Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Olytechnic of Amibia: Department of Mechanical Engineering Theory of Machines (TOM320S)
Transféré par
andrewzulu4455Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Olytechnic of Amibia: Department of Mechanical Engineering Theory of Machines (TOM320S)
Transféré par
andrewzulu4455Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA
Private Bag 13388, 13 Storch Street, Windhoek, Namibia Tel: +264 (61) 207 9111 Fax: +264 (61) 207 2444
http://www.polytechnic.edu.na
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
Email azulu@polytechnic.edu.na Tel: +264 (61) 207 2514 Fax: +264 (61) 207 2521
Department of Mechanical Engineering Theory of Machines (TOM320S)
Examination #1
Date: 18th August 2011 Duration: 2 hours Total marks: 60
Examiner: Mr. A. Zulu Moderator: Dr. R. Steenkamp
IMPORTANT NOTICES: Write neatly and legibly, as illegible work will not be considered for marks. If you are of the opinion that insufficient information was provided to solve a specific problem, make realistic assumptions, motivate these and continue solving the problem based on your assumptions made. Use F.B.Ds and illustrative diagrams wherever possible. Clearly show the reference Cartesian axes system used for each question. Pay attention to units and show the relevant unit in each calculated answer. No marks will be awarded for answers only. Calculations must contain a minimum number of logically sequenced steps followed by an answer. In cases where two or more different - and undeleted answers are given for the same item, the right answer will not be considered for marks. Use gravitational acceleration g = 9.81 m/s2. Answer all questions.
Section A [15] 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A mechanism has link lengths of 160 mm, 200 mm and 240 mm (ground). What link length(s) will give a class III (special-case Grashof) mechanism if the 240-mm link is the longest? [3]. What link length(s) in problem 1 above will give a class III (special-case Grashof) mechanism if the 160-mm link is the shortest? [3]. What do you understand by kinematic inversion of a linkage system? How many kinematic inversions are possible for four-bar mechanism? [3]. [MCQ] In linkage synthesis motion generation refers to the tracing of [a] a line [b] a point [c] both a point and a line [d] neither a point nor a line [e] a function generator [1]. [MCQ] What is the minimum value of the transmission angle for the Grashof crankrocker mechanism? [a] 0 [b] 180 [c] 40 [d] will depend whether the linkages are
extended or overlapping [e] I dont know (for no marks) [1].
6. 7. The rotatability of a linkage can be found using Grashof condition for 4 bars. This can be extended to multibar systems using the triangle inequality. Explain, in your own words, the concept of trianglular inequality [2]. In a four-bar mechanism, the lengths of the crank, coupler and rocker are 200 mm, 500 mm and 400 mm respectively. In the instant when the crank horizontal, the rocker (output) is vertical. What is the transmission angle? Is this a Grashof mechanism [3].
Section B [45] 8. Calculate the number of degrees of freedom of the mechanisms shown in Figure Q8a, b and c [12].
Figure 8a.
Figure 8b.
Figure Q8c.
9.
Using the graph paper provided, design a four-bar linkage system so that garage door of Figure Q9 can move from position 1 to position 2 to position 3. Show all your construction lines [16].
Figure Q9.
L2 = 40 mm; L3 = 96 mm; L4 = 122 mm; L1 = 162 mm Figure Q10.
-2-
10.
The linkage in Figure Q10 has the dimensions and crank angle given below. (a) Locate all the 6 instant centres of the mechanisms and label them [7]. (b) Given that for the position shown ( AO2O4 = 90 2 = 20 rad/s CCW, determine ), 4, VA and VB [10]. List of formulas
2 2 2 2 2 2 1 b + c ( d + a ) 1 b + c ( d a ) 1 = cos (extended); 2 = cos (overlap) 2bc 2bc
a 2 + d 2 b 2 c 2 bc n! = cos 1 ; DOF = 3 ( L 1) 2 J1 J 2 ;0 2toggle ; ICV = toggle 2ad ad ( n r ) !r ! v VA = ia2 ( cos 2 + i sin 2 ) = a2 ( sin 2 + i cos 2 ) v VBA = ib3 ( cos 3 + i sin 3 ) = b2 ( sin 3 + i cos 3 ) v VB = ic4 ( cos 4 + i sin 4 ) = c4 ( sin 4 + i cos 4 ) v 2 AA = a 2 ( sin 2 + i cos 2 ) a2 (cos 2 + i sin 2 ) v 2 ABA = b 3 ( sin 3 + i cos 3 ) b3 (cos 3 + i sin 3 ) v 2 AB = c 4 ( sin 4 + i cos 4 ) c4 (cos 4 + i sin 4 )
Reference four-bar linkage.
