Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
North Maharashtra University, Jalgaon: Syllabus For F.Y.B.Sc. Microbiology
Transféré par
Poonam ParedeshiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
North Maharashtra University, Jalgaon: Syllabus For F.Y.B.Sc. Microbiology
Transféré par
Poonam ParedeshiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SCIENCE FACULTY
NORTH MAHARASHTRA UNIVERSITY, JALGAON
SYLLABUS FOR F.Y.B.Sc. MICROBIOLOGY
(WITH EFFECT FROM JUNE, 2009)
SCIENCE FACULTY
North Maharashtra University, Jalgaon.
Class:- F.Y.B.Sc. Subject: Microbiology With Effect from June, 2009
The board of studies in Life Sciences in its meeting held on 15.04.2009 resolved to accept the revised syllabus for F.Y.B.Sc. (Microbiology) as per guidelines of Academic Council and with references to UGC model curriculum. The courses codes and titles for the courses are as given below. Mb: Microbiology YSC: Y- Year, S Semester, C Course No.
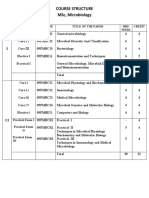
COURSE STRUCTURE
Course Code
Mb 111 Mb 112 Mb 121 Mb 122
Title of the Course
Elementary Microbiology Fundamental Methods in Microbiology Growth & Ultra Structure of Bacteria Isolation, Characterization & control of Microorganism
Semester 1 1 2 2
Lectures Ext. 40 40 40 40 40 40 40 40
Marks Int. 10 10 10 10
Mb 103
Practical Course
1&2
80
80
20
North Maharashtra University, Jalgaon
Syllabus for F.Y.B.Sc. Microbiology (With effect from June 2009) Mb 111: Elementary Microbiology Unit I- Types of Microorganism (General characteristics and Significance of Following microorganisms) A) Bacteria B) Archaebacteria C) Algae D) Fungi E) Protozoa F) Viruses G) Actinomycetes Unit II-Scope of Microbiology a) Microbes in food and Dairy industries b) c) d) e) Industrial products Genetic engineering and biotechnology Environment Agriculture (12 L) (12 L)
f) Bioterrorism Unit III-History of Microbiology a) Discovery of Microbial world b) Spontaneous generation-controversy c) The golden age of microbiology i) ii) iii) iv) Fermentation and Pasteurization The Germ theory of Disease Vaccination Chemotherapy- synthesis drugs and Antibiotics (16 L)
Mb-121: Growth and Ultra structure of Bacteria. Unit IV Growth and Reproduction of Bacteria a) b) c) d) e) f) Concept of Growth Reproduction (binary fission, Budding, Fragmentation Formation of Conidiospores and Sporagiospores) Growth rate and generation time Mathematical expression of growth Growth curve of bacterial population and its practical Applications Quantitative measurement of bacterial growth (Total Cell count, viable countbiomass determination, significance of growth measurement) (22 L) (18 L)
Unit V-Morphology and Fine Structure of Bacteria a) Morphology of Bacteria i) Size and shape ii) Arrangements Ultra structure of Bacteria Structure, function and chemical composition of the Following i) Capsule ii) Flagella iii) iv) v) vi) Pili and Fimbriae Cell Wall (Gram positive &Gram negative) Cell or cytoplasmic membrane Mesosome
b) c)
vii) Cytoplasm, Nucleoid (bacterial chromosome) and ribosomes. viii) Cytoplasmic inclusion volutine granules, PHB granules, glycogen, carbohydrates, Magnetosome, Gas vacicals, chlorosome, sulphur granules. d) Spore and Cyst i) ii) Endospore and Exospores Germination and Sporulation of endospore
