Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Phy Test
Transféré par
Leong KcDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Phy Test
Transféré par
Leong KcDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1.
The first ionisation energy down a group decreases. Why? A. ? The electrons are closer to the nucleus.
B. ? The electrons are furthur away from the nucleus and there is more shielding from the other electrons. C. ? It doesn't decrease, it increases becuase of the increased positive charge in the nucleus. D. ? Because energy is lost as the atoms get bigger.
2.
Why is the second electron affinity always endothermic? A. ? Because the repulsions charges of the two negative electrons need to be over come. B. C. D. ? ? ? Because the first electron affinity is exothermic. Because it needs to overcome the positive charge in the nucleus. Because electrons are actually protons but smaller.
3.
Define relative atomic mass. A. ? electrons. B. ? carbon. The mass of all the protons in the nucleus + the mass of all the The mass of an isotope of that element divided by the mass of
C. ? The mass of an average atom of carbon-12, taking into account all its isotopes. D. ? The ratio of the mass of an average atom of an element to the 1/12 of the mass of carbon-12.
4.
What is the electron configuration of Na? (atomic number 11) A. B. ? ? 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s4 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
C. D.
? ?
s2 s2 p6 s1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
5.
Define an isotope. A. ? A isotope a different atom of the same element. It has the same number of electrons but different numbers of protons. B. ? An isotope is a larger version of the original atom.
C. ? An isotope is a different atom of the same elemnet. It has the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons. D. ? An isotope is a different atom of the same element it the same number protons and neutrons but different number electrons.
6.
Sodium is in group one. What does this say about it's atomic structure? A. B. C. D. ? ? ? ? It has one orbital. It will become a 1- ion. It has one electron in its outer shell. It has a diameter of 1cm.
7.
What is the difference between relative atomic mass and relative isotopic mass? A. B. ? ? Isotopic masses have more neutrons and therefore are more. Nothing.
C. ? Relative isotopic mass takes into account all the isotopes of that element while relative atomic mass just looks at one isotope of that element. D. ? Relative atomic mass takes into account all the isotopes of that element while relative isotopic mass just looks at one isotope of that element.
1.
What is an Atom made from? A. B. C. D. ? ? ? ? Cheese?? Protons and electrons Protons, electrons and neutrons Gas
2.
What is the relative charge of an atom? A. B. C. ? ? ? 1 2 -1
3.
What is an isotope??? A. ? It has a different number of electrons but the same numbr of neutrons B. C. ? ? It has the same number of protons and electrons It has a different number of neutrons and protons
D. ? It has the same number of protons but a different number of electrons
4. What happens to the Atoms when they enter the Mass spectrometer? A. ? Vaporisation Acceleration Deflection Ionisation Detection
B. ? Vaporisation Ionisation Acceleration Deflection Detection C. ? Ionisation Detection Deflection Acceleration Vaporisation D. ? vaporisation Acceleration Ionisation Deflection Detection
5.
What is an atomic orbital? A. ? A region in the space around a nucleus in which there is a high probability of finding an electron B. C. D. ? ? ? The place where the electrons go. An s, a p or a d. They come in different shapes and sizes.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Building Integrated Photovoltaics - p021 PDFDocument1 pageBuilding Integrated Photovoltaics - p021 PDFarunghandwalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2023Document28 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2023Rohee TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- 3.2 Properties of Solids StudentDocument7 pages3.2 Properties of Solids StudentZachary Daniel UyPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Solid State Chemistry - EPMDocument8 pagesSolid State Chemistry - EPMjahidul islamPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Master Card - Coordination CompoundsDocument2 pagesMaster Card - Coordination CompoundsgudiPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Particle in One Dimensional Box Reviewed 2 FinalDocument9 pagesParticle in One Dimensional Box Reviewed 2 FinalSagar Meitei SoraishamPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- DetectorsDocument282 pagesDetectorsMoch. Syamsul AlamsyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- CrystallographyDocument17 pagesCrystallographyDolih GozaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument2 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsKing AshokPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Anomalous Zeeman EffectDocument2 pagesAnomalous Zeeman EffectSantiago Cifuentes AlmanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect01 PDFDocument75 pagesLect01 PDFRao FamilyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Introduction To Microelectronics FabricationDocument53 pagesIntroduction To Microelectronics FabricationEmilio Pardo EstebanPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To MOSFET Operation: ECE/CS 5720/6720 Analog Integrated Circuit DesignDocument52 pagesIntroduction To MOSFET Operation: ECE/CS 5720/6720 Analog Integrated Circuit DesignitsmyturnPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- EENG 292 NotesDocument30 pagesEENG 292 NotesSimion OngoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Term SymbolDocument23 pagesTerm SymbolCyriac Mathew73% (11)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles For Biomedical Applications-2020-06-23-10-55Document18 pagesCobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles For Biomedical Applications-2020-06-23-10-55Karina EndoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drift and Diffusion CurrentsDocument6 pagesDrift and Diffusion Currentsprabhat_prem50% (4)
- Integrated CircuitDocument6 pagesIntegrated CircuitPatrick JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Solution For Semiconductor Physics & Devices 3rd EdDocument188 pagesSolution For Semiconductor Physics & Devices 3rd EdShiningStar Jee67% (6)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Exciton Comsol Yao - PresentationDocument13 pagesExciton Comsol Yao - Presentationhhakim32Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edited Grade 8 Science 3rd QuarterDocument9 pagesEdited Grade 8 Science 3rd QuarterYalu EinahpetsPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculate Band Structure Using VASPDocument5 pagesCalculate Band Structure Using VASPatash10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clausius-Mossotti RelationDocument4 pagesClausius-Mossotti Relationcorsairsan0% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Fred Alan Wolf - Quantum ConsciousnessDocument2 pagesFred Alan Wolf - Quantum ConsciousnessAnonymous tp9Xatf3U50% (2)
- Question Bank On Electronic Conf.Document6 pagesQuestion Bank On Electronic Conf.Harsh TyagiPas encore d'évaluation
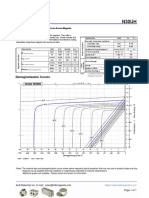
- N30UH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocument1 pageN30UH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1 - Introduction - BiochemistryDocument59 pagesLec 1 - Introduction - BiochemistryKen WalkerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Structure of Matter CEDocument74 pagesStructure of Matter CERubaiyat Kabir100% (1)
- Demon Particle Official PaperDocument20 pagesDemon Particle Official PaperRohan GubbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Matching: Match Each Item With The Correct Statement BelowDocument16 pagesMatching: Match Each Item With The Correct Statement BelowwallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)