Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
New Microsoft Office Word Document
Transféré par
Vishwas VishuDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
New Microsoft Office Word Document
Transféré par
Vishwas VishuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
1. Introduction
1.1 About Project
The typical clinical facility or hospital has several HL7 enabled applications and devices. To reduce data entry time and increase overall efficiency of the facility, these applications or devices need to communicate with each other. One way to accomplish this is by: Using an interface engine that is placed between all the applications to aid in information exchange and monitoring. Facilities that use an interface engine model find that: It is much less expensive and takes less time to initially implement an interface because
an engine allows for leveraging of data and an engine is flexible in its acceptance of data. The cost and time required to add new or replace existing applications is frequently less
than half that required in a point-to-point model It requires considerably less time and money to maintain and monitor the interfaces
because of the availability of centralized monitoring
Figure 1.1:DataFlow of Interface Engine
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 1
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
An interface engine is designed to simplify connecting, maintaining, monitoring, and sharing data between interfaces. An interface engine can take data from a sending application and filter it or change the format of the data to match each individual applications needs. This feature greatly reduces the number of individual endpoints required to communicate between applications which in turn, saves on the price of implementing of an integrated system. HL7 has established itself as a standard in healthcare information exchange. In order for an electronic health record system to integrate or exchange data with HL7 systems, an adapter layer must be implemented to transform messages. Mirth allows messages to be filtered, transformed, and routed based on user-defined rules. A web-based interface and channel creation wizard associates applications with Mirth engine components. Mirth uses a channel-based architecture to connect systems with other HL7 systems. Channels consist of endpoints (both inbound and outbound), filters, and transformers. Multiple filters and a chain of transformers can be associated with a channel. The Mirth web interface allows for reuse of filters and transformers on multiple channels. Endpoints are used to configure connections and their protocol details. Inbound endpoints are used to designate the type of listener to use for incoming messages, such as TCP/IP or a web service. Outbound endpoints are used to designate the destination of outgoing messages, such as an application server, a JMS queue, or a database
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 2
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 1.2 Organization Profile
1.2.1 About Starmark Starmark Services is a global services provider for software products and IT solutions development. Our extensive business process and domain expertise helps converting client's business requirements to technology based solutions. The leadership team has worked together over a period of time, and the realization of common values and beliefs evolved into the Starmark we know today. The team has a diverse background that includes consulting, product management, product development and corporate strategy while holding senior technology positions in Fortune 500 and Software companies. The synergies supplemented with the breadth and depth in expertise and experience has helped shape Starmark to be professional, credible, client focused software Solutions Company. It is these traits that have led clients to follow us from previous assignments. At Starmark, we believe in the power of reaching for goals. Goals give us direction and provide a roadmap for where we're going, where we want to be, and how we plan to get there. Goals are also a strong motivational force - we at Starmark thrive on the challenge of meeting goals within strict operational parameters. Product supremacy, quality and reputation First-class customer service and customer satisfaction Strong, consolidated corporate profitability, financial strength and success Honesty and integrity in all aspects of business Recognizing and rewarding our people for dedication and high levels of achievement Creating opportunities for our people to grow and share in the success of the enterprise
1.2.2 Our services Leverage our specialized staff comprising of analysts, architects, managers, engineers, support executives and testers to establish an exclusive, scalable and effective team to suit your project needs. Customers have come to us initially to cut costs, stayed with us for quality and
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 3
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
moved onto investing for innovation. Starmark provides services under the following specializations: R&D Services IT Services System Integration Maintenance & Support Services
Starmark is a premier software product development and enterprise solutions service provider. We enable enterprises to leverage software and internet technology to build value across their customers, partners, suppliers and employees. We supplement capabilities of software product companies in building scalable R&D, product development, sustenance and support operations.
1.2.3 Corporate Goals At Starmark, we believe in the power of reaching for goals. Goals give us direction and provide a roadmap for where we're going, where we want to be, and how we plan to get there. Goals are also a strong motivational force - we at Starmark thrive on the challenge of meeting goals within strict operational parameters.
We understand the axiom that companies have goals, but it's management and employees that accomplish them. That's why our corporate goals revolve around values rather than sales targets. We believe in: Product supremacy, quality and reputation First-class customer service and customer satisfaction Strong, consolidated corporate profitability, financial strength and success Honesty and integrity in all aspects of business Recognizing and rewarding our people for dedication and high levels of achievement Creating opportunities for our people to grow and share in the success of the enterprise
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 4
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
2. Literature Survey
2.1 HL7 Overview
Health Level Seven International (HL7) is a not-for-profit, ANSI-accredited standards developing organization dedicated to providing a comprehensive framework and related standards for the exchange, integration, sharing, and retrieval of electronic health information that supports clinical practice and the management, delivery and evaluation of health services. An international standard development organization established more then 20 years ago. Enables interoperability of healthcare information. Creates standards for the exchange management and integration of electronic healthcare information. Develops specification, e.g., a messaging standards that enable disparate healthcare application to exchange key sets of clinical and administrative data. HL7 is an international community of healthcare subject matter experts and information scientists collaborating to create standards for the exchange, management and integration of electronic healthcare information. The HL7 community is organized in the form of a global organization (Health Level Seven, Inc.) and country-specific affiliate organizations: Health Level Seven, Inc. (HL7, Inc.) is headquartered in Ann Arbor, Michigan. HL7 affiliate organizations, not-for-profit organizations incorporated in local
jurisdictions, exist in over 40 countries. The first affiliate organization was created in Germany in 1993
