method
1.2 Side Gate Method
Figure 2 shows the structure of side gate method for a multiimpression mould in general. This method is also used for a single-impression mould in special shape.
Figure 2: Side Gate Method
1.3
Side Gate with stripper plate Method
Figure 3 shows the structure of side gate method with stripper plate.
Figure 3: Side Gate with stripper plate method
2. Three Plate Mold
A three plate mold differs from a two plate in that it has two parting planes, and the mold splits into three sections every time the part is ejected. Since the mold has two parting planes, the runner system can be located on one, and the part on the other. Three plate molds are used because of their flexibility in gating location. A part can be gated virtually anywhere along its surface.
2.1 Pin Point Gate Method:
Figure 4, illustrates the structure for a single impression mould. In general, this method is taken for a multi- impression mould and for a multi-point gate.
Figure 4: Pin Point Gate Method
2.2
L type Runner Method;
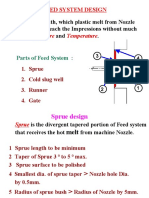
STANDRD MOULD BASE (2 PLATE MOULD):
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
TOP CLAMPING PLATE. LOCATING RING. CAVITY PLATE. CORE PLATE. SUPPORT PLATE. BOTTOM CLAMPING PLATE. 7. PARELLELS / SPACER BLOCK 8. EJECTOR RETAINER PLATE. 9. EJECTOR PLATE. 10. STOP BUTTON / STOP PIN. 11. PILLAR. 12. SPRUE BUSHING. 13. SPRUE PULLER PIN. 14. RETURN PIN / EJECTOR RETAINER PIN 15. GUIDE PIN. 16. GUIDE BUSH.
Function of Mold Base Parts
I. T0P CLAMPING PLATE: Holds the stationary part of the mold to the stationary platen of the injection machine. 2. LOCATING RING OR SPRUE RUSHING RETAINER RING: Fits into a counterbore in the top clamping plate and is used to locate the mold on the platen of the press so the nozzle and sprue bushing are aligned. 3. CAVITY PLATE: Part of the stationary section of the mold into which the leader or guide pins are mounted. Also used to hold core, cavity blocks, and sprue bushing. 4. CORE PLATE: Top plate of the movable section of the mold. Forms the parting line of the mold with cavity retainer plate. Used to hold the leader pin bushings as well as core and cavity blocks. 5. SUPPORT PLATE: Mounted behind the core retainer plate to keep this plate from bending under the high pressure used in injection molding. 6. BOTTOM CLAMPING PLATE: Holds the moving portion of the mold to the moveable platen of the injection machine. 7. PARALLELS/SPACER BLOCK: Mounted on the bottom clamping plate under the support plate to form a space which allows the ejector bar to move when the piece parts are ejected. 8. EJECTOR RETAINER PLATE (Knockout pin plate): Counterbore for the heads of ejector pins, ejector return pins, and sprue puller pin. 9. EJECTOR PLATE (Knockout bar ): Bolted together with the ejector retainer plate to form a unit. Acts as a back up plate for the pins in the ejector retainer plate.
10. STOP BUTTONS/STOP PIN: Pressed into the bottom clamping plate, they are lands for the ejector plate. 11. PILLARS: Round bars placed between the support plate and the bottom clamping plate. The same height as the parallels. Bolted to the bottom clamping plate, they are used as additional support for the core retainer plate. 12. SPRUE BUSHING: Butted up against the nozzle of the injection machine. Has a conicalshaped hole through which the material is forced into the mold runner. 13. SPRUE PULLER PIN: Pin located directly under the opening of the sprue. Used to pull the molded sprue out of the bushing after a shot has been made. 14. RETURN PINS (Ejector return pins) (Safety pins) (Push backs): Located in the ejector retainer plate. Force the ejector plate and ejector retainer plate, and therefore the ejector pins, to the bottom position as the mold closes l5. GUIDE PINS: Hardened and ground steel pins pressed into one of the plates. Align the two halves of the mold base. 16. GUIDE BUSH: Hardened and ground steel bushings which are pressed into one of the plates. Serve as bearing surfaces for the leader pins.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ejection System: Advantage DisadvantageDocument5 pagesEjection System: Advantage DisadvantageRaj ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Mould ElementsDocument72 pagesMould Elementsvinayak100% (4)
- 2.describe Mould Parts and ConstructionDocument49 pages2.describe Mould Parts and ConstructionNazri100% (4)
- Mould Starndard Parts PDFDocument13 pagesMould Starndard Parts PDFMohd Nazri SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive - Presentation - Plastics-3rd June-2015 (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)Document108 pagesAutomotive - Presentation - Plastics-3rd June-2015 (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)Annavarapu Gopalakrishna100% (1)
- Mould Design Part OneDocument15 pagesMould Design Part Oneazizmaarof100% (3)
- EJECTIONDocument11 pagesEJECTIONRatnesh Patel100% (1)
