Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Elg2138 HW#1 Solution: P1) P2.5-2 - (The Resistor Voltage Does Not Depend On The
Transféré par
scara_dukeDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Elg2138 HW#1 Solution: P1) P2.5-2 - (The Resistor Voltage Does Not Depend On The
Transféré par
scara_dukeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Elg2138 HW#1 Solution
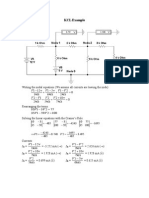
P1) P2.5-2 (a) By KCL, current through the resistor is 3A. From Ohms law v R i s 5 3 15 V . (The resistor voltage does not depend on the voltage source voltage.) v 2 152 45 W . Next P R 5 By KVL using sum of voltage rise = sum of drop, voltage across the current source is 10+15=25 V (with +ve at the end where current is coming out) By passive sign convention, i) power developed at the voltage source is (3)(10)=30W. Therefore power absorbed by the voltage source. ii) power developed at the current source is (-3)(25)=-75W. Therefore power delivered by the current source In summary, we have power delivered by the current source = sum of power absorbed by the resistor and by the voltage source (b) Since v and P do not depend on v s the values of v and P are 15 V and 45 W
both when vs =10V and when vs =5V .
P2) P2.7-5
4 2 (by Ohms Law) a 2 2 V Since A i a = A(-0.5) = 2, we have A 4 0.5 A R
P3) P3.2-9 A
KVL: vR 56 24 0 vR 80 V
At node A: KCL: iR 8 0 iR 8 A
vR 80 10 iR 8 by Ohms Law
Page 1 of 4
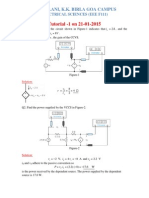
P4) P3.2-13 We can label the circuit as follows:
The subscripts suggest a numbering of the circuit elements. Apply KCL at node b to get i 4 0.25 0.75 0 i 4 1.0 A Next, apply KCL at node d to get i 3 i 4 0.25 1.0 0.25 0.75 A Next, apply KVL to the loop consisting of the voltage source and the 60 resistor to get v 2 15 0 v 2 15 V Apply Ohms law to each of the resistors to get v 2 15 i2 0.25 A , 60 60 v 3 10 i 3 10 0.75 7.5 V and
v 4 20 i 4 20 1 20 V
Next, apply KCL at node c to get i1 i 2 i 3 i1 i 3 i 2 0.75 0.25 1.0 A Next, apply KVL to the loop consisting of the 0.75 A current source and three resistors to get v 6 v 4 v 3 v 2 0 v 6 v 4 v 3 v 2 20 (7.5) 15 12.5 V Finally, apply KVL to the loop consisting of the 0.25 A current source and the 20 resistor to get v 5 v 4 0 v 5 v 4 20 20 V
Page 2 of 4
Using passive sign convention on the assigned directions and polarities, the power of each component is as follows: i) 15V-voltage source: 15(i1)= 15(-1) = -15W therefore power generated ii) 0.75A-current source : v6(0.75)=(-12.5)(0.75)= -9.375W. therefore power generated iii) 0.25A-current source : v5(-0.25)= (20)(-0.25) = -5W therefore power generated iv) 60 resistor: v2i2 = (15)(0.25) = 3.75W therefore power absorbed v) 20 resistor: v4i4 = (-20)(-1) = 20W; therefore power absorbed vi) 10 resistor: v3i3 = (-7.5)(-0.75) = 5.625W; therefore power absorbed One can check that total power absorbed = 29.375W = total power generated
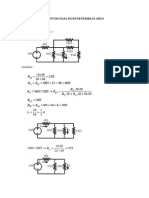
P5) P3.2-19 We assign current and voltage as shown. Then, using passive sign convention on the power generated at the voltage source we have 3.6 i 0.3 A 12 Similarly, v(-0.5) = -4.8 for the current source 4.8 v 9.6 V 0.5 Using KVL on the left loop in clockwise direction, sum of voltage rise = 12= sum of voltage drop = iR1 + v (Ohms Law on the resistor) 12 9.6 R1 8 0.3 By KCL, current (moving down ward) on R2 =0.3+0.5. Since voltage across R2 = v (KVL) on right loop. 9.6 Then by Ohms Law R 2 12 0.3 0.5
P6) P3.2-20 Apply KCL at node a to determine the current in the horizontal resistor as shown. Apply KVL to the loop consisting of the voltages source and the two resistors to get -4(2-i) + 4(i) - 24 = 0 i = 4 A
Page 3 of 4
P7) P3.8-5
By KCL, the current through the 2 ohm resister is diagram. Top mesh: we would like to check that First, we have Proceeding, Substituting in the given values of by Ohms Law. +1-2 , we have
in the direction shown in the
Similarly, we want to check if lower left mesh gives
vs 10 2 i a 0.5 i b 10 2 2 14 V by Ohms law
Lower right mesh, check that Checking, we have . Therefore, KVL is satisfied.