2.1.1 The Name "Health Level-7" The name "Health Level-7" is a reference to the seventh "application" layer of the ISO OSI Reference model. The name indicates that HL7 focuses on application layer protocols for the health care domain, independent of lower layers. HL7 effectively considers all lower layers merely as tools.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 5
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
2.1.2 HL7s Mission is: "To provide (global) standards for the exchange, management and integration of data that supports clinical patient care and the management, delivery and evaluation of healthcare services. Specifically, to create flexible, cost effective approaches, standards, guidelines, methodologies and enable healthcare information system interoperability and sharing of electronic health records." 2.1.3 HL7 Standards HL7 specifies a number of flexible standards, guidelines, and methodologies by which various healthcare systems can communicate with each other. Such guidelines or data standards are a set of rules that allow information to be shared and processed in a uniform and consistent manner. These data standards are meant to allow healthcare organizations to easily share clinical information. HL7 version 2 defines a series of electronic messages to support administrative, logistical, and financial as well as clinical processes. The HL7 Version 2 Messaging Standard Application Protocol for Electronic Data Exchange in Healthcare Environments is considered to be the workhorse of data exchange in healthcare and is the most widely implemented standard for healthcare information in the world. HL7 v2.x has allowed for the interoperability between electronic Patient Administration Systems (PAS), Electronic Practice Management (EPM) systems, Laboratory Information Systems (LIS), Dietary, Pharmacy and Billing systems as well as Electronic Medical Record (EMR) or Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. The HL7 Standard covers messages that exchange information in the general areas of: Patient Demographics Patient Charges and Accounting Patient Insurance and Guarantor Clinical Observations Encounters including Registration, Admission, Discharge and Transfer Orders for Clinical Service (Tests, Procedures, Pharmacy, Dietary and Supplies)
Page 6
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
2.1.4 HL7 Messages A message is the atomic unit of data transferred between systems. It is comprised of a group of segments in a defined sequence. Each message has a message type that defines its purpose. For example the ADT Message type is used to transmit portions of a patients ADT data from one system to another. Message o Segment (Some are Repeatable) Fields (Some are Repeatable) Components o Subcomponents
A segment is a logical grouping of data fields. Segments of a message may be required or optional. They may occur only once in a message or they may be allowed to repeat. Each segment is given a name. For example, the ADT message may contain the following segments: Message Header (MSH), Event Type (EVN), Patient ID (PID), and Patient Visit (PV1). 2.1.5 HL7 Message Types ORU (Observation Result) The ORU message transmits observations and results from the producing system/filler i.e. LIS, EKG system) to the ordering system/placer (i.e. HIS, physician office application). It may also be used to transmit result data from the producing system to a medical record archival system, or to another system not part of the original order process. ORU messages are also sometimes used to register or link to clinical trials, or for medical reporting purposes for drugs and devices. Types of observations reported in the ORU message include: Clinical lab results Imaging study reports Patient condition or other data (i.e. vital signs, symptoms, allergies, notes, etc.)
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 7
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
The ORU message is a structured report where each observation is separated into an individual entity, and then separated into fields. ORU messages do not carry images; they use varying data types but most often use text, numbers and codes.
In the ORU message, the ORC (Common Order Segment), the OBR (Observation request) and OBX (Observation) segments are most significant due to their functions: The Common Order segment (ORC) is used to transmit fields that are common to all orders (all types of services that are requested). The OBR segment is used in all ORU messages as a report header, and contains important information about the order being fulfilled (i.e. order number, request date/time, observation date/time, ordering provider, etc.). This segment is part of a group that can be used more than once for each observation result that is reported in the message. The OBX segment transmits the actual clinical observation results as a single observation or observation fragment.
DFT (Detailed Financial Transaction)
The DFT message describes a financial transaction that is sent to a billing system and s used for patient accounting purposes. This message might include things like ancillary charges or patient deposits, and is sent between the DSS/Order Filler and the Charge Processor. Trigger events for the DFT-P03 message include: Procedure ordered Procedure scheduled Procedure completed Future will define Report events for professional fees.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 8
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 2.2 MIRTH-Interface Engine
2.2.1 Introduction Mirth is an open source cross-platform HL7 interface engine that enables bi-directional sending of HL7 messages between systems and applications over multiple transports. Mirth uses a channel-based architecture to connect systems with other HL7 systems. Channels consist of endpoints (both inbound and outbound), filters, and transformers. Multiple filters and a chain of transformers can be associated with a channel. The Mirth web interface allows for reuse of filters and transformers on multiple channels. The Mirth is a healthcare interface engine and interface repository created and professionally supported by Web Reach. Mirth provides standards-based tools to develop, test, and deploy interoperability solutions for healthcare information systems and information exchanges. Mirth is middleware that connects health information systems so they can exchange clinical and administrative data. Mirth is released under the Mozilla Public License v1.1 and is professionally supported by Web Reach, a Health information technology (IT) solutions company based in California. There are many standards in healthcare, with a diverse range of protocols and types of data. There are different health information systems such as labs, pharmacies, clinics, hospitals, and many others. Each of these systems might have different protocols, mismatched versions, and incompatible data. Some systems might actively use HL7, X12, and DICOM images, while others simply have a database to read from or communicate with XML and comma separated values. Add to that the lacks of control administrators have over current and legacy applications, and the healthcare interoperability problem becomes apparent. This is where Mirth steps in as the easy to use and deploy middleware solution. Mirth can lie between any number of health information systems, whether they speak a standard healthcare language or not, and help them communicate.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 9
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
2.2.2 Features of mirth A rich interface channel development and monitoring environment that allows you to generate filter rules and transformation steps using an intuitive drag-and-drop template-based editor Real-time connection monitoring through the interface dashboard. Message reprocessing through the message browser. The Channels View to created, modified, deleted, and deployed a channel. Mirth provides the Users section for editing the set of users allowed to use the application. Setting area can be used to configure option values that affect the Mirth Administrator and Mirth Server. It also can be used for configuration maintenance. Integrated alerting based on user-defined rules to continuously monitor your interfaces and notify users to take action.
