Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Solution V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test CH 6 Work, Energy and The Power
Transféré par
Epic WinDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Solution V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test CH 6 Work, Energy and The Power
Transféré par
Epic WinDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power.
NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
In the multi-choice problems below, i.e. problems 1-9 write the answer clearly in the space provided under the problem as alternative: ________. In some of these problems you may need to explain or show the details of your solutions. All explanations and solutions to these problems must be written clearly under the problem in the space provided to. The solutions to the problems 10-16 will be written in a separate sheet provided. Problems 13, 14, and 15 are extremely important for the highest possible grade, MVG. You need at least an hour to solve these problems. Maximum score: 51/28/ G: 17 points VG: 34 points/ at least 9 VG points: MVG: 38 points/ at least 18 VG points; MVG-quality work Only the marked problems in the box below will be graded.
Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
1.
Frida moves her 2.0 kg physics book which lies on the desk 1.5 m in various directions as shown in the figures below. In which direction does the 1.5 m displacement of the book produce the largest gain in the potential energy?
[1/0]
a)
b)
c)
d) Answer: Alternative d. The potential energy gained in the vertical displacement is the largest. a) In the case of 0 -displacement, the change in the potential energy of the book is zero. b) In the case of 30 -displacement, the change in the potential energy of the book is: E PE = mgh = 2.0 9.82 1.5 sin 30 = 14.73 J 15 J c) In the case of 60 -displacement, the change in the potential energy of the book is: E PE = mgh = 2.0 9.82 1.5 sin 60 = 25.5 J d) In the case of 90 -displacement, the change in the potential energy of the book is: E PE = mgh = 2.0 9.82 1.5 = 29.46 J 30 J
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
2.
A truck moving at a constant speed of 90.0 km / h has 6.25 MJ kinetic energy. The mass of the truck is: [1/0] a) 20 ton 10 ton b) c) 30 ton d) 1000 kg Answer: Alternative a. 1000 Suggested solutions: v = 90.0 km / h = 90.0 m / s = 25 m / s 3600 2E 1 2 6.25 10 6 E KE = mv 2 m = 2KE = = 20000 kg = 20 ton 2 v 25 2
3.
The spring in a bathroom scale is compressed 5.00 cm when 55.0 kg zge climbs on it. What is the spring constant of the scales spring? [1/0] a) 10.8 kN / m b) 108 N / m c) 275 N m d) 11 N / m
Answer: Alternative a: k 10.8 kN / m Suggested solution: Data: m = 55.0 kg , x = 5.00 cm = 5.00 10 2 m ,
F = mg mg 55.0 9.82 N = 10802 N / m 10.8 kN / m = r r mg = kx k = x 5.00 10 2 m F = kx A constant force of 20.0 kN is required to maintain the speed of a 1200 kg at a constant value of 72. km / h . The work done by the force in moving the car 5.00 km is: [1/0] 5 a) 4.0 10 J b) 6.0 10 6 J c) 100 10 6 J d) 1440 kJ Why? Show the details of your calculations: [0/1] 6 Answer: Alternative c: W = 100 10 J = 100 MJ Suggested solution: Data: F = 20.0 kN = 20.0 10 3 N , x = 5.00 km = 5.00 10 3 m , m = 1200 kg , 1000 v = 72. km / h = 72. m / s = 20 m / s 3600 r W = F x = 20.0 10 3 5.0 10 3 = 100 10 6 J = 100 MJ 4.
)(
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes
Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
5.
