Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Math 2000
Transféré par
rdialfinCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Math 2000
Transféré par
rdialfinDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Entrance exam to technical curriculums 05.06.
2000
Entrance exam to technical curriculums: calculation tasks (part 3):
ANSWER EACH QUESTION IN THE SEPARATE RESULT SHEET IN THE CORRECT PLACE
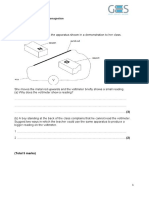
1. One corner of a triangle has a 60 angle and the length of the two adjacent sides are in ratio 1 : 3. Calculate the angles of the other triangle corners (0,1:s precision, 1 point / correct angle). 2. A pit is 0,76 meter deep and diameter is 0,66 m. A light pole with a diameter of 0,34 m is erected in the pit. After that the pit is filled with concrete. How many liters of concrete is needed to fill up the pit? (1 l precision, the pit is as cylinder) (2 p)
3. Heat exchanger raises the temperature of air before blowing it into to the factory hall. Transferred heat energy and the air temperature changes can be determined with the following equation: Q = q c p t After inserting the values we get the following equation, where the unknown value is the air temperature after the heat exchanger. Calculate the value of temperature t2. Give the answer in one decimal precision. ( 2 p ) 1000 = 0 ,05 1,16 1006 (t 2 25 )
4. Calculate the sum and the product of the equation roots. Give the answer in fractions (ex: x = 3 ). (1 + 1 p) -3x2+2x+4=0
5. Solve the equation group. Give the answer in fractions (ex: x = 3 ). (1 correct=1 p; 2 correct 1 p; all correct=2 p)
3x + y = 0 2 y + 4 z = 1 1 x + 2z = 2 6
Entrance exam to technical curriculums 05.06.2000
CALCULATE IN THE TASKS 6-10 ONLY ONE OF THE ALTERNATIVES (EITHER A OR B OR C) 6. a) An electrical device consumes 600 W of power, when connected to 220 V voltage. Calculate the power consumption of the device, when it is connected in 160 V voltage. Give the answer in 1 W precision. (2 p) b) Calculate the concentration of water and table salt, when 250 grams of table salt NaCl is in 3 litres of liquid. Table salt has a molecular mass of 58,5 g/mol. Give the answer in two decimal precision. (2 p)
7. a) An engineer earns 12 125 mk/month. The general salary rise was 3,1 % starting on 1.4.2000, but the engineers labor union was not satisfied and started a strike on 1.4.2000. During the strike the allowance was 1 800 mk/month, and a new contract was negotiated, where the engineers salary rose by 4,0 % starting 1.5.2000. This satisfied parties and the engineer came back to work on 1.5.2000. How big a percentage would he earn more (+ %) or less (%) during that year, compared with not striking and accepting the general 3,1 % salary rise? Vacation pay, other income, or taxes are not considered. Give the answer in 0,1% precision. (2 p) b) Motorcyclist (total mass 320 kg) stops from a velocity of 36 km/h in 25 s without breaking. The same motorcyclist accelerates in the same conditions from full stop to velocity of 126 km/h in 6 s. Calculate the constant forward carrying force of the engine, if the forces restricting the motion remain constant. Give the answer in 1 N precision. (2 p) c) Which of the following compounds is (write the compound to the results sheet): Na2CO3, Na2B4O7, Na2SO4, KCl, Ca(OH)2, C2H5OH, H2O, HCl, FeSO4, Fe2O3, CaCO3, HNO3 1) sodium sulphate ( p each; total 2 p) 2) ethyl alcohol 3) hydrochloric acid 4) iron oxide
8. a) Calculate the variable x value of the following equation. Give the answer in fractions. (2 p) x=5(2-x)+1 b) The car velocity is 100 km/h. Suddenly, the driver sees a elk 120 m from the car standing on the road. The drivers reaction time is 1,5 s, after which time the driver starts braking. The braking is assumed steady and the deceleration is 7,5 m/s2. The car stops in 4 s. Calculate the distance between the standing elk and the car after the car has stopped. Give the answer in 1 m precision. (2 p)
Entrance exam to technical curriculums 05.06.2000
