Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Exp 9 Introduction To Machines
Transféré par
Muhammad AwaisDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Exp 9 Introduction To Machines
Transféré par
Muhammad AwaisDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
76478059.
doc9
National University of Science and Technology (NUST) School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (SEECS)
EE 231 Electro Mechanical System Lab Objectives:
Experiment #9 Introduction to Machines
Fall 2011
To get familiarized with different machines (DC, Induction, and Synchronous Machine) and their parts. To assemble different machines (DC, Induction, and Synchronous Machine) and appreciate the working and placement of different parts in a machine.
Equipment: For DC Machine:
Item 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Quantity 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 1 Description Support Module Faceplate Pulley Wing head screw Brush yoke end-bell Stator DC rotor Rear end-bell Potentiometer 1000
Table 01
Part No. 8163 8211-D5 25834 25843 25832 22037-D5 22038-D5 29088-5 25836-5
For Three Phase Wound-Rotor Induction Motor:
Item 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Quantity 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 1 Description Support Module Faceplate Pulley Wing head screw Front end-bell Stator Rotor Rear end-bell Brush holder
Table 02
Part No. 8163 8231-D5 25834 25843 23662-7 22062-D5 22190-D5 23662-8 25842
76478059.doc9
For Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor:
Item 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Quantity 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 Description Support Module Faceplate Pulley Wing head screw Front end-bell Stator Rotor Rear end-bell
Table 03
Part No. 8163 8211-D5 25834 25843 25832 22037-D5 22038-D5 29088-5
For Synchronous Machine:
Item 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Quantity 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 Description Support Module Faceplate Pulley Wing head screw Front end-bell Stator Rotor Rear end-bell Brush Holder Potentiometer 500
Table 04
Part No. 8163 8241-D5 25834 25843 23662-7 22062-D5 22094-D5 23662-8 25842 25835-5
Discussion: DC Machines: DC machines are generators that convert mechanical energy to dc electrical energy and motors that convert dc electrical energy to mechanical energy. Most dc machines are like ac machines in that they have ac voltages and currents within them - dc machines have a dc output only because a mechanism exists that converts the internal ac voltage to dc voltages at their terminals. Since this mechanism is also called a commutator, dc machinery is also known as commutating machinery. Induction Motor: An induction motor or asynchronous motor is the most commonly used industrial motor, finding application in many situations where speed regulation is not essential. It is simple and relatively inexpensive. There are two general types of Induction Motors: the squirrelcage type and the wound rotor machine. Both motors have an armature or stator structure similar to that of the alternating current generator, consisting of a hollow cylinder of laminated sheet steel in which are punched longitudinal slots. These motors are widely used in industrial drives because they are robust and have no brushes.
76478059.doc9
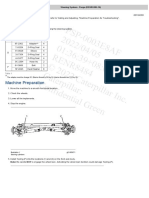
Synchronous Machine: Synchronous machines is an important electromechanical energy converter. Synchronous generators usually operate together (or in parallel) forming a large power system supplying electrical energy to the loads or consumers. For these applications synchronous machines are built in large units, their rating ranging from tens to hundreds of megawatts. For high-speed machines, the prime movers are usually steam turbines employing fossil or nuclear energy resources. Low speed machines are often driven by hydro-turbines that employ water power for generation. Smaller synchronous machines are sometimes used for private generation and as standby units, with diesel engines or gas turbines as prime movers. Synchronous machines can also be used as motors, but they are usually built in very large sizes. The synchronous motor operates at a precise synchronous speed, and hence is a constant-speed motor. Unlike the induction motor, whose operation always involves a lagging power factor, the synchronous motor possesses a variable power-factor characteristic, and hence is suitable for power factor correction applications. DC MACHINE - ASSEMBLY Recommendations: Be sure to use only the parts called for in the exercise. Many parts look similar but have different electrical characteristics. Keep your work table clear. Have only the parts needed for each assembly step. No tools are required to assemble the machine. However, a mallet is included to mount the end-bells to the frame. Refer to the exploded view drawing (Figure 01) before performing each assembly step. Procedure: 1. Assembling the rotor (Item 7) to the front end-bell (Item 5). Hold the rotor (7) in a vertical position with the commutator end at the top. b) Slide the end-bell (5) over the rotor shaft. With the tip of your index fingers, push back both brushes simultaneously. Apply hand pressure to the end bell to push the bearing into the end-bell housing. Release the brushes. c) Be careful not to damage the brushes or the commutator. If necessary use the mallet to seat the bearing in the housing.
a)
2.
