Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Poster
Transféré par
Elavarasan PandianDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Poster
Transféré par
Elavarasan PandianDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Catalysis for Sustainable Energy
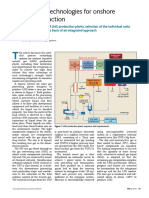
Direct Biomass Conversion to Fuels
Goal
Biomass contains a number of interesting building blocks that can be utilized to produce fuels and chemicals. Therefore the goal is to develop methods for cutting down biomass into intermediate platform molecules and subsequently transforming these into chemical fuels (cf. refs. [1,2]).
Ionic Liquids
Used ionic liquid[3]
a
N N +
Basic Principle
Biomass can be converted into smaller molecules either by (catalytic) flash pyrolysis or by using ionic liquids. The resulting pyrolysis oil or sugar entities are then transformed further to fuels. The main reactions for these transformations are dehydration, decarboxylation and hydrogenation using efficient zeolite-based and/or alloy catalysts.
Biomass:
Pyrolysis Oil
Biodiesel from fatty acids and glycerides
Decarbonylation/decarboxylation
+ H2 + H2
CO/CO2
Pyrolysis Grain Corn Plant oil Cellulose Reaction Glucose, Fructose, Lignin Ethanol, Lactic Acid, in ionic Fatty acids liquids
Fuels such as Ethanol, Hydrocarbons, etc.
Complete hydrogenation
Use of biomass molecules for fuels and chemicals[4]
Fuels, e.g. Alcohols, Ether, Hydrocarbons
Carbohydrates Catalyst
O O OH + OH O OH
Building blocks
Biodegradable plastic Fuels
Challenges
Effective pyrolysis process Catalysts to selectively break down biomass in ionic liquids Routes to convert pyrolysis oil or its major components Sufficiently active and stable zeolites and alloy catalysts Rational catalyst design and understanding of the catalysts
Catalyst Development
Catalysts for Conversions in ionic liquids Dehydration with zeolites Alloy catalysts for hydrogenations
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis oil contains Aldehydes and ketones (mainly gluconaldehyde) Furane derivatives Phenolic compounds Depends strongly on the type of biomass and conditions[2]
Approach
Design of catalysts for transformations in ionic liquids Transformation of model compounds from pyrolysis oil Gluconaldehyde to ethanol Synthesis and test of existing and new catalysts In-situ characterization of catalysts
DTU Participants
References [1] G. W. Huber, S. Iborra, A. Corma; Chem. Rev. 106 (2006): 4044 [2] A. V. Bridgwater et al.; Fast Pyrolysis of Biomass: A Handbook, CPL Press (1999), Newbury; Bech et al. WO 2006/117006 [3] Rogers et al.; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124 (2002): 4974 [4] E. Taarning, S. Saravanamurugan, M.S. Holm, J. Xiong, R.M. West, C.H. Christensen; Chem .Sus .Chem. 2(7) 2009: 625-627
Principal investigators
Jan-Dierk Grunwaldt Anker Degn Jensen John Woodley Rasmus Fehrman Anders Riisager
Sren Dahl
CASE contact person: Jan-Dierk Grunwaldt, jdg@kt.dtu.dk, + 45 4525 2838
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Carrier Handbook HVAC Design PDFDocument768 pagesCarrier Handbook HVAC Design PDFammg772030100% (8)
- Steel Delhi NCRDocument27 pagesSteel Delhi NCRabhay bhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Turbine Blade DesignDocument27 pagesWind Turbine Blade DesignKishore Ck100% (1)
- SAVANNAHSPASDocument29 pagesSAVANNAHSPASeriechris80% (5)
- Water Proofing MethodsDocument18 pagesWater Proofing MethodsreetPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Enhancing Power Plant Response To Partial Load RejectionsDocument4 pagesGuidelines For Enhancing Power Plant Response To Partial Load RejectionsManahan SinagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Generador ENGGADocument20 pagesManual Generador ENGGAmanuel100% (2)
- Induction Furnace HandbookDocument163 pagesInduction Furnace HandbookRaja Bharath Donthi0% (1)
- Shear Stresses in BeamsDocument12 pagesShear Stresses in Beamsrahul_patil85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report TemplateDocument4 pagesLab Report Templateapi-462603552Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biofuel: Hydrotreating of Vegetable Oil To Produce Renewable Diesel Fuel IBUKUN OLUWOYE NICOSIADocument13 pagesBiofuel: Hydrotreating of Vegetable Oil To Produce Renewable Diesel Fuel IBUKUN OLUWOYE NICOSIAIbukun OluwoyePas encore d'évaluation