References: 1. Modi, H.A. Elmentary microbiology Vol .I,Akta Prakashan,Nadiyad. 2. Modi, H.A. Elmentary microbiology Vol.II,Akta Prakashan,Nadiyad. 3. Dubey, R.C.and maheshwari,A. Text Book of Microbiology,S.Chand Publications New Delhi. 4. Tortora,Funke & Case Microbiology-An Introduction ,8 Edn, Pearson Education, Delhi. 5. Pawar and Daginawala, General Microbiology Vol.II. Himalaya Publishing House,Mumbai. 6. Stainer, R.Y.Iingraham,J.L. Wheelis M.L.PainterR.K.(1995) General microbiology, 5 Edition,MacMillan Press Ltd.London. 7. Pelczar,m.j.Chan ECS,Krieg NR(1998)5 Edition,Tata McGraw Hill Publication Co.Ltd.New DELHI. 8. Salle, S.J.(1974).Fundamental Principals of Bacteriology, Tata McGraw Hill Publication Co.Ltd.New DELHI. 9. Frobisher M.Hinsdill,Crabtree and Goodherat(1974) Fundamentals of Microbiology, 9 Edition,WB Saunders Co.USA. Mb-112: Fundamental Methods in Microbiology Unit I -: Microscopy a) Definition b) Comparison of Bright field and Dark Field Microscope c) d) e) f) Lenses of cofound microscope Image formation in compound microscope. Numerical aperture and immersion oil Resolving power (12 L)
g) Magnification h) Aberration. Unit II: Biological Staining a) Concept of stains and Dyes b) Uses of staining c) Acidic and basic dyes d) Mordents. e) Simple and differential staining (Acid Fast and Gram Staining)
4
(12 L)
Unit III: Cultivation of Microbes a) Bacteria i) ii) Nutritional requirements of bacteria. Media Common ingredients -Construction of culture medium -Types of Media iii) iv) b) i) ii) Enrichment culture method. Cultivation of Anaerobic bacteria.
(16 L)
Viruses Cultivation of animal viruses (in living animals, Embryonated eggs and cell cultures.) Cultivation of bacteriophage in laboratory.
Mb-122: Isolation, characterization and Control of Microbes Unit IV: Pure culture technique and identification of Bacteria a) b) c) d) e) Isolation by plating method ( Streak plate, pour plate Spread plate and roll tube method) Isolation in liquid media Two membered cultures Cultural characteristics on solid and in liquid media. Biochemical Characteristics. (22 L) (16 L)
Unit V: Control of Microorganisms a) b) c)
Fundamentals of Control. Mode of Action of antimicrobial agents. Physical agents High Temperature, Low temperature, Desiccation, Osmotic PRESSURE, Radiation, Ultraviolet lights,X- rays, Gamma rays,Cathod rays, surface tension and interfacial tension, filtration. Chemical agents : Characteristics of an ideal antimicrobial chemical agent, Definition of Sterilization, Disinfectant, Antiseptic, Sanitizer, Germicidal, Bactericides.
d)
Major groups of chemical antimicrobial agents with practical allocation and mode of action. 1. Phenol and phenolic compound. 2. Alcohol 3. Halogen 4. Heavy metals and their compounds 5. Dyes 6. 7. 8. 9. Detergents Quaternary ammonium compounds Aldehydes Gaseous sterilization Practical course: Basic Techniques in Microbiology 1. 2. 3. Use and care of compound Microscope. Introduction of laboratory Instruments. Water bath,Autoclave,Hot air oven,pH meter, Weighing balance Specrtophotometer, Centifuge Refrigerator. Introduction and use of common Laboratory Glass Wares: i) Test tube, culture tube, screw-capped tubes ii) iii) iv) v) Petri dish. Pipettes Pasture pipette Erlenmeyer flask
4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
vi) Numeric flask vii) Glass spreader Monochrome staining. Negative staining Gram staining Acid fast staining Hanging drop technique Preparation of culture medium-(a)nutrient broth and agar,(b)MacConkeys broth and agar Isolation of bacteria by streak plate technique Enumarition of bacteria by pour plate technique from soil sample (serial dilution) Enumerations of bacteria by serial dilution and spread plate technique from soil sample .
6
13. 14.
Study of commen colony characteristics of (a)E.coli,(b)Staph.aureus. Biochemical test for Identification of bacteria (a) Sugar,GlucoseLactose,Sucrose,Maltose (b)H2s test byT.S.I. and Lead acetate paper technique. IMViC Test. Effect of temperature on growth of bacteria. Effect of pH on growth of bacteria. Effect of heavy metal on growth of bacteria. Demonstration of permanent slides (Anabena, chlorell, mucor, yeast, penicillium, amoeba, paramecium). Growth curve of E.coli.
15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
References: 1. Dubey R.C.and Maheshwari D.K. 2004 Practical Microbilogy, S.Chand and Co. Delhi. 2. Aneja K.R.(1996) Experiments in Microbiology, 3 Edition Wishwa Prakashan,New Delhi. 3. Deshmukh A.M. (1997) 1 Edition, Handbook of Media, Stain and reagents in Microbiology pama publications. 4. Goud R.S. AND Gupta G.D.Practical microbiology, Nirali prakashan, pune.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 50 Innovative Tching Strat. in ScienceDocument19 pages50 Innovative Tching Strat. in ScienceHoneyjo NettePas encore d'évaluation
- Religion As A Meaning System IDocument24 pagesReligion As A Meaning System IVincent van der Burg - UNLP100% (2)
- Microbiology and MycologyDocument70 pagesMicrobiology and MycologyIbrahim Elkamash100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology - B.pharmDocument383 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology - B.pharmkeyurPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Molecular Biology and GeneticsDocument146 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Biology and GeneticsRedaGaafar100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology 3Document382 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology 3Dina El GarhyPas encore d'évaluation
- Inquirylearning Kath MurdochDocument5 pagesInquirylearning Kath Murdochapi-255097024Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Employee MotivationDocument79 pagesProject On Employee MotivationBharat AhujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Portfolio Cover LetterDocument3 pagesPortfolio Cover Letterapi-242347912100% (1)
- An Improved Automated Method For Identification of Bacterial Cell Morphological CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesAn Improved Automated Method For Identification of Bacterial Cell Morphological CharacteristicsVanessaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Microbiology SyllabusDocument10 pagesGeneral Microbiology SyllabusMD Tristan100% (2)
- Biosurfactants: Research and DevelopmentD'EverandBiosurfactants: Research and DevelopmentGloria Soberon-ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology Question PaperDocument8 pagesMicrobiology Question PaperpharmafreakPas encore d'évaluation
- FYBSC MicrobiologyDocument12 pagesFYBSC MicrobiologyHansa Boricha100% (1)
- Syllabus BSC Hons MicrobiologyDocument72 pagesSyllabus BSC Hons MicrobiologySANTOSH KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- B.E. (Biotechnology) Fourth Year-Seventh Semester (Syllabus) BIO701 Environmental BiotechnologyDocument5 pagesB.E. (Biotechnology) Fourth Year-Seventh Semester (Syllabus) BIO701 Environmental BiotechnologyFahad RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- WordDocument1 pageWordNaincy ChandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology First Year e ContentDocument4 pagesMicrobiology First Year e ContentAnjali JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 Syllabus 11 BiotechnologyDocument3 pages2012 Syllabus 11 BiotechnologyDeepak DhariwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbio CcssDocument21 pagesMicrobio CcssbasheerskPas encore d'évaluation
- Bp504tp Bpharm Summer 2022 MergedDocument8 pagesBp504tp Bpharm Summer 2022 MergedAbhi PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacterial Morphology & Staining TechniquesDocument6 pagesBacterial Morphology & Staining TechniquesTuli UguluPas encore d'évaluation
- Elective - Vocational Biotechnology StructureDocument10 pagesElective - Vocational Biotechnology Structure5paisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank of Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy 5th Edition Robert BaumanDocument21 pagesTest Bank of Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy 5th Edition Robert Baumandaniellediazmdgoefakyn100% (11)
- 69 Science FacultyDocument300 pages69 Science FacultyMedha KaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioprocess Technology: Course Code: BTB 701 Credit Units: 03Document5 pagesBioprocess Technology: Course Code: BTB 701 Credit Units: 03Sahil GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology and MycologyDocument76 pagesMicrobiology and MycologyAhmad Said AliPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 BiotechnologyDocument4 pages2 BiotechnologyAmit DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Structure MSC, Microbiology: Sem Component Sub Code Title of The Paper HRS/ Week CreditDocument6 pagesCourse Structure MSC, Microbiology: Sem Component Sub Code Title of The Paper HRS/ Week CreditT Anusha MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- BTT312 - Ktu QbankDocument7 pagesBTT312 - Ktu QbankAnn JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Detail Syllabus BSC (Microbiology) Sem 6Document17 pagesDetail Syllabus BSC (Microbiology) Sem 6akshaypatel535caPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of B.SC Microbiology Semester Pattern2013Document21 pagesSyllabus of B.SC Microbiology Semester Pattern2013Dnyaneshwar DahakePas encore d'évaluation