Coupling the end-bells to the stator frame (Items 4,6, and 8). a) Place the stator (Item 6) on the work table with the connector plug at the rear as in Figure 1. Insert the assembled rotor/end-bell inside the
3
76478059.doc9
b) c) d) e) f) g) h) 3.
stator with the brush-shifting lever in the upward position. Be careful not to scratch the wires of the stator winding. Align the end-bell assembly holes with the holes in the stator. Insert the four wing head screws (Item 4) into the front end-bell and through the stator assembly hole. Mount the front end-bell to the frame. Use the mallet, if necessary. Slide the rear end-bell (Item 8) over the rotor shaft. Feed the connector plug out through the bottom opening of the end-bell. The larger opening must be at the top. Align the rear end-bell assembly holes with the stator holes and mount the end-bell to the frame. Use the mallet, if necessary. Engage the assembly screws in the rear end-bell. Secure the end-bells to the frame by tightening each screw alternately. Hand-tighten evenly. Rotate the shaft by hand in both directions to ensure that the rotor is centered inside the stator and turns freely.
Installing the pulley (Item 3) on the shaft of the machine. a) Slide the pulley (Item 3) over the front end of the shaft. Line up the pulley keyway with the shaft key. Push firmly to lock the pulley in place against the stopper ring. Setting the machine on the support module (Item 1). a) Place the assembled machine on the base of the support module (1) between hold-down clamps X and Y (pulley side toward the front of the module). Make sure that the clamps are turned as shown in Figure 1. Line up the two holes in the stator base with the studs between the two clamps and seat the machine on the support base. b) Turn the hold-down clamps 90o so that the plastic pins engage in the slots on the stator base. Hand-tighten the wing nuts to fasten the machine to the support base. Electrical connections and mounting of the components on the support module. a) Plug the polarized male connector A from the stator into the corresponding female connector A on the support base. b) Plug the polarized male connector B from the brush yoke end-bell into the corresponding female connector B on the support base. c) Install the schematic symbols faceplate (Item 2) in the front panel of the support module and hand tighten the retaining screws. d) Unscrew the front panel retaining screws and lower the hinged panel. e) Install the variable-resistance/breaker unit (Item 9) from the rear and hand-tighten the retaining screws. f) Raise the front panel and secure it with the retaining screws. Congratulations! You have just assembled a direct current machine.
4.
5.
6.
76478059.doc9
Figure 01. Exploded view of a DC Machine.
THREE PHASE WOUND-ROTOR INDUCTION MOTOR - ASSEMBLY Recommendations: Be sure to use only the parts called for in the exercise. Many parts look similar but have different electrical characteristics. Keep your work table clear. Have only the parts needed for each assembly step. No tools are required to assemble the machine. However, a mallet is included to mount the end-bells to the frame. Refer to the exploded view drawing (Figure 02) before performing each assembly step. Procedure: 1. Assembling the rotor (Item 7) to the front end-bell (Item 5). a) Hold the rotor (Item 7) in a vertical position with the slip ring end at the bottom.
76478059.doc9
b) Slide the end-bell (Item 5) over the rotor shaft. Apply hand pressure to the end-bell to push the bearing into the end-bell housing. If necessary, use the mallet to seat the bearing on the housing. 2. Coupling the end-bells to the stator (Item 6) frame. a) Place the stator (Item 6) on the work table with the connector plug at the rear as shown in Figure 02. Insert the assembled rotor/end-bell inside the stator. Be careful not to scratch the wires of the stator winding or the finished surface of the rotor. b) Align the end-bell assembly holes with the holes in the stator. c) Insert the four wing head screws (4) into the front end-bell and through the stator assembly holes. d) Mount the front end-bell to the frame. Use the mallet if necessary. e) Slide the rear end-bell (Item 8) over the slip rings on the rotor shaft. (Be careful not to scratch the polished surface of the slip rings.) Feed the connector plug out through the bottom opening of the end-bell. The larger opening must be at the top. f) Align the rear end-bell assembly holes with the stator holes and mount the end-bell to the frame. Use the mallet, if necessary. g) Engage the assembly screws in the rear end-bell. Secure the end-bells to the frame by tightening each screw alternately. Hand-tighten evenly. h) Rotate the shaft by hand in both directions to ensure that the rotor is centered inside the stator an runs freely. 3. Installing the pulley (Item 3) on the motor shaft. a) Slide the pulley (Item 3) over the front end of the shaft. Line up the pulley keyway with the shaft key. Push firmly to lock the pulley in space against the stopper ring.