- LNG Onshore ProductionDocument4 pagesLNG Onshore ProductionAnil B YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- TransesterificationDocument14 pagesTransesterificationElilisya MarooskinPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiesel Production From Waste Cooking Oil Using Sulfuric Acid and Microwave Irradiation ProcessesDocument7 pagesBiodiesel Production From Waste Cooking Oil Using Sulfuric Acid and Microwave Irradiation ProcessesmetashriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Catalysis for the Sustainable Production of Bio-fuels and Bio-chemicalsD'EverandThe Role of Catalysis for the Sustainable Production of Bio-fuels and Bio-chemicalsKostas TriantafyllidisPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Biomass Pyrolysis Oil Properties and Upgrading ResearchDocument6 pagesReview of Biomass Pyrolysis Oil Properties and Upgrading Researchnguyennha1211Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eco-Friendly Bio-Products: Lecture By: Dr. Indu Chauhan Assistant Professor Department of BiotechnologyDocument24 pagesEco-Friendly Bio-Products: Lecture By: Dr. Indu Chauhan Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnologykumar shivamPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiesel OverviewDocument5 pagesBiodiesel OverviewMuhammad FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar ReportDocument15 pagesSeminar ReportDepepanshu MahajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Oil Upgrading by Means of Ethyl Ester ProductionDocument6 pagesBio Oil Upgrading by Means of Ethyl Ester ProductionVlad IonitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction and ObjectivesDocument7 pagesIntroduction and ObjectivesLale CovetPas encore d'évaluation
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Radiation Physics and ChemistryDocument27 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Radiation Physics and ChemistryMuhammad WahyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalysts 11 00818 v2Document10 pagesCatalysts 11 00818 v2victor japposanPas encore d'évaluation
- Patent Review On "Biodiesel Production Process": April 2011Document16 pagesPatent Review On "Biodiesel Production Process": April 2011Anton AlgrinovPas encore d'évaluation
- Mansoura University Master Report NourDocument8 pagesMansoura University Master Report NourNour Aldeen YassenPas encore d'évaluation
- Shraddha PresenationDocument17 pagesShraddha PresenationAnushka ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Resources (2016)Document40 pagesRenewable Resources (2016)Lindelwa MthembuPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermochemical Four PagerDocument4 pagesThermochemical Four PagerFahmi AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Sythesis of Bioavture Through Hydrodeoxygenation and Catalytic Cracking From Oleic Acid Using Nimo/Zeolit CatalystDocument5 pagesSythesis of Bioavture Through Hydrodeoxygenation and Catalytic Cracking From Oleic Acid Using Nimo/Zeolit Catalystaisyahzafira26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre PDFDocument38 pagesPre PDFChirag ThanviPas encore d'évaluation
- Aee Module 4Document46 pagesAee Module 4kannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Production of Biodisel From Melon Seed: January 2013Document7 pagesProduction of Biodisel From Melon Seed: January 2013Richard Merck MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalysts: An Overview On Catalytic Hydrodeoxygenation of Pyrolysis Oil and Its Model CompoundsDocument22 pagesCatalysts: An Overview On Catalytic Hydrodeoxygenation of Pyrolysis Oil and Its Model CompoundsTusharPas encore d'évaluation
- LAB IV REPORT (Group 3)Document13 pagesLAB IV REPORT (Group 3)Sanjeev NehruPas encore d'évaluation
- Varanda, Pinto, Martins - 2011 - Life Cycle Analysis of Biodiesel ProductionDocument8 pagesVaranda, Pinto, Martins - 2011 - Life Cycle Analysis of Biodiesel ProductionJalcamPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxidation Stability of Biodiesel Fuel As Prepared by Supercritical MethanolDocument7 pagesOxidation Stability of Biodiesel Fuel As Prepared by Supercritical MethanolNakao SakurabaPas encore d'évaluation
