Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Personal Area Network
Transféré par
shahed_mdbDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Personal Area Network
Transféré par
shahed_mdbDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
A.
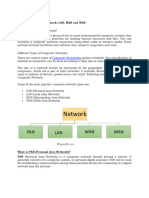
PERSONAL AREA NETWORK (PAN): A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for communication among computer devices, including telephones and personal digital assistants, in proximity to an individual's body. The devices may or may not belong to the person in question. The reach of a PAN is typically a few meters. PANs can be used for communication among the personal devices themselves (intrapersonal communication), or for connecting to a higher level network and the Internet. Personal area networks may be wired with computer buses such as USB and FireWire. A wireless personal area network (WPAN) can also be made possible with wireless network technologies such as IrDA, Bluetooth, UWB, Z-Wave and ZigBee. Diagram:
Advantages: 1. Personal Area Network helps to communicate in a short range. 2. Using PAN one can wirelessly communicate with portable devices (i.e. Mobile phone, PDA etc.). 3. PAN can also be used to connect to higher level network or Internet. 4. A personal area network (PAN) enable wearable computer devices to communicate with other nearby computers and exchange digital information using the electrical conductivity of the human body as a data network.
B. Local Area Network (LAN): A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as home, school, computer laboratory or office building.[1] The defining characteristics of LANs, in contrast to wide area networks (WANs), include their usually higher data-transfer rates, smaller geographic area, and lack of a need for leased telecommunication lines. ARCNET, Token Ring and other technology standards have been used in the past, but Ethernet over twisted pair cabling and Wi-Fi are the two most common technologies currently in use. Advantages: 1. Files can be stored on a central computer (the file server) allowing data to be shared throughout an organization. 2. Files can be backed up more easily when they are all on a central fileserver rather than when they are scattered across a number of independent workstations. 3. Networks also allow security to be established, ensuring that the network users may only have access to certain files and applications. 4. Software and resources can be centrally managed. 5. Network versions of software often allow for their speedy installation on workstations from the file server. 6. Expensive devices such as laser printers or scanners can be shared. 7. Users can access their files from any workstation Diagram:
C. Campus Area Network (CAN): A campus network, campus area network, corporate area network or CAN is a computer network made up of an interconnection of local area networks (LANs) within a limited geographical area. The networking equipments (switches, routers) and transmission media (optical fiber, copper plant, Cat5 cabling etc) are almost entirely owned by the campus tenant / owner: an enterprise, university, government etc. Diagram:
Advantages: 1. Campus Area networks (CAN) are economical, beneficial and easy to implement in the specific kilometers of locality 2. It is very helpful for the universities and other corporate organizations to work from any block and receive the same speed of data transfer.
D. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A MAN is optimized for a larger geographical area than a LAN, ranging from several blocks of buildings to entire cities. MANs can also depend on communications channels of moderate-to-high data rates. A MAN might be owned and operated by a single organization, but it usually will be used by many individuals and organizations. MANs might also be owned and operated as public utilities. They will often provide means for internetworking of local networks. Diagram:
Fig: 1
Fig: 2
Advantages: 1. Sharing of resources such as printers; hence cost effective. 2. Can send local emails.
E. Wide Area Network (WAN): A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a broad area (i.e., any network whose communications links cross metropolitan, regional, or national boundaries). This is in contrast with personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), campus area networks (CANs), or metropolitan area networks (MANs) which are usually limited to a room, building, campus or specific metropolitan area (e.g., a city) respectively. Diagram:
] Advantages: 1. Covers a large geographical area so long distance businesses can connect on the one network 2. Shares software and resources with connecting workstations 3. Messages can be sent very quickly to anyone else on the network. These messages can have pictures, sounds, or data included with them (called attachments). 4. Expensive things (such as printers or phone lines to the internet) can be shared by all the computers on the network without having to buy a different peripheral for each computer. 5. Everyone on the network can use the same data. This avoids problems where some users may have older information than others. 6. Share information/files over a larger area 7. Large network cover
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Personal Area NetworkDocument2 pagesA Personal Area NetworkShaziya UmairPas encore d'évaluation
- Campus Area NetworkDocument4 pagesCampus Area NetworkanuyawellingPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Area Network (PAN)Document10 pagesPersonal Area Network (PAN)nasirahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Database System Model and ArchitectureDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Database System Model and ArchitecturesfdPas encore d'évaluation
- XDSL TutorialDocument15 pagesXDSL TutorialTharjendra SelvarajahPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Electronics CommunicatioDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Electronics CommunicatioTom CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- WLan ArchitectureDocument4 pagesWLan ArchitectureseventhsensegroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet & e CommerceDocument13 pagesInternet & e CommerceLaetitia EspérancePas encore d'évaluation
- Campus Area Network Project Report PDFDocument116 pagesCampus Area Network Project Report PDFJay SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.living in A Network Centric WorldDocument34 pages1.living in A Network Centric WorldRajesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- By Network LayerDocument43 pagesBy Network Layerrachitganatra100% (4)
- Teacher's Notes - Lab Chapter 1 - Intro To SolarisDocument3 pagesTeacher's Notes - Lab Chapter 1 - Intro To SolarisFrancisEmmanuelGonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lan, Wan, IntranetDocument21 pagesLan, Wan, IntranetMurthy GrandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Design 1Document22 pagesNetwork Design 1Ian Jasper FuriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organizing Computer Facility Centralized, Distributed, and Decentralized Computing FacilitiesDocument16 pagesOrganizing Computer Facility Centralized, