Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Therories and Failure
Transféré par
Rahul YadavDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Therories and Failure
Transféré par
Rahul YadavDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Department of Mechanical Engg. SET, SHARDA UNIVERSITY Course Name: Mechanical Engg.
Design Class: III (C) Lecture No. 7 Theories of failure When a machine element is subjected to a system of complex stress system, it is important to predict the mode of failure so that the design methodology may be based on a particular failure criterion. Theories of failure are essentially a set of failure criteria developed for the ease of design. In machine design an element is said to have failed if it ceases to perform its function. There are basically two types of mechanical failure: Yielding- This is due to excessive inelastic deformation rendering the machine part unsuitable to perform its function. This mostly occurs in ductile materials. Fracture- in this case the component tears apart in two or more parts. This mostly occurs in brittle materials. There are following types of theories of failure: Maximum principal stress theory (Rankines theory) Maximum shear stress theory (Tresca or guests theory) Maximum principal strain theory (saint venant theory) Maximum strain energy theory (Haighs theory) Maximum distortion energy theory (Henky or von Mises theory) Maximum principal stress theory (Rankines theory) Failure or yielding occurs in member when the maximum principal or normal stress in biaxial stress system reaches the limiting strength of material in simple tension test. = u/fs Used for brittle material.
Maximum shear stress theory (Tresca or guests theory) Failure or yielding occurs in member when the maximum shear stress in bi-axial stress system reaches equal to the shear stress at yield point in simple tension test. max =yt /fs Since yt = yt, therefore max =yt /2*fs Used for ductile material. Maximum Principal Strain Theory (Saint Venants Theory) According to this theory, the failure or yielding occurs at a point in a member when the maximum principal (or normal) strain in a bi-axial stress system reaches the limiting value of strain (i.e. strain at yield point) as determined from a simple tensile test. The maximum principal (or normal) strain in a bi-axial stress system is given by
Maximum strain energy theory Failure or yielding occurs in member when strain energy per unit volume in bi-axial stress system reaches the limiting strain energy(at yield point ) in simple tension test. 12+ 22 212 = (yt/fs)2 May be used for ductile material Maximum distortion energy theory or Von Mises Failure or yielding occurs in member when distortion strain energy(shear strain energy) per unit volume in bi-axial stress system reaches the limiting distortion energy(at yield point) in simple tension test. 12+ 22 212 = (yt/fs)2
Mostly used for ductile material
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Notation For Differentiation - WikipediaDocument11 pagesNotation For Differentiation - WikipediaTibor VéghPas encore d'évaluation
- A Textbook of Optics For BSC Classes As Per Ugc Model Syllabus 23nbsped 8121926114 9788121926119 CompressDocument689 pagesA Textbook of Optics For BSC Classes As Per Ugc Model Syllabus 23nbsped 8121926114 9788121926119 CompressSawon KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gauge TheoryDocument15 pagesGauge TheoryLillyOpenMindPas encore d'évaluation
- Alice in Wonderland: Chapter 1: Down The WormholeDocument9 pagesAlice in Wonderland: Chapter 1: Down The WormholeCho Xiang LongPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Liquid Gas Grade 3Document23 pagesSolid Liquid Gas Grade 3Eloisa Micah Guabes100% (1)
- Physics Wave Speed Wavelength FrequencyDocument3 pagesPhysics Wave Speed Wavelength FrequencyNor Zawani Abdul HalimPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 554 Problem Set-03 Nozzle Theory-Part-1Document1 pageME 554 Problem Set-03 Nozzle Theory-Part-1rahul prakash100% (1)
- Vanden Berghe G, de Meyer H - A Special Identity Between Three 2F1 (A, B C 4) Hyper Geometric Series - J. Comput. and Appl. Math. 160 (2003) 315-321Document7 pagesVanden Berghe G, de Meyer H - A Special Identity Between Three 2F1 (A, B C 4) Hyper Geometric Series - J. Comput. and Appl. Math. 160 (2003) 315-321Renee BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Exhaust Fans As Source of Power: Archit Patnaik, S.M.AliDocument4 pagesIndustrial Exhaust Fans As Source of Power: Archit Patnaik, S.M.Alidedi sanatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Assignment 1Document4 pagesPhysics Assignment 1Trí Võ PhạmPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Cell Troubleshooting Tips PDFDocument38 pagesLoad Cell Troubleshooting Tips PDFThong Kin MunPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal AnalysisDocument37 pagesThermal AnalysisZaid Majed100% (1)
- 2022 AP Student Samples and Commentary - AP Physics 1 FRQ 1Document14 pages2022 AP Student Samples and Commentary - AP Physics 1 FRQ 1Bánh Mì & FamilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gizmos - Magnetic InductionDocument7 pagesGizmos - Magnetic Inductionoctavie ahmed80% (10)
- Design For X-X Direction Check For Bending: CK y S CDocument12 pagesDesign For X-X Direction Check For Bending: CK y S CRaj BharaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Retention TimeDocument13 pagesRetention TimejowarPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscosity ChartDocument12 pagesViscosity ChartFrancisco HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Delta - Ia-Mds - VFD-C2000 - Um - en - 201606 PDFDocument684 pagesDelta - Ia-Mds - VFD-C2000 - Um - en - 201606 PDFFelipe Raul Chumpitaz GuevaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Unit 2 DEMDocument2 pagesTutorial Unit 2 DEMbalafetPas encore d'évaluation
- QRD Diffusers - Technical OverviewDocument30 pagesQRD Diffusers - Technical Overviewnathan_hw100% (1)
- UNIT 14-PHY 131-Chapter 29-Nuclear PhysicsDocument26 pagesUNIT 14-PHY 131-Chapter 29-Nuclear PhysicscharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Einstein Solid Specific Heat Model ExplainedDocument12 pagesEinstein Solid Specific Heat Model ExplainedFederico Alejandro GeserPas encore d'évaluation
- David L. Bergman and J. Paul Wesley - Spinning Charged Ring Model of Electron Yielding Anomalous Magnetic MomentDocument10 pagesDavid L. Bergman and J. Paul Wesley - Spinning Charged Ring Model of Electron Yielding Anomalous Magnetic MomentJuiomSDFPas encore d'évaluation
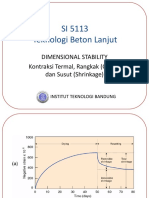
- Creep, Shrinkage EtcDocument80 pagesCreep, Shrinkage EtcEuneke WidyaningsihPas encore d'évaluation
- Schapellern Rex ResearchDocument16 pagesSchapellern Rex Researchmrhemped100% (1)
- Mata Pelajaran Tingkatan TajukDocument16 pagesMata Pelajaran Tingkatan TajukmalaomarPas encore d'évaluation
- History of SI UnitDocument10 pagesHistory of SI UnitEunice Cuerdo Peñamora100% (1)
- 3D ConsolidationDocument25 pages3D ConsolidationHashir ChPas encore d'évaluation
- Part Iib Quantum Mechanics 1. 2. 3Document7 pagesPart Iib Quantum Mechanics 1. 2. 3rizal123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 19, Solution 5.: X X T K MDocument1 pageChapter 19, Solution 5.: X X T K MMario MartinezPas encore d'évaluation