- B.SC Microbiology Semester-I - 0Document15 pagesB.SC Microbiology Semester-I - 0sreenitthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bachelor of Science in MicrobiologyDocument39 pagesBachelor of Science in MicrobiologyShravani SalunkhePas encore d'évaluation
- bbl132 0Document1 pagebbl132 0Aditya MurtiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th Semester SyllabusDocument8 pages4th Semester SyllabusMy UniversePas encore d'évaluation
- SEM 3 MLT BACTERIOLOGY PAPER 2 (QUESTION PAPER) RectifyDocument2 pagesSEM 3 MLT BACTERIOLOGY PAPER 2 (QUESTION PAPER) RectifyAditya sonawanePas encore d'évaluation
- NEP 101 Notification SECDocument78 pagesNEP 101 Notification SECmosesms252Pas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation and Characterization of MicroorganismDocument27 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Microorganismpratiwi kusumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of The Bacterial Strains Using Biolog Plates in The Contaminated Soil From Riyadh CommunityDocument24 pagesAnalysis of The Bacterial Strains Using Biolog Plates in The Contaminated Soil From Riyadh CommunityFranky zPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Biofilms: Challenges and Advances in Metabolomic StudyD'EverandMicrobial Biofilms: Challenges and Advances in Metabolomic StudySanket JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- BE262 Practical Microbiology and Genetics Lab Manual 2020 PDFDocument44 pagesBE262 Practical Microbiology and Genetics Lab Manual 2020 PDFsarath6142Pas encore d'évaluation
- F. Y. B. Sc. Wine Technology (Microbiology Syllabus)Document19 pagesF. Y. B. Sc. Wine Technology (Microbiology Syllabus)Avinash KalePas encore d'évaluation
- BP504TPDocument1 pageBP504TPKavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gurukula Kangri University: M.Sc. Microbiology Syllabus (W.e.f. Session 2008-2009)Document10 pagesGurukula Kangri University: M.Sc. Microbiology Syllabus (W.e.f. Session 2008-2009)Abhishek SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Microfluidics - Review Paper - s13068-019-1369-zDocument25 pagesMicrofluidics - Review Paper - s13068-019-1369-zEmmanuel FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Odel Uestion Aper: I D Q PDocument11 pagesOdel Uestion Aper: I D Q PAshritha SirivuriPas encore d'évaluation
- In Vitro Study of Biofilm: Growth On Biologic ProstheticsDocument4 pagesIn Vitro Study of Biofilm: Growth On Biologic Prostheticsapi-310193189Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biosafety Resource Books PDFDocument573 pagesBiosafety Resource Books PDFSerenityPas encore d'évaluation
- Endodontic Biofilm 2020Document7 pagesEndodontic Biofilm 2020HllerdPas encore d'évaluation
- FSQC Unit-5Document12 pagesFSQC Unit-5Kumar KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolation and Screening of Biosurfactant Producing Bacteria From Soil and Water For Their Potential ApplicationsDocument10 pagesIsolation and Screening of Biosurfactant Producing Bacteria From Soil and Water For Their Potential ApplicationsIJRASETPublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- XII Biology MCQDocument33 pagesXII Biology MCQsairishiPas encore d'évaluation
- Format For Seed MoneyDocument5 pagesFormat For Seed MoneykiranPas encore d'évaluation