Summarizing the analysis and observations from the 3 meshes, we conclude that the analysis is correct. Note: ia and ib are in Amperes in the above solution from the author. The conclusion is the opposite if mA is used as given in the text.
Page 4 of 4
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Transformer Lab ManualDocument68 pagesTransformer Lab ManualRolando Cruz100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Homework SolutionDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Homework SolutionözlemArtuk100% (5)
- 1KB04 - Tugas EldasDocument30 pages1KB04 - Tugas Eldasmaster farhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Circuits 9th Chapter 2Document31 pagesElectric Circuits 9th Chapter 2Johny BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions To Assignment 1 of ELEG2202Document3 pagesSolutions To Assignment 1 of ELEG2202DuncanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thevenin PDFDocument12 pagesThevenin PDFHorvat ZoltánPas encore d'évaluation
- Dwnload Full Electric Circuits 9th Edition Nilsson Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Electric Circuits 9th Edition Nilsson Solutions Manual PDFpeterrodriguezcwbqomdksi100% (11)
- Lec2 BranchCurrentDocument71 pagesLec2 BranchCurrentKuro ShiroPas encore d'évaluation
- S - Chapter 3Document50 pagesS - Chapter 3usa2017lapPas encore d'évaluation
- Kirchoffs Current LawDocument10 pagesKirchoffs Current LawLloyd PagalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 3 PDFDocument47 pagesChap 3 PDFDiego7120100% (1)
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Document30 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh Soal Hukum Pembagi ArusDocument7 pagesContoh Soal Hukum Pembagi ArusTomi MentariPas encore d'évaluation
- Clipper Clamper CircuitsDocument15 pagesClipper Clamper CircuitsAnilaSaghirPas encore d'évaluation
- Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) :: V V V V V V V V V VDocument7 pagesKirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) :: V V V V V V V V V VNoor AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Numericals1Document3 pagesAC Numericals1Pavan KhetrapalPas encore d'évaluation
- Driven, Parallelrlccircuit : Transientsinsecond-OrdercircuitsDocument2 pagesDriven, Parallelrlccircuit : Transientsinsecond-OrdercircuitsKurt CargoPas encore d'évaluation
- ASD Assignment - IDocument3 pagesASD Assignment - IAnkit AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No.-1 Date: Verification of KVL and KCL For DC CircuitsDocument3 pagesExperiment No.-1 Date: Verification of KVL and KCL For DC Circuitssakshi rainaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Voltage DividerDocument37 pagesLecture Voltage DividerGaurav SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam Report, This Report Is Submitted To The Electrical Department, College of Engineering, Kirkuk UniversityDocument7 pagesFinal Exam Report, This Report Is Submitted To The Electrical Department, College of Engineering, Kirkuk UniversityyasinPas encore d'évaluation
- L-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document11 pagesL-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)nvnmnitPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SPas encore d'évaluation
- BENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaDocument39 pagesBENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaWan MamatkPas encore d'évaluation
- Transients 6Document42 pagesTransients 6Remaz Mutasim Yusuf100% (1)
- Verification of KVL and KCLDocument3 pagesVerification of KVL and KCLVarun Vadluri80% (5)
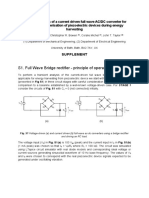