-End-
-3-
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Digital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsD'EverandDigital Electronics 2: Sequential and Arithmetic Logic CircuitsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- SE 2008 ElectricalDocument46 pagesSE 2008 ElectricalMuhammad MujtabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsD'EverandMathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsRoderick MelnikPas encore d'évaluation
- rr420305 RoboticsDocument8 pagesrr420305 RoboticsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionD'EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionPas encore d'évaluation
- BE ElectricalDocument45 pagesBE ElectricalOmkar ShetePas encore d'évaluation
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlD'EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlPas encore d'évaluation
- 01feb2016-Industrial Robotics,Design With Advanced Materials,Applied Mathematics,Optical Communication Technology,Advanced Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis,Mathematical Modeling,Analysis OfDocument15 pages01feb2016-Industrial Robotics,Design With Advanced Materials,Applied Mathematics,Optical Communication Technology,Advanced Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis,Mathematical Modeling,Analysis OfsirapuPas encore d'évaluation
- Guessing Papers 1-2-12th Electronics Sub Code C2Document6 pagesGuessing Papers 1-2-12th Electronics Sub Code C2snigdhagulhane0922Pas encore d'évaluation
- r05410207 Vlsi DesignDocument7 pagesr05410207 Vlsi Design9010469071Pas encore d'évaluation
- 07a81002 RoboticsandautomationDocument8 pages07a81002 RoboticsandautomationSharanya ThirichinapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear and Dig Italic Applications Jntu Model Paper WWW Student Yogi Com 100113195343 Phpapp02Document8 pagesLinear and Dig Italic Applications Jntu Model Paper WWW Student Yogi Com 100113195343 Phpapp02Ranjith ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aprilmay 2007Document7 pagesAprilmay 2007Viswa ChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- r05320204 InstrumentationDocument6 pagesr05320204 InstrumentationMounikaManuPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Electronics Ii Revision Examples 2002Document12 pagesDigital Electronics Ii Revision Examples 2002Hoan Tran VanPas encore d'évaluation
- B Tech21911R07 PDFDocument52 pagesB Tech21911R07 PDFRajeev BujjiPas encore d'évaluation
- En123 - SM2 2022 Department of Electrical & Communications Engineering DepartmentDocument6 pagesEn123 - SM2 2022 Department of Electrical & Communications Engineering DepartmentDavid Jnr PeraPas encore d'évaluation
- FY Btech - EX - Electrical & Electronics Engineering - SEM - I - JAN 2023Document3 pagesFY Btech - EX - Electrical & Electronics Engineering - SEM - I - JAN 2023kumbhalkarvalay8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unisa MOM3602 Theory of Machines III Mock Exam 2015 - Preparation Practice ProblemsDocument9 pagesUnisa MOM3602 Theory of Machines III Mock Exam 2015 - Preparation Practice ProblemsDaniel MabengoPas encore d'évaluation
- QP of UniversityDocument1 132 pagesQP of UniversityKunal Ranjane100% (1)
- IIUM Electronics ECE 1312/ECE 1231 Final Exam Sem 1 (2012 - 2013)Document8 pagesIIUM Electronics ECE 1312/ECE 1231 Final Exam Sem 1 (2012 - 2013)Ridhwan Asri100% (1)
- APR2013P21Document63 pagesAPR2013P21qsashutoshPas encore d'évaluation
- BE 2008 Electronics&Telecommunication PDFDocument71 pagesBE 2008 Electronics&Telecommunication PDFcontrasterPas encore d'évaluation
- Jntuk MT Feb 2016 - 2Document15 pagesJntuk MT Feb 2016 - 2MhappyCuPas encore d'évaluation
- r05220403 Switching Theory and Logic DesignDocument8 pagesr05220403 Switching Theory and Logic DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 3Document5 pagesSheet 3Mohamed Tag EldeenPas encore d'évaluation
- 32126Document26 pages32126chuku7Pas encore d'évaluation
- RR420305 Robotics PDFDocument9 pagesRR420305 Robotics PDFSarath ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- 07a60204 - InstrumentationDocument5 pages07a60204 - InstrumentationMounikaManuPas encore d'évaluation
