Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NCP - Impaired Gas Exchange
Transféré par
Rryje SallevaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NCP - Impaired Gas Exchange
Transféré par
Rryje SallevaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
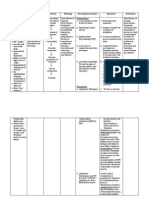
Assessment Actual Abnormal Cues: Dyspnea Visual disturbances Headache upon awakening Confusion Restlessness Irritability Lethargy Abnormal
Abnormal ABG result Risk factors: Age Stress Smoking Occupation Exposure to airborne irritants
Nursing Diagnosis Impaired gas exchange related to inflammation of that lungs that altered the blood flow as evidenced by verbal reports of difficulty of breathing
Rationale Exposure to irritants
Desired Outcomes After 4 days of nursing intervention the client will be able to: 1.Demonstrate improved ventilation and adequate oxygenation of tissues within clients normal limits. 2. Participate in treatment regimen(e.g, breathing exercises, effective coughing, use of oxygen) within level of ability/situation. 3. Verbalize understanding of causative factors and appropriate intervention.
Intervention Independent: 1. Assess for respiratory depth, rate. Note use of accesory muscles, pursed lip breathing, inability to speak/converse 2. Routinely monitor skin and mucous membrane.
Justification
Evaluation After 4 days of nursing intervention, client was able to:
Toxic injury to endothelial and epithelial cells
1.To evaluate the degree of respiratory distress and chronicity of the disease process. 2.Cyanosis may be peripheral or central. Duskiness and central cyanosis indicates advance hypoxemia 3.Decrease of vibratory tremors suggest fluid collection or air trapping 1.PaCO2 usually is elevated and PaO2 is decreased: hypoxia is present in lesser or greater degree 2.to correct or prevent worsening of hypoxia 3.reduce dyspnea by controlling the anxiety
Accumulation of leukocytes Definition: -Excess or deficit in oxygenation and/or carbon dioxide elimination at the alveoli-capillary membrane.
3. palpate for crepitus
Inflammation of the lungs
Constriction of bronchus
Collaborative 1. Monitor serial ABG and pulse oximetry.
Impaired gas exchange
2. Administer oxygen therapy 3. Administer anti anxiety drugs
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncp-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNcp-Ineffective Airway Clearancelouanne0550% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pulmonary TuberculosisLionel Richie Pedraza50% (2)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Document2 pagesImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- BronchiectasisDocument40 pagesBronchiectasisyana jaePas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeKM67% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care Planapi-38118511380% (10)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern TalaDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern TalaJhen Bitco Fidel70% (10)
- Impaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanCristina Centurion100% (10)
- Copd NCPDocument16 pagesCopd NCPSuperMaye100% (1)
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearancemichelle_010379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma NCPDocument3 pagesAsthma NCPjaijai magbanuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocument1 pageImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP DobDocument2 pagesNCP DobTata Wendz100% (1)
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesNCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP Pneumoniakaiserdominick100% (2)
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument6 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPDoo NahPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP PneumoniaDocument47 pagesNCP Pneumoniabhevpat251100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - CopdDocument3 pagesNCP - CopdhystericoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - AnxietyDocument1 pageNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobilePas encore d'évaluation
- Health Teaching Plan CalalangDocument5 pagesHealth Teaching Plan CalalangPhilip R. Marallag0% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Nursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and OxygenationDocument2 pagesNursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and Oxygenationlodeth100% (2)
- NCP - TBDocument2 pagesNCP - TBPahw BaluisPas encore d'évaluation
- Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaDocument9 pagesLopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaSofia Lopez100% (2)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageImpaired Gas ExchangeAdelaine LorestoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP CopdDocument4 pagesNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDocument5 pagesNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaSummer Ilu100% (1)
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_sanePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- Competencymr McdougalcopdDocument17 pagesCompetencymr Mcdougalcopdmac_rymrt7569Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanAl RizkyPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Kochs2Document2 pagesNCP Kochs2Ava VierPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (COPD) : Is An Obstructive Lung Diseases in Which Irreversible Lung Damage Has OccuredDocument25 pagesChronic Obstructive Lung Disease (COPD) : Is An Obstructive Lung Diseases in Which Irreversible Lung Damage Has OccuredOmar AbdillahiPas encore d'évaluation
- PNEUMONIADocument24 pagesPNEUMONIAwheeyycoldandhot55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyDocument3 pagesPre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Module PulmoDocument7 pagesModule Pulmosmart reyPas encore d'évaluation
- Woman With PneumoniaDocument9 pagesWoman With PneumoniaNohaira SADANGPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthama & COPDDocument84 pagesAsthama & COPDAbdullah BhattiPas encore d'évaluation