c) The electrochemical series of metals is as follows: Li, K, Ba, Ca, Na, Mg, Al, Zn, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Sn, Pb, H, Cu, Hg, Ag, Au, Pt In this series the metals are organized in decreasing order of oxidation capacity. Conclude, with the help of the electrochemical series, which two of the following claims are correct (answer using only the letters of correct answers; 1 + 1 p). a) The more on the left the metal is in the electrochemical series, the more powerful is the tendency to give electrons. b) Copper roofing panels should be nailed with iron nails. c) Platinum gives the electrons of the outer orbit most easily. d) Silver reacts with the common acids. e) If a gold ring is dropped into a silver nitrate liquor, nothing happens to the gold ring. 9. a) The lengths of a triangle sides are 5 m, 5 m and 2 m. Calculate the area of the triangle. Give the answer in 0,1 m2 precision. (2 p) b) What is the total pressure (absolute pressure) against the porthole of a submarine, when the submarine is at a 35 m depth, and the density of the seawater is 1020 kg/m3. Air pressure is 1 bar and 1 bar = 1105 Pa. Give the result using unit bar. (2 p) c) When acid and metal oxide react the product is salt and water. Write the reaction formula, when hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium oxide. (2 p)
10. a) The heat transfer into and from a gas, in one change in the condition of state is described with following formula: Q=
V2
R n T dV V V1
After inserting the values we get a formula, where the only variable is the volume V: Q=
V2
8,314 10 294 dV V V1
Calculate the value of the heat content Q, when the values are V1=0,1 and V2=0,3. Give the answer in whole number. (2 p)
b) In a cabin sauna, 85 l of lake water at a temperature of +7C is heated in an iron pot of 29 kg. The water temperature must be +86C. The temperature of the iron pot is +12 C before the water is poured in. The water is heated by fire wood and 65 % of the thermal energy released in combustion is wasted. The heating value of the fire wood (thermal energy released in combustion of one kilogram) is 12 MJ/kg. How much fire wood is needed to heat the water? The specific heat capacity of iron is 473 J/kgC, and the specific heat capacity of water is 4190 J/kgC. Give the answer in 0,1 kg precision. (2 p)
Entrance exam to technical curriculums 05.06.2000
Equations of physics: Uniform motion: speed acceleration v=s/t a=v/t Steady variable motion: final speed final speed distance final angular speed angle of rotation v = v0 + a t v2 = v02 + 2 a s s = v0 t + a t2 = 0 + t = 0 t + t2
Equation of motion Work W = F s cos Power Pressure p = F / A
F=ma Position work W = m g h P=W/t Hydrostatic pressure p=gh
g = acceleration of free fall = 9,81 m/s2 Heat content: smelting evaporation combustion Heat capacity Q = c m t Q=sm Q=rm Q=Hm C=cm P=UI Capacitance C =
Resistance R=U/I Electrical power Q/U Electrical energy E = U I t Equation of state for ideal gas Periodic table of elements
pV=nRT
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- SAT Session 8Document58 pagesSAT Session 8Arjuna PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- S A TDocument53 pagesS A TGhaleb W. Mihyar100% (1)
- Lecture - Scalar Vector FieldsDocument4 pagesLecture - Scalar Vector FieldsMarlon BoucaudPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus Ap Calculus BC 2019Document6 pagesSyllabus Ap Calculus BC 2019api-318044188Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scoring Sat Practice Test 1 PDFDocument9 pagesScoring Sat Practice Test 1 PDFbernardPas encore d'évaluation
- 1704 PDFDocument64 pages1704 PDFDung TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfscoring Sat Practice Test 5Document9 pagesPdfscoring Sat Practice Test 5Sunil Kumar BhagatPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Test 3Document52 pagesSAT Test 3Nguyen VuPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT PresentationDocument30 pagesSAT Presentationukesh_kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- ChE102 Final Exam ReviewDocument29 pagesChE102 Final Exam ReviewalyPas encore d'évaluation
- ARCO SAT Subject Math Level 2 Practice TestDocument24 pagesARCO SAT Subject Math Level 2 Practice TestRekhaBhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Calculus Limits and ContinuityDocument2 pagesAP Calculus Limits and ContinuitySyaifudinZuhriPas encore d'évaluation
- Sat Math Practice Test 3 AnswersDocument6 pagesSat Math Practice Test 3 AnswerswwwmacyPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Math 1 NotesDocument47 pagesSAT Math 1 NotesSergioPas encore d'évaluation
- 947D368F - 4 2021 UsDocument19 pages947D368F - 4 2021 UsJaruwat somsriPas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Most Common SAT WordsDocument5 pages100 Most Common SAT WordsRiya UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Predicting Reaction NotesDocument4 pagesPredicting Reaction NotesCindy MoPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz Apcspracticemultiplechoicetest2016Document31 pagesQuiz Apcspracticemultiplechoicetest2016api-255636511100% (1)
