Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiovascular Examination
Transféré par
wakemeup143Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cardiovascular Examination
Transféré par
wakemeup143Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
Cardiovascular
Examination
2
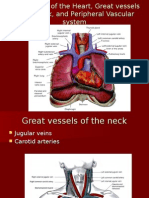
Anatomy
3
4
nspection
1 Precardial projection
and excavation
2 Apical impulse
3 Abnormal pulsations
of precardium
5
1 Precardial projection and
excavation
1) Precardial projection
congenital heart disease: tetralogy of
Fallot
Valvular heart disease--
MS,PS
pericardial effusion (large , childhood)
nspection
%he second right intercostal
space(2nd ICS-RS)
aneurysm of aortic arch
dilatation of ascending aorta
2) flat chest
3) pigeon chest/funnel chest
2 Apical impulse
`Normal:
position-the fifth left intercostal
space 0.5-1.0cm medial to the
midclavicular line
range-2.0-2.5cm in diameter
nspection
`Abnormal
1) Location
#diaphragm:
~transverse position upper,outward
obesity ,child, pregnacy;
ascites; tumor of abdominal cavity
~vertical position (thin, high,
emphysema) inferior,inner
10
one side pleural effusion or
pneumothorax-to the healthy
side
one side atelectesis or pleural
adhesion-to the affected
#mediastinum:
11
#enlargement of the heart
right ventricular dilatation -left or
slightly upper
left ventricular dilatation-left
inferior
LV &RV dilatation -left inferior
(both side dilatation)
12
13
#Posture:
recumbent position-upper
left lateral position-to the left 2-
3cm
right lateral position-to the right
1.0-2.5cm
Dextrocardia: 5-ICS-RS
14
Decrease Increase
Physiological Chest wall pachynsis
Narrow intercostol space
Thin chest wall
Broaden intercostol space
exercise,euphoric mood
Pathological . myopathy(AMI,DCM)
. pericardial eIIusion
. emphysema
.constrictive pericarditis
. leIt side massive pleural
eIIusion or
pneumothroax
.LV hypertrophy
.hyperthyroidism
. Iever
.anemia
2)Intensity and extent changes
nspection-
apical impulse - abnormal
15
3)Inward impulse:
apex excavation in the systole
seen: adhensive pericarditis
prominent RV hypertrophy
nspection
-apical impulse - abnormal
1
nspection
1)left third-forth intercostal space
lateral to the sternum(3,4ICS-LS)
seen: RV hypertrophy
3 Abnomal pulsations of
percardium
1
2)hypoxiphoid process
seen:
difference deep inspiration
RV hypertrophy
abdominal aorta (aneurysm)
1
3)basal part of the heart
2 ICS-LS: dilatation of the
pulmonary artery or pulmonary
hypertensin, occasionally healthy
young man
2 ICS-RS: aneurysm of aortic arch
or dilatation of ascending aorta
1
Palpation
1 Apical impulse and
pulsation of precardium
2 %hrill
3 Pericardial friction rub
20
1 Apical impulse and
pulsation of precardium
Exact position of apex
%he beginning of systole of
ventricle first sound
Heaving apex impulse: reliable
of LV hypertrophy
Palpation
21
2 %hrill
One of characteristic signs of organic heart disease.
Mechanism : the flow of bloodnarrowed
orificevortices
vibrationchest wall
thrill-high frequency
murmurs-low frequency
Method:position,phase of cardiac cycle,clinical
significance
seen: CHD or valvular stenosis ,
occasionally insurficiency
22
Clinical signiIicance oI thrill
Location phase Disease
2 ICS-RS Systole AS (RHD,CHD,senile)
2 ICS-LS Systole PS (CHD)
3,4 ICS-LS Systole VSD (CHD)
Apex Systole MI (severe)
Apex Diastole MS (RHD)
2 ICS-LS Continous PDA
CHD:congenital heart disease
23
1)Precardium-4
th
ICS-LS
2) both phases of the cardiac cycle
3) systolic period, sitting erect and leaning
forward, the end of expiration
4)mechanism: rub of the visceral and
parietal layers of pleura
5)seen:acute pericarditis
3 Pericardil friction rub
24
Percussion
Aim:to determine the size and
shape of the heart .
