Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
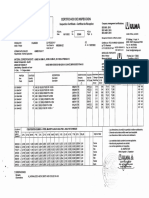
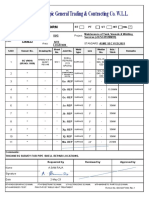
R132281
R132281
Transféré par
Sam Raja0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
7 vues2 pagesCstools asme
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentCstools asme
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
7 vues2 pagesR132281
R132281
Transféré par
Sam RajaCstools asme
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
2)
‘ASME BPE-2012
Part MM
Metallic Materials
MM-1 PURPOSE AND SCOPE
‘The purpose of this Part is to identify metallic materi-
als considered acceptable for use in hygienic service,
It identifies material specifications, grades and alloys,
‘matching filler metals, fabrication guidelines, and other
attributes necessary for this service. It also specifies the
data that must be submitted to the MM Subcommittee
for any new or unlisted alloy that is proposed for inclu-
sion into Part MM.
MM-2 ALLOY DESIGNATIONS
MM-2.1 General
This Part identifies for use those metallic materials of
construction that have demonstrated the ability to meet
welding and surface finish criteria as set forth in other
parts of this Standard. It is the responsibility of the
owner/user to ensure that any metallic materials
selected for use from those listed in Tables MM-2.1-1
through MM-2.1-3are appropriate for its intended appli-
cation. The guidelines and criteria listed in this Part of
the standard indicate a general acceptability for use and
do not address the specifics of fabrication or require-
ments of any given service.
MM-3 USES OF SPECIFICATIONS
‘MM-3.1. General
The documents listed in MM-4.2, MM..3, MM-44,
MM-45, and MM-46 may contain references to codes,
standards, or specifications not listed in this Part of this
Standard. Such unlisted codes, standards, or specifica
tions are to be used only in the context of the listed
documents in which they are referenced. Where docu-
‘ments listed in MM-4.2, MM-43, MM-4.4, MM-4.5, and
MM-46 contain design rules that are in conflict with
this Standard, the design rules of this Standard shall
govern
‘MM-3.2 Listed Specifications
Materials purchased to specifications listed in the
appropriate sections of MM-4.2, MM-4.3, MM-4.4,
MM-45, and MM-416 may be used for applications gov-
emed by this Standard. Fittings must be purchased to
the requirements of Part DT. Valves must meet the
im
requirements of SG-3.3.2.3. Materials used in applica-
tions governed by this Standard shall conform toa speci-
fication listed in the above paragraphs, except as
provided in MM-33.
(MM-3.3 Unlisted Specifications
Alloys in specifications not listed in MM-4.2, MM-43,
MM-44, MM-45, and MM-4.6 may be used for applica-
tions governed by this Standard provided they conform
toa published specification covering composition, phys-
ical and mechanical properties, method and process of
‘manufacture, heat treatment and quality control, and
otherwise meet the chemical composition requirements,
Of one of the-specifications listed in MM-L2, MM-43,
MM-4.4, MM-45, and MM-4.6. Alloys not listed in
‘Tables MM-2.1-1 through MM-21-3 may be used for
applications governed by this Standard provided the
following requirements are met
(a) the applicable requirements of MM-8 are met
(b) the specific written permission of the owner/user
is obtained
MM-3.4 Unknown Materials
Materials of unknown or
be used in hygienie service,
in or specification shall not
‘MM-3.5 Reclaimed Materials
Reclaimed pipe/tube and other piping components
‘may be used, provided they are properly identified as
conforming to a published specification listed in
MM-42, MM-4.3, MM-£4, MM-45, or MM-4.6 or to a
published specification not listed in those paragraphs
and otherwise meeting the minimum requirements of
MM<8. Sufficient cleaning and inspection shall be made
todetermine minimum wall thicknessand freedom from
imperfections that would be unacceptable in the
intended service.
MM-3.6 Designation of Alloy and Fluid Service
The user is responsible for designating the spge
alloy, rom MM-2, to be used for each system hay
product-conta face
The user is also responsible for identifying the appro.
Pilate fluid service category for piping or tubing, in
accordance with the definitions in the current edition
of ASME B31.3, Process Piping Code.
ASME BPE-2012
platinum, gold, and others, may be used for product
contact surfaces in process instrumentation.
MM-5.2 Filler Metals and Consumable inserts
Filler material shall conform to a published specifica-
tion. Table MM-5.1.2-1 lists the recommended filler met-
als for welding the listed austenitic, superaustenitic, and
duplex stainless steels and nickel alloys.
Table MM-5.1.2-2 lists the recommended materials
from which inserts may be made for use in welding the
Listed superaustenitic and duplex stainless steels.
Filler materials other than those listed in
‘Tables MM-5.1.2-1 and MM5.1.2-2 may be used with,
the prior approval of the owner/user provided that:
(a) they produce weld metal having corrosion resist:
ance equal to or greater than that of the base metal
(©) the welding procedure is qualified in accordance
with Section IX of the ASME BPVC
Proprietary filler materials may be used with the prior
agreement of the owner/user, provided all procedure
and performance qualification requirements of Part MJ
of this Standard and Section IX of the ASME BPVC
are met
MM-5.2.1 Austenitic Stainless Steels. Only the low-
carbon gracies of stainless steel filler metals may be used
to weld these alloys.