- 003 PDFDocument7 pages003 PDFNakao SakurabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Green Heterogeneous Base Catalyst From Ripe and Unripe Plantain Peels Mixture For The Transesterification of Waste Cooking OilDocument11 pagesGreen Heterogeneous Base Catalyst From Ripe and Unripe Plantain Peels Mixture For The Transesterification of Waste Cooking OilAldo IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Resources Chemicals and Materials: Nichaboon Chaihad, Surachai Karnjanakom, Abuliti Abudula, Guoqing GuanDocument17 pagesResources Chemicals and Materials: Nichaboon Chaihad, Surachai Karnjanakom, Abuliti Abudula, Guoqing GuanYasemin KaradağPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversion of Waste Cooking Oil Into BiodieselDocument48 pagesConversion of Waste Cooking Oil Into BiodieselMUHAMMAD ADNANPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Conversion and ManagementDocument9 pagesEnergy Conversion and ManagementSriArthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anto, Et Al ('21) - Activation Strategies For Biochar To Use As An Efficient Catalyst in Various Applications (Fuel)Document8 pagesAnto, Et Al ('21) - Activation Strategies For Biochar To Use As An Efficient Catalyst in Various Applications (Fuel)aida-69Pas encore d'évaluation
- 095 104Document10 pages095 104hongduc6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bio DieselDocument5 pagesBio DieselShobhit ThukralPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiesel Production From Palm Kernel Oil Using CalciumDocument28 pagesBiodiesel Production From Palm Kernel Oil Using CalciumifiokPas encore d'évaluation
- Switch GrassDocument41 pagesSwitch GrassArjun MacPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis PresentationDocument71 pagesThesis PresentationsyedladainPas encore d'évaluation
- Production of Biodiesel Using Homogeneous Alkali Catalyst and Its Effect On Vehicular EmissionDocument7 pagesProduction of Biodiesel Using Homogeneous Alkali Catalyst and Its Effect On Vehicular EmissionSriArthiPas encore d'évaluation
- BiodieselDocument25 pagesBiodieselmano19me019Pas encore d'évaluation
- 19 ArticleText 48 1 10 20200108 - SandhyDocument5 pages19 ArticleText 48 1 10 20200108 - Sandhyfitri rowiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0016236111000068 Main Microondas Cao TranseDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S0016236111000068 Main Microondas Cao TranseFernanda TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0016236111006739 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0016236111006739 MainVVG LabPas encore d'évaluation
- Production of Conventional Liquid Fuels From SugarsDocument14 pagesProduction of Conventional Liquid Fuels From SugarsNuc LeusPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil Refining 04Document16 pagesOil Refining 04Nisha KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- CATALYTIC-PYROLYSIS-OF-BIOMASS ReviewDocument13 pagesCATALYTIC-PYROLYSIS-OF-BIOMASS ReviewBolWolPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 - Microwave Assisted Pyrolysis and Distillation of Cooking Oils For Liquid Biofuel ProductionDocument12 pages2021 - Microwave Assisted Pyrolysis and Distillation of Cooking Oils For Liquid Biofuel ProductionTrisna Kumala DhaniswaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Catalyst in Esterification and Transesterification Reactions For Biodiesel Production: A ReviewDocument7 pagesSolid Catalyst in Esterification and Transesterification Reactions For Biodiesel Production: A ReviewMuhammad Husein HizbullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Production of Biodiesel Using The Microwave Technique: Journal of Advanced ResearchDocument6 pagesProduction of Biodiesel Using The Microwave Technique: Journal of Advanced ResearchMihir ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiesel NanoDocument9 pagesBiodiesel NanoDhea NiidiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Suitability of Some Fruit Seeds Oil For Use As Biodiesel FuelDocument4 pagesSuitability of Some Fruit Seeds Oil For Use As Biodiesel FuelyohannesPas encore d'évaluation
- Artículo II ParcialDocument27 pagesArtículo II ParcialGabriel GómezPas encore d'évaluation
