Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Parts and Their Functions
Transféré par
Jonathan MayoDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cell Parts and Their Functions
Transféré par
Jonathan MayoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cell Parts and Their Functions
Nucleus - Large Oval body near the centre of the cell. - The control centre for all activity. - Surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Nucleoplasm - is the protoplasm in the nucleus. - contains genetic material ---> CHROMOSOMES (DNA) Nucleolus - is found in the nucleus. - contains more genetic information (RNA) Cell Membrane - the outer boundary of the cell. - it separates the cell from other cells. - it is porous ---> allows molecules to pass through. Cell Wall ( Plant Cells Only ) - non living structure that surrounds the plant cell. - protects + supports the cell. - made up of a tough fibre called cellulose. Cyto Plasm - cell material outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane. - clear thick fluid. - contains structures called organelles. Vacuoles - are clear fluid sacs that act as storage areas for food, minerals, and waste. - in plant cell the vacuoles are large and mostly filled with water. This gives the plant support. - in animal cells the vacuoles are much smaller. Mitochondria - power house of the cell. - centre of respiration of the cell. - they release energy for cell functions.
Chloro Plasts ( Plant cells only ) - contains a green pigment known as chlorophyll which is important for photosynthesis. Ribosomes - tiny spherical bodies that help make proteins. - found in the cyto plasm or attached to the endo plasmic reticulum. Endo Plasmic Reticulum ( ER ) - systems of membranes throughout the cyto plasm. - it connects the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane. - passageway for material moving though the cell. Golgi Bodies - tube like structures that have tiny sacs at their ends. - they help package protein. Lysosomes - " suicide sacs " - small structures that contain enzymes which are used in digestion. - if a lysosome were to burst it could destroy the cell.
Cell Membrane It provides shape to the cell. It is semi-permeable, regulating the entry and exit of substances, namely solutes and ions. The cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane. It is the outermost covering of the animal cell. It protects the cell and regulates the entry and exit of substances, namely ions and solutes. Cell Wall It provides protection, shape and rigidity to the cell. It is freely permeable, allowing substances in the form of solutions to enter and leave the cell without any hindrance.The cell wall is the outermost covering of the plant cell made up of cellulose, and surrounds the cell membrane. It protects the cell, provides mechanical support and is responsible for maintaining pressure inside the cell. CentrosomeIt initiates and regulates cell division. It also helps in forming spindle fibres, with the help of asters.The centrosome of the animal cell contains one or two centrioles, and is surrounded by microtubules or the centrosphere. It initiates and regulates cell division. CytoplasmIt is the house of all metabolic activities and functions in the cell. In other words, it contains most of the cell organelles, each of which perform a specific function.The cytoplasm is composed of a mixture of water and soluble organic & inorganic compounds, and contains most of the cell organelles. It is the house of all metabolic functions and activities of the animal cell. Endoplasmic ReticulumIt provides support to the cell. It also helps in the synthesis and transport of proteins and fats.The endoplasmic reticulum consists of tubular structures (convoluted tubules) lying near the nucleus. It provides support to the plant cell and the animal cell. It is of two types, namely the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (does not have ribosomes attached to it) and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (has ribosomes attached to it) Golgi ApparatusIt synthesizes and secretes certain substances, namely hormones and enzymes. It also helps in the formation of acrosome of sperm.The golgi apparatus of the animal cell consists of flat vesicular structures placed one on top of the other. It synthesizes and secretes certain substances,
namely hormones and enzymes. LysosomeIt performs intracellular digestion. It also helps in destroying foreign substances.The lysosome of the animal cell is a membranous sac budded off from the golgi apparatus, and contains several types of enzymes. It performs intracellular digestion and destroys foreign substances.
MitochondrionIt is the site of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) synthesis. It also synthesizes respiratory enzymes.The mitochondrion of the cell has two layers of membrane, of which the inner one is folded to
form cristae. It is the site of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) synthesis. Nuclear MembraneIt is semi-permeable, allowing substances to enter and leave the nucleus of the cell. It also provides protection to the nucleus of the cell.The nuclear membrane is the covering of the nucleus of the cell, and has numerous pores. It allows substances to enter and leave. NucleolusIt synthesizes proteins by producing and storing RNA (Ribonucleic acid). At the same time, it orders ribosomes to synthesize proteins.The nucleolus is contained in the nucleus of the cell, and is round in shape. It synthesizes proteins by producing and storing RNA (Ribonucleic acid). NucleoplasmIt contains chromatin fibres, which are made up of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid). After cell division takes place, these chromatin fibres undergo certain structural changes, and are called chromosomes. These chromosomes carry the hereditary information of the genes.The nucleoplasm is a dense fluid containing chromatin fibres, which are made up of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid). After cell division takes place, these chromatin fibres undergo certain structural changes, and are called chromosomes. These chromosomes carry the hereditary information of the genes. NucleusIt controls and coordinates all the activities and functions of the cell. It plays a vital role in cell division.The nucleus is the most important part of the cell, and contains large amounts of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid). It controls and coordinates all the activities and functions of the cell. RibosomeIt is known as the 'site of protein synthesis in the cell', and synthesizes proteins. It is chiefly composed of RNA (Ribonucleic acid).The ribosome is chiefly composed of RNA (Ribonucleic acid). It synthesizes proteins. VacuoleIt helps in the storage of water and several other substances, namely food, waste products and pigments. It also provides turgidity to the cell.The vacuole of the plant cell is a very large and abundant vesicle. It is filled with fluids, and helps in the storage of water and other substances.
Parts of a Cell and What They Do Parts of a Cell Functions of Parts of a Cell The outermost covering of a cell is called the cell membrane. The cell membrane acts like a traffic police man, that regulates entry and exit of Cell Membrane substances, that is, ions and solutes. This helps in regulating the internal cell balance. Cell Wall Centrosome Chloroplast Chromoplast The outermost covering of a plant cell is called the cell wall. It is made up of cellulose and helps provide mechanical support to the cell. It surrounds the cell membrane and helps maintain the pressure within the cell. The centrosome is a part of the animal cell. An animal cell may contain one or two centrosomes that helps in mitosis. Chloroplasts are green colored plastids that are plant cell parts. They help in production of food in the presence of sunlight by photosynthesis. These are also plant cell organelles that have different colors in different cells. They contain xanthophyll and carotene that helps give the flowers and fruits their color. The mixture of water and soluble organic and inorganic compounds is called the cytoplasm. Most of the parts of a cell are suspended in the cytoplasm. All the metabolic functions and activities of an animal cell takes place here. The tubular structures that are found near the nucleus and help provide support to both plant and animal cells is called the endoplasmic reticulum. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum, the smooth reticulum without the attached ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum with the attached ribosomes. The golgi apparatus or bodies are flat vesicular structures that are stacked one above the other. They secrete and store hormones and enzymes that help in transportation out of the cell. These are plant cell organelles that are a type of colorless plastid and help in the storage of starch. This part of an animal cell that is a membranous sac. It is part of the golgi apparatus that contains different enzymes. It helps in intracellular digestion and in the elimination of foreign substances. They are also known as the 'suicide sacs' as, if one of them bursts, the entire cell will be destroyed. The mitochondria has two layers of membrane of which the inner membrane is folded to form cristae. It is the powerhouse of the cell where ATP is generated by cellular respiration. The covering of the nucleus is the nuclear membrane. It has many pores that aid in the transport of substances. The nucleoulus contains the RNA and sends out the RNS to ribosomes along with the blueprints of the protein to be synthesized.
Cytoplasm
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Bodies Leukoplasts
Lysosome
Mitochondria Nuclear Membrane Nucleoulus
Nucleoplasm
The dense fluid that contains chromatin fibers made up of DNA is called nucleoplasm. The chromatin fibers undergo a change in structure after cell division and are called chromosomes. This chromosome contains the hereditary information of genes. The brain of a cell, the cell nucleus controls all the functions occurring in the cell. It contains the blueprint of life, that is, DNA. The part of a cell that contains RNA that helps in protein synthesis. The large and abundant vesicle of a plant cell is called a vacuole. It contains fluids and helps in storage of substances, building material and water.
Nucleus Ribosomes Vacuole
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- This Study Resource Was: Lab 16 Taxonomy Experiment 1: Dichotomous Key PracticeDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Lab 16 Taxonomy Experiment 1: Dichotomous Key PracticeHugsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument8 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet537777333% (3)
- Cell Structure and Function WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Structure and Function WorksheetKiersten RobertsPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition by Pierce ISBN Solution ManualDocument5 pagesGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition by Pierce ISBN Solution Manualrose100% (24)
- 2.5 Notes-1Document8 pages2.5 Notes-1John von steinbechPas encore d'évaluation
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- EnzymeDocument16 pagesEnzymePrecious DerainPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive Enzymes WorksheetDocument2 pagesDigestive Enzymes WorksheetSaima UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 Solution, Suspension, ColloidsDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 Solution, Suspension, ColloidsJigisha SanyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Composition of The CellDocument132 pagesChemical Composition of The Cellazfdin100% (3)
- Prokaryoticneukaryoticgenome 160514180458 PDFDocument7 pagesProkaryoticneukaryoticgenome 160514180458 PDFrahul ssgiPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument38 pagesTransport Across Cell MembraneViswadeep DasPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.3 Understanding Genes and ChromosomesDocument11 pages5.3 Understanding Genes and ChromosomesNoor Hidayah SambliPas encore d'évaluation
- Population Ecology Graph Worksheet - KEY PDFDocument4 pagesPopulation Ecology Graph Worksheet - KEY PDFBinal DaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDocument49 pagesEukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDaezel Deux100% (1)
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 4 Notes 2.3Document2 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes 2.3gelgabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Composotion of The CellDocument38 pagesChemical Composotion of The CelliQalyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz - Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesQuiz - Cell MembraneTieku NoblePas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinsDocument3 pagesProteinsJun Hong TeePas encore d'évaluation
- Modul 1 CHP 2Document14 pagesModul 1 CHP 2Fendy HamidPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIC 2 - CellDocument9 pagesTOPIC 2 - CellAl Johan Atienza100% (1)
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-11 Transport in PlantsDocument10 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-11 Transport in PlantsPriyanshu BhadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dna Replication Worksheet 1Document2 pagesDna Replication Worksheet 1Lovryan Tadena AmilingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Basis of Life: Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemical Basis of Life: Basic ChemistryMauanay, Marjelyn P.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 7 J23.Document15 pagesHomework 7 J23.mauoshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Excretory System ResonanceDocument40 pagesExcretory System ResonanceEkta ManglaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Enzyme NotesDocument8 pagesBiochem Enzyme NotesBeatriz NideaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Regulation of Prokaryotic TranscriptionDocument17 pagesGene Regulation of Prokaryotic TranscriptionAyu Tri AgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Notes (Proteins)Document9 pagesBiology Notes (Proteins)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas100% (1)
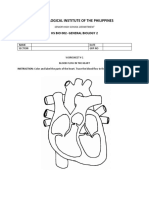
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: Hs Bio 002-General Biology 2Document2 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: Hs Bio 002-General Biology 2AndreaNicoleBanzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structures and Functions 02Document22 pagesCell Structures and Functions 02YASMEROPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Techniques Lecture Notes 2008: by Dr. David NGDocument45 pagesMolecular Techniques Lecture Notes 2008: by Dr. David NGNicolas BergerPas encore d'évaluation
- Living Processes in Unicellular OrganismsDocument20 pagesLiving Processes in Unicellular OrganismsZarina Mohammed100% (2)
- Renal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFDocument37 pagesRenal Physiology Handout 2 Slides Per Page PDFmike hunt100% (1)
- 2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer-SNC2DDocument2 pages2.7 Cell Division Going Wrong - Cancer-SNC2DBob Dharam0% (1)
- MeiosisDocument24 pagesMeiosisMuhammad HamzaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsDocument13 pages8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsEnmuskPas encore d'évaluation
- Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmErvin WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesCarbohydratesJada HartPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Guide To Vce Unit 1 BiologyDocument8 pagesStudent Guide To Vce Unit 1 Biologyapi-348068677Pas encore d'évaluation
- What's in A Cell - Worksheet & ColoringDocument2 pagesWhat's in A Cell - Worksheet & ColoringNuria Tarancon0% (1)
- Chapter 4: Chemical Composition in A CellDocument14 pagesChapter 4: Chemical Composition in A CellEma FatimahPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Worksheet AnswersDocument1 pageBiology Worksheet AnswersBrent Kenneth CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Roots Reviewer PDFDocument4 pagesRoots Reviewer PDFGAILE MEIZTY MOSADAPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 - Bacterial Cell Structure and FunctionDocument90 pagesLecture 2 - Bacterial Cell Structure and FunctionOdurPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle Worksheet 2Document4 pagesCell Cycle Worksheet 2Rodolf Jones RaboPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement MembraneDocument2 pagesCell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement Membranerahul mauryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mendelian Genetics Heredity Biology Lecture PowerPoint VCBCDocument26 pagesMendelian Genetics Heredity Biology Lecture PowerPoint VCBCGhost hackerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Importance of ReproductionDocument7 pagesThe Importance of ReproductionSiti Choiriyah100% (1)
- (BIOLOGY) Cellular RespirationDocument12 pages(BIOLOGY) Cellular RespirationHAJIRA RAMLANPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity and Conservation A Level NotesDocument8 pagesBiodiversity and Conservation A Level NotesNaseer SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Life Processes of Living ThingsDocument25 pagesLife Processes of Living Thingszanu winfred kwame100% (1)
- Worksheet in BloodDocument12 pagesWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell+ +Cell+MembraneDocument26 pagesCell+ +Cell+Membraneemancipation1506Pas encore d'évaluation
- ATP WorksheetDocument5 pagesATP WorksheetRyan De AlloPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of A CellDocument1 pageParts of A CellLaurence RoiPas encore d'évaluation
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes - Chapter 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument7 pagesNotes - Chapter 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationRogie P. BacosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth & Life ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth & Life ScienceYhazmeen Lily LibrodoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lysosomes From Fawcett CellDocument20 pagesLysosomes From Fawcett CellCORYNEBACTERIUMPas encore d'évaluation
- Jake Facciobene Cells Practice Worksheet 2 1 PDFDocument2 pagesJake Facciobene Cells Practice Worksheet 2 1 PDFJake FacciobenePas encore d'évaluation
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Cellular Biology QuestionsDocument5 pagesSAT Cellular Biology QuestionsMido MidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell AnalogyDocument24 pagesCell AnalogyBOBOBOYS TVPas encore d'évaluation
- Dwnload Full Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Martini Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Martini Test Bank PDFwaterycobstone.yg9zl100% (6)
- Plant CellDocument47 pagesPlant CellIraanurainiPas encore d'évaluation
- AY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Document7 pagesAY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Lim Liang XuanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ribosomes and The ER: The Cytoplasm: The Factory FloorDocument7 pagesThe Ribosomes and The ER: The Cytoplasm: The Factory FloorMarco Fidel Naranjo GómezPas encore d'évaluation
- CELL DIVISION From BookDocument2 pagesCELL DIVISION From BookJunell TadinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise # 2: Cells and Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesExercise # 2: Cells and Cell DivisionEnyong LumanlanPas encore d'évaluation
- S.4 Biology - Cell Division 2020 PDFDocument11 pagesS.4 Biology - Cell Division 2020 PDFJovia TPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: Name: Jarule Matthew S. Del Pilar Week: 2 Activity 1Document1 pageDepartment of Education: Name: Jarule Matthew S. Del Pilar Week: 2 Activity 1deymgoodsPas encore d'évaluation
- CH-8 Notebook Work-Answer KeyDocument2 pagesCH-8 Notebook Work-Answer KeyEeshan SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDocument4 pagesModule 4-The Cell's Life Cycle10. Briol AlvinPas encore d'évaluation
- GB - 1st Quarter - wk3 - PDFDocument20 pagesGB - 1st Quarter - wk3 - PDFHeaven LeighPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular Level of Organization PDFDocument13 pagesCellular Level of Organization PDFMa Ronalyn Abogne SiguePas encore d'évaluation
- 1.introduction To Physiology, The Cell and General PhysiologDocument3 pages1.introduction To Physiology, The Cell and General PhysiologCLEMENT100% (1)
- Quiz (Class 9 Science.)Document2 pagesQuiz (Class 9 Science.)Raj SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Hirarki Biologi (Kehidupan)Document18 pagesHirarki Biologi (Kehidupan)lailatus syafi'ahPas encore d'évaluation
- Flash Card InfoDocument45 pagesFlash Card Infosheila may valiao-de asisPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell City Worksheet Answer KeyDocument7 pagesCell City Worksheet Answer KeyNorain TalanganPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Sheet Formative AssessmentDocument4 pagesAnswer Sheet Formative Assessmentapi-328130455Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Analogy ProjectDocument12 pagesCell Analogy Projectapi-318478166100% (1)
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetDocument2 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetAra Hella JordasPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises of Reversible InjuriesDocument6 pagesExercises of Reversible InjuriesRamel Yen CerantesPas encore d'évaluation