Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Biology, Chapter 1 Reviewer
Transféré par
Drew DiosoDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Biology, Chapter 1 Reviewer
Transféré par
Drew DiosoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Biology, Chapter 1
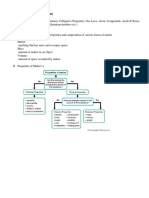
LIFEs HIERARCHY of ORGANIZATION Biosphere All the environments on earth that support life Ecosystem All of the organisms living in a particular area inclusive of the non-living things they interact with Community Entire array of organisms inhabiting a particular ecosystem Poupulation Individuals of the species living in an area. Organism Individual living thing Organ system Group of organs that works in a system to perform functions Organ An independent part of the organ system that performs functions Tissues Makes up an organ; made by groups of similar cells Cell Basic unit of life Separated from its environment by a membrane Molecule Cluster of atoms held together by chemical bonds Atom Smallest particle of ordinary matter DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Found in the chromosome Genetic information responsible for heredity and programming the production of an organisms molecules. Unit/s of inheritance that transmit information from parents offspring Double helix-ed (two strands) The diversity of life results from differences in DNA structure A <> T nucleotides C <> G Gene discreet unit of the DNA RNA A <> U C <> G
PROPERTIES THAT ARE COMMON TO ALL ORGANISMS Order o all things exhibit complex organization e.g. structure and organization of bones in the body Regulation o mechanisms that maintain an organisms internal environment e.g.: regulation of blood flow Growth and Development o genes control the pattern of growth Energy Processing o organisms take in energy, transform it to perform activites Response to the Environment o responds to environmental stimuli e.g.: venus flytrap, perspiration of humas Reproduction o the ability to produce their own kind Evolutionary Adaptation Taxonomy The branch of biology that names and classifies species Charles Darwin Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection o presented evidence to support idea of evolution o species today are descendants of ancestral species Theory: descent with modification Natural Selection o The process of nature, acc. to Darwin, selects organisms Evolution o Core theme of biology o Explains the unity and diversity of life unity: vertical (hierarchal organization) diversity: horizontal (evolution of species) Genome full set of chromosomes; all the inheritable traits of an organism Science Derived from a Latin verb meaning to know the goal of science is to understand natural phenomena discoveries Technology applies scientific knowledge for some specific purpose inventions Science helps Technology, vice versa o Technological advances come from scientific research; research benefits from technology Discovery Science Data: verifiable observations and measurements Detailed dissection and description Uses inductive reasoning o Derives general principles from a large number of specific observations Hypothesis-based Science Seeks natural causes and explanations for observations o Hypothesis Proposed explanation for a set of observations Uses deductive reasoning o From general to specific o Logic used to come up with ways to test hypothesis Discovery Science vs. Hypothesis-based Science Ds: scientists observe and describe objects and phenomena HbS: proposes hypotheses, scientists make deductions, test predictions
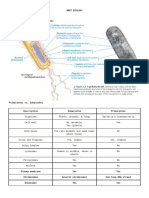
Producers Plants and other photosynthetic organisms Consumers Organisms that eat plants and/or other animals Bacteria/Fungi Decompose wastes and remains of organisms; recyclers in the ecosystem Two things for ecosystem to be successful recycle chemicals necessary for life move energy through the ecosystem o energy enters as light; exits as heat CELLS basic unit/s of life enclosed by a membrane; regulates passage of materials between the cell and its surroundings o Eukaryotic has DNA has nucleus has organelles separated by membranes organelles are found in the cytoplasm e.g.: plants, animals, protists, fungi o Prokaryotic has DNA has nucleoid mostly unicellular e.g.: bacteria
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Biology ReviewerDocument9 pagesBiology Reviewerflay1618100% (3)
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Why Analysis Presentation-TPm-training-materialDocument43 pagesWhy Why Analysis Presentation-TPm-training-materialsaravanananusha67% (6)
- God's Gift of Life ScienceDocument96 pagesGod's Gift of Life Sciencemicx ramos100% (2)
- General Science and Biology Reviewer for College StudentsDocument3 pagesGeneral Science and Biology Reviewer for College StudentsRomelyn LaguraPas encore d'évaluation
- NMAT - Must Know-ChemistryDocument45 pagesNMAT - Must Know-ChemistryElise TraugottPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument17 pagesChemistry ReviewerRalph Castillo100% (3)