- Harus Selesai Hari IniDocument11 pagesHarus Selesai Hari IniZefanya Maranatha MangunsongPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio-Fuels: Presented By, Leo George Me S1:BDocument13 pagesBio-Fuels: Presented By, Leo George Me S1:Bleo GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Bio-Hydrocarbons Through Catalytic Pyrolysis of Used Cooking Oils: Towards Sustainable Jet and Road FuelsDocument7 pagesBio-Hydrocarbons Through Catalytic Pyrolysis of Used Cooking Oils: Towards Sustainable Jet and Road Fuelsahmad zikriPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalysts: Bio-Derived Catalysts: A Current Trend of Catalysts Used in Biodiesel ProductionDocument28 pagesCatalysts: Bio-Derived Catalysts: A Current Trend of Catalysts Used in Biodiesel ProductionEmmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Various Nano Catalysts For Biodiesel Production-A Review: Corresponding Author: EmailDocument6 pagesVarious Nano Catalysts For Biodiesel Production-A Review: Corresponding Author: EmailMech HoD DAITPas encore d'évaluation
- Art 3A10.1007 2Fs11244 010 9458 ZDocument6 pagesArt 3A10.1007 2Fs11244 010 9458 ZHadnan FauziPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel OilDocument22 pagesDiesel OilTRISHA NICOLE YU GERMANESPas encore d'évaluation
- The Optimization of The Esterification Reaction in BiodieselDocument12 pagesThe Optimization of The Esterification Reaction in BiodieselPablo PaganiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sequential Fractionation of Ligning Pyrolysis Bio-OilDocument10 pagesSequential Fractionation of Ligning Pyrolysis Bio-OilAs Augusto Rios MuñozPas encore d'évaluation
- Biller2011 - Catalytic Hydrothermal Processing of Microalgae - DecompositionDocument8 pagesBiller2011 - Catalytic Hydrothermal Processing of Microalgae - Decompositionfarida_crPas encore d'évaluation
- SheetMetal - Me - Design GuidelinesDocument3 pagesSheetMetal - Me - Design GuidelinestepaPas encore d'évaluation
- 【Hail Netting】-Technical DATA SHEET - Raschel -TriangleDocument1 page【Hail Netting】-Technical DATA SHEET - Raschel -TriangleVipul AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Dewalt Other Power ToolsDocument19 pagesDewalt Other Power Toolszexi84Pas encore d'évaluation
- A325n X SCDocument1 pageA325n X SCAnonymous ARMtmNKLPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG DS PCN Series Relay Data Sheet E 0820-728817Document3 pagesENG DS PCN Series Relay Data Sheet E 0820-728817servicoMITPas encore d'évaluation
- Tangguh Condensate - Summary Crude Oil Assay Report: Source of Sample Light Hydrocarbon Analysis Assay Summary / TBP DataDocument5 pagesTangguh Condensate - Summary Crude Oil Assay Report: Source of Sample Light Hydrocarbon Analysis Assay Summary / TBP DatarudiandriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Jorge e Ramalho, Lda.: High Standard CutleryDocument6 pagesJorge e Ramalho, Lda.: High Standard CutleryGeafir NicoletaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0008884621002027 MainDocument19 pages1 s2.0 S0008884621002027 MainEverton AndradePas encore d'évaluation
- E WasteDocument10 pagesE WasteVarsha RkPas encore d'évaluation
- Alati Stuhne Brochure Moulds 2016Document16 pagesAlati Stuhne Brochure Moulds 2016wardaddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Embody Chairs Disassembly InstructionsDocument4 pagesEmbody Chairs Disassembly Instructionsguiness_joe9154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Noise and VibrationDocument5 pagesNoise and VibrationIbrahim LotfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensors ApplicationsDocument8 pagesSensors ApplicationsmentongPas encore d'évaluation
- Amount of Substance: WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - UkDocument38 pagesAmount of Substance: WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - UkAsaph AharoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Stepwise Analysis of Gasification Reactions With Aspen Plus and CPFDDocument12 pagesStepwise Analysis of Gasification Reactions With Aspen Plus and CPFDabcd123Pas encore d'évaluation
- DirectionalControlValves NACHIDocument47 pagesDirectionalControlValves NACHICarlos Mauricio Guerrero Aguilar100% (1)
- Fs-1030 Quick G... R Jam (Eng)Document1 pageFs-1030 Quick G... R Jam (Eng)paliouras11Pas encore d'évaluation
- BS en 14303-2009Document38 pagesBS en 14303-2009Iveel PurevdorjPas encore d'évaluation
- Danfoss TP4:TP5 Thermostat PDFDocument84 pagesDanfoss TP4:TP5 Thermostat PDFABW35Pas encore d'évaluation