MM-5.2.2 Superaustenitic Stainless Steels. ‘The
superaustenitic stainless steels in Tables MM-2.1-1 and
MM-2.1°3 are prone to the precipitation of undesirable
secondary intermetallic phases such as sigma and chi,
Thisprecipitation typically occurs in the range of 1,000°F
(640°C) to 1,900°F (1 040°C). This is a concern during
welding and other thermomechanical processes, includ
ing solution annealing. Its, therefore, desirable to keep
exposure time within this temperature range to a
‘minimum.
Owners/users are cautioned that any service temper-
ature, heat treatment, or welding procedure that exposes
this material to these temperatures should be mini-
mized. The material manufacturer should be consulted
for specific instructions regarding heat treatment
MM-5.2.3. Consumable Inserts for Orbital Welding of
Listed Alloys. Table MM-5.1.2-2 lists the most common
alloys from which consumable inserts are machined for
use in welding specific superaustenitic and duplex stain-
less steels. Other nickel-chromium-molybdenum
inserts may be used as long as the corrosion resistance
of the final weldment meets or exceeds that of the base
metal.
MM-5.2.4 Duplex Stainless Steels. The corrosion
resistance and mechanical properties of duplex stainless
steels are based on having roughly equal amounts of
ferrite and austenite in the microstructure at room
temperature.
180
‘The listed duplex stainless steel, UNS $32205, may
bbe prone to the precipitation of undesirable secondary
{intermetallic phases such as sigma and chi. This prectpi-
tation occurs continually in the range of 1,200°F (650°C)
to 1,830°F (1 000°C). Owner/users are cautioned that
any service temperature, heat treatment, or welding pro-
cedure that exposes this material to these temperatures
should be minimized. The material manufacturer should
be consulted for specific instructions regarding heat
treatment.
‘MM-5.3 Field Bending of Tubing
Field bending of tubing is permitted for diameters up
to and including } in. (12.7 mm), Post-bending heat
treatment isnot required. Bending of tubing of any diam-
ter requires prior written permission from the owner/
user. Consult the material manufacturer for recom-
mended minimum bend radi
(MM-5.4 Heat Treatment
Heat treatment of process components madie from the
common autenitic stainless steels in Table MM-2.1-1 is
not addressed by this Standard. For other alloys and/
or fabrication processes, components may require heat
treatment. The material manufacturer should be
consulted.
MM-6 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
MM-6.1. General
‘The specific service environment for which the alloys:
in Tables MM-2.1-1 through MM-2.1-3 may be used is
‘not within the scope of this Standard. The possibility of
material deterioration in service should be considered
by the owner /user. Carbide phase degradation of cort0-
sion resistance, susceptibility to intergranular corrosion
of austenitic materials, or grain boundary attack of
nickel-based alloys are among those items requiring
attention,
MM-6.2 Tubing/Piping
All tube or Tifact surfaces,
‘leaning solution contact surfaces] and nonproduct con-
tact surfaces shall meet the mechanical property requiire-
ments of the specification to which they are
manufactured,
MN-6.3 Fittings and Welded Components
Refer to DT-2 for strength requirements for fittings
and valves.
‘MIRs for fittings are not required to list mechanical
properties; however, if they do, they must comply with
the specifications for the raw materials from which the
fittings were fabricated. It should be understood that
the mechanical properties for worked products, such as
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (843)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (822)
- Koc Vec List-May 2023Document523 pagesKoc Vec List-May 2023Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Binder 1Document3 pagesBinder 1Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- RT 170Document1 pageRT 170Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuwait Tamil ChurchDocument1 pageKuwait Tamil ChurchSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fi 0081Document1 pageFi 0081Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 X 80 Ss Bolt 316 TheDocument1 page16 X 80 Ss Bolt 316 TheSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.4 Faculty RetentionDocument1 page5.4 Faculty RetentionSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- CS FLG WNRF 4 #150 SCH40 - Po Item 2Document1 pageCS FLG WNRF 4 #150 SCH40 - Po Item 2Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- AML 23.5 GateValvesDocument582 pagesAML 23.5 GateValvesSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Binder 1Document2 pagesBinder 1Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- MTC For FlangeDocument1 pageMTC For FlangeSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 05 02Document11 pages1 05 02Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mtc-Lot2-1629-Item 5, 10 & 13Document4 pagesMtc-Lot2-1629-Item 5, 10 & 13Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jo RT Request-13Document6 pagesJo RT Request-13Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- HT 001Document1 pageHT 001Sam Raja100% (1)
- Tank Typical DrawingshDocument43 pagesTank Typical DrawingshSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mrir 036Document17 pagesMrir 036Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Asme DPT 093Document1 pageAsme DPT 093Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- C-203 6 Inch FlangeDocument1 pageC-203 6 Inch FlangeSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- DPT 229Document1 pageDPT 229Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- DWR S 036Document1 pageDWR S 036Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1995 InterpsDocument16 pages1995 InterpsSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fabrication and Welding General Requirements 103188871Document18 pagesFabrication and Welding General Requirements 103188871Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nde Request - RTDocument1 pageNde Request - RTSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- DPT 166Document1 pageDPT 166Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nde Request - Thickness SurveyDocument1 pageNde Request - Thickness SurveySam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nde Request - DPTDocument1 pageNde Request - DPTSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nde Request - HTDocument1 pageNde Request - HTSam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- HT 003Document1 pageHT 003Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- DPT 171Document1 pageDPT 171Sam RajaPas encore d'évaluation