4.
Installing the brush holder (Item 9) on the rear end-bell. a) Slide the brush holder (Item 9) over the rear end of the shaft by successively clearing and releasing the brushes over the slip rings. (Be careful not to scratch the brushes or the polished surface of the slip rings.) Secure the brush holder to the rear end-bell by tightening the retaining screws. Setting the motor on the support module (Item 1). a) Place the assembled motor on the base of the support module (Item 1) between hold down clamps X and Y (pulley side toward the front of the module.) Make sure that the clamps are turned are shown in Figure 02. Line up the two holes in the stator base with the studs between the two clamps and seat the motor on the support base.
b)
5.
Turn the hold down clamps 90o so that the plastic pins engage in the slots on the stator base. Hand-tighten the wing nuts to fasten the motor to the support base.
6.
Electrical connections and mounting of the faceplate (Item 2) on the support module.
6
76478059.doc9
a) Plug the polarized male connector A from the stator into the corresponding female connector A on the support base. b) Plug the polarized male connector B from the brush holder (Item 11) into the corresponding female connector B on the support base. c) Install the schematic symbols faceplate (Item 2) on the front panel of the support module and hand tighten the retaining screws.
7.
Congratulations! You have just assembled a three phase wound-rotor induction motor.
Figure 02. Exploded view of a three phase wound-rotor Induction Motor.
THREE PHASE SQUIRREL CAGE INDUCTION MOTOR - ASSEMBLY Recommendations: Be sure to use only the parts called for in the exercise. Many parts look similar but have different electrical characteristics. Keep your work table clear. Have only the parts needed for each assembly step. No tools are required to assemble the machine. However, a mallet is included to mount the end-bells to the frame.
7
76478059.doc9
Refer to the exploded view drawing (Figure 03) before performing each assembly step. Procedure: 1. Assembling the rotor (Item 7) to the front end-bell (Item 5). a) Hold the rotor (Item 7) in a vertical position with the key end of shaft at the top. b) Slide the end-bell (Item 5) over the rotor shaft. Apply hand-pressure to the end-bell to push the bearing into the end-bell housing. If necessary, use the mallet to seat the bearing in the housing. 2. Coupling the end bells to the stator (Item 6) frame. a) Place the stator (Item 6) on the work table with the connector plug at the rear as shown in Figure 03. Insert the assembled rotor /end-bell inside the stator. Be careful not to scratch the finished surface of the rotor. b) Align the end-bell assembly holes with the holes in the stator. c) Insert the four wing head screws (Item 4) into the front end-bell and through the stator assembly holes. d) Mount the front end-bell to the frame. Use the mallet, if necessary. e) Slide the rear end-bell (item 8) over the rotor shaft. Feed the connector plug out through the bottom opening of the end-bell. The larger opening must be at the top. f) Align the rear end-bell assembly holes with the stator holes and mount the end-bell to the frame. Use a mallet, if necessary. g) Engage the assembly screws in the rear end-bell. Secure the end-bells to the frame by tightening each screw alternately. Hand-tighten evenly. h) Rotate the shaft by hand in both directions to ensure that the rotor is centered inside the stator and turns freely. 3. Installing the pulley on the motor shaft. a) Slide the pulley (Item 3) over the front end of the shaft. Line up the pulley keyway with the shaft key. Push firmly to lock the pulley in place against the stopper ring.
4.
Setting the motor on the support module (Item 1). a) Place the assembled motor on the base of the support module (Item 1) between the hold-down clamps X and Y (pulley side toward the front of the module). Make sure that the clamps are turned as shown in Figure 03. Line up the two holes in the stator base with the studs between the two clamps and seat the motor on the support base. b) Turn the hold-down clamps 90o so that the plastic pins engage in the slots on the stator base. Hand-tighten the wing nuts to fasten the motor to the support base. Electrical connections and mounting of the faceplate (item 2) on the support module. a) Plug the polarized male connector A from the stator into the corresponding female connector A on the support base.