Calculate the maximum height to which a 20. kW motor may lift an object of minimum mass 5000 kg in 25. s [1/0] a) 2.5 m b) 5.0 m c) 7.5 m d) 10. m Why? Explain and show the details of your calculations: [0/2] Answer: Alternative d: h 10. m Suggested solution: Data: 20. kW , m = 5000 kg , h = ? , t = 25. s
P= W mgh P t 20 10 3 25 = mgh = P t h = = = 10.2 m 10. m t t mg 5000 9.82
Adam exerts an average force of 700.0 N on a rope to lift 65.0 kg box a vertical distance of 4.00 m up. The gravitational potential energy gained by the 65.0 kg box is [1/0] a) Exactly equal to the work done by Adam. b) 247 J more than the work done by Adam. c) 247 J less than the work done by Adam. d) 638 N Why? Show the details of your calculations: [0/1] Answer: Alternative c: EPE W 247 J Suggested solution: Data: F = 700.0 N , h = 4.00 m , m = 65.0 kg The potential energy gained by the box is: E PE = mgh = 65.0 9.82 4.00 = 2553.2 J 2550 J The work done by Adam is: r r W = F x = 700.0 4.00 = 2800 J W E PE = 2800 J 2553.2 J = 246.8 J 247 J Answer: EPE W 247 J
6.
Isabelle who is 62.0 kg climbs 6.00 m up a rope in 5.00 s . What is Isabelles power output? Why? Show your calculations. [1/0] 3653 J a) b) 731 W 74.4 W c) d) 18.3 kW Why? Show your calculations. [0/1] Answer: Alternative b: P 731 W Suggested solution: Data: m = 62.0 kg , h = 6.00 m , t = 5.00 s W = mgh = 62.0 9.82 6.0 = 3653 J 3.65 kJ W 3653 J P= = = 730.6 W 731 W P 731 W t 5.00 s
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes Sjdalsgymnasiet
7.
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
8.
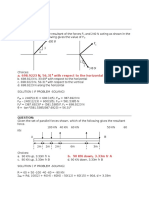
Which one of the figures below best represents the potential energy of a freely falling object near the surface of the Earth? [1/0]
Why? Explain [0/1] Answer: Alternative b: Potential energy of a falling object Suggested solution: The 5000 potential energy of the system decreases as the 4000 objects height from the ground is decreasing, i.e. as 3000 the object is getting closer and closer to the ground. 2000 The loss in the gravitational energy is the gain in the 1000 kinetic energy of the 0 system, assuming that there 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 is not air resistant and Displacement [m] friction. E PE = mgh0 mgh = mg (h0 h ) This is a linear equation with a negative slope, and y-intercept mgh0 . According to the figure, the object is released from the height of h0 = 100 m . As the reference level, we may take the potential energy of the lowest point, i.e. the potential energy on the surface of the Earth is taken equal to zero.
Potential Energy [J]
9.
Which graph best represent the elastic potential energy stored in a spring as a function of its elongation (or compression)? [1/0]
Elastic potential energy Elastic Potential Energy [J] 3,5 3,0 2,5 2,0 1,5 1,0 0,5 0,0 0 0,05 0,1 0,15 0,2 0,25 elongation x [m]
Serie1 Serie2 Serie3 Serie4
Explain. [0/1] Answer: Alternative c. Suggested solution: The Elastic potential energy is a quadratic function of the displacement 1 from the equilibrium (elongation or compression) x : E PE = kx 2 2
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes
Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
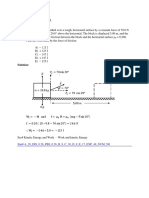
10. The x component of the force on an object varies as shown below. Determine the work done by the force to move the object i from x = 0.0 to x = 30.0 m , [3/0] ii from x = 0.0 to x = 100.0 m . [0/3]
400 300 200 100 F [N] 0 -100 0 -200 -300 -400 -500 X [m] 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Answer: W0a 30 = 6.0 kJ ; W0a100 = 1500 J Suggested solution: The work done by the force is the area under the curve of (x-component of the) force vs displacement between the desired boundaries: I. The work done by the force to move the object from x = 0.0 to x = 30.0 m : is the area under the curve from x = 0.0 to x = 30.0 m :: 1 W0a30 = (20 )(300 ) + (30 20 )(300 ) = 3000 + 3000 = 6000 J = 6.0 kJ 2 Answer: W0a 30 = 6.0 kJ
II.
