Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pemrograman Perangkat Keras VB
Transféré par
Bambang RiswantoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pemrograman Perangkat Keras VB
Transféré par
Bambang RiswantoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
174
Lampiran 9 Pemrograman Perangkat Keras Pada Visual Basic Artikel ini akan menjelaskan fungsi file .dll serta cara pembuatan file 8255.dll untuk Visual Basic dengan menggunakan bahasa C yang kemudian di-compile dengan Visual C++, sehingga memungkinkan untuk pemrograman perangkat keras dalam hal ini pengaksesan port pada PPI 8255.
Programming Custom Hardware in Visual Basic Author : Dr. Pauh Oh, Drexel University Introduction Audience : You are developing custom hardware for Windows 95 You are frustrated learning how to create a DLL You want Port I/O in Visual Basic You want to mimic QuickBasic's INPUT and OUTPUT statements in VB You want to mimic Turbo C's inportb() and outportb() statements in VB Level : ALL Pre-requisites: Some Visual Basic programming, Win95 PC. Compilers : Visual Basic 4.0 or 5.0, Microsoft Visual C++ 4.0 or 5.0 (not neccessary if you just want to use the DLL and not program your own) Downloads: All source code to DLL, compiled DLL and apps programs.
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
175
Motivation : You might be curious how to write Visual Basic (VB) applications for your unique hardware device. For example, you custom developed a PC card. It might be a data acquisition card, or perhaps a motor controller. This tutorial will show you can write VB programs using a Dynamically linked library (DLL). This tutorial is in response to the dozens of postings on the VB usenet group every month: "How do I create a DLL?" "How do you get VB to call functions written in Visual C++ or other languages?" Sadly, you might be frustrated with the posted responses. You might be frustrated scouring over reference books. You might be frustrated that the DLL's on the Internet don't provide source code - thus wondering what magic is used to create it. Here, this tutorial gives you step-by-step instructions along with GIF image screen shots to show you how to easily make your own DLL. This tutorial is also in response to the hundreds of email Boondog gets each month about writing VB apps for the 8255 PC Interface Card. This simple tutorial will show you how to get started.
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
176
Dynamically Linked Libraries (DLL) Why do I need DLLs? You might have just started using Visual Basic (VB), appreciating how easy it is to write Win95 32-bit applications with it. The learning curve is relatively quick. You might have migrated from QuickBasic or Turbo C, thus having some knowledge of the fundamental statements. If you have migrated from DOS' QuickBasic to VB, you soon realize that QuickBasic's INPUT and OUTPUT (or Turbo C's inportb and outportb) functions were not implemented in VB. These functions are crucial for PC hardware developers and programmers because they allowed you to read and write to ports. Thus without INPUT or OUPUT you can't read from or write to your device. There is a way around this, using a DLL. As the name implies, DLLs allows VB to link (a step before compiling) code (libraries you coded up in another language like Delphi, Borland C++ or Microsoft's Visual C++) during run-time (dynamically). VC++ has port I/O (input and output) read/write functions. Also VC++'s compiler allows you to create DLLs (in addition to executable EXE files). Thus you: 1. Write VC++ code that uses these read/write functions 2. Compile it into a DLL (instead of an executable EXE file) file 3. Call your functions from VB
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
177
Writing your own DLL or just using one? If you don't have VC++ don't worry. You can still use the FREE DLL here to read/write to ports. Download 8255.ZIP which contains 8255.def, 8255.cpp and the 8255.dll files. You just copy the 8255.DLL file to your C:\windows directory. You can then have your VB program use them. But if you are curious then writing a DLL is very easy. The steps in this tutorial specifically use Visual C++ 5.0, but easy enough to mimic in Delphi, Visual C++ 4.0 and Borland C++. Writing the DLL There are two files you need to create. The first is a DEF (define) file. The second is the CPP (C++ source) file. Both are simple ASCII text files. You can use any editor (e.g. DOS' edit, or Windows' Notepad). These are listed below: 8255.def listing: ------------------------------------------------------LIBRARY 8255 DESCRIPTION DLL FOR 8255 CARD EXPORTS Out8255 @1 In8255 @2 ------------------------------------------------------The name of your DLL library is given on the first line. It is 8255. The second line is just a comment. Exports list the names of the functions you will eventually define in your VC++. These functions are: Out8255 and In8255. If you eventually wish to add more functions, give the name of your function and the next number, like MyFunction @3.
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
178
8255.cpp listing: ------------------------------------------------------// FILE: 8255.cpp // AUTH: P.OH/Boondog Automation // DATE: 07/01/98 // DESC: CPP source file for 8255 DLL - compiled with Microsoft Visual C++ 5.0 #include #include functions
// contains Visual C++'s inp and out
// ---------------------------------------------------// FUNC: Out8255 // DESC: uses Microsoft's Visual C++ _outp() function // to output a PortData to PortAddress // ---------------------------------------------------short _stdcall Out8255( int PortAddress, int PortData ) { short Dummy; // Need Dummy since _outp officially returns int // short is a 16-bit integer in Win32 C++ // whereas int is 32-bit integer Win32 C++ // use (short) to force returning 16-bit integer // back to VB Dummy = (short)(_outp( PortAddress, PortData )); return(Dummy); }; // end of Out8255
// ---------------------------------------------------// FUNC: In8255 // DESC: uses Microsoft's Visual C++ _inp() function // to read PortAddress // ---------------------------------------------------short _stdcall In8255( int PortAddress ) { short PortData; // short is a 16-bit integer in Win32 C++ // whereas int is 32-bit integer in Win32 C++ // use (short) to force returning 16-bit integer // back to VB
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
179
PortData = (short)(_inp( PortAddress )); return( PortData ); }; /* end of In8255 */ ------------------------------------------------------8255.cpp defines In8255 and Out8255. It uses VC++'s _inp() and _out() functions. The single underscore before inp and outp are needed. This underscore notation refers to downloadly compatiable functions that were defined in older versions of VC++.
Step 1: Write your .def and .cpp files Create a directory called c:\port. Type and save the DEF file as 8255.def and the CPP file as 8255.cpp - if you want, just cut, paste and save these files, or just download and save them. Step 2: Visual C++ 5.0 Bring up Visual C++. Select FILE - NEW as seen in Figure 1:
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
180
Step 3: Create Your Project This brings up the NEW window. Make sure the Projects tab is selected and choose Win32 Dynamic-Link Library (Figure 2). Make sure that Location is c:\port (you can click the ... button to explore your directories). This is why you created a directory c:\port in Step 1. Type 8255 in the Project Name field. Click on OK. You should now see the result (Figure 3). If not, click on the classes tab. You have just created a project called 8255.
Figure 2
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
181
Figure 3
Step 4: Add your .cpp file Left click on 8255 classes once. This selects it and turns it blue. Next, right click your mouse and choose Add Files to Project (Figure 4).
Figure 4
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
182
An Insert Files to Project (Figure 5) will pop up. Make sure the Files of Type is set to C++ files. Next, choose the 8255.cpp file and hit OK
Figure 5
Step 5: Add your .def file Similar to Step 4, click on 8255 classes once. Right click and select Add Files to Project. Again the Insert File into Project window pops up (Figure 6). This time make sure the Files of Type is set for Definition (.def) files. Click on 8255.def and hit OK. Your 8255 Project now has the 8255.def and 8255.cpp files added (Figure 7). Save everything by clicking FILE - SAVE ALL.
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
183
Figure 6
Figure 7
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
184
Step 6: Build your .dll file On the top bar click on Build and select Build 8255.dll (Figure 8). This will start compiling and create th2 8255.dll file. If you didn't mistype and lines in 8255.def or 8255.cpp (or just cut/paste/save or download/save) VC++ will respond with 0 errors. Your new 8255.dll file is now saved in c:\port\8255\debug (Figure 9).
Figure 8
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
185
Figure 9
Step 7: Copy your .dll file to c:\windows
Figure 10
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
186
Copy your new DLL file to your c:\windows directory. You can do this from DOS (my habit), by bringing up MS-DOS prompt and cd`ing to c:\port\8255\Debug (Figure 10). Of course, you can drag-and-drop from Explorer. Congradulations! Your .dll is ready to use in your Visual Basic programs! Easy right?
Using Your DLL in Your VB Programs To use your DLL functions, you add the following lines in your VB program's declaration section. Typically right after the Option Explicit statement. (Note: the underscore in VB means that the statement is spread over several lines) Private Declare Function Out8255 Lib "8255.dll" _ (ByVal PortAddress As Integer, _ ByVal PortData As Integer) As Integer Private Declare Function In8255 Lib "8255.dll" _ (ByVal PortAddress As Integer) As Integer To write to a port, use Out8255: Dummy = Out8255(Cntrl, 128) where Dummy, Cntrl are integers. Here, the decimal value 128 is written to the port address assigned to Cntrl. It is necessary to use associate an integer variable (I called it "Dummy" here) with the Out8255 function. This is because the DLL was built using VC++'s outp(), which returns an integer (1 if successfully accomplished and and 0 if failed). To read from a port, use In8255: PortValue = In8255(PortSelected)
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
187
where PortValue and PortSelected are integers. The 8-bit number at port PortSelected will be assigned (in decimal form) to PortValue.