- MENTAL MATH AND ESTIMATIONDocument8 pagesMENTAL MATH AND ESTIMATIONDanial AimanPas encore d'évaluation
- June Fresh 2014Document49 pagesJune Fresh 2014AmyLili100% (1)
- AndyPrep Summer 2021 Level TestDocument34 pagesAndyPrep Summer 2021 Level TestphilipPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry Exam: University of Houston 2009Document11 pagesGeometry Exam: University of Houston 2009สฮาบูดีน สาและPas encore d'évaluation
- Previous Year Paper: Physics - 2017Document11 pagesPrevious Year Paper: Physics - 2017jay soniPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Sat Topics ListDocument1 pageDigital Sat Topics ListVanya AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- PrepScholar Scoring Sat Practice Test 3Document9 pagesPrepScholar Scoring Sat Practice Test 3Syed Asad Asif HashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chemistry Chapter 19 Thermodynamics - Free Energy and PressureDocument2 pagesAP Chemistry Chapter 19 Thermodynamics - Free Energy and Pressurephuonglehuuyen100% (1)
- BC Practice Test 3Document7 pagesBC Practice Test 3Tim JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test CDocument64 pagesPractice Test CAneri100% (1)
- Scoring Sat Practice Test 3Document9 pagesScoring Sat Practice Test 3Aishwarya SangalPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Waterloo Physics 115 Final ExamDocument13 pagesUniversity of Waterloo Physics 115 Final ExamAashish GauravPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Analysis TechniquesDocument57 pagesData Analysis Techniquesahmed khaledPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedDocument43 pagesSection 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedgesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 Mathematical Expressions and SentencesDocument3 pagesLesson 5 Mathematical Expressions and SentencesPlacido BucyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Princeton 6 Exams PDFDocument572 pagesPrinceton 6 Exams PDFAn AnPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Test - No Calculator: 25 Minutes, 20 QuestionsDocument23 pagesMath Test - No Calculator: 25 Minutes, 20 QuestionsĐình ThịnhPas encore d'évaluation
- MATHEMATICS SUBJECT TEST LEVEL IIC LESSON 8Document23 pagesMATHEMATICS SUBJECT TEST LEVEL IIC LESSON 8Jam GeejeePas encore d'évaluation
- Document That Can HelpDocument18 pagesDocument That Can HelpVikram JohariPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Sat Prep: Shortcuts and Tricks To Save Time While Testing! Bell-WorksDocument18 pagesMath Sat Prep: Shortcuts and Tricks To Save Time While Testing! Bell-WorkskamalkantmbbsPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Math Mediums atDocument387 pages1 Math Mediums atSHAURYA JINDALPas encore d'évaluation
- Complex Numbers Multiple-ChoiceDocument4 pagesComplex Numbers Multiple-ChoiceAbhishek VirmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Manual Nov 14 2019Document56 pagesSAT Manual Nov 14 2019Cicy IrnaPas encore d'évaluation
- New SAT Math Practice No CalculatorDocument6 pagesNew SAT Math Practice No CalculatorHorizonAcademyPas encore d'évaluation
- The SQ3R Reading Method: A Step-by-Step Guide to Active ReadingDocument11 pagesThe SQ3R Reading Method: A Step-by-Step Guide to Active ReadingCristina Vajaitu100% (1)
- Sat PTDocument17 pagesSat PTAkmal AlfariziPas encore d'évaluation
- AP CalculusDocument13 pagesAP CalculusJoanna WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Prep SeriesDocument26 pagesTest Prep Seriessambath jayakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Calculus BC IntegrationDocument1 pageAP Calculus BC IntegrationteachopensourcePas encore d'évaluation
- International Students Can Register For The SAT in Any of Three WaysDocument8 pagesInternational Students Can Register For The SAT in Any of Three WaysMebin SunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Physics 1 Summer PacketDocument14 pagesAP Physics 1 Summer PacketAkhil DonapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- ACT Prep Syllabus (Fall 2019)Document7 pagesACT Prep Syllabus (Fall 2019)Fallon HowePas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test 8Document51 pagesPractice Test 8Peter LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric functionsDocument13 pagesTrigonometric functionsEdcel CincoPas encore d'évaluation