The work done by the force to move the object from x = 0.0 to x = 100.0 m is the area under the curve from x = 0.0 to x = 100.0 m : 1 1 W0a100 = W0a30 + W30a100 = 7000 + (40 30 )(300 ) + (100 50 )( 400 ) J 2 2 W0a100 = 7000 + 1500 10000 = 1500 J Answer: W0a100 = 1500 J Note that the area under the x-axis is negative. Note also the total energy is negative. The total negative work indicates that the work is don by (and not on) the system.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes
Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
11. Martin driving a car at 90 km / h suddenly sees a rabbit jumping to the middle of the road about 100 m away in front of the car. Naturally, he does not want to hit the rabbit and cause a possible damage to himself as well as the car. He knows his physics and therefore, he decides not to take a sudden break. He decides to reduce the speed of the car to a level which he can be completely in control, say 18 km / h . He knows the maximum coefficient of friction between the tires and the road is 0.70 . Calculate the minimum coefficient of friction between the tires and the road such that Martin can successfully reduce the speed of the car to the desired value of 18 km / h within 60 m . . [1/3] 2 2 v v2 Answer: = 1 ; = 0.51 2 g x Suggested solution: 1000 Data: v0 = 90 km / h = 90 m / s = 25 m / s , max = 0.70 , 3600 1000 v = 18 km / h = 18 m / s = 5.0 m / s , x = 60 m 3600 Problem: = ? The initial energy of Martins car is just its kinetic energy. This energy will be converted to heat as he makes the brake and reduces the speed of the car. Therefore, part of the initial kinetic energy of the car must be converted to the work done against friction: E K 1 = E K 2 + W f , W = f f x = mg x
1 2 1 2 mv1 = mv2 + mg x / / / 2 2 2 v12 v2 = 2 g x
2 v12 v2 2 g x
252 52 = = 0.51 2 9.8 60 Answer: Martin is able to reduce the speed of the car by softly breaking so that the minimum coefficient of friction in the process is = 0.51 . This is quite possible because it is less than the maximum value of the coefficient of friction, max = 0.70 .
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes
Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
12. In height jumping the kinetic energy of the athlete is transformed into the gravitational potential energy. The world record of high jumping without the aid of a pole for females is at the present 250 cm . Estimate the minimum kinetic energy and speed required by 65.0 kg Frida whose center of mass is 98.0 cm above the ground and whishes to break the world record of high jumping. The safety requirement requires that the athlete must cross the bar with a minimum speed of 0.650 m / s ? The gravitation acceleration is 9.82 m / s 2 . [1/3] Answer: Fridas minimum take off speed must be: v1 = 5.50 m / s = 19.8 km / h Suggested solutions: Data: m = 65.0 kg , h1 = 98.0 cm = 0.980 m , h2 = 250 cm = 2.50 m , g = 9.82 m / s 2 Problem: v1 = ? if v2 = 0.650 m / s Ignoring all dissipative forces and using conservation of energy we may state: Etot1 = Etot 2 E P1 + E K 1 = E P 2 + E K 2 1 1 2 mgh1 + mv12 = mgh2 + mv2 / / / / 2 2 2 2 gh1 + v12 = 2 gh2 + v2 2 v12 = 2 g (h2 h1 ) + v2
2 v1 = 2 g (h2 h1 ) + v2
v1 = 2 9.82(2.50 0.98) + 0.652 m / s v1 5.50 m / s v1 = 5.50 m / s = 5.50 3.6 km / h = 19.81 km / h Answer: Fridas minimum take off speed must be: v1 5.50 m / s = 19.8 km / h . 1 1 2 EKEi = mv12 = (65.0 )(5.5022 ) J 983 J 2 2 Fridas minimum initial kinetic energy is therefore: EKEi 983 J Clearly, the initial angle of the take off is important. The best result may be achieved by realizing that, it is sufficient with only 0.650 m / s in the horizontal direction. This would mean that the takeoff angle may be calculated as:
v0 x 0.560 = cos 1 84.2 5.50 v0 It is not so easy to achieve this angle, so in action, the smaller angle is compensated by a higher initial speed at the takeoff.