Absolute dullness: contain no gas
Relative dullness : real size
25
1 murneuver of percussion
patient in erect position -the
pleximeter is vertical with the
intercostal space
patient in the recumbent position
-the pleximeter is parallel with the
intercostal space
2
2 order :
left-right ; upwards ; inward
left margin : from 2-3 cm lateral to
the apex beat up to the 2
nd
ICS
right margin : one intercostal space
higher than the border of liver
dullness up to the 2
nd
ICS
size: vertical distance from margin
to the anterior midline
2
2
3 Normal heart borders
(area oI relative dullness)
Right(cm) ICS LeIt(cm)
2~3
2~3
2~3 III 3.5~4.5
3~4
5~
~
(LMCLML:~10cm)
Percussion
2
4 The composition oI various parts oI
the border oI the heart
(1)
Right ICS LeIt
SVC,SA II PA
RA III LA
RA
LV
LV
Percussion
30
(2)%he upper border -the lower
border of the anterior end of the
third rib
(3)%he basal part -the second
intercostal space upward
left: aortic node and PA
(4)Concave part -between the aorta
and the left ventricle
31
5 Changes in the area of cardiac
dullness and its significance
Cardiac factors :
1)LV enlargement: ~boot shape
Seen:aortic valvular disease ,
hypertension heart disease
Percussion
32
2)RV enlargement :
slightly--absolute dullness
Prominent--relative dullness
to the left side prominently
Seen:PHD, MS
3)%wo ventricle :
~generally enlarged heart
seen:DCM , Kashan cardiomyopathy
33
4)LA and/or pulmonary artery:
LA:concave part disappear
LA+PA:2,3 ICS-LS outwards
~pear shape
Seen: MS--- ~mitrial type
34
5)pericardial effusion: enlargement of
both sides of the border
bodys position.
recumbent positionwidening of base of
the heart
erect position:~triangular shape
35
)dilatation of the aorta /ascending
aortic aneurysm:
widening if the dull area of first and second
intercostal space (with systolic pulsation)
3
Extacardial factors :
1)large pleural effusions and
pneumothorax to the healthy side
2)atelectasis /pleural pachynsis to the
affected
3)a large amount of ascites or big
abdominal tumor:
diaphragm elevatedtransverse
position left side enlargement
3
Ausclutation
3
1 Ausclutatoty valve areas
1)ausclutatory mitral area: apical area
2)ausclutatory pulmonary area:2 ICS-
LS
3)ausclutatory aortic area: 2 ICS-RS
4)second ausclutatory aortic area: 3
rd
ICS-LS-Erb area
5)tricuspid area :4,5 ICS-LS
3
40
2 Order:
MV---PV---AV1---AV2---%V
3 Contents : 1) rate 2)rhythm
3)heart sound 4)extra heart sound
5)murmurs )pericardial friction
sound
41
1)heart rate:
0~100bpm FM
child (3 years) 100bpm
tachycardia: normal adult 100bpm
child(3 years) 150bpm
bradycardia: HR 0 bpm
42
Ausclutation
heart rate:0-100bmp
43
2)cardiac rhythm:
`sinus arrythmia-affected by breath
`premature beat:
classification:atrial~ ventricular ~
junctional ~
frequently: bpm
occasionally: bpm
bigeminy trigeminy
44
`atrial fibrillation:
absolute irregular rhythm
S1 intensity inequality
Pulse deficit
seen:MS,CHD,hyperthyroidism,
PHD,DCM
45
Ausclutation
atrial Iibrillation
4
Cycle Nature Duration Site Mechanism
S1 Isovolumetric
contraction phase
Blunt
0.1
Apical
area
Closure oI the
MV and TV
S2 Isovolumetric
relaxation phase
Distinct
0.0
Basal
part
Closure oI the
AV and PV
S3 The end oI
ventricular rapid
Iilling phase
Weak
Blunt
0.04
aIter S2
0.12~0.1
Apex
(inner-
upper)
Ventricular
vibration
S4 The end oI
ventricular
diastolic phase
Weak
0.1
Iorward S1
Apex Atrium
contraction
3) cardiac sound
4
Ausclutation
content
cardiac sound
S1
S2
4
4
4)Abnormal cardiac sound
`Intensity:
position of the atrioventricular
valve
Ventricular contractility and
output
Valvular integrity and activity
50
S1: Accentuation:
MS
HRcontractility
fever,anemia,hyperthyroidism
complete AVB cannon sound
51
52
S1 attenuation :
MI
P-R interval enlong
AI
myocarditis,myopathy,MI,HF
inequality: af, IIIgAVB
53
54
S2---A2,P2
S2 ---pressure and flow of
blood
A2 : hypertensin, arterisclerosis
P2 : PHD,CoHD(L--R),LVF
S2 ---pressure flow
Seen:hypotension,AS/AL,PS/PI
55
5
`Quality
mono rhythm
pendular rhythm---embryocardia
`Splitting of heart sound
S1 splitting:
seen-RBBB, right heart failure
Ebetein malformation ,MS
LA myxoma
5
5
S2 splitting:
(1)physiological splitting :end of
inspiration
(2)general splitting : most commonly
seen: CRBBB, PS, MS,MI ,VSD
(3)fixed splitting :ASD
(4)paradoxical splitting(reversed
splitting) :pathological
seen: CLBBB ,AS, hypertension
5
0
5)extra cardiac sound
Diastolic period
1)gallop rhythm:
--protodiastolic gallop: S1+S2+S3 the third
sound gallop (sign of organic heart disease)
seen : HFAMI, severe myocarditis ,
myopathy etc.
