Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Fernando Felix Manuel Reyes Victor Vazquez Grammar Adverbs Clauses
Transféré par
Victor VazqzDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Fernando Felix Manuel Reyes Victor Vazquez Grammar Adverbs Clauses
Transféré par
Victor VazqzDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Fernando Felix Manuel Reyes Victor Vazquez Grammar Adverbs clauses: They are a connecting word, and are
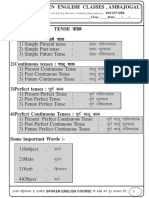
in the sentences with particular function: Because/since/-cause Although/even though- opposition when/while/as/since/until/once/before/after- time Etc. EXAMPLE: I run very fast because they want to steal me. Parallelism: Words in the sentences with same grammatical form and function: EXAMPLE: we have the homework of mathematics, English, chemistry, geology and literature. Some Tenses: Simple past: subject+ verb in past (or did not in negative form+ verb simple form)+ complement (in question the subject and the verb are inverted). I ran in the park yesterday Present perfect: subject+ have (not)/has (not) + verb past participle+ complement We have gone to school since 1995 Inversion Occur in sentences like question, with negative words as nowhere, never, seldom, at no time, etc. and in presence of only . EXAMPLE: not only read I books, also read the newspaper. Comparative: In short adjectives, finished with ER, and after+ THAN the other object. In large word before it is the word MORE: you are bigger THAN she/ the human is MORE intelligent THAN other animals.
Superlative In short adjectives, finished with EST. In large word before it is the word MOST: You are the MOST intelligent in your class/ The Vatican is the smallest country in the world.
Passive voice: The object in the sentences become in the subject. The tense is the same but plus the verb TO BE in that tense, after the original verb in past participle: Victor Hugo wrote The Miserables------The Miserables was wroten by Victor Hugo Irregular plurals Some words dont have the finish S or ES when pass since singular to plural, they change the structure of the word, for example, man dont is mans, the correct form is MEN. Others dont change, fish is in singular and in plural: I have some fish/ I brush my teeth Appositives: Is a noun phase that explain or give more information about another noun phase, can be between commas or in the first or finish of the sentences, separate by commas. The last tlatoani Cuauthmoc, Moctezumas nephew, died 3 years after the Fall of Tenochtitlan. Incomplete adjective clauses: Adjective clauses are a way of joining two sentences; it modifies a noun in another clause of sentence. It begins with adjective clauses marker. This is a topic. It interests me. This is a topic that interests me. Some adjective clause marker: Who whom whose which that where when. Incomplete or missing appositives An appositive is a noun phrase that explains or rephrases another noun phrase. Buffalo Bill, a famous frontiersman, operated his own Wild West Show. Jerome Kerns most famous work is Showboat, one of the finest, most enduring musical comedies.
Errors with word forms Common noun endings: -tion. sion. ence. ance. ity. hood. ment. Common verb endings: -ize. en. er. ify. ate Common adverb endings: -ly. ally. Example: differ difference different differently
Errors with verbs. Errors in subject-verb agreement. Some examples: A sentence with two subjects: the chemistry lab and the physics lab are Subjects with each and every are singular: each state has, everyone wants. Quantities of time, money, distance: five hundred dollars was, two years has, ten miles is. Irregular plurals do not end in-s but take plural verbs: his feet are, the women were.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Back to School: 1,001 Facts You Learned and Forgot in High SchoolD'EverandBack to School: 1,001 Facts You Learned and Forgot in High SchoolÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Words and Pieces of WordsDocument27 pagesWords and Pieces of Wordskkurd7674Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesThe Parts of SpeechAvinash AsokanPas encore d'évaluation
- English Grammar Analysis Understanding The BasicsDocument8 pagesEnglish Grammar Analysis Understanding The BasicsMohammad Alzein100% (1)
- Definition of A SentenceDocument43 pagesDefinition of A SentenceElate PlacementsPas encore d'évaluation
- Stucture Word ClassesDocument10 pagesStucture Word ClassesDwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sat Writing Grammar RulesDocument18 pagesSat Writing Grammar Rulesyvg95100% (1)
- A Grammar of The English LanguageDocument12 pagesA Grammar of The English LanguageLâm VănPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 7 Semantics of Phrase and Sentence - Lecture Notes2022 2023Document3 pagesWeek 7 Semantics of Phrase and Sentence - Lecture Notes2022 2023Maria TeodorescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Independent Clause.: Parallelism (Grammar)Document17 pagesIndependent Clause.: Parallelism (Grammar)Christian MayugaPas encore d'évaluation
- IcpnaDocument6 pagesIcpnaLuz Maria CarreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1Document4 pagesGroup 1Bunso GuadalupePas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Handout Final PDFDocument36 pagesSeminar Handout Final PDFRobin SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Smallest Unit of Language That Has A Meaning of Its OwnDocument33 pagesThe Smallest Unit of Language That Has A Meaning of Its OwnabaclavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit III - Level of Analysis DraftDocument32 pagesUnit III - Level of Analysis DraftErick junior colque huarachiPas encore d'évaluation
- Асанова Семинар 2 The basic notions concerned with the analysis of the categorial structure of the word: grammatical category, opposition, paradigm. Grammatical meaning and means of its expressionDocument6 pagesАсанова Семинар 2 The basic notions concerned with the analysis of the categorial structure of the word: grammatical category, opposition, paradigm. Grammatical meaning and means of its expressiondinaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lexis and MorphologyDocument5 pagesLexis and MorphologyqamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syntax 1Document4 pagesSyntax 1Monica Benitez RicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Document64 pagesGramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Adam DmochowskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Glossary PDFDocument11 pagesGrammar Glossary PDFPecky27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Egyptian Grammar Glossary PDFDocument11 pagesEgyptian Grammar Glossary PDFPecky27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah MorphologyDocument16 pagesMakalah MorphologyDMaliezPas encore d'évaluation
- Apuntinis Grammar II (Autoguardado) (Recuperado Automáticamente)Document22 pagesApuntinis Grammar II (Autoguardado) (Recuperado Automáticamente)amina.menehemPas encore d'évaluation
- Agreement: The Core SentenceDocument80 pagesAgreement: The Core SentenceMariacris CarnicePas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 Term 2 Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesGrade 8 Term 2 Exam ReviewOmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Teorías Preguntas Llamados F2Document4 pagesTeorías Preguntas Llamados F2Rocío RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture One Word Order. The Simple Sentence. Terminological Distinctions: Sentence, Clause, Phrase. SyntaxDocument10 pagesLecture One Word Order. The Simple Sentence. Terminological Distinctions: Sentence, Clause, Phrase. SyntaxMaria PuscasPas encore d'évaluation
- The Article in EnglishDocument84 pagesThe Article in EnglishsorelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To English Language - 231009 - 173858Document57 pagesIntroduction To English Language - 231009 - 173858nicholas.ssekyanziPas encore d'évaluation
- Wuolah-Free-Conceptos-Completos (1) - Gulag-FreeDocument6 pagesWuolah-Free-Conceptos-Completos (1) - Gulag-FreeMariangeles Laguna BenítezPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar: Happens Word, Bark. These Kinds of Words Are The Most Basic Parts of Any StatementDocument7 pagesGrammar: Happens Word, Bark. These Kinds of Words Are The Most Basic Parts of Any StatementWahid BarechPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing: Sentences, Paragraphs and Essays Elements of A Sentence: PunctuationDocument11 pagesWriting: Sentences, Paragraphs and Essays Elements of A Sentence: PunctuationKimYotPas encore d'évaluation
- CELTA Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCELTA Cheat SheetmcgwartPas encore d'évaluation
- Professional English Grammar Handbook INTERMEDIATE 2011Document79 pagesProfessional English Grammar Handbook INTERMEDIATE 2011Carlos CanulPas encore d'évaluation
- MorphemesDocument18 pagesMorphemesmufidolaPas encore d'évaluation
- AdjactiveDocument6 pagesAdjactiveKutman UlanbekovPas encore d'évaluation
- ELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Document38 pagesELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Becira LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Purposive Communication.Document8 pagesPurposive Communication.Kyla Ramos Diamsay100% (1)
- Word Classes in English GrammarDocument3 pagesWord Classes in English GrammarGalang Legowo100% (1)
- Grammer - Preposition, Adjective, InterjectionDocument17 pagesGrammer - Preposition, Adjective, InterjectionNor Zuraidah JaafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument5 pagesParts of SpeechMariola JurczykPas encore d'évaluation
- Charles FillmoreDocument8 pagesCharles FillmoreНурик ЕрмековPas encore d'évaluation
- Noun Phrase (I)Document7 pagesNoun Phrase (I)Alina RPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Reader GrammarDocument20 pagesCritical Reader GrammarShrey GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Materi Kuliah Morphology & SyntaxDocument8 pagesMateri Kuliah Morphology & SyntaxcoriactrPas encore d'évaluation
- Wuolah Free HISTORIA DE LA LENGUA INGLESA IIDocument22 pagesWuolah Free HISTORIA DE LA LENGUA INGLESA IIAzul RusoPas encore d'évaluation
- Final OxxoDocument26 pagesFinal OxxoErick junior colque huarachiPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument17 pagesParts of SpeechJuank_14_12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Facultad: Ciencias Económicas Carrera: Administración Cátedra: Ingles IV Sección: A Catedrática: Kevin Torres 4to. SemestreDocument19 pagesFacultad: Ciencias Económicas Carrera: Administración Cátedra: Ingles IV Sección: A Catedrática: Kevin Torres 4to. SemestreLN NLPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced TEFLDocument240 pagesAdvanced TEFLMustafa Elazazy90% (10)
- Parts of Speech HandoutDocument7 pagesParts of Speech HandoutSafya BnhPas encore d'évaluation
- SUMMER Remediation Lingva LATINA VII Grammar I, Ii, Iii: Lessons 1 - 2 - 3Document23 pagesSUMMER Remediation Lingva LATINA VII Grammar I, Ii, Iii: Lessons 1 - 2 - 3Gabriela MccawleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesParts of SpeechValentina SeoanePas encore d'évaluation
- Vrste Rijeci EngleskiDocument7 pagesVrste Rijeci EngleskiTarik AlicPas encore d'évaluation
- 4B07 VoNguyenThuyVy Adverbials in Vietnamese and EnglishDocument20 pages4B07 VoNguyenThuyVy Adverbials in Vietnamese and EnglishDerek Deleon100% (1)
- English Glossary of Grammar TermsDocument73 pagesEnglish Glossary of Grammar TermsArash Karimi100% (1)
- NounsDocument26 pagesNounsKhongorzul EnkhbaatarPas encore d'évaluation
- 5th Grade Ela Study GuideDocument5 pages5th Grade Ela Study Guideapi-292325707100% (6)
- Lesson Plan in Grade 8Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Grade 8Cristine Mae E. ArevaloPas encore d'évaluation
- English Skills Entry Test BDocument2 pagesEnglish Skills Entry Test BV HPas encore d'évaluation
- Summer EnglishDocument2 pagesSummer EnglishAngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Expressions For Verb TensesDocument3 pagesTime Expressions For Verb Tensesmisogenesis100% (2)
- Exercises - Auxiliary VerbsDocument1 pageExercises - Auxiliary VerbsCamila MolinariPas encore d'évaluation
- Initial Test 6th Grade ADocument2 pagesInitial Test 6th Grade ACristina MTPas encore d'évaluation
- Hebrewbooks Org 49975Document892 pagesHebrewbooks Org 49975edgar marroquinPas encore d'évaluation
- SEA 2001 Language ArtsDocument15 pagesSEA 2001 Language ArtsAnna Del Rey ValtersenPas encore d'évaluation
- Shona Noun Class SystemDocument1 pageShona Noun Class SystemAnonymous BQcnG1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mabato National High School-Annex Pre - Final Test English 7Document3 pagesMabato National High School-Annex Pre - Final Test English 7Mench Andaya QuinilitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Past ContinuousDocument1 pageGrammar Past ContinuousAmalPas encore d'évaluation
- Guessing MeaningDocument2 pagesGuessing MeaningRisdian E. FlamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Word Formation in Tamil PDFDocument96 pagesWord Formation in Tamil PDFStanly Jebaroons SPas encore d'évaluation
- SOLT 1 Arabic Module 2 Lesson 1: Student ManualDocument37 pagesSOLT 1 Arabic Module 2 Lesson 1: Student ManualOmar Marghani SalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions - Language ProfiencyDocument9 pagesQuestions - Language ProfiencyChesterJerichoRamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 8 - PronounsDocument10 pagesLesson 8 - PronounsVanessa ForeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject and Verb Agreement: Basic RuleDocument27 pagesSubject and Verb Agreement: Basic RuleMayla Lei PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Preface A Handbook of Korean Verbal ConjugationDocument2 pagesPreface A Handbook of Korean Verbal ConjugationDobozi SergiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Adverbs / Adverbios: Adverb PlacementDocument8 pagesAdverbs / Adverbios: Adverb PlacementSara E. GalarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 8. (Textbook) Phrasal Verbs - Carry On - Put Off PDFDocument4 pages1.1 8. (Textbook) Phrasal Verbs - Carry On - Put Off PDFyunus karakasPas encore d'évaluation
- A Wordnet For Bodo LanguageDocument4 pagesA Wordnet For Bodo LanguageMustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- English GrammarDocument160 pagesEnglish GrammarBabu Bhosale100% (4)
- Verb Tenses Timeline ChartDocument2 pagesVerb Tenses Timeline ChartTanupriya GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Definite and Indefinite Articles: The, A, An: GrammarDocument2 pagesDefinite and Indefinite Articles: The, A, An: GrammarKrushna Chandra PanditPas encore d'évaluation
- The Comparison Between The Tenses of English and Those of ArabicDocument14 pagesThe Comparison Between The Tenses of English and Those of Arabicmus1974100% (1)
- Identify The Tense: Underline The Verbs in The Following Sentences and State Their TenseDocument3 pagesIdentify The Tense: Underline The Verbs in The Following Sentences and State Their Tensefirdhaus.alhusaini100% (4)
- Reporting Verbs Table PDFDocument1 pageReporting Verbs Table PDFlubagigPas encore d'évaluation
- Word FormationDocument25 pagesWord FormationMuhammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Past TenseDocument1 pagePast TenseBruno ForgiariniPas encore d'évaluation
- CONJUNCTIONDocument13 pagesCONJUNCTIONevlynPas encore d'évaluation