= cos 1
At the aspect assessment of your work with exercise 13-15 the teacher will consider the depth of understanding of physics you have demonstrated how well you have carried through the task how well you have explained your work and motivated your conclusions how well you have accounted for your work.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes
Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
13. In an early test flights for the space shuttle using a glider of mass 1000 kg including the pilot, after a horizontal launch at 500 km / h at a height of 3500 m , the glider eventually landed at a speed of 200 km / h a) What would its landing speed have been in the absence of air resistance? b) What was the average force of air resistance if it came at a constant glide of 10 to the Earth? [2/4/] Suggested solutions: 1000 // 1250 m = 1000 kg , v0 x = 500 km / h = 500 m/s = 140 m / s , h = 3500 m , // 3600 9 // 1000 v = 200 km / h = 200 m / s = 55.6 m / s 56 m / s // 3600 a) Answer: In the absence of air resistance, the landing speed of the glider would be v f 297 m / s almost sonic instead of much smaller speed of
v = 200 km / h = 67 m / s Using conservation of energy, and taking the potential energy of the ground as the reference potential energy zero: 0 1 1 EPi + EKi = E Pf + EKf mgh + mvi2 = mv 2 v 2 = 2 gh + vi2 v f = 2 gh + vi2 / / / / f f 2 2
1250 v f = 2 9.82 3500 + Answer: v f 297 m / s 9 b) Answer: The average force of air resistance is FR 2.1 kN if it came at a constant glide of 10 to the Earth: First method: The very large difference between v f 297 m / s and v = 67 m / s is due to the dissipative force of the air resistance. If it is assumed that the glide came at a constant glide of 10 to the Earth 3500 m h h 20156 m d 20156 m h = 3500 m x sin 10 = d = ,d= sin 10 d sin 10 v f 297 m / s , d 20156 m , v 56 m / s , FR = ?
d 20156 m h = 3500 m
10
m v2 v2 1 2 1 2 f mv f mv = FR d FR = 2 2 2d 2 2 1000 (296.7 ) (55.6) Answer: FR 2.1 kN FR = = 2107 N 2.1 kN 2 20156 Second method: At the presence of air resistance, the initial mechanical energy is converted to the final kinetic energy and the work done against the air resistance: 1 1 mgh + mvi2 = mv 2 + FR d 2mgh + mvi2 mv 2 = 2 FR d f f 2 2 2 2 9.82 3500 + 1250 (55.6)2 1000 m 2 gh + vi2 v 2 9 f = 2107 N FR = FR = 2 20156 2d
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes
Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
14. A block of mass m is attached to a light spring of force constant k on a plane surface. The spring is elongated a distance A from its equilibrium and then released. a) If the block comes to rest when it reaches to its equilibrium position, calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction, k , between the block and the plane surface. 2 b) Calculate the velocity of the block when it is A from its equilibrium position. 3 c) If the surface of the block is oiled it is found that its coefficient of friction is reduced to 25% of its normal value. If now block is compressed to a distance A from equilibrium, how far will it ravel before it stops and turns back in its first period of oscillation? [2/4/]
A
Data m , k , A ; k = ? from its equilibrium and then released. kA a) Answer: The coefficient of kinetic friction is k = . 2mg The total energy of the system on this case is totally used up by the work done against the friction force: 1 k A2 = f f A = k mg A 2 kA k A = 2 k mg Answer: k = 2mg b) Answer: The block is moving at v =
2
2k 2 A at x = A from the equilibrium. 3 9m
1 1 2 kA 1 1 in the equation results in: k A2 = k A + k mg A + mv 2 Replacing k = 2 2 3 2mg 3 2 1 1 4 kA A 1 k A2 = k A2 + mg + mv 2 / / / / 2 2 9 2mg 3 2 7 4 1 4 + 3 2 2 2 k A2 = k A2 + + mv 2 = k A2 + mv = k A + mv 9 9 3 9 7 2 2k mv 2 = k A2 k A2 = k A2 v 2 = A2 9 9 9m Answer: v =
2k A 9m
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes
Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
c) Answer: If the surface of the block is oiled it, its coefficient of friction is reduced to 25% kA of its normal value, knew = 0.25k = . If the block is now compressed to a distance 8mg 3A A from equilibrium, it will travel x = = .75 A beyond the equilibrium, before it stops 4 and turns back. kA kA Data: knew = 0.25k = using k = . 8mg 2mg We may assume that the block will be stretched beyond its equilibrium point by x m . Conservation of energy requires that: kA 1 1 k A2 = k x 2 + knewmg ( A + x ) , using knew = 0.25k = 2 2 8mg kA 1 1 mg ( A + x ) k A2 = k x 2 + // 2 2 8mg // A A2 x+ A2 = 0 4 4 A 3 A2 x2 + x =0 4 4 x2 +
3A 3A =0 x= 3A x (x + A) x = 0 4 Answer: 4 4 x + A = 0 x = A 3A x= = 0.75 A 4 This is the most expected logical result. If the coefficient of the friction is reduced to 25% of its normal value, due to the fact that by the normal friction it would use up all of its original potential energy, now only 25% of the total mechanical energy is used up by the friction and the rest, i.e. 75% is left that would by sufficient to an expansion of only 75% of the original amplitude.
