Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
XI Math Ch8 Binomial Theorem Chapter Notes Nov
Transféré par
Abhijit GopeDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
XI Math Ch8 Binomial Theorem Chapter Notes Nov
Transféré par
Abhijit GopeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
1
Class XI: Math
Chapter 8: Binomial Theorem
Chapter Notes
Key Concepts
1. A binomial expression is an algebraic expression having two terms, for
example (a+b),(a-b) etc.
2. The expansion of a binomial for any positive integral n is given by
Binomial Theorem. The binomial theorem says that
(x+y)
n
= x
n
+
n
C
1
x
n-1
y+
n
C
2
x
n-2
y
2
+----+
n
C
r
x
n-r
y
r
+ -----+
n
C
n-1
xy
n-1
+
n
c
n
y
n
In summation notation (x+y)
n
=
n
n n k k
k
k 0
C x y
3. (i)In the binomial expansion of (x+y)
n
the number of terms is (n+1)
i.e one more than the exponent.
(ii)The exponent of x goes on decreasing by unity and y increases by
unity. Exponent of x is n in the first term, (n - 1) in the second term,
and so on ending with zero in the last term.
(iii)The sum of the indices of x and y is always equal to the index of
the expression.
4. The coefficients C
r
, the number of combinations of n objects taken r
at a time, occurring in the binomial theorem are known as binomial
coefficients.
5. Binomial coefficients when arranged in the form given below is known
as Pascals Triangle
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
2
6. The array of numbers arranged in the form of triangle with 1 at the
top vertex and running down the two slanting sides is known as
Pascals triangle, after the name of French mathematician
Blaise Pascal. It is also known as Meru Prastara by Pingla.
7. Pascal's Triangle is a special triangle of numbers. It has an infinite
number of rows. Pascal's Triangle is a storehouse of patterns.
8. In order to construct the elements of following rows, add the number
directly above and to the left with the number directly above and to
the right to find the new value. If either the number to the right or left
is not present, substitute a zero in its place.
9. Using binomial theorem for non negative index
(x y) = [x + (-y)]
(x y) =
( )
n n n n n 1 n n 2 2 n n 3 3 n n
0 1 2 3 n
C x C x y C x y C x y 1 C y
+ + .+
In summation notation (x y) =
n
k n n k k
k
k 0
( 1) C x y
10.Binomial theorem can be used to expand trinomial by applying the
binomial expansion twice.
11. General term in the expansion of (x+y)
n
is T
k+1
=
n
C
k
x
n-k
y
k
12.General term in the expansion of (x-y)
n
is T
k+1
=
n
C
k
(-1)
k
x
n-k
y
k
13.If n is even , there is only one middle term in the expansion of (x + y)
n
and will be the
th
n
1
2
| |
+
|
\ .
term
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
3
14.If n is odd, there are two middle terms in the expansion of
(x + y)
n
and they are
th
n 1
2
+ | |
|
\ .
and
th
n 3
2
+ | |
|
\ .
term.
15.In the expansion
2n
1
x
x
| |
+
|
\ .
, where x 0, the middle term is
th
2n 1 1
2
+ + | |
|
\ .
i.e., (n + 1)
th
term, as 2n is even
Get the Power of Visual Impact on your side
Log on to www.topperlearning.com
4
Summary
+ , which is (a + b) = C
0
a + C
1
a
n-1
b + C
2
a
n-2
b + + C
n-1
a.b
n-1
+
C
n
b.
+ The coefficients of the expansions are arranged in an array. This array
is called Pascals triangle.
+ The general term of an expansion (a + b) is T
r+1
= C
r
a
n-r
. b
r
.
+ In the expansion (a + b), if n is even, then he middle term is the
th
n
1
2
| |
+
|
\ .
term. If n is odd, then the middle term are
th
n 1
2
+ | |
|
\ .
and
th
n 1
1
2
+ | |
+
|
\ .
terms.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Iit Maths Solved PaperDocument569 pagesIit Maths Solved PaperAshish Gupta100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Math 214 NotesDocument466 pagesMath 214 NotesLuis Javier IxtepanPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 9 Maths Ncert SolutionsDocument445 pagesClass 9 Maths Ncert SolutionswawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Derivative AnalysisDocument8 pagesPressure Derivative AnalysissethkakPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics 9 Teaching Guide - Revised 2020Document382 pagesMathematics 9 Teaching Guide - Revised 2020Santy Enril Belardo Jr.100% (1)
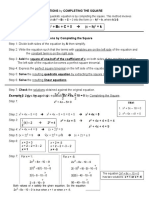
- + BX + C 0 (X - H) K: Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareDocument16 pages+ BX + C 0 (X - H) K: Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareAserHelloPas encore d'évaluation
- A P P L e P I e o R D e RDocument149 pagesA P P L e P I e o R D e RJan LubinaPas encore d'évaluation
- TOS SampleDocument3 pagesTOS SampleSusan T. Laxamana100% (1)
- Haar Measure On Compact GroupsDocument12 pagesHaar Measure On Compact GroupsAsad AbozedPas encore d'évaluation
- Mat102 q2 PrepDocument2 pagesMat102 q2 Prepsanjanabulusu07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document80 pagesChapter 1eshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Add Maths Trial Paper 1 PDFDocument13 pages2017 Add Maths Trial Paper 1 PDFChin VennPas encore d'évaluation
- Discrete Mathematical Structures Jan 2014Document2 pagesDiscrete Mathematical Structures Jan 2014Prasad C MPas encore d'évaluation
- Infinite Limits and Limits at InfinityDocument22 pagesInfinite Limits and Limits at Infinityvalerie lagmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Equations Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesDifferential Equations Tutorial Sheet 1AV YogeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 11 Derivative of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument12 pagesMath 11 Derivative of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsFranco Louis RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPLEX ANALYSIS 1 LATEST (Repaired)Document118 pagesCOMPLEX ANALYSIS 1 LATEST (Repaired)koskeyemmanuel82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Limits and Continuity PDFDocument8 pagesLimits and Continuity PDFCeren ŞirinPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexible CordsDocument6 pagesFlexible CordsSifat SammoPas encore d'évaluation
- Convergence Tests PDFDocument35 pagesConvergence Tests PDFPraeMaiSamartPas encore d'évaluation
- Keep 208Document18 pagesKeep 208AshutoshYelgulwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Integration by Partial FractionDocument23 pagesIntegration by Partial FractionMisa KurobanePas encore d'évaluation
- All Solutions For Math 456Document70 pagesAll Solutions For Math 456Hope HamamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Area and Surface Integrals. (Sect. 16.6) : TheoremDocument8 pagesSurface Area and Surface Integrals. (Sect. 16.6) : TheoremTidal SurgesPas encore d'évaluation
- 17.functions WatermarkDocument20 pages17.functions WatermarkSomay KelankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes On Classical Integrability and On The Algebraic Bethe Ansatz For The XXX Heisenberg Spin ChainDocument36 pagesLecture Notes On Classical Integrability and On The Algebraic Bethe Ansatz For The XXX Heisenberg Spin ChainDieff_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Richardson ExtrapolationDocument2 pagesRichardson ExtrapolationPanot ChaimongkolPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Xii Maths Marking Scheme KV NeristDocument13 pagesClass Xii Maths Marking Scheme KV NeristBot1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- MATHS EXAM QUESTION AIRE (Nov) 2022Document3 pagesMATHS EXAM QUESTION AIRE (Nov) 2022swastik aroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1Document13 pagesModule 1shaina sucgangPas encore d'évaluation