8
5.
76478059.doc9
b) Install the schematic symbols faceplate (Item 2) on the front panel of the support module and hand-tighten the retaining screws.
6.
Congratulations! You have just assembled a three phase squirrel cage induction motor.
Figure 03. Exploded view of a three phase squirrel cage Induction Motor.
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINE - ASSEMBLY Recommendations: Be sure to use only the parts called for in the exercise. Many parts look similar but have different electrical characteristics. Keep your work table clear. Have only the parts needed for each assembly step. No tools are required to assemble the machine. However, a mallet is included to mount the end-bells to the frame. Refer to the exploded view drawing (Figure 04) before performing each assembly step.
76478059.doc9
Procedure: 1. Assembling the rotor (Item 7) to the front end-bell (Item 5). a) Hold the rotor (Item 7) in a vertical position with the slip ring end at the bottom. b) Slide the end-bell (Item 5) over the rotor shaft. Apply hand pressure to the end-bell to push the bearing into the end-bell housing. If necessary, use the mallet to seat the bearing in the housing. 2. Coupling the end-bells to the stator (Item 6) frame. a) Place the stator (Item 6) on the work table with the connector plug at the rear as shown in Figure 04. Insert the assembled rotor/end-bell inside the stator. Be careful not to scratch the wires of the stator winding or the finished surface of the rotor. b) Align the end-bell assembly holes with the holes in the stator. c) Insert the four wing head screws (Item 4) into the front end-bell and through the stator assembly holes. d) Mount the front end-bell to the frame. Use the mallet, if necessary. e) Slide the rear end-bell (Item 8) over the slip rings on the rotor shaft. (Be careful not to scratch the polished surface of the slip rings.) Feed the connector plug out through the bottom opening of the end-bell. The larger opening must be at the top. f) Align the rear end-bell assembly holes with the stator holes and mount the end-bell to the frame. Use the mallet, if necessary. g) Engage the assembly screws in the rear end-bell. Secure the end-bells to the frame by tightening each screw immediately. Hand-tighten evenly. h) Rotate the shaft by hand in both directions to ensure that the rotor is centered inside the stator and turns freely. 3. Installing the pulley (Item 3) on the shaft of the machine. a) Slide the pulley (Item 3) over the front end of the shaft. Line up the pulley keyway with the shaft key. Push firmly to lock the pulley in place against the stopper ring. 4. Installing the brush holder (Item 9) on the rear end-bell. a) Slide the brush holder (Item 9) over the rear end of the shaft by successively clearing and releasing the brushes over the slip rings. (Be careful not to scratch the brushes of the polished surface of the slip rings.) Secure the brush holder to the rear end-bell by tightening the retaining screws. 5. Setting the machine on the support module (Item 1). a) Place the assembled machine on the base of the support module (Item 1) between the hold down clamps X and Y (pulley side toward the front of the module. ) Make sure that the clamps are turned as shown in Figure 04. Line up the two holes in the stator base with the studs between the two clamps and seat the machine on the support base.
10
76478059.doc9
Turn the hold down clamps 90o so that the plastic pins engage in the slots on the stator base. Hand-tighten the wing nuts to fasten the machine to the support base. 6. Electrical connections and mounting of the components on the support module. a) Plug the polarized male connector A from the stator into the corresponding female connector A on the support base. b) Plug the polarized male connector B from the brush holder into the corresponding female connector B on the support base. c) Install the schematic symbols faceplate (Item 2) on the front panel of the support module and hand-tighten the retaining screws. d) Unscrew the front panel retaining screws and lower the hinged panel. e) Install the variable-resistance/breaker unit (Item 10) from the rear and hand-tighten the retaining screws. Plug lead C into female banana jack C located on the front panel. f) Raise the front panel and secure it with the retaining screws.
b) 7.
Congratulations! You have just assembled a synchronous machine.
Figure 04. Exploded view of a Synchronous Machine.