2.2.3 Mirth provide solution for: Hospitals face increasing pressure to drive down cost and improve both safety and clinical quality while becoming the preferred practice venue for providers and the most convenient and service-friendly place for patients and their families. Mirth can help in streamlining the flow of information across departments and legacy systems within the organization, speeding results delivery to clinicians across the community, or becoming part of a community-wide health information exchange. Labs compete on timeliness, service and accuracy, and to a growing degree to how they enable results delivery directly into referring physicians EHR systems. Mirth can help in connecting LIS to other units within an integrated delivery system or to practice locations across the community.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 10
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
2.2.4 Mirth Architecture
Figure 2.1: Mirth Architecture
2.3 JAVA
The Java programming language is a high-level language that can be characterized by all of the following buzzwords: Simple Object-oriented Distributed Interpreted Robust Secure In the Java programming language, all source code is first written in plain text files ending with the .java extension. Those source files are then compiled into .class files by the javac compiler. A .class file does not contain code that is native to your processor; it instead contains bytecodes the machine language of the Java Virtual Machine (Java VM). Architecture-neutral Portable High-performance Multithreaded Dynamic
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 11
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
2.3.1 The Java Platform A platform is the hardware or software environment in which a program runs. Most platforms can be described as a combination of the operating system and underlying hardware. The Java platform differs from most other platforms in that it's a software-only platform that runs on top of other hardware-based platforms. The Java platform has two components: The Java Virtual Machine The Java Application Programming Interface (API)
A Java Virtual Machine is the base for the Java platform and is ported onto various hardwarebased platforms. The API is a large collection of ready-made software components that provide many useful capabilities. It is grouped into libraries of related classes and interfaces; these libraries are known as packages. 2.3.2 Features of Java Platform Independent The concept of Write-once-run-anywhere (known as the Platform independent) is one of the important key feature of java language that makes java as the most powerful language. Not even a single language is idle to this feature but java is more closer to this feature. The programs written on one platform can run on any platform provided the platform must have the JVM. Simple There are various features that makes the java as a simple language. Programs are easy to write and debug because java does not use the pointers explicitly. It is much harder to write the java programs that can crash the system but we can not say about the other programming languages. Java provides the bug free system due to the strong memory management. It also has the automatic memory allocation and deallocation system.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 12
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Object Oriented To be an Object Oriented language, any language must follow at least the four characteristics. Inheritance: It is the process of creating the new classes and using the behavior of the existing classes by extending them just to reuse the existing code and adding the additional features as needed. Encapsulation: abstraction. Polymorphism: As the name suggest one name multiple form, Polymorphism is the way of providing the different functionality by functions having the same name based on the signatures of the methods. Dynamic binding: Sometimes we don't have the knowledge of objects about their specific types while writing our code. It is the way of providing the maximum functionality to a program about the specific type at runtime. Distributed The widely used protocols like HTTP and FTP are developed in java. Internet programmers can call functions on these protocols and can get access the files from any remote machine on the Internet rather than writing codes on their local system. Dynamic While executing the java program the user can get the required files dynamically from a local drive or from a computer thousands of miles away from the user just by connecting with the Internet. Multithreaded Java is also a multithreaded programming language. Multithreading means a single program having different threads executing independently at the same time. Multiple threads execute instructions according to the program code in a process or a program. Multithreading works the similar way as multiple processes run on one computer.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 13
It is the mechanism of combining the information and providing the
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
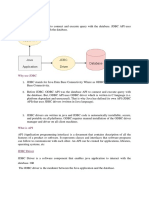
2.3.3 JDBC-ODBC Bridge The JDBC-ODBC bridge, is a database driver implementation that employs the ODBC driver to connect to the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into ODBC function calls. The driver is platform-dependent as it makes use of ODBC which in turn depends on native libraries of the underlying operating system the JVM is running upon. Also, use of this driver leads to other installation dependencies; for example, ODBC must be installed on the computer having the driver and the database must support an ODBC driver. The use of this driver is discouraged if the alternative of a pure-Java driver is available. The other implication is that any application using a type 1 driver is non-portable given the binding between the driver and platform. This technology isn't suitable for a high-transaction environment. Type 1 drivers also don't support the complete Java command set and are limited by the functionality of the ODBC driver.
Figure 2.2:JDBC_ODBC Driver
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 14
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Functions Translates query obtained by JDBC into corresponding ODBC query, which is then handled by the ODBC driver. Sun provides a JDBC-ODBC Bridge driver. sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver. This driver is native code and not Java, and is closed source. Client -> JDBC Driver -> ODBC Driver -> Database There is some overhead associated with the translation work to go from JDBC to ODBC. Advantages Almost any database for which ODBC driver is installed, can be accessed. A JDBD-ODBC driver is easy to install.
2.4 Introduction to SQL Server 2008
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 is a family of products that meet the data storage requirements of the largest data processing systems and commercial Web sites, yet at the same time can provide easy-to-use data storage services to an individual or small business.
Figure 2.2 SQL Server Environment
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 15
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
The data storage needs of a modern corporation or government organization are very complex. Some examples are:
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) systems must be capable of handling thousands of
orders placed at the same time.
Increasing numbers of corporations are implementing large Web sites as a mechanism for
their customers to enter orders, contact the service department, get information about products, and for many other tasks that previously required contact with employees. These sites require data storage that is secure, yet tightly integrated with the Web.
Organizations are implementing off-the-shelf software packages for critical services such
as human resources planning, manufacturing resources planning, and inventory control. These systems require databases capable of storing large amounts of data and supporting large numbers of users.
Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) must be able to distribute data storage capabilities
with applications targeted at individuals or small workgroups. This means the data storage mechanism must be transparent to the users who purchase the application. This requires a data storage system that can be configured by the application, and then tune itself automatically so that the users do not need to dedicate database administrators to constantly monitor and tune the application.
2.4.1 Database Architecture Microsoft SQL Server 2008 data is stored in databases. The data in a database is organized into the logical components visible to users. A database is also physically implemented as two or more files on disk.
When using a database, you work primarily with the logical components such as tables, views, procedures, and users. The physical implementation of files is largely transparent. Typically, only the database administrator needs to work with the physical implementation.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 16
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Each instance of SQL Server has four system databases (master, model, tempdb, and msdb) and one or more user databases. Some organizations have only one user database, containing all the data for their organization. Some organizations have different databases for each group in their organization, and sometimes a database used by a single application. For example, an organization could have one database for sales, one for payroll, one for a document management application, and so on. Sometimes an application uses only one database; other applications may access several databases.
It is not necessary to run multiple copies of the SQL Server database engine to allow multiple users to access the databases on a server. An instance of the SQL Server Standard or Enterprise Edition is capable of handling thousands of users working in multiple databases at the same time. Each instance of SQL Server makes all databases in the instance available to all users that connect to the instance, subject to the defined security permissions.
When connecting to an instance of SQL Server, your connection is associated with a particular database on the server. This database is called the current database. You are usually connected to a database defined as your default database by the system administrator, although you can use connection
options in the database APIs to specify another database. You can switch from one database to another using either the Transact-SQL USE database name statement, or an API function that changes your current database context.