- S1. Full Wave Bridge Rectifier - Principle of OperationDocument7 pagesS1. Full Wave Bridge Rectifier - Principle of OperationVicPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee TutorialDocument2 pagesEe TutorialRajesh AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- HW2 SolutionDocument10 pagesHW2 Solution劉德信Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Resistive Circuits: Assessment ProblemsDocument50 pagesSimple Resistive Circuits: Assessment ProblemsSabrine SannakyPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Circuit Analysis LawsDocument50 pagesBasic Circuit Analysis LawsMuhd RzwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternating CurrentDocument39 pagesAlternating CurrentRichard GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Example: Determine The Power Supplied by Each of The Sources, Independent and Dependent, inDocument6 pagesExample: Determine The Power Supplied by Each of The Sources, Independent and Dependent, inSakthivelraj SPas encore d'évaluation
- Verification of KCL and KVLDocument3 pagesVerification of KCL and KVLCOLD FIREPas encore d'évaluation
- Week OneDocument44 pagesWeek OneSideman123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ee6211 - Electric Circuit LabDocument101 pagesEe6211 - Electric Circuit Labsujith100% (1)
- Tutorial de ElectricidadDocument78 pagesTutorial de ElectricidadfrederypsPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 6 Kirchhoff and PowerDocument13 pagesExperiment 6 Kirchhoff and PowerVenus IlaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Balanced Unbalanced Polyphase Systems 1 23 13Document36 pagesBalanced Unbalanced Polyphase Systems 1 23 13Wyatt C. Lewis67% (3)
- ECE Department ECI Lab ManualDocument80 pagesECE Department ECI Lab ManualArputharaj JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tut-1 Modified PDFDocument8 pagesTut-1 Modified PDFShailendra DhakadPas encore d'évaluation
- Currents Through Inductances, Capacitances and ResistancesDocument14 pagesCurrents Through Inductances, Capacitances and ResistancesZulu LovePas encore d'évaluation
- L2-Single Phase Part 1-Sem1-2016-17-Ver2 PDFDocument42 pagesL2-Single Phase Part 1-Sem1-2016-17-Ver2 PDFVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesPas encore d'évaluation
- HW1 SolutionDocument6 pagesHW1 Solution劉德信Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Resistive Circuits: Assessment ProblemsDocument51 pagesSimple Resistive Circuits: Assessment ProblemsMateo Sanchez CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit Elements of DC CircuitsDocument8 pagesCircuit Elements of DC CircuitsLighto LastoPas encore d'évaluation
- KCL Example: K V V K V K VDocument6 pagesKCL Example: K V V K V K VRafael CossPas encore d'évaluation
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Power Electronics EeeDocument62 pagesGate Power Electronics Eee15530% (3)
- BSC Project Report - Kirchhoff's LawDocument26 pagesBSC Project Report - Kirchhoff's Lawrudra narayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) :: Kirchhoff's First & Second Laws With Solved ExampleDocument20 pagesKirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) :: Kirchhoff's First & Second Laws With Solved Examplenobody126Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I - DC CircuitsDocument7 pagesUnit I - DC Circuitstanjiromanjiro20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) : TitleDocument3 pagesKirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) : Titleafaq ahmad khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Further Problems On Electricity: MBS3211 - Engineering Science For BS Electricity - TutorialsDocument4 pagesFurther Problems On Electricity: MBS3211 - Engineering Science For BS Electricity - TutorialsCool DouglasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5 - Characteristics of A BJT and DC Load LineDocument9 pagesLab 5 - Characteristics of A BJT and DC Load Linevishvajeettiwari96Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesD'EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsD'EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsPas encore d'évaluation
- Intel Centrino Mobile TechnologyDocument26 pagesIntel Centrino Mobile TechnologySimmi JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Chart: Analog and Digital Signals Are Used To TransmitDocument4 pagesComparison Chart: Analog and Digital Signals Are Used To TransmitsuyogshahPas encore d'évaluation
- TX 492Document20 pagesTX 492Dimitrios ChristodoulouPas encore d'évaluation
- Specification For Approval: SafetyDocument69 pagesSpecification For Approval: SafetyErnesto Díaz S.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vda Riasspowertv05 IngDocument9 pagesVda Riasspowertv05 IngRedah HamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Thevenin's Theorem ReportDocument5 pagesThevenin's Theorem ReportAzir Ollin UyPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Lecture by BUETDocument69 pagesCommunication Lecture by BUETnehal hasnain refath100% (1)
- Harmonics and Harmonic Frequency in AC CircuitsDocument5 pagesHarmonics and Harmonic Frequency in AC CircuitsRoboconDKPas encore d'évaluation
- MPI 2019 AssessmentDocument10 pagesMPI 2019 AssessmentkumarklPas encore d'évaluation
- Mt1000 Parts List and AccessoriesDocument14 pagesMt1000 Parts List and AccessoriespatatepoilePas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Recognition of Vehicle Position Using UHF Passive RFID Tags PDFDocument4 pagesSelf-Recognition of Vehicle Position Using UHF Passive RFID Tags PDFsrcembeddedPas encore d'évaluation
- Deepsea 7420 CAD DrawingDocument2 pagesDeepsea 7420 CAD Drawingsnipie renz100% (1)
- Bandwidth of FM Video SignalsDocument3 pagesBandwidth of FM Video Signalsgreen0426Pas encore d'évaluation
- DSP QuestionDocument1 pageDSP QuestionVasanthLogarajLPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisa Tehnica 500WDocument2 pagesFisa Tehnica 500WFrancisco Antonio Martínez RayaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4d6fc COmpal LA-B161PDocument44 pages4d6fc COmpal LA-B161PDj-Samuel OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Irgp 4063 DPBFDocument11 pagesIrgp 4063 DPBFluizcpimentaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluenrg 2 PDFDocument175 pagesBluenrg 2 PDFShivbraham Singh RajawatPas encore d'évaluation
- GPS Cable Installation and SurgeDocument6 pagesGPS Cable Installation and SurgeMohammed NouzalPas encore d'évaluation
- 9300 Decoder User Manual-V1.0Document30 pages9300 Decoder User Manual-V1.0Roberto Leonardo RiveroPas encore d'évaluation
- GoodWe Inverters DS Series User ManualDocument50 pagesGoodWe Inverters DS Series User ManualJose Luis ArellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- DV78 DVD Player: Service ManualDocument41 pagesDV78 DVD Player: Service ManualeduardPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Igbt High Current Gate Driver: Semiconductor Technical DataDocument13 pagesSingle Igbt High Current Gate Driver: Semiconductor Technical DataBojan ErcegPas encore d'évaluation
- Esp-S3-12k Module Datasheet v1.0.0Document25 pagesEsp-S3-12k Module Datasheet v1.0.0vmsperandioPas encore d'évaluation
- 74 Ls 138Document1 page74 Ls 138Ricardo EspañaPas encore d'évaluation
- DSP Notes KAR Part2Document23 pagesDSP Notes KAR Part2Srinivas VNPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.multi Level InverterDocument2 pages1.multi Level InverterYoungstarTarunPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of A Boost Converter: Department of Electrical Engineering National Institute of Technology RourkelaDocument31 pagesDesign of A Boost Converter: Department of Electrical Engineering National Institute of Technology Rourkela2k18-EE-243 Vethushan VinnayagamoorththiPas encore d'évaluation
- Adder or Subtractor Using CircuitsDocument5 pagesAdder or Subtractor Using CircuitsRaja PatelPas encore d'évaluation