- Before the Application: How to Become the Ideal College Candidate (A Step-by-Step Guide to Making Each Year of High School Count)D'EverandBefore the Application: How to Become the Ideal College Candidate (A Step-by-Step Guide to Making Each Year of High School Count)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Boot Camp for Your Brain: A No-Nonsense Guide to the Sat Fifth EditionD'EverandBoot Camp for Your Brain: A No-Nonsense Guide to the Sat Fifth EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam IIACSDocument13 pagesExam IIACSRebecca LauPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set Thermal PhysicsDocument12 pagesProblem Set Thermal PhysicsTidal SurgesPas encore d'évaluation
- ###Questions Model PDFDocument2 pages###Questions Model PDFDave DMPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel PropertiesDocument26 pagesSteel PropertiesLutfy AzanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tracking sports training efficiency with surface EMGDocument8 pagesTracking sports training efficiency with surface EMGsdjuknicPas encore d'évaluation
- Fe in Black TeaDocument6 pagesFe in Black TeaHerni Nur AeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Design Hardware Guide for EVM CE-2Document7 pagesReference Design Hardware Guide for EVM CE-2Angie FoleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Modelling of Laterally Loaded Piles Captures Field Test ResponseDocument244 pagesNumerical Modelling of Laterally Loaded Piles Captures Field Test ResponseXiang ming GePas encore d'évaluation
- Coley A4Document49 pagesColey A4mfiarkeeaPas encore d'évaluation
- 100kw TSP Agenitor-404b Biogas 60-hz 480v En-827879Document9 pages100kw TSP Agenitor-404b Biogas 60-hz 480v En-827879Julian BarreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesYousab CreatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Mahindra Powertrain - Market StrategyDocument4 pagesMahindra Powertrain - Market StrategyEshan KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Collab#2 (Edited)Document14 pagesCollab#2 (Edited)Yani BatoctoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6 - FormworksDocument8 pagesModule 6 - FormworksAldrich Francis Ortiz Peñaflor100% (1)
- Rahim Acar - Talking About God and Talking About Creation. Avicennas and Thomas Aquinas Positions 2005 PDFDocument134 pagesRahim Acar - Talking About God and Talking About Creation. Avicennas and Thomas Aquinas Positions 2005 PDFPricopi VictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition Effects of VitaminsDocument21 pagesNutrition Effects of Vitaminsblessed cccPas encore d'évaluation
- Turkey ImportDocument14 pagesTurkey ImportMani 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- CIVL-365 Tutorial 8 SolutionDocument3 pagesCIVL-365 Tutorial 8 SolutionIvsPas encore d'évaluation
- Reconsilation of Major Materials Steel SDA Lattice Ribs Rockbolts Admixture Etc.Document99 pagesReconsilation of Major Materials Steel SDA Lattice Ribs Rockbolts Admixture Etc.Rajat SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- NQ-NQM Panelboards and Qonq Load Centers Information Manual 80043-712-06 Rev.02 06-2015 2 PiezasDocument144 pagesNQ-NQM Panelboards and Qonq Load Centers Information Manual 80043-712-06 Rev.02 06-2015 2 PiezasNadia EspinozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronized Natural Incubation by Free-Range Native ChickensDocument2 pagesSynchronized Natural Incubation by Free-Range Native ChickensFilbert John MillanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mercedes ManDocument7 pagesMercedes Manien yeyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Life Below WaterDocument10 pagesLife Below Watertrisha sobito0% (1)
- Service Manual: EQ1030T47D-820 Light Commercial TruckDocument175 pagesService Manual: EQ1030T47D-820 Light Commercial TruckYonny ColquePas encore d'évaluation
- Delay-Tolerant NetworksDocument66 pagesDelay-Tolerant NetworksMegi YantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Matrix Algebra by A.S.HadiDocument4 pagesMatrix Algebra by A.S.HadiHevantBhojaram0% (1)
- Journal of Alloys and Compounds: Wei Li, Zhijun Xu, Ruiqing Chu, Peng Fu, Guozhong ZangDocument4 pagesJournal of Alloys and Compounds: Wei Li, Zhijun Xu, Ruiqing Chu, Peng Fu, Guozhong ZangSamah SamahPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDocument45 pages2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDaondy Friarsa SoehartoPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Tattoo-June 2021Document114 pagesTotal Tattoo-June 2021Comicgek100% (2)
- F588 PDFDocument8 pagesF588 PDFOscar Gutiérrez-JuncoPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Law Theory ApproachDocument35 pagesNatural Law Theory ApproachseventhwitchPas encore d'évaluation
- Metric Heavy Hex Nuts: ASME B18.2.4.6M-2010Document16 pagesMetric Heavy Hex Nuts: ASME B18.2.4.6M-2010CarlitosPas encore d'évaluation