SQL Server 2008 allows you to detach databases from an instance of SQL Server, then reattach them to another instance, or even attach the database back to the same instance. If you have a SQL Server database file, you can tell SQL Server when you connect to attach that database file with a specific database name.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 17
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
3. Software Requirement Specification
Software Requirement Specifications is the starting point of the software development activity. It allows the developer/analyst to understand the system, functions to be carried out, performance levels to be maintained and corresponding interfaces to be established. Software requirement specification is the medium through which the client and the user needs are accurately specified. An SRS convey information about the applications requirements, both functional and nonfunctional.
3.1 Purpose
The purpose of HL7 Integration is to develop an Outbound Interface from a Laboratory Information System(Vitalaxis) to Electronic Medical Record System(NextGen).
3.2 Scope
The Result Outbound integration would help laboratories to send the result for the cases in LIS to hospitals EMR system. A result hl7 file and the PDF report would be sent to EMR system. The DFT outbound integration intends to help laboratories send out the billing information to the Ordering facility in order to create charge transactions. Billing information would be in hl7 file format.
3.3 Functional Requirement
Functional requirement for Result Outbound Laboratory Information system (LIS) should have a background job that inserts every new case into database with proper caseid and status=new. HL7 integration framework retrieves all the information related to that case from the database in the form of an XML Create a ORU^R01 (Observation Result) message using dedicated mirth channel. The successful creation of HL7 file should update the status to generated. Generated HL7 file and the related pdf is uploaded into specified EMR system.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 18
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Functional requirement for DFT Outbound Medical assistant at ordering facility enters the patients, case information into the specified EMR system. The system generates a unique id for each patient (#account No) and orders the case to specified LIS. Case is assigned to a proper pathologist and the pathologist performs diagnosis and will sign-out the case. When a case is signed-out, a job running in the background populates the database. The Claims table gets populated with the values for Financial Transactions carried out or as mentioned by the Pathologist. The pathologist, once done with the Diagnosis, would charge for the tests conducted at the laboratory. The financial transaction details would be updated under FT1 segment of the HL7 file and is sent to the Ordering facility. Create a DFT^P03 (Detailed Financial Transaction) message using dedicated mirth channel. Generated HL7 file is uploaded into specified EMR system.
3.4 Non-Functional Requirements
Reliability Reliability is the correlation of an item, scale, or instrument with a hypothetical one, which truly measures what it is supposed to. Since the true instrument is not available, the program according to the requirement can perform the intended function Backup option for backing up the database etc. Error-handling-exception occurring while accessing database need to be addressed
Usability Usability refers to the capability of the product to be understood, learned, and used. It must be user friendly, when used under specified conditions. This section should include all of those requirements that affect usability. Specify the required training time for a normal users and a power user to become productive at particular operations.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 19
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Maintainability Maintainability is the ease with which a program / specification can be corrected if an error occurs desires a change in requirements. Specify attributes of software that relate to the ease of maintenance of the software itself. Performance Performance is measured in terms of the output provided by the application. Requirement specification plays an important part in the analysis of a system. Only when the requirement specifications are properly given, it is possible to design a system, which will fit into required environment. The requirement specification for any system can be broadly stated as given below: The system should be able to interface with the existing system. The system should be accurate.
3.5 Requirements for Result Outbound
3.5.1 Introduction
The software (Theranostics Lab Results Application) that is outlined in these specifications will enable the NextGen Electronic Medical Records (EMR) System to receive lab results from an external lab system via the HL7 communications standard. Rosetta lab results interface application is based on the 2.3 version of the HL7 Standard. Both systems will execute concurrently and continually, exchanging information when entered by the computer operator.
3.5.2 Operational Concerns
Using TCP/IP protocol to exchange information. The systems will transfer information through TCP/IP with Minimal Lower Level Protocol (MLLP). The format is based on HL7 version 2.3.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 20
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Using files to exchange information. The systems will transfer information through ASCII files. Two directories will exist, one directory for each direction of the transfer. Each system will poll the retrieval directory for new data files to load into the system. Each system will name the transfer files with a unique name. Transfer file names will begin with a letter followed by a sequential number that is right justified
to seven digits and zero filled. Files will be imported into the database on a first-in first-out order. A new line character will terminate each record.
Message Segment Layouts Sequence Max Size
This is the order in which the fields should be sent to/from the external system. Although HL7 allows for variable length fields within each record type, this column represents the maximum length for each data element as set in the HL7 manual. This is the size that is guaranteed to be placed in NextGen records in its entirety. If there are sizes indicated for subcomponents, it means that each sub-component is placed in a separate column in the database. If there is only one value for the maximum size for the composite field, it means that the entire composite field is placed in a single column in the NextGen database (the field is not parsed). If the maximum sizes are provided for certain sub-components of the composite field only, it means that only these sub-components are saved in the NextGen database. If this column contains the value of R, then this field is required by Rosetta (always sent). If this column contains the value of C, then this field is sent conditionally, depending on value in some other field. If this column contains the value of O, then this field is optional. Contains the maximum number of times the field can be repeated. If this field is left blank, there are no repeats. Contains an HL7 data type that is used for this field. This column contains the name of the data element to be sent or received in this field and, if applicable, its sub-components. Contains additional information about the field. If the comment has the text in quotation marks, then the corresponding field will contain exactly Page 21
REQUIRED
REPEATS
DATA TYPE
DESCRIPTIO
N
COMMENT
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
this text, or, in case of multiple texts, one of them as it appears inside quotation marks. For example, MSH in the comment column means that this field will always contain the following value: MSH Table 3.1 Segment Layout
When a field is completely shaded, this indicates that NO data will be expected or sent in this field. The receipt of data in this field by Rosetta will be discarded. The HL7 Segments outlined below contain all of the fields in the HL7 specification. Many fields are not used by NextGen or Vital axis and are therefore ignored.
Notation : [ ] { } Repeating elements Optional elements
Message Format:
HL7 ORU Transmission of Lab Observation Message
HL7 ORU messages will be received by the Theranostics Lab Results Application either via TCP/IP communication or whenever a batch file containing lab results is placed in the input directory. NextGen Healthcare must be informed whether the lab intends to send lab results via TCP/IP or through batch files in order to install the appropriate version of the Vital Axis software at the client site. Segments listed in the table below are the only ones that are processed by Theranostics lab.
Grayed out fields are received by Theranostics, but not processed. Always optional.
Segment MSH Name Message Header Required Yes
[{EVN}] [{NTE}]
Event Type
Notes and Comments (Header specific)
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 22
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
{ PID [PD1] [{NTE}] PV1 [{NTE}] { [ORC] [{NTE}] { OBR [{NTE}] { [{OBX}] [{NTE}] Observation/Result Notes and Comments (for Observation/Result) Order Request Notes and Comments (for Order Request) Yes Common Order Notes and Comments (for Common Order) Patient Identification Additional Demographics Comments (Patient specific) Patient Visit Comments (for Patient Visit) Yes
} [ZPS]
}
Place of Service Facility Information
} [{DSP}] [BTS] [FTS] Display Segment (handled conditionally) Batch Trailer Segment File Trailer Segment Table 3.1: Result OutBound Segments Format
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 23
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
4. Hardware and Software Specification
4.1 hardware Requirements
Processor : Pentium 4
RAM
1 GB
Hard Disk
40 GB
4.2 Software Requirement
Platform : Windows 98/2000/XP
Languages
Java 1.6
Interface Engine
Mirth
Database Environment
: :
MS-SQL Server Eclipse & MS-SQL Server 2008
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 24
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
5. System Definition
5.1 Existing System
Paper Based Record The existing system requires personally carrying paper medical records from laboratory to hospital. Disadvantages of paper based record are: Using paper medical records increases the risk of grammar errors, improper data entry
and other record inaccuracies. Paper also requires physical storage, which could be a costly expense for businesses. Productivity decreases because paper records are often unavailable, important
information may not be written on them, or the handwriting of a health professional may not be legible. Information in paper records are often duplicated, either by health professionals from
different departments because of the luck of concordance among specialists, or during the time spans in the same department.
5.2 Proposed System
Proposed system is providing an interface between Theranostics laboratory (VitalAxis, a LIS) and Mid Atlantic Urology Associates (NextGen, a EMR) using HL7 protocol The typical clinical facility or hospital has several HL7 enabled applications and devices. To reduce data entry time and increase overall efficiency of the facility, these applications or devices need to communicate with each other. This can be accomplished by: Using an interface engine that is placed between all the applications to aid in information exchange and monitoring.
A HL7 interface engine is an interface or integration engine built specifically for the healthcare industry. It connects legacy systems by using a standard messaging protocol. Because hospitals and other healthcare providers usually have different systems for different
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 25
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
aspects of services, they are often unable to communicate with each other. HL7 gets around that problem by providing the framework for the exchange, integration, sharing and retrieval of electronic health information. These standards are most commonly used throughout the world. Advantages Of Proposed System:
Effortless: Complete and fully functional HL7 interfaces can be configured within hours. Using an interface engine translates into huge savings in both time and costs. Easy to Use: An HL7 interface engine minimizes the internal work required to establish and maintain HL7 communication channels. Electronic medical files are readily transferable from one doctor or hospital to another. Electronic filing also eliminates the physical space needed to retain patient records and facilitates more accurate documentation of medical files.
HL7 interface engine provides more control and saves time and money in a clinical or healthcare environment
The following figure shows workflow diagrams for interface engine model:
Figure 5.1: Workflow of Interface Engine
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 26
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
6. Detailed Design
System design describes overall architecture of the system. It guides the design process and provides details about how to translate functional requirement of the user into design specification. This phase is a transition from the users perspective of the system to the developers viewpoint. System definition helps in developing a logical design of the system. The design phase is with the requirement specification for the software to be developed. Design is the first step to moving from the problem domain towards the solution domain. Design is essentially the bridge between requirements. It is the most critical factor affecting the quality of the software. In detailed design the interconnection of the modules or how the specification of the modules can be satisfied is decided. Some properties for a software system design are: Verifiability Completeness Consistency Traceability Simplicity
The following guidelines were taken into account while designing the system: A design should exhibit hierarchical organization that makes intelligent use of control
among the components of the software. A design should be modular i.e., that software should be logically partitioned into
components that perform specific function and sub function. A design should contain distinct and separable representation of data and procedure. A design should lead to interface that reduces the complexity of connections between and
modules and with the external environment.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 27
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 6.1 Data Flow Analysis
As information moves through software, it is modified by a series of transformations. Data flow Diagrams is a graphical technique that depicts the information flow and transforms that are applied as data move from input to output. The data flow diagram may be used to represent a system or software at any level of abstraction. In fact, DFD may be partitioned into different levels that represent increasing information flow and functional detail. A functional DFD also called a Context Model which represents the entire software element as a single bubble with input and output data indicated by incoming and outgoing arrows respectively. Additional processes and information flow paths are represented in different levels. DFD for HL7 Integration Level-1
Laborotary Information system(LIS)
populates
HL7 Database
Mirth
Sending process
uploads it to
Electronic Medical Record(EMR)
Figure 6.1: DFD for HL7 Integration.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 28
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
DFD of HL7 Integration From VitalAxis to NextGen Level -2
VitalAxis
Pathologist Signs out
Pre-configured Location
Places HL7 file W700 Framework populates
Distridution Framework
HL7Integartion log Table
Local Folder
Gets data
Mirth
Creates HL7 file
Figure 6.2.:Level 2-Data Flow Diagram The MAUA Medical Assisstant (MA) would requisition a case and order the case to Theranostix (THX). The THX Lab Technician would accession that case and perform grossing and processing for that case. The Pathologist would SignOut that case Or correct the Signed-Out case. The distribution framework would populate the hl7IntegrationLog table for this signedOut case with the status = 'New' and the handler = 'THX_VA-MAUA_NextGenResults_Outbound' and direction = 'Out Bound' The dedicated VA-Mirth channel (THX_VA-MAUA_NextGen-Results_Outbound) would generate the result hl7 file and place that hl7 file along with the PDF report in a preconfigured location.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 29
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
DFD of Interface Engine
Labarotary
Billing
Charges/Result ORU
ADT
Charges/ADT
ADT
EMR
ADT/ORU/DFT
Mirth
Lab Results/charges
HIS
ORU/Charges ADT ORU
RIS
EHR
Figure 6.3: DFD of Mirth Example workflow: The workflow of an example small acute care setting is shown in the following table:
Information Type Demographics
Workflow Entered in registration system and sent to all ancillary systems. Lab Orders entered on order entry system (EMR/HIS) and ORM messages delivered electronically to both systems. An order response is sent from the Lab back to EMR/HIS. Radiology Entered on HIS but printed and re-entered into radiology. Once typed into radiology an electronic confirmation is sent to the HIS.
Orders
Results
Lab Sent to EMR System/HIS
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 30
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 6.2 Database Design
Database designing is all about designing the tables with the required fields, data type and proper relationship between them. Database schema describes the physical structure of the database. That is, it gives details of all the tables that form the database of the application. The tables that form SPINeeds database are login and request tables. 6.2.1 Cases Table
Table 6.1:Design of Cases Table Cases Table stores details of case like casetype, extraction procedure used to extract the specimen, number of specimens collected and etc.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 31
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
6.2.2 Patients Table
Table 6.2:Design of Patients table Patients table stores patient information like name of the patient, address, responsible person name, insurance policy number and etc.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 32
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
6.2.3 Diagnosis Table
Table 6.3:Design Diagnosis Table Diagnosis table contains diagnosis details like summary, final icd9 codes and etc.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 33
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
6.2.4 HL7IntegrationLog Table
HL7IntegrationLog is monitored by mirth, whenever a case is inserted with status as new mirth pick up related caseid and logid. Case, patients and diagnosis details are retrieved using the caseid. Cases, patients and diagnosis are primary table from which details related to patients case are retrieved. There are many other tables, namely specimens, test, case assignments, casetype, organization, accounts, user, userroles, varules, VAintevent, hl7IntegartionMaster, etc, which are used to create HL7 files.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 34
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
7. SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION
Implementation is the stage of the project where the theoretical design is turned into working system. At this stage the main work load, the greatest upheaval and the major impact on the existing system shifts to the customer department. If the implementation is not carefully planned a controlled it can cause chaos and confusion. Implementation includes all those activities that take place to convert from the old system to the new one. The new system may be totally new, replacing an existing manual or automated system or it may be a major modification to an existing system. Proper implementation is essential to provide a reliable system to meet the organization requirements. Successful implementation may not guarantee improvement in the organization using the new system, but improper installation will prevent it. Implementation Procedures Implementation of software refers to the final installation of the package in its real environment, to the satisfaction of the intended users and the operation of the system. In many organizations some one who will not be operating it, will commission the software development project. The people are unaware that the software is meant to make their job easier. In the initial stage, they doubt about the software but we have to ensure that the resistance does not build up as one has to make sure that The active user must be aware of the benefits of using the system Their confidence in the software is built up Proper guidance is imparted to the user so that he is comfortable in using the
application.
User Training To achieve the objectives and benefits expected from computer based system, it is essential for the people who will be involved to be confident of their role in the new system. As systems become more complex, the need for education and training is more and more important.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 35
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Operational Documentation Once the implementation plan is decided, it is essential that the user of the system is made familiar and comfortable with the environment. Education involves right atmosphere & motivating the user. A documentation providing the whole operations of the system is being developed. Points to consider while implementing HL7 Integration 1. HL7 Interfaces are not plug and play Unfortunately the HL7 V2 standard is interpreted in different ways by implementers and software developers. The outcome is two similar but not exactly matching interfaces that require analysis in order to identify the differences. 2. Translation of HL7 messages Once the differences have been identified, the messages from one application needs to modified before they can be processed by the other application. Some translations may be relatively simple, such as moving a particular field from one place in the message to another. For example the sending system may place an insurance number in the insurance segment (IN1). However another vendor may not support that segment and instead expects the insurance number to be placed in the patient identification segment (PID) or perhaps in a proprietary segment. 3.Code table mismatching HL7 messages are littered with coded data. For example the martial status field contains a coded value such as M for Married, D for divorced and so on. However the receiving system may expect 1 for married and 2 for divorced. 4.HL7 PID Identifier List The patient identification segment has three fields dedicated to identifiers. PID-2 Patient ID (external ID), PID-3 Patient ID (internal ID) and PID-4 Alternative Patient ID. The recommended use of these fields has changed with successive revisions of HL7 ( HL7 V2.1, HL7 V2.2, HL7 V2.3, HL7 V2.3.1, HL7 V2.4). Different vendors have interpreted these fields differently. Almost everyone puts the patients medical record number (MRN) in PID-3.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 36
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
5. Repeating segments Segments that repeat, such as Observation segment(OBX) depends on the number of specimens sent for diagnosis. Repeating segment such as Next of Kin (NK1) also pose similar challenges to repeating fields. Different systems support different numbers of repeats. For example the sending system
may support 7 patient contacts (sent as 7 NK1 segments) and the receiving system may support only 2. The sending system may add, update or delete the repeating field. Deleting a field can
cause headaches for the downstream system. Sometimes this is overcome by the downstream system replacing the entire set of repeating fields each time.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 37
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
8. Testing
8.1 HL7 Interface Testing
HL7 interface testing is part of the overall HL7 interface planning process, which includes HL7 interface analysis, HL7 interface requirements, HL7 interface specification, and HL7 interface testing. HL7 interface testing is linked to other project testing activities and typically includes: HL7 interface unit testing - typically interface specification based aiming to confirm that
HL7 messages sent and/or received from each application conform to the HL7 interface specification. HL7 interface integration testing - testing of business scenarios to ensure that information
is able to flow correctly between applications. HL7 interface system testing - end-to-end scenario testing focused on ensuring all
relevant modules of all relevant applications are able to integrate correctly. Other testing such as additional application functional testing and end user acceptance
testing would typically follow interface testing.