- 4301CIV - 22 Revision 2Document11 pages4301CIV - 22 Revision 2dtl projectPas encore d'évaluation
- Emf Question PaperDocument54 pagesEmf Question PaperRambabu DanduriPas encore d'évaluation
- Elctengg Ii Kas12Document2 pagesElctengg Ii Kas12Asif ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aprilmay 2009Document8 pagesAprilmay 2009Viswa ChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Universityquestions.in: Unit 1 Number Systems and Digital Logic Families Part ADocument7 pagesWWW - Universityquestions.in: Unit 1 Number Systems and Digital Logic Families Part Abunny_589318117Pas encore d'évaluation
- Me Oct2011 PDFDocument1 050 pagesMe Oct2011 PDFrahimmullaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elec1041y 1 2007 2 PDFDocument7 pagesElec1041y 1 2007 2 PDFchetsPas encore d'évaluation
- November-December 2011 R07 ALL in ONEDocument25 pagesNovember-December 2011 R07 ALL in ONEAlwyzz Happie RaamzzPas encore d'évaluation
- Be First Year Fe Engineering Semester 1 2019 November Basic Electronics Engineering Pattern 2019Document2 pagesBe First Year Fe Engineering Semester 1 2019 November Basic Electronics Engineering Pattern 2019Tushar PagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2 - KKKL2163 - 20182019Document2 pagesTutorial 2 - KKKL2163 - 20182019Muhd Hijazz FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lista 5Document22 pagesLista 5vsabioniPas encore d'évaluation
- B.E - (2008 Patt.) - 1-5Document5 pagesB.E - (2008 Patt.) - 1-5Ravikiran JadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Robert Bosch Placement Pattern 2 - Freshers ChoiceDocument14 pagesRobert Bosch Placement Pattern 2 - Freshers ChoicefresherschoicePas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Logic DesignDocument126 pagesDigital Logic Designmt21215015 Navdeep GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 01 - QuestionsDocument6 pagesModule 01 - QuestionsJeff GrahamPas encore d'évaluation
- Pcc-Ee 305Document4 pagesPcc-Ee 305Amlan SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- 9D15102 Advanced MechanismsDocument2 pages9D15102 Advanced MechanismsMuni MuneendranPas encore d'évaluation
- Elx305 Ref Exam SolutionsDocument7 pagesElx305 Ref Exam SolutionsNadeesha Bandara100% (1)
- S T L DDocument12 pagesS T L DMohan Krishna0% (1)
- University of NairobiDocument3 pagesUniversity of NairobijavoPas encore d'évaluation
- APRMAY18Document6 pagesAPRMAY18fantin amirtharajPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem1 1213 SolutionDocument17 pagesSem1 1213 SolutionThinesh StPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Electronics Question BankDocument6 pagesDigital Electronics Question BankReshna ShowkathPas encore d'évaluation
- Dec 2009Document8 pagesDec 2009Viswa ChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Terminal Examination, Fall 2020Document3 pagesTerminal Examination, Fall 2020Umer NaeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Industry Internship ReportDocument3 pagesSample Industry Internship ReportKamarul NizamPas encore d'évaluation
- InstrumentationDocument7 pagesInstrumentationNagaValliPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 1Document436 pagesMe 1Akshay Mane0% (1)
- 110id0625 18 PDFDocument40 pages110id0625 18 PDFPatel RonakPas encore d'évaluation
- A Novel Multi Objective Constraints Based Industrial Gripper Design With Optimized Stiffness For Object GraspingDocument14 pagesA Novel Multi Objective Constraints Based Industrial Gripper Design With Optimized Stiffness For Object GraspingtayzarlwintunPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Aided Analysis and Optimization of Mechanical System DynamicsDocument706 pagesComputer Aided Analysis and Optimization of Mechanical System DynamicsValencia Luis ErnestoPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Mobility of Mechanisms A Critical Review-Grigore GoguDocument30 pages6 Mobility of Mechanisms A Critical Review-Grigore GoguAlin Florescu100% (1)
- MMSDocument12 pagesMMSDuke Stan100% (1)
- 15334-ME8492 KOM Course File 2021-2022Document20 pages15334-ME8492 KOM Course File 2021-2022MICHEL RAJ MechPas encore d'évaluation