Second method: Conceptual solution: If the coefficient of the friction is reduced to 25% of its normal value, due to the fact that by the normal friction it would use up all of its original potential energy, now only 25% of the total mechanical energy is used up by the friction and the rest, i.e. 75% is left that would by sufficient to an expansion of only 75% of the original amplitude.
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes
Sjdalsgymnasiet
Suggested Solutions V1 Ch6FyANVC06 Test Ch 6 Work, energy and the power. NV-College; Sjdalsgymnasiet
15. A car of mass 1200 kg may accelerate from rest to 90.0 km / h in 10.0 s . Assume that normal force on each tire is 25% of the weight of the car, and that only the two rear tires provide the acceleration force. a) Calculate the minimum coefficient of friction between the rear tires and the road. b) Calculate the average power delivered to the car by the engine. [2/4/] Suggested solutions: Data: m = 1200 kg , v0 = 90 km / h = 90 FN _ tire = 0.25mg 1000 m / s = 25 m / s , t = 10.0 s , 3600
2a = 0.51 . g v v0 F = ma 2 m / g = ma = 2 a = t [1/1] / m g g 2 F = FN = g 2 2(v v0 ) 2(25 0 ) Answer: = [1/0] = = 0.51 gt 9.82 10 Second method: The Energy Method. 2 v 2 v0 v2 v2 v2 2v m 1 1 2 = = / g x = mv 2 mv0 = = = / / 2 2 2 gx gx g v t g v t g t 2 2 mv b) Ans.: The average power delivered to the car by the engine P = = 37.5 kW 2t First method: 1 2 mv 0 W EKE 2 mv 2 mv 2 [1/1] P = F v = ma v P = = = = P= t t t 2t 2t 2 2 1200 25 mv [1/0] Answer: P = P= = 37500 W = 37.5 kW = 37.5 kW 2 10 2t Second method: [0/1] P = F v = ma v v v0 25 0 v + v0 25 + 0 [1/0] a= = = 2 .5 m / s 2 v= = = 12.5 m / s 2 2 t 10 F = ma = 1200 2.5 = 3000 N
a) Answer: Minimum coefficient of friction =
P = 3000 12.5 W = 37500 W = 37.5 kW
[0/1]
Answer: P =
mv 2 = 37.5 kW 2t
Note that the motor must be able to provide a much larger power, namely Pmax = 3000 25 W = 75000 W = 75.0 kW which is the power needed to accelerated the car to its maximum speed of v0 = 90 km / h = 25 m / s . Pmax = 75.0 kW Third method: E F x P= = = F v = 3000 12.5 W = 37500 W = 37.5 kW t t
behzad.massoumzadeh@huddinge.se Not for sale. Free to use for educational purposes Sjdalsgymnasiet
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Solution Manual Linear Circuits Analysis - 2e, DecarloDocument945 pagesSolution Manual Linear Circuits Analysis - 2e, DecarloJorge Silva Velez75% (4)
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)D'EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - Work and Energy: Application of Work-Energy Method: Constant Forces (ProblemDocument8 pagesChapter 6 - Work and Energy: Application of Work-Energy Method: Constant Forces (ProblemRiver RunPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhodes Solutions Ch9Document9 pagesRhodes Solutions Ch9Joson ChaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tes 3 Practice Test-SolutionsDocument9 pagesTes 3 Practice Test-Solutionsdavidchoikekekek100% (1)
- Double Integration MethodDocument35 pagesDouble Integration MethodPuma Tychingco Rañeses96% (27)
- Aircraft Dispatcher Sample Test QuestionsDocument11 pagesAircraft Dispatcher Sample Test Questionsrashashwin100% (1)
- IFR Flight PlanningDocument34 pagesIFR Flight PlanningcarlosvistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerodynamic Forces and MomentsDocument21 pagesAerodynamic Forces and Momentsاحمد عبد الله طنطاوى عبد الرحمن طنطاوى، 3615Pas encore d'évaluation
- A109E Rotorcraft Flight ManualDocument1 418 pagesA109E Rotorcraft Flight Manualalex castro100% (1)
- Solution V2 Ch6FyANVC08 Test CH 6 Work, Energy and The PowerDocument10 pagesSolution V2 Ch6FyANVC08 Test CH 6 Work, Energy and The PowerEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- V1 Suggested Solution FyANVCO09 Ch6Document7 pagesV1 Suggested Solution FyANVCO09 Ch6Epic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Warning Warning:: There Are More Than One Versions of The TestDocument10 pagesWarning Warning:: There Are More Than One Versions of The TestEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Warning Warning:: There Are More Than One Versions of The TestDocument10 pagesWarning Warning:: There Are More Than One Versions of The TestEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- ContinueDocument7 pagesContinuekenfackPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Complementary Test On Electricity and Magnetism CH 16-19, & 20Document7 pagesPhysics B: Fybnvc08 G-Level Complementary Test On Electricity and Magnetism CH 16-19, & 20Epic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 P1 Worked Solutions: EtontuitioncentreDocument7 pages2021 P1 Worked Solutions: EtontuitioncentrealacerrrrPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 8Document23 pagesChap 8Ryan MyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Examples - PhysicsDocument8 pagesExamples - Physicslaila1001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 71 TWHFW 1 Semester 2013-14: Recitation Quiz 8 Lecturer: FIN de VeraDocument3 pagesPhysics 71 TWHFW 1 Semester 2013-14: Recitation Quiz 8 Lecturer: FIN de VeraChai BagasalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Directions Please Write Your Name On All of The Papers On Your Table, NOW!Document5 pagesDirections Please Write Your Name On All of The Papers On Your Table, NOW!Epic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Physics Concepts of Charge and CurrentDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Physics Concepts of Charge and CurrentMarie Joy EngayPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 9 Work Energy Power Solved Numerical Questions - 7Document4 pagesClass 9 Work Energy Power Solved Numerical Questions - 7tamishraza26Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9702 w12 QP 12Document28 pages9702 w12 QP 12Agus Ahmadi IrvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Problem Set 2Document7 pagesChapter 6 Problem Set 2Vyomika TewaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Test FyBNVC07 CH 5 Circular MotionDocument6 pagesSolution Test FyBNVC07 CH 5 Circular MotionEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- GEAS Solving - CompiledDocument22 pagesGEAS Solving - Compiledcajaro100% (1)
- Phy11 Reviewer FinalsDocument32 pagesPhy11 Reviewer FinalsasaadadadsaddPas encore d'évaluation
- Maximum Range of ProjectileDocument31 pagesMaximum Range of ProjectileOmprakash Dhaka100% (2)
- Homework Problems on Forces, Motion and EnergyDocument7 pagesHomework Problems on Forces, Motion and EnergyQuinnNgo100% (1)
- Phys1012 T102 ZeroDocument17 pagesPhys1012 T102 ZeroYohana Christyn SinagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics exam questions cover forces, motion, and gravityDocument8 pagesPhysics exam questions cover forces, motion, and gravitySamantha GornickPas encore d'évaluation
- H.W 9 AnsDocument16 pagesH.W 9 AnsJudah Okeleye100% (1)
- Physics Cumulative Test # 1 - SolutionDocument6 pagesPhysics Cumulative Test # 1 - SolutionTalha Syed NaqviPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument28 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelJazzPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 Board Part 1Document20 pages2018 Board Part 1Ira MejiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Rotors - SolutionDocument25 pagesTutorial Rotors - SolutionMuntoiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Exam - SolnsDocument5 pagesPractice Exam - SolnsbevinjPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 06 SolnDocument19 pagesHW 06 SolnKristin Dikiciyan100% (1)
- Work Power EnergyDocument27 pagesWork Power EnergyElvie CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- ESAS Physics QuestionsDocument22 pagesESAS Physics QuestionsErika Mae OrlinaPas encore d'évaluation
- R A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis SDocument945 pagesR A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis STommyc102477% (13)
- Physics B Projectile, Circular Motion, Energy and Linear MomentumDocument14 pagesPhysics B Projectile, Circular Motion, Energy and Linear MomentumEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Conservation of Energy Problems and SolutionsDocument22 pagesConservation of Energy Problems and Solutionsmukesh3021Pas encore d'évaluation
- Example: Given: A 0.5 KG Ball of Negligible SizeDocument9 pagesExample: Given: A 0.5 KG Ball of Negligible SizegPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics: Chapter 8Document22 pagesPhysics: Chapter 8Jessica NicholsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Work and Energy: Younes SinaDocument49 pagesWork and Energy: Younes SinayounessinaPas encore d'évaluation
- VG2 62FyA 1D MotionDocument1 pageVG2 62FyA 1D MotionEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Work and EnergyDocument21 pagesWork and Energyapi-3722337100% (1)
- Work and Kinetic Energy Concepts ExplainedDocument28 pagesWork and Kinetic Energy Concepts Explainedملهم العبدالسلامةPas encore d'évaluation
- CH19Document79 pagesCH19Diego Orlando Garzón VPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Year Physics NumerDocument45 pages2nd Year Physics NumerMoin YaqoobPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculate Energy Used by EV on 20km TripDocument9 pagesCalculate Energy Used by EV on 20km Tripanishkhadgi4officialatscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 111 Homework Solution #5Document20 pagesPhysics 111 Homework Solution #5jhunPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 22 Solutions: e W Q Q W Q WDocument32 pagesChapter 22 Solutions: e W Q Q W Q Wysrra94Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digiclass - Mohammad Hussien C. Malna - Chapter 1-3 ActivitiesDocument21 pagesDigiclass - Mohammad Hussien C. Malna - Chapter 1-3 ActivitiesRahima AloyodanPas encore d'évaluation
- FAP0025 Tutorial Solutions PDFDocument25 pagesFAP0025 Tutorial Solutions PDFRuben BenjaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsD'EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2D'EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Mathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLDocument6 pagesMathematics and The Mind: Nelson/papers - HTMLEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- FogDocument5 pagesFogEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- InequalitiesDocument192 pagesInequalitiesEpic Win100% (2)
- Warning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsDocument12 pagesWarning Signs of A Possible Collapse of Contemporary MathematicsEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- FaithDocument8 pagesFaithceceph354Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nelson BibDocument5 pagesNelson BibEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- RomeDocument7 pagesRomeEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsDocument18 pagesThe Mystery of Stochastic MechanicsEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Syntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocument7 pagesSyntax and Semantics: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- IstDocument34 pagesIstEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- OutlineDocument7 pagesOutlineEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- ElemDocument101 pagesElemEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Ram RecDocument8 pagesRam RecEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- New 18Document5 pagesNew 18Epic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Intuitionism: WWW - Math.princeton - Edu Nelson Papers - HTMLEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- HopeDocument4 pagesHopeEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Zhang TDocument4 pagesZhang TEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Hilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityDocument27 pagesHilbert's Mistake: Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton UniversityEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- J. P. MayDocument17 pagesJ. P. MayEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Zhang QDocument15 pagesZhang QEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Edward NelsonDocument1 pageEdward NelsonEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- EDocument9 pagesEEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Set TheoryDocument26 pagesInternal Set TheoryEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- WoolfDocument9 pagesWoolfEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- WeinerDocument6 pagesWeinerEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- J-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationDocument9 pagesJ-Spectra For A Quotient Group J of G. That Context Gives An Interesting SituationEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Probability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionDocument17 pagesProbability Theory: 1 Heuristic IntroductionEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- WaddleDocument10 pagesWaddleEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- WalijiDocument6 pagesWalijiEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- VParticipantsDocument1 pageVParticipantsEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Cargo Logistics Strategy PaperDocument132 pagesAir Cargo Logistics Strategy Paperamal_millstone07@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- LEVEL III - ATA 23 CommunicationsDocument50 pagesLEVEL III - ATA 23 CommunicationswagdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hermann OberthDocument4 pagesHermann Oberth田原 一樹Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toward Space-Based Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument21 pagesToward Space-Based Wireless Sensor NetworksAhmed El ShafiePas encore d'évaluation
- Ice Protection EnableDocument7 pagesIce Protection EnableMonindika WarshakoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Progress in Aerospace Sciences: Yicheng Sun, Howard SmithDocument27 pagesProgress in Aerospace Sciences: Yicheng Sun, Howard SmithArturo PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cases Exclusivly Engineering Ethics (PE 2)Document102 pagesCases Exclusivly Engineering Ethics (PE 2)Muhammad Aslam MusyafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rpas Cdti Aena 26novDocument23 pagesRpas Cdti Aena 26novgestesoPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Drag ForcesDocument5 pagesNon Drag ForcesRelining MineralsPas encore d'évaluation
- KAMAN ToolingDocument33 pagesKAMAN ToolingbashirsbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hungarian Aeronautical Industry 2014Document44 pagesHungarian Aeronautical Industry 2014Anonymous KaoLHAktPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexural Analysis of Balsa Core Sandwich Composite - Failure MechaDocument104 pagesFlexural Analysis of Balsa Core Sandwich Composite - Failure MechaManjinderSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 04Document46 pagesCH 04AlonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Physics: - Projectile MotionDocument12 pagesAP Physics: - Projectile MotionsuperultimateamazingPas encore d'évaluation
- DSN Doc 892 000004 A StatmanDocument40 pagesDSN Doc 892 000004 A StatmanprasobhPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Chart 2011 Low Copy 8371994ad16feDocument1 pageSuper Chart 2011 Low Copy 8371994ad16feapi-172854854Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Turbo-Expander Case History - EmersonDocument11 pages6 Turbo-Expander Case History - EmersonxinghustPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceasiom TutorialDocument23 pagesCeasiom TutorialsovsepPas encore d'évaluation
- 212MM212MMCH07Document8 pages212MM212MMCH07cristianPas encore d'évaluation
- CMM 3-1527 - Main Wheel - (32-45-45) - Cessna 525Document91 pagesCMM 3-1527 - Main Wheel - (32-45-45) - Cessna 525Lucas AlvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cessna 208 (B) Caravan I T.T.R.Document7 pagesCessna 208 (B) Caravan I T.T.R.Junior Mebude SimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Army CH-47D Operators Manual PDFDocument717 pagesArmy CH-47D Operators Manual PDFDave91Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Stress Analysis of Naval Trainer NLGBDocument8 pagesDesign and Stress Analysis of Naval Trainer NLGBAnonymous ZnmWTVVvvPas encore d'évaluation
- UAV - Ch1Document61 pagesUAV - Ch1jayaramjaya1996Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ac8401 Aerodynamics QPDocument3 pagesAc8401 Aerodynamics QPPrasanth SamyPas encore d'évaluation