8.2 Test cases
Test cases for ORU Positive Test cases 1.HL7 and PDF files should be copied to the pre-configured local file system 2. HL7 file should be generated at the pre-configured location. 2. PDF Report file should be generated and stored at the pre-configured location. 4. Hl7Integration log table should be updated with summary =New Hl7 file: generated and uploaded successfully.' and status='Uploaded'
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 38
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Negative Test cases 1. HL7 file should not be generated. 2. PDF report file should not be generated. 3. Hl7Integration log table should be updated with summary =' Failed to generate Hl7File.' and status='Failed' Test cases for DFT Positive Test cases 1. DFT HL7 file should be generated at the pre-configured location. 2. The DFT HL7 files should be copied to the pre-configured local file system 3. Claims table should be populated with all the relevant billing details. 4. Hl7Integration log table should be updated with Summary ='New DFT Hl7 file: generated.' and status='Uploaded' Negative Test cases 1. HL7 file should not be generated. 2. Hl7Integration log table should be updated with Summary =' Failed to generate Hl7File.' and status='Failed'
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 39
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
9. Conclusion and Future Enhancement
9.1 Conclusion
A HL7 interface has been developed and implemented successfully. HL7 interfaces are running successfully between Theranostics laboratory (VitalAxis LIS) and Mid Atlantic Urology Associates (NextGen EMR). The main objective of the HL7 Integration is to generate HL7 file along PDF report. Once case is created and pathologist sign out then data will save in the database, then mirth will pick the data through source and generates result set in form of XML. Using this result set mirth destination will generates an HL7 message along with PDF report and place it specified directory. By using a HL7 interface engine, Theranostix laboratory can realize the benefits of existing legacy information systems without major re-investment in new technologies, lowering costs and extending the life and efficiencies of current systems. There is also opportunity to link to systems outside the healthcare provider such as providers of outsourced services like radiology HL7 interface engines are software, which works as a go-between for different systems. They monitor different types of interfaces and communication points and perform actions according to rules defined by the organization. HL7 works with a number of standards (Conceptual Standards, Document Standards, Application Standards and Messaging Standards). Messaging standards define how information is packaged and communicated from one system to another The Mirth Interface Engine is a simple and effective solution to the problems of healthcare interoperability. The unique design of the Mirth HL7 Interface Engine allows for seamless routing and transforming of HL7 data with minimal setup required. The Mirth HL7 Interface Engine has been designed to make it exceptionally easy to configure and maintain HL7 interfaces.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere. Page 40
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 9.2 Future Enhancement
Currently HL7 version 2, which supports hospital workflows, is being used. HL7 version 3, which supports any and all healthcare workflows, can be used.
Key differences between HL7 V2 and HL7 V3 are
HL7 V2 Not Plug and Play it provides 80 percent of the interface and a framework to
negotiate the remaining 20 percent on an interface-by-interface basis Historically built in an ad hoc way because no other standard existed at the time Generally provides compatibility between 2.X versions Messaging-based standard built upon pipe and hat encoding
HL7 V3 Approaching Plug and Play less of a framework for negotiation Many decades of effort over ten year period reflecting best and brightest thinking NOT backward compatible with V2 Model-based standard built upon Reference Information Model (RIM) provides
consistency across entire standard
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 41
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10. Screen Shots 10.1 Login Page
Figure 10.1:Mirth Login page
This page is used to login.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 42
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.2 Channel
Figure 10.2: Channel The Channels View is where channels are created, modified, deleted, and deployed.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 43
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.3 Summary
Figure 10.3:Summary Summary page is used to entry basic information about the channel like name, incoming data format and initial status of the channel.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 44
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.4 Source Connector
Figure 10.3 Source Database Reader
Source connector is used to configure database. By selecting connector type as database reader we can specify the driver using which data can be retrieved from the database. Using Javascript database configuration is done.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 45
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.5 Source Transformer
Figure 10.4 Source Transformer
Source transformer is used maps values to variable which can be used in destination connector.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 46
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.6 Destination Connector
Figure 10.4: Destination-File Writer A File Writer connector writes messages to files located on the machine running the Mirth server.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 47
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.7 Destination Transformer-ORU
Figure 10.7: ORU Destination Transformer
ORU transformer processes the incoming XML data and creates an HL7 file and places HL7 file in the pre-configured location. .
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 48
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.8 Destination Transformer Updater
Figure 10.8: Updater HL7 IntegrationLog Updater transformer update the Log table in the database with status field set to Success and processingnotes to Hl7 and pfd files generated.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 49
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.9 DashBoard
Figure 10.2: DashBoard When the channels are deployed, the status of the channels is shown in dashboard. Dashboard is used to monitor the channels. Deployed channels status is started. Started channels create HL7 files and deploy the files in pre-defined location.
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 50
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.10 Result Outbound
HL7 Message:
MSH|^~\&|VitalAxis|Theranostix|NextGen|MAUA|201006021147||ORU^R01|7|T|.5||Report_7.pdf|AL PID|1|205320|||Robert^Wadra^T||19901010|M|||8401 GARLAND AVE^^Takoma Park^MD^20912||301-585-2292|464-45-9748||||| OBR|1||THS10-00001|THS10-00001^Bladder Biopsy^VitalAxis|||20100601000000|||||||20100602000000|^^^^^Forcep Biopsy|^Melograna^Frank^S|||||||||F OBX|1|ST|1^Urachus^VitalAxis||Urothelial mucosa without significant histopathologic abnormalities.||||||F OBX|2|ST|2^Posterior Wall^VitalAxis||Follicular cystitis.||||||F OBX|3|ST|3^Right Ureteral Orifice^VitalAxis||Chronically inflamed and denuded urothelium||||||F OBX|4|ST|4^Left Ureteral Orifice^VitalAxis||Urothelial atypia, can not exclude a dysplastic or neoplastic disorder.||||||F OBX|5|ST|5^Bladder Neck^VitalAxis||Urothelial papilloma.||||||F
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 51
HL7 Integration Using Mirth PDF Report
Figure 10.8 PDF Report
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 52
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 53
HL7 Integration Using Mirth 10.11 DFT Outbound HL7 Message:
MSH|^~\&|VitalAxis|MDE|NJU|MDE|200912070922||DFT^P03|237037|T|2.3|||AL EVN|P03|20091207212256 PID|1|135664|PS0900062|3412|Test^Test^Test||19831227|F|||Addr1^Addr2^Detroit^MI^48201|TC Breast Histology|||||200912071200||2367237623 PV1|||ABCDE1223||||^Physician^Test OBX|1|TX|90^^BENIGN. NEGATIVE FOR INVASIVE CARCINOMA.|1|BENIGN. NEGATIVE FOR INVASIVE CARCINOMA.||||||F|||||UNKNOWN^Path^Test OBX|2|TX|91^^BENIGN BREAST TISSUE SHOWING FIBROCYSTIC CHANGES, NEGATIVE FOR ATYPIA OR MALIGNANCY.|2|BENIGN BREAST TISSUE SHOWING FIBROCYSTIC CHANGES, NEGATIVE FOR ATYPIA OR MALIGNANCY.||||||F|||||UNKNOWN^Path^Test OBX|3|TX|233^^ATYPICAL LOBULAR HYPERPLASIA, NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.|3|ATYPICAL LOBULAR HYPERPLASIA, NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.||||||F|||||UNKNOWN^Path^Test OBX|4|TX|90^^BENIGN BREAST TISSUE WITH MASTITIS IDENTIFIED. MASTITIS IS AN INFECTION COMMONLY CAUSED BY BACTERIA FOUND ON NORMAL SKIN.|4|BENIGN BREAST TISSUE WITH MASTITIS IDENTIFIED. MASTITIS IS AN INFECTION COMMONLY CAUSED BY BACTERIA FOUND ON NORMAL SKIN.||||||F|||||UNKNOWN^Path^Test OBX|5|TX|91^^POSITIVE FOR ADENOCARCINOMA.|5|POSITIVE FOR ADENOCARCINOMA.||||||F|||||UNKNOWN^Path^Test FT1|1|||200912061200||D|88305PC|||5|||||||||1;2;3;4|UNKNOWN^Path^Test|UNKNOWN^Physician^Te st||200912061200||88305PC FT1|2|||200912061200||D|88342PC|||2|||||||||1;2;3;4|UNKNOWN^Path^Test|UNKNOWN^Physician^Te st||200912061200||88342PC GT1|1||Last^First^Middle||Addr1^Addr2^Detroit^MI^48201|^^^^^^undefined||||| IN1|1||Default Payer^^^^^-100|Default Payer|^^^^|||56434||||||||Test^Test^Test|Self||^^^^|||P|||||||||||||| IN1|2||Default Payer^^^^^-100|Default Payer|^^^^|||2123||||||||Last^First^|Life Partner||^^^^|||S||||||||||||||5333 IN1|3||Default Payer^^^^^-100|Default Payer|^^^^|||53223||||||||Test^Test^Test|Self||^^^^|||T||||||||||||||
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 54
HL7 Integration Using Mirth
11. Bibliography
Book References:
Pressman, Roger S. "Software Engineering: A Practitioner's Approach, 6th edition. Herbert Schildt The Complete Reference Seventh Edition Ramez Elmasri, Shamkant B. Navathe Fundamentals of Database Systems, 2nd Edition. Cliff Wootton JavaScript Programmer's Reference 2001
Website References:
http://www.corepointhealth.com/services/implementation http://www.hl7.org http://www.neotool.com/resources/HL7-Overview http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Health_Level_7 www.google.com www.mirthcorp.com
Dept Of MCA,B.I.E.T,Davangere.
Page 55
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Project Report On Event Management PDFDocument55 pagesProject Report On Event Management PDFKeleti Santhosh72% (46)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- JDBC Test Quiz FPTDocument68 pagesJDBC Test Quiz FPTminh60% (5)
- IBM Data Movement Tool (Developerworks)Document19 pagesIBM Data Movement Tool (Developerworks)WDPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory ManagementDocument5 pagesInventory Managementanon_810660790Pas encore d'évaluation
- Best Practices To Improve Performance in JDBCDocument20 pagesBest Practices To Improve Performance in JDBCAnirban PoddarPas encore d'évaluation
- PRJDBCDocument212 pagesPRJDBCpmishra3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ajt Paper Solution.... For Gtu Student.... Advance Java TechnologyDocument186 pagesAjt Paper Solution.... For Gtu Student.... Advance Java TechnologyShaili PalejkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Shibasish Chatterjee (2153203) Big Data SME Hands-OnDocument85 pagesShibasish Chatterjee (2153203) Big Data SME Hands-OnManojit RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- JDBC Test Quiz FPTDocument68 pagesJDBC Test Quiz FPTvăn cường NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- WT Practical 2Document18 pagesWT Practical 2Anjani KumariPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Advance JavaDocument35 pagesReport On Advance JavaVertika Srivastava63% (8)
- Elements of Hibernate ArchitectureDocument8 pagesElements of Hibernate ArchitectureShreyas PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- JDBC NotesDocument18 pagesJDBC NotesNandini Chowdary0% (1)
- JDBC Driver ManagerDocument9 pagesJDBC Driver ManagersowmiyaasPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Business Intelligence Suite Enterprise Edition 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.9.0) Certification MatrixDocument27 pagesOracle Business Intelligence Suite Enterprise Edition 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.9.0) Certification Matrixlilwayne hardiPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Java QuestionsDocument33 pagesBest Java QuestionsAnonymous dUZFpCzLPas encore d'évaluation
- Vultar JDBC Driver For T24/jBaseDocument30 pagesVultar JDBC Driver For T24/jBaseAnonymous XQTLKiqCePas encore d'évaluation
- Course Recommender System Aims at Predicting The Best Combination of Courses Selected by Students-1Document29 pagesCourse Recommender System Aims at Predicting The Best Combination of Courses Selected by Students-1ShivaniPas encore d'évaluation
- J2EE, RMI and JDBCDocument34 pagesJ2EE, RMI and JDBCShinde SarikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Criminal Face IdentificationDocument94 pagesCriminal Face Identificationsonaiya software solutionsPas encore d'évaluation
- E BankingDocument49 pagesE BankingParas PundirPas encore d'évaluation
- JDBC NotesDocument3 pagesJDBC Notesshalakha1992Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory Management SystemDocument62 pagesInventory Management SystemIshan MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Archelogical Survey of IndiaDocument34 pagesArchelogical Survey of IndiaSunny KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming WebLogic JDBCDocument162 pagesProgramming WebLogic JDBCapi-25930603Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Databse JDBC Dvelopers GuideDocument432 pagesOracle Databse JDBC Dvelopers GuideTsegaye AndargiePas encore d'évaluation
- SQLWorkbench ManualDocument194 pagesSQLWorkbench ManualCristiano TiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document25 pagesUnit 1mananrawat537Pas encore d'évaluation
- ODI TrainingDocument79 pagesODI TrainingNguyen Ba Quoc AnPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 JDBC PrinciplesDocument4 pages3.1 JDBC PrinciplesravicsPas encore d'évaluation