11
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- How to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheD'EverandHow to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Connecting Rod Bearings - Install - Connecting Rods in PositionDocument4 pagesConnecting Rod Bearings - Install - Connecting Rods in PositionTatiano BrolloPas encore d'évaluation
- Encendido Del Motor Del SolenoideDocument6 pagesEncendido Del Motor Del SolenoideKrz F. BlancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Generator - Align: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenDocument6 pagesGenerator - Align: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenNimPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogue-Dye Cutting MCDocument11 pagesCatalogue-Dye Cutting MCTaposhPas encore d'évaluation
- E2063 Teknologi Elektrik 2 UNIT7Document36 pagesE2063 Teknologi Elektrik 2 UNIT7dbu2952Pas encore d'évaluation
- Alineacion CatDocument4 pagesAlineacion CatAndrea Zalamea100% (1)
- Alinieación Del GeneradorDocument5 pagesAlinieación Del Generadordamian_pelonPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation Instructions For Vilter 25972Document8 pagesInstallation Instructions For Vilter 25972jorge castilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Ms Clamshell Operating ManualDocument28 pagesMs Clamshell Operating ManualEhsan50% (2)
- Etg TG32P31 Generator Op ManualDocument76 pagesEtg TG32P31 Generator Op Manualits_yours2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Parts of Lathe MCDocument7 pagesBasic Parts of Lathe MCKrishna Patel100% (1)
- MSD 4151Document8 pagesMSD 4151rxhughesPas encore d'évaluation
- MK RepairsDocument141 pagesMK RepairsAnonymous SJyuwb0DPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibracion InyectoresDocument4 pagesCalibracion InyectoresWladimir AmaguañaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - Camshaft - Install PDFDocument11 pages02 - Camshaft - Install PDFNimPas encore d'évaluation
- Caterpillar Cat 225 EXCAVATOR (Prefix 76U) Service Repair Manual (76U01200-02728)Document26 pagesCaterpillar Cat 225 EXCAVATOR (Prefix 76U) Service Repair Manual (76U01200-02728)rpoy9396615Pas encore d'évaluation
- Title:To Practically Configuration and Characteristic ofDocument14 pagesTitle:To Practically Configuration and Characteristic ofKelvin YipPas encore d'évaluation
- Cigüeñal - Instalar: Tabla 1Document5 pagesCigüeñal - Instalar: Tabla 1Miguel Angel Garrido CardenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Replace Governor ActuatorDocument8 pagesReplace Governor ActuatorSteven ManuputtyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pistons and Connecting Rods - InstallDocument5 pagesPistons and Connecting Rods - Installeshopmanual limaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sgs3468ahd PDFDocument62 pagesSgs3468ahd PDFDilan BvlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Converting Car Starter Motors For Your Robot: 2.1 Disconnecting The Field WindingDocument9 pagesConverting Car Starter Motors For Your Robot: 2.1 Disconnecting The Field WindingSenadGrabovacPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Injector Synchronization - AdjustDocument5 pagesUnit Injector Synchronization - AdjustAhmed Rezk100% (1)
- Blade - Remove and InstallDocument8 pagesBlade - Remove and InstallJohn GrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Crankshaft - InstallDocument7 pagesCrankshaft - InstallCamila Vasques QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- 1953 Lucas Dynamos E3L E3LM E3NDocument7 pages1953 Lucas Dynamos E3L E3LM E3NedelapolloPas encore d'évaluation
- Kearney and Trecker Installation ManualDocument12 pagesKearney and Trecker Installation Manualaa987100% (1)
- Et500plus Install ManualDocument26 pagesEt500plus Install ManualDirk HennPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual For 1215 Kva Rig AlternatorDocument18 pagesManual For 1215 Kva Rig Alternatorprem080910Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Injector Synchronization - Adjust: 3114, 3116 and 3126 Industrial, Marine and Generator Set EnginesDocument6 pagesUnit Injector Synchronization - Adjust: 3114, 3116 and 3126 Industrial, Marine and Generator Set EnginesChristian Vinueza VillavicencioPas encore d'évaluation