Conclusion As you can read in this tutorial, VB programming using DLL's is quite simple. There are many compiler's today like VC++ 4.0, 5.0, Delphi, and Borland C++ that can generate DLLs. Furthermore, these compilers all have port I/O functions. By writing the DLL you can have VB access them. Hopefully the step-by-step tutorial on DLL creation sheds light on how they are made. This is in response to the flood of questions on DLL programming on the VB usenet groups. One caveat is that if you use the wrong memory address (e.g you mistype the address) you can cause Windows 95 to freeze. As a developer/programmer, you might wish to use some error checking in your VB program to make sure that you always write/read to your custom-build card's address. Boondog hopes that you have found this tutorial useful. Hopefully a new world of VB/Win95 programming/PC interfacing brings you a lot of excitement and fun.
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.softwarelabs.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Changong 860-Alz-M713w-F Power Supply For LCD Monitors With Bit3193 Inverter Lien Chang Ai-0088 Board (ET)Document1 pageChangong 860-Alz-M713w-F Power Supply For LCD Monitors With Bit3193 Inverter Lien Chang Ai-0088 Board (ET)Cristina NistorPas encore d'évaluation
- DATA COMMS AND NETWORKS Assignment 1Document23 pagesDATA COMMS AND NETWORKS Assignment 1farai nyakudangaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ca 3524Document20 pagesCa 3524rmsharma1970Pas encore d'évaluation
- Volte Daily Combined DB-PLMN-day-PM 13192-2019 05 22-09 17 07 602Document39 pagesVolte Daily Combined DB-PLMN-day-PM 13192-2019 05 22-09 17 07 602Sultan JavedPas encore d'évaluation
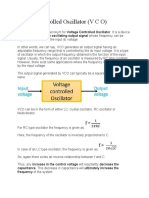
- Voltage Controlled OscillatorDocument7 pagesVoltage Controlled OscillatorHemantha DalugamaPas encore d'évaluation
- HP AlmDocument248 pagesHP AlmVicky BindassPas encore d'évaluation
- Lbistarchitect Process Guide: Software Version 2017.3 September 2017Document172 pagesLbistarchitect Process Guide: Software Version 2017.3 September 2017Anonymous yeYBahPas encore d'évaluation
- Computers GenerationsDocument7 pagesComputers GenerationsBubrikaPas encore d'évaluation
- SumanthBrainard DLP Engineer MphasisDocument4 pagesSumanthBrainard DLP Engineer MphasisSoniya chaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Salim Tadvi Reg No: 201070042: Computer NetworksDocument5 pagesName: Salim Tadvi Reg No: 201070042: Computer NetworksSALIM TADVIPas encore d'évaluation
- Ty 1803Document11 pagesTy 1803JugoslavikPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadmeDocument6 pagesReadmebetabloqueantePas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Clock Using 8051 Microcontroller With RTCDocument47 pagesDigital Clock Using 8051 Microcontroller With RTCsiddharthPas encore d'évaluation
- Ha 17555Document7 pagesHa 17555Brzata PticaPas encore d'évaluation
- RC10PRD 10 11 AwrDocument52 pagesRC10PRD 10 11 AwrAnonymous URVO3VDKPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 CMP Troubleshooting E11-15, 51Document13 pages03 CMP Troubleshooting E11-15, 51Tomas RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- ThinkPad L480 Spec PDFDocument1 pageThinkPad L480 Spec PDFGema RamdaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle® Demantra: System Requirements Guide Release 12.2Document28 pagesOracle® Demantra: System Requirements Guide Release 12.2Sundar PurushothamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Systems Analysis and Design by Dennis AllanDocument4 pagesSystems Analysis and Design by Dennis AllanGrace Ann Aceveda Quinio100% (1)
- RTK Wi-Fi Direct Programming GuideDocument9 pagesRTK Wi-Fi Direct Programming GuidevijayPas encore d'évaluation
- ADM1.Using DL Define in T24Document12 pagesADM1.Using DL Define in T24Trần Hữu Lượng100% (1)
- Tekno Cam 4300 UhdDocument2 pagesTekno Cam 4300 UhdRaymundo Olayo EspírituPas encore d'évaluation
- Syndicate Bank Clerical Solved Paper 2010Document16 pagesSyndicate Bank Clerical Solved Paper 2010Saurabh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib Lite 2011 12 CpleibliDocument2 pagesIb Lite 2011 12 Cpleiblialexander900616Pas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet Cisco GS7000Document7 pagesDatasheet Cisco GS7000jorwyonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.4G NRF24L01+PA+LNA Wireless Module With Antenna - ZboticDocument5 pages2.4G NRF24L01+PA+LNA Wireless Module With Antenna - ZboticvenkatasathPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Front EndDocument5 pagesActive Front EndDaleel LillaPas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual: Mvi56E-DnpnetDocument133 pagesUser Manual: Mvi56E-DnpnetJuan K PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanaced Selenium SyllabusDocument4 pagesAdvanaced Selenium Syllabuspawas19930% (1)
- BSP 170Document9 pagesBSP 170MozãoFragaPas encore d'évaluation