- ROLL NO .. RKDF UniversityDocument2 pagesROLL NO .. RKDF UniversityAhmad AslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiol NotesDocument6 pagesMicrobiol NotesKim LuuPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledTarun GautamPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Techniques To Study Microbial Biofilm On Abiotic Surfaces: Pros and Cons of The Main Techniques Currently in UseDocument12 pagesAnalytical Techniques To Study Microbial Biofilm On Abiotic Surfaces: Pros and Cons of The Main Techniques Currently in Usenaima aminaPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY 83 - Introduction To Medical Microbiology and Parasitology Mae Brigitt Bernadel L. Villordon, PH.D., MPH, RMT Course DescriptionDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY 83 - Introduction To Medical Microbiology and Parasitology Mae Brigitt Bernadel L. Villordon, PH.D., MPH, RMT Course DescriptionMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Book by DR Yamini Shah1Document58 pagesBook by DR Yamini Shah1talibh577Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class - XII: Multiple Choice Question Bank (MCQ) Term - IDocument90 pagesClass - XII: Multiple Choice Question Bank (MCQ) Term - IKanishkarPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Isoletion and Differentiation of BacteriaDocument67 pages4 Isoletion and Differentiation of BacteriaSamson NigussiePas encore d'évaluation
- Course Overview: Inesrau@sebs - Rutgers.eduDocument5 pagesCourse Overview: Inesrau@sebs - Rutgers.eduEmmanuel MacaraegPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal of King Saud University - ScienceDocument5 pagesJournal of King Saud University - ScienceBeshoy RafatPas encore d'évaluation
- Advances in Biological Science Research: A Practical ApproachD'EverandAdvances in Biological Science Research: A Practical ApproachSurya Nandan MeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 SetsDocument8 pages03 SetsZubair MadniPas encore d'évaluation
- التفكير الإبداعي للإدارة..والتغيير في المنظمةDocument16 pagesالتفكير الإبداعي للإدارة..والتغيير في المنظمةtetoPas encore d'évaluation
- WICSDocument78 pagesWICSJulios Salodaga Bulan100% (1)
- Islands of Eight-Million Smiles (Aoyagi Hiroshi)Document361 pagesIslands of Eight-Million Smiles (Aoyagi Hiroshi)エルナンデス クリスティアンPas encore d'évaluation
- Philosophy of AssessmentDocument5 pagesPhilosophy of Assessmentapi-349873749Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book Club EssayDocument2 pagesBook Club EssayNicole WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ayurvedic Case RecordingDocument75 pagesAyurvedic Case Recordingnilesh_manakikarPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 4 DLL Quarter 4 Week 3 (Sir Bien Cruz)Document36 pagesGrade 4 DLL Quarter 4 Week 3 (Sir Bien Cruz)Mariyah QPPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 ScienceinterimreportDocument4 pages07 ScienceinterimreportAlyssa ColePas encore d'évaluation
- Weebly - Lesson Plan Photo For DesignDocument3 pagesWeebly - Lesson Plan Photo For Designapi-506277968Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Visit ReportDocument3 pagesHospital Visit ReportRania FarranPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 13 Suheil PDFDocument9 pagesLesson 13 Suheil PDFrusilawati sallehPas encore d'évaluation
- ARELLANO - ENVI-SCI2 - RIZAL - PART 2 - COMPLETE - RexarellanoDocument15 pagesARELLANO - ENVI-SCI2 - RIZAL - PART 2 - COMPLETE - RexarellanoJunjun CaoliPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Selection Lab ReportDocument7 pagesNatural Selection Lab Reportapi-2980676930% (2)
- BingDocument157 pagesBingGina NegiPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Lesson Plan (DLP) : Approved by Method TeacherDocument7 pagesDigital Lesson Plan (DLP) : Approved by Method TeacherMeghraj PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Module6 Chapter3 Lesson2 PROFED108Document7 pagesModule6 Chapter3 Lesson2 PROFED108Jhonas YarasPas encore d'évaluation
- ETHICS - Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesETHICS - Reflection PaperErika Nell LachicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan State ICTDocument2 pagesLesson Plan State ICTVon Glydel MicabaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 2 EappDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 EappDennis De JesusPas encore d'évaluation
- Beauty Myth Book ReviewDocument2 pagesBeauty Myth Book Reviewoliviafish28Pas encore d'évaluation
- IS2184 Information Systems ManagementDocument2 pagesIS2184 Information Systems ManagementMihirinie AbhayawardhanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Policy Changes: Offered in The Morning or Is Clashing With Another Core Course Then They May Take Core Course in TheDocument1 pagePolicy Changes: Offered in The Morning or Is Clashing With Another Core Course Then They May Take Core Course in ThesirfanalizaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Magic BusDocument29 pagesMagic BusAshworth Vaz100% (1)
- Pop Cycle Cunningham 11Document5 pagesPop Cycle Cunningham 11api-518590777Pas encore d'évaluation