- Injection Moulding Defects: BlisterDocument10 pagesInjection Moulding Defects: BlisterAmith S KaratkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Runners and GatesDocument35 pagesRunners and Gatesbjdavies2010100% (2)
- PS Injection Mold Tool StandardsDocument107 pagesPS Injection Mold Tool StandardsНикола МедићPas encore d'évaluation
- Mold Tooling Design CatiaDocument163 pagesMold Tooling Design CatiacarlogsPas encore d'évaluation
- Feed Is The Path, Which Plastic Melt From Nozzle Traverses To Reach The Impressions Without Much Loss of andDocument26 pagesFeed Is The Path, Which Plastic Melt From Nozzle Traverses To Reach The Impressions Without Much Loss of andS Karthick KeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Press Working TerminologyDocument16 pagesPress Working TerminologyAadrika UmashankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic of Mould DesignDocument79 pagesBasic of Mould DesignKamal Krishna Kashyap100% (4)
- New Injection Molding Machine SY200 I PDFDocument5 pagesNew Injection Molding Machine SY200 I PDFkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On Split Cavity MouldDocument43 pagesSeminar On Split Cavity MouldasgrutuPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Moulds - ContentsDocument9 pagesTheory of Moulds - Contentsnagesh_sprao19275% (4)
- Injection Mould Design: Central Institute of Plastics Engineering and TechnologyDocument64 pagesInjection Mould Design: Central Institute of Plastics Engineering and TechnologyAnirudh100% (2)
- MoldDesign PDFDocument320 pagesMoldDesign PDFManny GambinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Molds Ug NX Mold MakingDocument24 pagesInjection Molds Ug NX Mold Makingdeekayengg100% (2)
- 9 Ejection System PDFDocument10 pages9 Ejection System PDFBa BuPas encore d'évaluation
- Snap-Fit Joints DesignDocument26 pagesSnap-Fit Joints DesignDavid García SalvatierraPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Mold DesignDocument12 pagesInjection Mold DesignbobPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection MoldingDocument25 pagesInjection MoldingHarshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Molding CavityDocument7 pagesMolding CavitySudarno BaraPas encore d'évaluation
- TM POM Moulding ManualDocument50 pagesTM POM Moulding ManualprisimparamPas encore d'évaluation
- Moulding Technology: by Balraj TanwarDocument37 pagesMoulding Technology: by Balraj TanwarVinod KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Core Cavity ExtractionDocument159 pagesCore Cavity ExtractionSaggam NarasimharajuPas encore d'évaluation
- MLD TheoryDocument96 pagesMLD TheorySheik Abdullah100% (1)
- Injection Mold Design DetailsDocument43 pagesInjection Mold Design DetailsKen100% (1)
- Mold Design Important Features Part 3Document21 pagesMold Design Important Features Part 3Jesus hernandez floresPas encore d'évaluation
- FeedDocument33 pagesFeedPrajwal PPas encore d'évaluation
- Techdesign Study: Plastic Mould Technology Duration: 30 DaysDocument14 pagesTechdesign Study: Plastic Mould Technology Duration: 30 DaysAnkit NaphadePas encore d'évaluation
- MoldDocument44 pagesMoldrohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Mold Design Basics PDFDocument154 pagesMold Design Basics PDFAyesha RubianaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mould Construction: CipetDocument64 pagesGeneral Mould Construction: CipetKamal Krishna KashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Strip LayoutDocument35 pagesStrip LayoutJay PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Plastics Part Design FundamentalsDocument48 pagesPlastics Part Design FundamentalsSrinivas TanarapuPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Guides For PlasticsDocument103 pagesDesign Guides For PlasticsLong NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of The Injection MouldDocument19 pagesDesign of The Injection MouldSiddhant Prakash GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Two Plate Three PlateDocument15 pagesTwo Plate Three PlateHarshvardhan KharatPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Mold Standards 80 Eng D 20Document21 pagesInjection Mold Standards 80 Eng D 20Deep ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- PIM 101 Ebook-1Document33 pagesPIM 101 Ebook-1agniflamePas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Injection Mould DesignDocument175 pagesAdvance Injection Mould DesignŠetkić SemirPas encore d'évaluation
- Core and Cavity ExtractionDocument129 pagesCore and Cavity ExtractionSaggam Narasimharaju100% (1)
- Mold and Die - PPTDocument110 pagesMold and Die - PPTThaloengsak Kucharoenpaisan100% (2)
- Injection Molding CycleDocument3 pagesInjection Molding CyclepavankumarsrsPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Tips Guide 2015Document12 pagesDesign Tips Guide 2015Ba BuPas encore d'évaluation