-- late diastolic gallop: atrial gallop S1+S2+S4
seen : HBP ,HCM ,AS ,CHD
-- summation gallop: quadruple rhythm
seen:HF,cardiomyopathy
1
2
3
5) extra cardiac sound
Diastolic period
2)opening snap:MS
3)pericardial knock: constrictive
pericarditis
4)tumor plop: LA myxoma
4
5
Ausclutation
CONTENT
Tumor plop
Systolic period
(1)early systolic ejection sound(click)
pulmonary :pulmonary hypertension;
pulmonary artery dilatation
PS, ASD, VSD
Aortic: hypertension, aneurysm ,
AS, AI ,aorta constriction
(2)mid and late systolic click:
S1----mid0.08" late0.08"
seen: mitral prolapse
iatrogenic
(1)prosthetic valvular sound
(2)pacemaker
0
)cardiac murmurs
*Mechanism:
acceleration oI blood Ilow
stenosis oI valvular oriIice
or great vessles turbulent Ilow
valvular insuIIiciency vortices
abnormal passage
Ioreign body
dilatation oI vessles(aneurysm)
1
2
`characterization of murmur and
ausclutatory key points
(1)location:L3,4 -VSD L2,3-PDA
(2)transmission:
MI ---left axilla AS---neck
(3)phase: systolic murmurs
diastolic ~
continuous ~
biphasic ~
early,mid,late,whole
murmurs
3
(4)quality: blowing-MI
rumbling-MS
sighing--AI
machinery--PDA
(5)intensity :Levine grade classification
shape: crescendo---MS
decrescendo---AI
crescendo-decrescendo---AS
continuous---PDA
regular---MI
murmurs
4
() others:
body position:
MS--left lateral position
AI--sitting erected and forward
MI,%I,PVS--lie on one` back
Lie stand: HCM
breath:expiration--LV murmurs
inspiration --RV murmurs
valsalva--HCM
exercise: HR--murmurs
murmurs
5
clinical significance murmurs:
functional and organic
7)pericardial friction sound:
both phases , unaffected by
respiration .
seen: pericarditis ,
RHD ,AMI ,renal failure, SLE
` clinical significance of cardiac
murmurs
systolic murmurs
MVIunctional:exercise,Iever,anemia,pregnancy,
hyperthyroidism
relative:HBP,CHD,DCM,anemia
organicMI(RHD),mitral prolapse
` clinical significance of cardiac
murmurs
systolic murmurs
Aortic areaorganicAS
relativedilatation oI ascending aorta
0
` clinical significance of cardiac
murmurs
systolic murmurs
pulmonary physiology
relativeMSASD
organicPS
TVrelative RV enlarged
organic rare
1
` clinical significance of cardiac
murmurs
Diastolic murmurs
MV:organic:RHD(MS)
relative:AI(severe)
Austin Flint murmur
AV:AI
2
3
4
` clinical signiIicance oI cardiac
murmurs
Diastolic murmurs
PV:organic murmur is rare
PI(dilatation oI pulmonary artery)
MSP2 ---- Graham Steell murmur
TV:rare
5
` clinical signiIicance oI cardiac
murmurs
continuous murmurs
PDA
innocent murmur
'ascular examination
The second clinical hospital of CNU
pulse
pulse rate
pulse rhythm
tensions and state oI arterial
wall
intensity
pulse wave
pulse
pulse rate
Atrial Iibrillation and Irequent premature
beat stroke volume peripheral artery
no pulse pulse rate less than HR(pulse
deIicit)
pulse
pulse rhythm
pulse deIicit
bigeminal pulse,trigeminal pulse
dropped pulse
0
pulse
tensions and state oI arterial wall
Artery tension depending on blood
pressure (mainly SBP).
Judge state oI artery wall
1
pulse
intensity
Bownding pulse
seen:high Iever, hyperthyroidism, AI
Microsphygmia
seen:HF,AS and shock
2
pulse
pulse wave
normal pulse wave
composed oI upstrokeknocking wave
peak tide waveand downstroke
dicrotic wave
3
pulse
pulse wave
water hammer pulse seen:AI,hyperthyroidism,PDA,
severe anemia
pulse tardus seen:AS
dicrotic pulse seen:HCM
pulsus alternans seen:HBP,AMI,AI
paradoxical pulse
seen:cardiac tamponade,constrictive pericarditis
Pulseless
seen:serious shock, arteritis
4
blood pressure
method oI measurement
direct measurement method
indirect measurement method
5
blood pressure
standard
deIinition oI Bp level and classiIication(older than 1 years old)
classiIication SBP(mmHg) DBP(mmHg)
Ideal BP 120 0
Normal BP 130 5
High limit oI BP 130-13 5-
Grade 1mild 140-15 0-
subgroup
boundline hypertension 140-14 0-4
Grade 2moderate 10-1 100-10
Grade 3severe _ 10 _110
Simple systolic hypertension 140 0
subgroup
boundline systolic hypertension 140-14 0
blood pressure
clinical signiIicance oI BP changes
hypertensionhigher than 140/0mmHg Ior 3 times not in
the same day
hypotensionlower than 0/0-50mmHg
Shock,,MI,acute cardiac tamponade
obvious diIIerence between bilateral upper limbsmore than
10mmHg---arteritis,congenital artery malIormation
diIIerence between upper and lower limbslower limb BP is
20-40mmHg higher than upper one normally
pathological:constrictive aorta ,arteritis(chest-abdominal aorta)
change oI pulse BP
40mmHgwide pulse BP---hyperthyroidism,AI
30mmHgnarrow pulse BP---AS,pericardial eIIusion
blood pressure
dynamic BP monitoring
Average BP Ior 24h 130/0mmHg;
bright day 135/5mmHg;
night: 125/5mmHg
Peak:am10am,4pmpm
Vessel murmur and peripheral
vessel sign
venous murmur
jungular murmuris caused by the rapid
Ilow oI jungular vein into SVC
(superior vena cava)
Vessel murmur and peripheral
vessel sign
artery murmur
Continuous murmur in the lateral lobe oI
thyroid in the patient with hyperthyroidism
Systolic murmur in the upper abnormal region
or lumber region caused by stenosis oI renal
artery.
Arterio-venous Iistula
100
peripheral vessel sign
pistol shot sound
Seen:AI,hyperthyroidism,severe anemia
Durozier`s murmur
capillary pulsation
Vessel murmur and peripheral
vessel sign
101
%e main symptoms and
signs of common
diseases of circulatory
system
102
Causes:
RHD:rheumatic heart disease
CHD:congenital heart disease
Other reasons: senile retrograde
Mitrial stenosis
103
Symptoms:
cough;
hemoptysis;
dyspnea: dyspnea on exertion
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
pneumonedema
104
Signs:
Inspection :
mitrial Iace
Apex impulse may be displaced to the leIt
Palpation :diastolic thrill palpable over the
apical area
Percussion :
normal heart borderspear shape heart
105
Auscultation :
1)the Iirst sound (S1)
2)diastolic murmur :apical area; localized; mild
and late diastolic ;crescendo ;rumbling; more
clearly when the patient is lying on his leIt side.
3) opening snap may be auscultatory
4)accentuation oI second pulmonary sound (P2),
splitting
5)Graham Steel`s murmur (PV diastolic)
)Maybe atrial Iibrillation(late stage)
10
Mitral InsuIIiciency
RHD / non-RHD ; acute/chronic
Symptoms:
Iatigue,
palpitations,
dyspnea on exertion,
LeIt heart Iailure
10
Signs :
Inspection : apex beat is
displaced downwards and to the
leIt
10
Palpitation :
apical impulse IorceIul
Heaving apex impulse
Severe systolic thrill
Percussion :
the area oI dullness to leIt and
downwards
10
Auscultation :
1)S1 (attenuation)
2)murmurs: harsh;
pansystolic murmur;
blowing;
3/ grade
wide spread-transmitted to leIt axilla
leIt inIrascapular angle
110
Aortic Stenosis
Causes: RHD
Congenital
Senile retrograde
Symptoms :
palpitation ,dizziness, angina pectoris,
syncope, HF-dyspnea
111
Signs :
Inspection : apical impulse increase
Displaced to leIt and downwards
Palpation :
apex beat is elevated and IorceIul
systolic thrill can be palpated over aortic
auscultatory valve area
Pulse tardus
112
Percussion:
the area oI dullness is normal or to leIt and
downward
Auscultation :
1)murmur:
aortic auscultatory valve area systolic murmur
harsh ,ejection sound ,
3/ grade (thrill)
transmitted to neck
2)A2 ,reversed splitting
3)S4
113
Aortic InsuIIiciency
Causes:
RHD
Non-RHDcongenital
prolapse
syphilis aortitis
arteriosclerosis
endocarditis
acute/chronic
114
Symptoms :
palpitation, dizziness, LHF
Signs
Inspection :
apical impulse to leIt and downwards
Palpation :
apex impulse to leIt and downwards
Heaving apex impulse
115
Percussion :
the area oI cardiac dullness is enlarged
downwards and to the leIt;
the concave part oI the heart is not
enlarged (boot shape)
11
Auscultation :
1)speciIic murmur:
diastolic ;
sighing ;
aortic area;
heard clearly sitting erect and Iorward
2)Austin Flint murmur :relative MS
(rumbling mid-diastolic murmur)
11
Peripheral vascular signs
`head bobbing (Musset`s sign):nodding motion oI
the head with each systole;
*signs oI capillary pulsation;
*water hammer pulse;
*pistol shot sounds : esp. Femoral arteries;
*Duroziez`s murmur;
*Visible pulsation oI carotid arteries
11
Pericardial eIIusion
Causes:
inIective and non-inIective pericarditis
Symptoms :
pain over the pericardial region
Dyspnea, cough, Iever, lassitude
Shock
11
Signs :
Inspection :
diminution in strength oI the apex beat
or absence oI the apex beat ;
jugular venous enlargement
120
Palpation :
*diminution in strength oI the apex beat or the
apex beat palpated uneasily
*paradoxical pulse may be present
121
Percussion :
enlargement oI the cardiac dullness
bilaterally, changed with posture
122
Auscultation :
*pericardial Iriction sound
*HR,diminution oI intensity oI cardiac
sound (S1/S2)
*pericardial knock may be heard
123
*Large eIIusion:
Jugular varicosity
Liver enlargement
Paradoxical pulse
Pulse pressure
124
* Kussmaul sign:
deep inspiration jugular vein distension
*Ewart sign: leIt inIrascapular region
vocal Iremitus
dullness -- percussion
bronchovesicular breath sound--
auscultation
125
Heart Failure
Causes :
myopathy ; ventricular load
promote Iactors
Symptoms:
1 LHF: Iatigue, cough, Irothy sputum
dyspnea(on exertion orthopnea paroxysmal
nocturnal ~)
2 RHF: abdominal distension, oliguria, nausea, vomiting
12
Signs :
1 LHF:
*Inspection : tachypnea , cyanosis,
semireclining/sitting position
Acute pneumoedema:
Irothy sputum, hyperhidrosis
*Palpation :pulse alternans
*Percussion :
*Auscultation :diastolic gallop rhythm
P2
Fine rales, rhonchi
12
2 RHF:
*Inspection :Jugular distension
Pericardial cyanosis
Edema(pitting, pendulous)
*Palpation : liver enlargement, tenderness
Hepatojugular reIlux()
*Percussion :
pleural eIIusion (right side)
ascites
*Auscultation : RV diastolic gallop rhythm
TV systolic blowing murmurs
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Comparative Cardiac Imaging: A Case-based GuideD'EverandComparative Cardiac Imaging: A Case-based GuideJing Ping SunPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Examination FindingsDocument117 pagesCardiovascular Examination FindingsdrnadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology-1 ValvDocument34 pagesCardiology-1 ValvMahmoud RamadanPas encore d'évaluation
- Final PhysicalDocument409 pagesFinal PhysicalAbhishiktaAbhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Imaging of the Heart: Radiographic Findings of Normal Anatomy and Common PathologiesDocument51 pagesImaging of the Heart: Radiographic Findings of Normal Anatomy and Common PathologiesadystiPas encore d'évaluation
- CardiologyDocument52 pagesCardiologyusmani_nida1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chest XrayDocument31 pagesChest XrayBiscuits and milkPas encore d'évaluation
- CVS HX and ExDocument11 pagesCVS HX and Exjen262004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology DR Osama MahmoudDocument138 pagesCardiology DR Osama MahmoudIsmail Habib100% (4)
- Mitral RegurgitationDocument43 pagesMitral Regurgitationraissasafitry100% (1)
- Cardiology A. Woo PDFDocument52 pagesCardiology A. Woo PDFiuliPas encore d'évaluation
- 12. Circulatory system-朱Document71 pages12. Circulatory system-朱mirabel IvanaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument95 pagesPediatric Congenital Heart DiseaseShikya AbnasPas encore d'évaluation
- 20160509percussion and Auscultation of The HeartDocument108 pages20160509percussion and Auscultation of The HeartMar ClrPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Physical ExaminationDocument29 pagesCardiovascular Physical ExaminationannisPas encore d'évaluation
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument54 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseRommanah AzmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Severe Calcified Mitral Stenosis and Atrial Fibrillation Lead to Ischemic StrokeDocument10 pagesSevere Calcified Mitral Stenosis and Atrial Fibrillation Lead to Ischemic StrokeDarawan MirzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential Revision Notes for CardiologyDocument41 pagesEssential Revision Notes for CardiologyMudassar Waseem100% (1)
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument34 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseRebecca FeltonPas encore d'évaluation
- Flamm CXR InterpretationDocument56 pagesFlamm CXR InterpretationRyan TownsendPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Congenital Disease Types and PresentationsDocument27 pagesCardiac Congenital Disease Types and Presentationsnovitafitri123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Auscultation of HeartDocument92 pagesAuscultation of Heartsanjivdas100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Pericardial DiseaseDocument36 pagesPathophysiology of Pericardial DiseaseivaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Inferior Wall ST Elevation (STEMI)Document46 pagesInferior Wall ST Elevation (STEMI)Hendrik100% (1)
- Physical Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemDocument31 pagesPhysical Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemaagPas encore d'évaluation
- CardiologyDocument62 pagesCardiologysee yinPas encore d'évaluation
- CHF FC III Ec Mitral StenosisDocument36 pagesCHF FC III Ec Mitral Stenosisbroken18bear100% (1)
- Aortic StenosisDocument16 pagesAortic StenosisAbdur RaqibPas encore d'évaluation
- History Taking and Ce of Cardiac PatientsDocument89 pagesHistory Taking and Ce of Cardiac Patientsapi-3858544100% (1)
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument18 pagesAortic RegurgitationAbdur RaqibPas encore d'évaluation
- IM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitDocument12 pagesIM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitCzara DyPas encore d'évaluation
- CardioDocument106 pagesCardioPotato PceePas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument54 pagesUnderstanding Congenital Heart DiseaseYemata HailuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chest RadiologyDocument129 pagesChest RadiologyNadiya SafitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Cardiac SystemDocument51 pagesAssessment Cardiac Systemejarnmd100% (2)
- Лекция 7Document76 pagesЛекция 7ramtin malekshahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Pathology FINALDocument45 pagesCardiovascular Pathology FINALIanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument41 pagesCardiovascular Systemmoneer chancePas encore d'évaluation
- Heart DefectDocument41 pagesHeart Defectdevutty 123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Anatomy and Physiology PDFDocument100 pagesHeart Anatomy and Physiology PDFAndrés Menéndez Rojas100% (1)
- 1 Mitral Stenosis: InstructionDocument8 pages1 Mitral Stenosis: Instructionrashid.scribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2-Cardiovascular AssessmentDocument28 pagesLecture 2-Cardiovascular AssessmentSamuel Sebastian SirapanjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Valvular DiseasesDocument45 pagesValvular DiseasesKen WayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac physical exam guideDocument29 pagesCardiac physical exam guidedanradulescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To The Patient With A Heart MurmurDocument103 pagesApproach To The Patient With A Heart MurmurDarawan MirzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheumatic Heart Disease2Document61 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease2Puji Yunisyah RahayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument27 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseOwen J. WiesePas encore d'évaluation