- Autogard Series 820 Torque Limiter: Installation and Maintenance InstructionsDocument16 pagesAutogard Series 820 Torque Limiter: Installation and Maintenance InstructionsIvana Z. OgnjanovićPas encore d'évaluation
- XG Rack-Mount Install Guide M370078-05Document11 pagesXG Rack-Mount Install Guide M370078-05Dumi BogdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Heavy Duty Sewing Machine Servo MotorDocument15 pagesHeavy Duty Sewing Machine Servo MotorBill Jiang100% (3)
- Mini X Motor Replacement With Fan UpgradeDocument7 pagesMini X Motor Replacement With Fan UpgradeLucian ComanPas encore d'évaluation
- Semi Solid Link Solenoid Installation Instructions 50MT Motor 12V and 24VDocument2 pagesSemi Solid Link Solenoid Installation Instructions 50MT Motor 12V and 24VAbu Naufal HanifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Crankshaft - InstallDocument7 pagesCrankshaft - InstallLeonardo PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Manette 4SNDocument13 pagesManette 4SNOthmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3412E Piston and Connecting Rod AssemblyDocument11 pages3412E Piston and Connecting Rod AssemblyMohammed Mostafa100% (2)
- Rocker Arm BuminataDocument7 pagesRocker Arm BuminataRgin AlanPas encore d'évaluation
- (IJET-V1I2P4) Authors :mrs - Rita S. Pimpalkar, Rutuja U. Joshi, Rakesh R. Khandare, Rounak R. Agarwal, Bhushan S. BendaleDocument8 pages(IJET-V1I2P4) Authors :mrs - Rita S. Pimpalkar, Rutuja U. Joshi, Rakesh R. Khandare, Rounak R. Agarwal, Bhushan S. BendaleInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesPas encore d'évaluation
- Isp - 07Nt: Automatic Controller of Cutting Thickness For Conveyor Cutting MachinesDocument13 pagesIsp - 07Nt: Automatic Controller of Cutting Thickness For Conveyor Cutting MachinesпетрPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mechatronics Revolution: Fundamentals and Core Concepts: Robot Assembly ManualDocument30 pagesThe Mechatronics Revolution: Fundamentals and Core Concepts: Robot Assembly ManualdawssaPas encore d'évaluation
- Continental Aileron Cable Rigging Event Criteria: Page 1Document11 pagesContinental Aileron Cable Rigging Event Criteria: Page 1Jose Miguel Atehortua ArenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Steering Purge 14MDocument3 pagesSteering Purge 14MvaroPas encore d'évaluation
- SONY Z MechanismDocument64 pagesSONY Z MechanismHarinarayana ChennupatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Camshaft Timing: Testing and AdjustingDocument8 pagesCamshaft Timing: Testing and AdjustingsxturboPas encore d'évaluation
- Pistons and Connecting Rods - AssembleDocument5 pagesPistons and Connecting Rods - Assembleeshopmanual limaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cat 3176c Montagem Da Cabeça.Document7 pagesCat 3176c Montagem Da Cabeça.César PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cylinder Head - Install: Disassembly and AssemblyDocument8 pagesCylinder Head - Install: Disassembly and Assemblyhocine gherbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Lab Report 1 - AMMDocument14 pagesSample Lab Report 1 - AMMowais ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- PROFAB ESR 1580X2.0 Manual - 2017Document16 pagesPROFAB ESR 1580X2.0 Manual - 2017Kevin VarghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Balança 4182-A (Mecanica) - Revisão 02.08.2007 PDFDocument12 pagesBalança 4182-A (Mecanica) - Revisão 02.08.2007 PDFKadson AmaralPas encore d'évaluation
- MyDIYCNC Desktop CNC Machine Kit Assembly InstructionsDocument33 pagesMyDIYCNC Desktop CNC Machine Kit Assembly InstructionsKhairul Yop Azreen100% (1)
- Install Piston & Conrod 320 GCDocument3 pagesInstall Piston & Conrod 320 GCJebrodPas encore d'évaluation
- NOTICE! Starting Motor Must Be Removed From Vehicle Before The Semi-Solid Link Solenoid Can Be RemovedDocument4 pagesNOTICE! Starting Motor Must Be Removed From Vehicle Before The Semi-Solid Link Solenoid Can Be RemovedDaniel Jose FrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Fabrication of Toggle JackDocument30 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Toggle JackJitendra Rout0% (1)
- 6bearing - Remove and InstallDocument7 pages6bearing - Remove and InstallZawminhtunPas encore d'évaluation