- Plastics Mould and Die DesignDocument674 pagesPlastics Mould and Die DesignRagul Velu100% (2)
- Mould ElementsDocument41 pagesMould ElementsVindy CADPas encore d'évaluation
- Mould and DieDocument57 pagesMould and DieAkashPas encore d'évaluation
- Press Work For BeginnersDocument19 pagesPress Work For Beginnersranarani2013Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tool Design - Chapter 3 (Part 3)Document48 pagesTool Design - Chapter 3 (Part 3)Fiq IFTPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Instruction Title: Set Up Procedure For Fin Press: Revision RecordDocument4 pagesWork Instruction Title: Set Up Procedure For Fin Press: Revision RecordBalachandar SathananthanPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Molding Lecture 09-04-08Document20 pagesInjection Molding Lecture 09-04-08viswaforuPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection MoldingDocument4 pagesInjection MoldingMohak PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Abd 350 - 360 - 375Document64 pagesAbd 350 - 360 - 375Jose Rodriguez CorporanPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Injection MoldDocument8 pagesClassification of Injection Moldakhil05052002Pas encore d'évaluation
- BW 339C Instructions PDFDocument15 pagesBW 339C Instructions PDFMatt VennPas encore d'évaluation
- BE3DDocument63 pagesBE3DLoja De Telemóveis AlfPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Mains Failure Be22 enDocument19 pagesAuto Mains Failure Be22 enchetouani_salimPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Scope of Dual Axis Solar Tracking SystemDocument1 pageFuture Scope of Dual Axis Solar Tracking SystemArun GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fassi F290 Grua FassiDocument94 pagesFassi F290 Grua FassiSergio Raul Baez100% (1)
- Replacing An Engine Drive BeltDocument5 pagesReplacing An Engine Drive BeltHamza NoumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Streetstar Brp215: Brp215 Led23/Nw 18W 220-240V Dw3 Mp1Document2 pagesStreetstar Brp215: Brp215 Led23/Nw 18W 220-240V Dw3 Mp1Dewi SaraswatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Maha PowerEx MH-C9000 Battery ChargerDocument6 pagesMaha PowerEx MH-C9000 Battery ChargerdeejjjaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Da Lite Parts ManualDocument288 pagesDa Lite Parts Manualadcb704Pas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Safety and RestraintDocument12 pages20 Safety and RestraintIqtidar APas encore d'évaluation
- SV-520/550 Instruction ManualDocument32 pagesSV-520/550 Instruction ManualLe DuPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Backhoe 580n Service ManualDocument20 pagesCase Backhoe 580n Service Manualjeffery100% (31)
- Eaton AT-1202 Transmission Service ManualDocument58 pagesEaton AT-1202 Transmission Service Manualbernad evendiPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Digital VLSI Design (ECE 521) (Makeup) PDFDocument2 pagesAdvanced Digital VLSI Design (ECE 521) (Makeup) PDFRahul PinnamaneniPas encore d'évaluation
- Hexapod Master Slave CommunicationDocument22 pagesHexapod Master Slave CommunicationDigvijay MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- HRB Hydrostatic Regenerative Braking System TheDocument7 pagesHRB Hydrostatic Regenerative Braking System ThexxshPas encore d'évaluation
- Prem YadavDocument9 pagesPrem YadavPrem YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- TDS Ball 2014 enDocument14 pagesTDS Ball 2014 ensteve cookPas encore d'évaluation
- SST25VF040B: 4 Mbit SPI Serial FlashDocument33 pagesSST25VF040B: 4 Mbit SPI Serial FlashDario EzequielPas encore d'évaluation
- WeBuyCars Sell Cars For Cash Free Online Vehicle ValuationsDocument1 pageWeBuyCars Sell Cars For Cash Free Online Vehicle ValuationsTimidha GovenderPas encore d'évaluation
- FICHA TÉCNICA PLANTA 500kVA 1Document4 pagesFICHA TÉCNICA PLANTA 500kVA 1Mauricio González CaycedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual TG1Document19 pagesManual TG1Jose Manuel Pereira LópezPas encore d'évaluation
- BAE PVS Cell Engl 2012 12 PDFDocument2 pagesBAE PVS Cell Engl 2012 12 PDFCARLOS ANDRES SARMIENTO CUEVASPas encore d'évaluation
- DGCK50B07947 EngbDocument3 pagesDGCK50B07947 EngbJustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Muhammad Rafi: EducationDocument3 pagesMuhammad Rafi: Educationabid445875Pas encore d'évaluation
- FBS Ii enDocument10 pagesFBS Ii enunsalPas encore d'évaluation
- Kenmore FridgeDocument80 pagesKenmore FridgelarryPas encore d'évaluation
- Automation and Controls - Nick DawkinsDocument56 pagesAutomation and Controls - Nick DawkinsRiky Fitriadi100% (1)
- Lightning and Surge Protection For Wind TurbinesDocument12 pagesLightning and Surge Protection For Wind TurbinesJFREY1504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Very Impb Prog PDFDocument284 pagesVery Impb Prog PDFVishesh ShrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation