Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
PHY3 DJanuary 2003
Transféré par
api-3726022Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PHY3 DJanuary 2003
Transféré par
api-3726022Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PHY3 JANUARY 2003 - TOPIC D - MEDICAL PHYSICS 1
Topic D – Medical Physics
4. (a) An isotope of iodine 131I is produced when unstable
tellurium 13152Te undergoes β - decay.
Write a nuclear equation for this decay. (2)
The unstable tellurium is produced when stable 13052Te is
bombarded with neutrons.
Where might such a reaction be carried out? (1)
State three factors which must be considered when
choosing a radionuclide for organ imaging. (3)
131
I has a half-life of 8 days and a biological half-life of 21 days.
Calculate the effective half-life of 131I. (2)
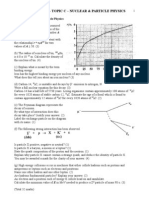
On a copy of the axes opposite and above sketch two curves, one
showing the activity of a sample of 131I kept in a laboratory
and the other showing the activity of a sample given to a patient.
Assume both samples have the same initial activity.
Label your curves L (laboratory) and P (patient). (3)
(b) The diagram below shows the main features of an X-ray tube.
Identify features A, B and C. (3)
An X-ray beam has an intensity of 20 MW m-2 at a distance
of 0.10 m from a point source of X-rays.
What will be the intensity 1.0 m from the source? (2)
(c) Describe how it is possible to obtain information about the
depths of structures in a patient's body by using an ultrasonic A-scan.
You may be awarded a mark for the clarity of your answer. (5)
Explain why a coupling medium is essential between the body surface and the ultrasound probe. (2)
State a suitable substance for use as a coupling medium. (1)
(d) Read the short passage below and answer the questions about it.
The piezoelectric effect is a reversible relationship between mechanical stress and electric potential difference exhibited
by certain crystals such as quartz. When a piezoelectric crystal is compressed, positive and negative charges appear on
opposite crystal faces producing a potential difference across the crystal. Replacing the pressure by tension reverses this
potential difference. If instead an electric potential difference is applied across the crystal then its thickness changes. A
piezoelectric crystal placed in an alternating electric circuit will thus expand and contract. These effects are used in
ultrasonic generators and detectors. The maximum transfer of energy occurs at a particular frequency called the
resonant frequency. The wavelength of the ultrasound produced by a piezoelectric crystal at its resonant frequency is
equal to twice the crystal thickness. [Adapted from Phaidon Concise Encyclopaedia of Science and Technology}
Explain what is meant by a reversible relationship. (2)
Diagram (i) shows the charge distribution on a compressed
piezoelectric crystal. Show the charge distribution on the
crystals on a copy of diagrams (ii) and (iii). (2)
Calculate the thickness of a quartz crystal which will have a
resonant frequency of 1.50 MHz..
( Speed of sound in quartz = 5740 ms-1 ) (3)
What is the benefit of applying the alternating potential
difference at the resonant frequency of the quartz crystal? (1)
(Total 32 marks)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 6102 01 Que 20080109Document20 pages6102 01 Que 20080109Inas ManurungPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Jan 2008 6101 QuestionDocument20 pagesBiology Jan 2008 6101 QuestionAdrees MeahPas encore d'évaluation
- Biojune 2008 U1qDocument16 pagesBiojune 2008 U1qapi-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biojune 2008 U4aqDocument24 pagesBiojune 2008 U4aqapi-3726022100% (1)
- PHY3 DJune 2006Document1 pagePHY3 DJune 2006api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 DJune 2002Document1 pagePHY3 DJune 2002api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 DJune 2004Document1 pagePHY3 DJune 2004api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 CJune 2002Document1 pagePHY3 CJune 2002api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 DJune 2005Document1 pagePHY3 DJune 2005api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 DJanuary 2005Document1 pagePHY3 DJanuary 2005api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 DJanuary 2004Document1 pagePHY3 DJanuary 2004api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 DJanuary 2002Document1 pagePHY3 DJanuary 2002api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 CJune 2006Document1 pagePHY3 CJune 2006api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 CJune 2004Document1 pagePHY3 CJune 2004api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 CJanuary 2006Document1 pagePHY3 CJanuary 2006api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 CJanuary 2003Document1 pagePHY3 CJanuary 2003api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 CJanuary 2005Document1 pagePHY3 CJanuary 2005api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 AJune 2005Document1 pagePHY3 AJune 2005api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 AJune 2003Document1 pagePHY3 AJune 2003api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 AJune 2006Document1 pagePHY3 AJune 2006api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 AJanuary 2004Document1 pagePHY3 AJanuary 2004api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 AJanuary 2006Document1 pagePHY3 AJanuary 2006api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY3 AJune 2004Document1 pagePHY3 AJune 2004api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Strategic ManagementDocument14 pagesStrategic ManagementvishakhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Policarpio Vs Manila Times - Unprotected Speech LibelDocument3 pagesPolicarpio Vs Manila Times - Unprotected Speech LibelStef BernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Peri Operative Nursing ManagementDocument19 pagesPeri Operative Nursing ManagementSabina KontehPas encore d'évaluation
- Bakhtin's Chronotope On The RoadDocument17 pagesBakhtin's Chronotope On The RoadLeandro OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 01ESS - Introducing Siebel ApplicationsDocument24 pages01ESS - Introducing Siebel ApplicationsRajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Customizable Feature Based Design Pattern Recognition Integrating Multiple TechniquesDocument191 pagesCustomizable Feature Based Design Pattern Recognition Integrating Multiple TechniquesCalina Sechel100% (1)
- DND Homebrew Ideas V1 - The HomebreweryDocument3 pagesDND Homebrew Ideas V1 - The HomebreweryKalazans CardialPas encore d'évaluation
- The Training Toolbox: Forced Reps - The Real Strength SenseiDocument7 pagesThe Training Toolbox: Forced Reps - The Real Strength SenseiSean DrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Annexure 8: Medical Certificate (To Be Issued by A Registered Medical Practitioner) General ExpectationsDocument1 pageAnnexure 8: Medical Certificate (To Be Issued by A Registered Medical Practitioner) General ExpectationsMannepalli RamakrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ideal Weight ChartDocument4 pagesIdeal Weight ChartMarvin Osmar Estrada JuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lead Workplace CommunicationDocument55 pagesLead Workplace CommunicationAbu Huzheyfa Bin100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPchesca_paunganPas encore d'évaluation
- Radio Network Parameters: Wcdma Ran W19Document12 pagesRadio Network Parameters: Wcdma Ran W19Chu Quang TuanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Minecraft Survival Quest ChallengeDocument4 pagesThe Minecraft Survival Quest Challengeapi-269630780100% (1)
- Origin of "ERP"Document4 pagesOrigin of "ERP"kanika_bhardwaj_2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Theater 10 Syllabus Printed PDFDocument7 pagesTheater 10 Syllabus Printed PDFJim QuentinPas encore d'évaluation
- RR 10-76Document4 pagesRR 10-76cheska_abigail950Pas encore d'évaluation
- AASW Code of Ethics-2004Document36 pagesAASW Code of Ethics-2004Steven TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Win Tensor-UserGuide Optimization FunctionsDocument11 pagesWin Tensor-UserGuide Optimization FunctionsadetriyunitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rem - Manila Bankers Vs NG Kok Wei - Noel DomingoDocument3 pagesRem - Manila Bankers Vs NG Kok Wei - Noel DomingoNoel DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding Summative TestDocument4 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding Summative TestFelix MilanPas encore d'évaluation
- Glickman - The Jewish White Slavery Trade (2000)Document152 pagesGlickman - The Jewish White Slavery Trade (2000)Alrik G. HamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversation Between God and LuciferDocument3 pagesConversation Between God and LuciferRiddhi ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Presentation BANK OF BARODA 1Document8 pagesFinal Presentation BANK OF BARODA 1Pooja GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathsnacks05 InfiniteDocument1 pageMathsnacks05 Infiniteburkard.polsterPas encore d'évaluation
- The Importance of Logo DesignDocument1 pageThe Importance of Logo DesignDanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Calendar of Cases (May 3, 2018)Document4 pagesCalendar of Cases (May 3, 2018)Roy BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Pumpkin Moon SandDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Pumpkin Moon Sandapi-273177086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 The Prodigal SonDocument2 pagesLesson 3 The Prodigal Sonapi-241115908Pas encore d'évaluation
- Your Free Buyer Persona TemplateDocument8 pagesYour Free Buyer Persona Templateel_nakdjoPas encore d'évaluation