- Introduction To Cell BiologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Cell BiologyReyvan FaltadoPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology ReviewerDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerElla UnicePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Quiz: Cell Structure, Organ Systems, Evolution & MoreDocument32 pagesBiology Quiz: Cell Structure, Organ Systems, Evolution & MoreChrisshalyn Sy PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesNmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cellssavina100% (1)
- Principles of Failure AnalysisDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Failure AnalysisLuis Kike Licona DíazPas encore d'évaluation
- The electron transport chain (ETCDocument99 pagesThe electron transport chain (ETCLauter Manaloto Franco100% (1)
- Biology Reviewer NotesDocument26 pagesBiology Reviewer Notesfkrugga11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Government and Constitution ReviewerDocument34 pagesPhilippine Government and Constitution Reviewermarygrace asuntoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Reviewer 1Document4 pagesPhysics Reviewer 1Liel Yap100% (2)
- Biology NotesDocument32 pagesBiology NotesTaylor BonnetPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQs DOMDocument5 pagesMCQs DOMyuvraj PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 ReviewerJames SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Reviewer Notes PDFDocument26 pagesBiology Reviewer Notes PDFAntonea50% (2)
- NMAT Biology Mitosis and Biomes QuestionsDocument122 pagesNMAT Biology Mitosis and Biomes QuestionsMikaela Rome BigayPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology NotesDocument20 pagesBiology NotesDannesa ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- NMAT Inductive Reasoning Practice Questions Set 1Document8 pagesNMAT Inductive Reasoning Practice Questions Set 1Junimy GamonganPas encore d'évaluation
- Math, Physics and Chem Exam 2 PDFDocument10 pagesMath, Physics and Chem Exam 2 PDFCha GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Packet SwitchingDocument28 pagesOptical Packet Switchingarjun c chandrathilPas encore d'évaluation
- NMAT Biology Simulation Mock ExamDocument4 pagesNMAT Biology Simulation Mock ExamPhen Montalbo100% (1)
- CHEM12 QUIZ 1 REVIEW KEY CONCEPTSDocument2 pagesCHEM12 QUIZ 1 REVIEW KEY CONCEPTSAngelo Montelibano Patron100% (2)
- Zoology Lecture (Reviewer)Document4 pagesZoology Lecture (Reviewer)Maria GrasyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concepts in ChemistryDocument34 pagesBasic Concepts in ChemistryEugene ConchaPas encore d'évaluation
- GENED ScienceDocument248 pagesGENED ScienceSer Gibo100% (2)
- Analytical Chemistry I Syllabus ExplainedDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry I Syllabus ExplainedDaniel TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Science Majorship Hand Outs m18Document11 pagesBiological Science Majorship Hand Outs m18Xenia Mae FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant and Animal Classification BasicsDocument47 pagesPlant and Animal Classification BasicsJaey EhmPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 150 Syllabus 2011Document3 pagesBio 150 Syllabus 2011Jolaine ValloPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimum Propeller Design Using Computerized MethodDocument10 pagesOptimum Propeller Design Using Computerized MethodPavan KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- General ScienceDocument46 pagesGeneral ScienceJosepino JosepinoPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Geolog Drilling Optimization ServicesDocument10 pages7 Geolog Drilling Optimization ServicespendexxPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 101 Chapter 1 NotesDocument3 pagesBio 101 Chapter 1 NotesAndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology ReviewerDocument7 pagesBiology ReviewerPatricia Ann Mae ToledoPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY AssessmemtDocument4 pagesBIOLOGY AssessmemtMei Joy33% (3)
- Biology Nmat @Document6 pagesBiology Nmat @Ma. Ellah Patricia M. GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Science IIIDocument16 pagesBiological Science IIIJennica Mae LptPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Biology ReviewerDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Biology ReviewerAnton Miguel Jordan83% (6)
- Hand-Outs Biology 2014Document38 pagesHand-Outs Biology 2014ISCCPas encore d'évaluation
- LET EXAM Bio Sci MajorDocument7 pagesLET EXAM Bio Sci MajorMa Zola EstelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pnu Let ReviewDocument136 pagesPnu Let ReviewVillafuerte Tayer JarnPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio102 ClassificationDocument19 pagesBio102 Classificationjoseph.covert100% (2)
- PE Reviewer Physical Education ConceptsDocument2 pagesPE Reviewer Physical Education ConceptsCharisse LeonardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument10 pagesChemistry Reviewerapi-19624513Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To BiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BiologyFransiel B. AkistoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoology ReviewerDocument5 pagesZoology ReviewerYearmeh CandiaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology QuizDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology QuizQueng ElediaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Problems in Genetics Plus Solutions Problems Involving One GeneDocument20 pagesPractice Problems in Genetics Plus Solutions Problems Involving One GeneGiovanni TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Microbiology DiscoveryDocument5 pagesHistory of Microbiology DiscoveryAlphonse Rossaint SambranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nmat Msa ConceptsDocument2 pagesNmat Msa ConceptsGeovin Dexter UyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini Mock Answer KeysDocument9 pagesMini Mock Answer KeysRosheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Majorship HandoutsDocument6 pagesScience Majorship HandoutsMei JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Syllabus in General ZoologyDocument3 pagesFinal Syllabus in General ZoologyEmman Acosta Domingcil100% (1)