- Linkages 69868Document33 pagesLinkages 69868Abi DemPas encore d'évaluation
- (Small Architecture Series) Esther Rivas Adrover-Deployable Structures-Laurence King Publishing (2015) PDFDocument161 pages(Small Architecture Series) Esther Rivas Adrover-Deployable Structures-Laurence King Publishing (2015) PDFDiego MV100% (1)
- Advances in Mechanism Design II: Jaroslav Beran Martin Bílek Petr Žabka EditorsDocument387 pagesAdvances in Mechanism Design II: Jaroslav Beran Martin Bílek Petr Žabka EditorsJabbar Aljanaby0% (1)
- CAM and Follower LectureDocument61 pagesCAM and Follower LectureNauman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
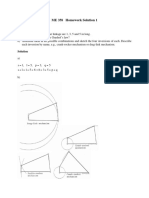
- ME 358 Homework Solution 1: Problem 1Document12 pagesME 358 Homework Solution 1: Problem 1Neo TarunPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 1Document37 pagesUnit - 1Hanan ShayiboPas encore d'évaluation
- 161 PDFsam Book Adams-Tutorial-3rdEditionDocument192 pages161 PDFsam Book Adams-Tutorial-3rdEditionShevon FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Theo JansenDocument8 pagesTheo JansenCarmensa LópezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mom Final ReportDocument23 pagesMom Final ReportAsim ShehzadPas encore d'évaluation
- UMP-xxx-FS Series 4-20ma Proportional Rotary Actuator Instruction Manual GeneralDocument4 pagesUMP-xxx-FS Series 4-20ma Proportional Rotary Actuator Instruction Manual GeneralPradeep TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematic and Dynamic Analysis ofDocument6 pagesKinematic and Dynamic Analysis ofAmirZukriPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of Four Bar Linkages: Input-Output Relationship: Freudenstein's EquationDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Four Bar Linkages: Input-Output Relationship: Freudenstein's EquationMuthoka VincentPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Blocks of MachineDocument7 pagesBuilding Blocks of MachineDeepak SahPas encore d'évaluation
- Gov Mec - WSM - 0001158 - 01Document36 pagesGov Mec - WSM - 0001158 - 01ARY TOGINHO100% (7)
- Tom MCQ UNIT 1Document25 pagesTom MCQ UNIT 1Kumar PacharePas encore d'évaluation
- 9339Document674 pages9339Hector Man100% (3)
- 4.1 Question 1: Analysis of Four-Bar Linkage (12 Marks Total)Document2 pages4.1 Question 1: Analysis of Four-Bar Linkage (12 Marks Total)Sh Younus QreshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document75 pagesChapter 3AzooPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6-7 Synthesis of Simple Planar MechanismsDocument12 pagesLecture 6-7 Synthesis of Simple Planar MechanismsmayankmaroliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Mechanism and KinematicsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Mechanism and Kinematicsboonjie100% (1)
- Steel-Smith PDF CatalogueDocument93 pagesSteel-Smith PDF CatalogueneetadaeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryDocument23 pagesAssignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryAman AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- MECH 343 Course Outline 2020Document10 pagesMECH 343 Course Outline 2020Navjot SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of Four Bar MechanismDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Four Bar MechanismDbz BoleroPas encore d'évaluation
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemD'EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsD'EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersD'EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70ED'EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (6)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeD'EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)D'EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.D'EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeD'EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormD'EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisD'EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignD'EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusD'EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyD'EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyPas encore d'évaluation