- RepymotDocument4 pagesRepymotEngin UzunPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Time Brother Frequency mp3: and Listen To A Performance by Brother Frequency (3.5MB)Document2 pagesDR Time Brother Frequency mp3: and Listen To A Performance by Brother Frequency (3.5MB)Muhammad AwaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Scaling Up 6. Policy Advocacy 7. Assembler of Resources 8. Knowledge Broker 9. Environment and Climate Change RoleDocument2 pagesScaling Up 6. Policy Advocacy 7. Assembler of Resources 8. Knowledge Broker 9. Environment and Climate Change RoleMuhammad AwaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Unemployed AffidavitDocument1 pageUnemployed AffidavitMuhammad AwaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Factor and Its Importance in Industrial SystemsDocument2 pagesPower Factor and Its Importance in Industrial SystemsMuhammad AwaisPas encore d'évaluation
- EN13480-3 Chap12 ModificationsDocument37 pagesEN13480-3 Chap12 ModificationsPrashant ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Sheet Tcg2032 DeutzDocument3 pagesData Sheet Tcg2032 DeutzMaximiliano SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Blacksmithing 101 - How To Make A Forge and Start Hammering Metal - Popular MechanicsDocument6 pagesBlacksmithing 101 - How To Make A Forge and Start Hammering Metal - Popular MechanicsByram JPas encore d'évaluation
- GROHE Pricelist-2020 en GB PDFDocument1 020 pagesGROHE Pricelist-2020 en GB PDFNikhil AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- ElecDocument40 pagesElecakela_life100% (4)
- SREA-ECET (Mechanical) 8 Years Topic Wise Bit Bank-1 PDFDocument68 pagesSREA-ECET (Mechanical) 8 Years Topic Wise Bit Bank-1 PDFDhanunjay JaguPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Design CriteriaDocument533 pagesElectrical Design CriteriaHimdad Bahri100% (3)
- Genius Plus: Electronic Engineering LTDDocument2 pagesGenius Plus: Electronic Engineering LTDpil;zoPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Specification of VSK PDFDocument28 pagesTechnical Specification of VSK PDFmaran.suguPas encore d'évaluation
- Towards 100%: ISC Osaka, 2018 JAN 23Document62 pagesTowards 100%: ISC Osaka, 2018 JAN 23taufanptrPas encore d'évaluation
- Megasan-Catalog CompressedDocument16 pagesMegasan-Catalog CompressedCasamed ServicePas encore d'évaluation
- SSGCDocument20 pagesSSGCAdnan119Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stem - Physics 1 CGDocument13 pagesStem - Physics 1 CGVictoria MabiniPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Electricity - With GRESADocument15 pages5 Electricity - With GRESADianne CalladaPas encore d'évaluation
- EE-442 (Electric Energy Utilization)Document2 pagesEE-442 (Electric Energy Utilization)dhineshkm10100% (1)
- Topic 1 Stoichiometric RelationshipsDocument56 pagesTopic 1 Stoichiometric Relationshipsapi-546066323Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rimula FamilyDocument1 pageRimula FamilyChemist Ahmed FoudaPas encore d'évaluation
- New Generation PlanningDocument3 pagesNew Generation PlanningSyed ArifPas encore d'évaluation
- VLT2800 Quick Guide PDFDocument2 pagesVLT2800 Quick Guide PDFlieldPas encore d'évaluation
- 1,917 New Applications in New Spark Plug & Glow Plug CatalogueDocument6 pages1,917 New Applications in New Spark Plug & Glow Plug Catalogue08088338Pas encore d'évaluation
- TNB Iar 2020Document360 pagesTNB Iar 2020yerio.dwiyantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Honeywell AQ2000Document8 pagesHoneywell AQ2000vsilickasPas encore d'évaluation
- Quasi Turbine EngineDocument18 pagesQuasi Turbine EngineKailas Sree Chandran100% (2)
- Socket and Spigot JointDocument5 pagesSocket and Spigot Jointsarath.kumarnmk930Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Differentiate Capacitances Using Trasatti and Dunn MethodsDocument56 pagesHow To Differentiate Capacitances Using Trasatti and Dunn Methodsgopi undavalliPas encore d'évaluation
- From Newton To Mandelbrot-A Primer in Theoretical PhysicsDocument277 pagesFrom Newton To Mandelbrot-A Primer in Theoretical PhysicsΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣ ΨΥΧΑΣ100% (1)
- AV65WP74Document19 pagesAV65WP74ElectroCenterPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen BombDocument3 pagesHydrogen BombirfuuPas encore d'évaluation
- Green BuildingDocument27 pagesGreen BuildingsaketPas encore d'évaluation
- Waec Syllabus For Building ConstructionDocument7 pagesWaec Syllabus For Building ConstructionOpadijo Adekunle ToheebPas encore d'évaluation