- Atrial Septal Defect: Dr. AninditaDocument30 pagesAtrial Septal Defect: Dr. AninditaDadangNoviantoPas encore d'évaluation
- د.عبدالكريم العثمان VHD Murmur With AnssDocument110 pagesد.عبدالكريم العثمان VHD Murmur With AnssBashar KhaleelPas encore d'évaluation
- Aortic Regurgitation CaseDocument38 pagesAortic Regurgitation CaseIka MagfirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument49 pagesCardiovascular DiseasesSHAMENI VINODPas encore d'évaluation
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideD'EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Cardiology: A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and ManagementD'EverandFetal Cardiology: A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and ManagementPas encore d'évaluation
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartD'EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartPas encore d'évaluation
- Adult Congenital Heart Disease in Clinical PracticeD'EverandAdult Congenital Heart Disease in Clinical PracticeDoreen DeFaria YehPas encore d'évaluation
- Tiếp Cận Khối Vùng Chậu: Gv Hướng Dẫn: Ths. Bs. Lê Thị Hồng VânDocument135 pagesTiếp Cận Khối Vùng Chậu: Gv Hướng Dẫn: Ths. Bs. Lê Thị Hồng Vânwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Helping Shape Your Future: Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)Document12 pagesHelping Shape Your Future: Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)wakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tra Case s54, 1996Document3 pagesTra Case s54, 1996wakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- VATon Financial Services PDFDocument5 pagesVATon Financial Services PDFwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- FBTDocument4 pagesFBTwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tax TalkDocument29 pagesTax Talkwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Taxable Supplies - DR MartinDocument22 pagesTaxable Supplies - DR Martinwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- VAT On Imports and ExportsDocument18 pagesVAT On Imports and Exportswakemeup1430% (1)
- The Taxation of Employee Fringe BenefitsDocument28 pagesThe Taxation of Employee Fringe Benefitswakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2014, T302, Topic 3, Taxable Activity & Regn, 1 SlideDocument18 pages2014, T302, Topic 3, Taxable Activity & Regn, 1 Slidewakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Job Costing ExampleDocument34 pagesJob Costing Examplewakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Company Law BasicsDocument21 pagesCompany Law Basicsrong004100% (1)
- Case Study Cam LTDDocument9 pagesCase Study Cam LTDwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Supply VATDocument25 pagesSupply VATwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 12 TaxationDocument30 pagesIAS 12 Taxationwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Property Plant and Equipment ModelsDocument41 pagesChapter 6 Property Plant and Equipment ModelsHammad Ahmad77% (13)
- IAS 2 - InventoriesDocument42 pagesIAS 2 - Inventorieswakemeup143100% (1)
- Business StructuresDocument1 pageBusiness Structureswakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gripping Guide to IFRS Revenue RecognitionDocument26 pagesGripping Guide to IFRS Revenue Recognitionwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17 Provisions and Post Balance Sheet EventsDocument29 pagesChapter 17 Provisions and Post Balance Sheet EventsHammad Ahmad100% (1)
- IAS 40 - Investment PropertyDocument16 pagesIAS 40 - Investment Propertywakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hatfield Ethics of Tax LawyeringDocument63 pagesHatfield Ethics of Tax Lawyeringwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Financial AccountingDocument746 pagesFinancial Accountingwakemeup143100% (4)
- Kiwi Life Insurance DebriefDocument7 pagesKiwi Life Insurance Debriefwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of A Good Tax SystemDocument1 pagePrinciples of A Good Tax Systemwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ssac2006.Hf5691.Jm1.1 StudentDocument18 pagesSsac2006.Hf5691.Jm1.1 Studentwakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Indirect Tax 2013Document120 pagesIndirect Tax 2013wakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Government Regulation and The Legal Environment of BusinessDocument901 pagesGovernment Regulation and The Legal Environment of Businesswakemeup143100% (2)