- NMAT BIO RATIO by KeiDocument8 pagesNMAT BIO RATIO by KeiKkk100% (1)
- Grade 9 Chemistry Lesson on Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Chemistry Lesson on Types of Chemical ReactionsMoises Von Rosauro De GraciaPas encore d'évaluation
- UPCAT Math Topics Algebra Geometry Trigonometry StatisticsDocument6 pagesUPCAT Math Topics Algebra Geometry Trigonometry StatisticsAndre Mikhail SerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysics Reviewerroy_dubouzetPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 UPlink NMAT Biology Part 2 PDFDocument39 pages2020 UPlink NMAT Biology Part 2 PDFDaphne Jorjeane Hernaez0% (1)
- Microbiology ReviewerDocument16 pagesMicrobiology ReviewerAnna CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- LET Reviewer Biology Part 2Document5 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Part 2Gemma HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution and The Theme of BiologyDocument3 pagesEvolution and The Theme of BiologyYazmin QuevedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes ReceptorsDocument2 pagesEnzymes ReceptorsDrew DiosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mill of The GodsDocument7 pagesMill of The GodsPitetLaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 32 Lecture Presentation Auto Saved) LectureDocument44 pages32 Lecture Presentation Auto Saved) LectureDrew DiosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter10 PhotosynthesisDocument61 pagesChapter10 PhotosynthesisMisrai FaraukPas encore d'évaluation
- JMeter OAuth SamplerDocument3 pagesJMeter OAuth SamplerFredy NataPas encore d'évaluation
- TemplateDocument148 pagesTemplateWahyu Tri JuniantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Korea Battery Product Catalogue 2023Document8 pagesKorea Battery Product Catalogue 2023Cesar GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- CoreLine LED Brochure 2013Document20 pagesCoreLine LED Brochure 2013Dragan VuckovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Singtel Satellite Coverage Maps1Document12 pagesSingtel Satellite Coverage Maps1Anh TúPas encore d'évaluation
- NDT For Steel Pipe PilingDocument2 pagesNDT For Steel Pipe PilingSaid Alauddeen FaiszPas encore d'évaluation
- R6 Relay ValveDocument2 pagesR6 Relay ValveveereshPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea 2. Design - of - Machinery NortonDocument10 pagesTarea 2. Design - of - Machinery Nortonbisiosote100% (1)
- Legendary Units 1.1Document5 pagesLegendary Units 1.1Alejandro Sanchez GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fujitsu-General ASYG07-12 LLC 2014Document2 pagesFujitsu-General ASYG07-12 LLC 2014Euro-klima BitolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vivek Pal-2Document36 pagesVivek Pal-2Vivek palPas encore d'évaluation
- Valvula Relief Pruebas y Ajustes 325blDocument9 pagesValvula Relief Pruebas y Ajustes 325blcristian chuquicondor torresPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3Adet the moralistaemPas encore d'évaluation
- Anixter Wire&Cable Catalog Armored Cables PDFDocument42 pagesAnixter Wire&Cable Catalog Armored Cables PDFAhmed H. HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Fall2018Document2 pagesAssignment Fall2018Frans LoekitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Boeing 777Document5 pagesBoeing 777anon_874255349Pas encore d'évaluation
- User Guide For Gateway NV57H / NV55SDocument1 087 pagesUser Guide For Gateway NV57H / NV55SAudrey D. ChatmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal 1 - Laganzo, Escarez, TabilangonDocument35 pagesJournal 1 - Laganzo, Escarez, Tabilangoncloy aubreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Architectural Design of Bangalore Exhibition CentreDocument24 pagesArchitectural Design of Bangalore Exhibition CentreVeereshPas encore d'évaluation
- Minimum drilling supplies stockDocument3 pagesMinimum drilling supplies stockAsif KhanzadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Philosophy Class Lesson PlansDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Philosophy Class Lesson PlansJennifer MagangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Define Material Groups in SAP MMDocument3 pagesDefine Material Groups in SAP MMHẬU Nguyễn NhưPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadMe STEP7 Professional V14 enUS PDFDocument74 pagesReadMe STEP7 Professional V14 enUS PDFAndre Luis SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- QMCS 16 - 2 Process CapabilityDocument27 pagesQMCS 16 - 2 Process CapabilityalegabipachecoPas encore d'évaluation