- WestpacTrust Case WK 7Document26 pagesWestpacTrust Case WK 7wakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- FCOM111 2013 Trimester One Course OutlineDocument31 pagesFCOM111 2013 Trimester One Course Outlinewakemeup143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Write The Missing Words of The Verb To Be (Affirmative Form)Document1 pageWrite The Missing Words of The Verb To Be (Affirmative Form)Daa NnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Specification For Diesel Engines: AugustDocument19 pagesSpecification For Diesel Engines: AugustSerge RINAUDOPas encore d'évaluation
- Geller (LonginusRhetoric'sCure)Document27 pagesGeller (LonginusRhetoric'sCure)Miguel AntónioPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP - 3 DatabaseDocument5 pagesCHP - 3 DatabaseNway Nway Wint AungPas encore d'évaluation
- Homeroom Guidance - Activity For Module 1Document3 pagesHomeroom Guidance - Activity For Module 1Iceberg Lettuce0% (1)
- U1 Presantation-MAK 032021Document15 pagesU1 Presantation-MAK 032021MD ANAYET ALI KHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Teaching Edtpa Lesson Plan TemplateDocument7 pagesStudent Teaching Edtpa Lesson Plan Templateapi-3531253350% (1)
- Times Leader 04-10-2013Document37 pagesTimes Leader 04-10-2013The Times LeaderPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of Time Management To Senior High School Honor StudentsDocument7 pagesImportance of Time Management To Senior High School Honor StudentsBien LausaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fish Culture Y4Document136 pagesFish Culture Y4KèlǐsītǎnKǎPáng100% (1)
- Artificial AirwayDocument3 pagesArtificial AirwayKusum RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Clique Pen's Marketing StrategyDocument10 pagesClique Pen's Marketing StrategySAMBIT HALDER PGP 2018-20 BatchPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Ulangan Harian Smester 1 Kelas 8 SMP BAHASA INGGRISDocument59 pagesSoal Ulangan Harian Smester 1 Kelas 8 SMP BAHASA INGGRISsdn6waykhilauPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 WORD White Paper TemplateDocument4 pages2009 WORD White Paper Templateomegalpha777Pas encore d'évaluation
- People V Gona Phil 54 Phil 605Document1 pagePeople V Gona Phil 54 Phil 605Carly GracePas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam, Business EnglishDocument5 pagesFinal Exam, Business EnglishsubtleserpentPas encore d'évaluation
- HSG Anh 9 Thanh Thuy 2 (2018-2019) .Document8 pagesHSG Anh 9 Thanh Thuy 2 (2018-2019) .Huệ MẫnPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate of Compliance ATF F 5330 20Document2 pagesCertificate of Compliance ATF F 5330 20Jojo Aboyme CorcillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Thompson Industrial Products Inc Is A DiversifiedDocument4 pagesThompson Industrial Products Inc Is A DiversifiedKailash KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Something About UsDocument18 pagesSomething About UsFercho CarrascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Schumann Op15 No5 PsuDocument1 pageSchumann Op15 No5 PsuCedric TutosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ra 1425 Rizal LawDocument7 pagesRa 1425 Rizal LawJulie-Mar Valleramos LabacladoPas encore d'évaluation
- European Vacancy and Recruitment Report 2012Document200 pagesEuropean Vacancy and Recruitment Report 2012Joaquín Vicente Ramos RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Doña PerfectaDocument317 pagesDoña PerfectadracbullPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF To Sas DatasetsDocument6 pagesPDF To Sas DatasetsSiri KothaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Story Behind..: Dimas Budi Satria Wibisana Mario Alexander Industrial Engineering 5Document24 pagesA Story Behind..: Dimas Budi Satria Wibisana Mario Alexander Industrial Engineering 5Owais AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- International Waiver Attestation FormDocument1 pageInternational Waiver Attestation FormJiabao ZhengPas encore d'évaluation
- Metatron AustraliaDocument11 pagesMetatron AustraliaMetatron AustraliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors of Cloud ComputingDocument19 pagesFactors of Cloud ComputingAdarsh TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- ESS 4104 AssignmentDocument9 pagesESS 4104 AssignmentSamlall RabindranauthPas encore d'évaluation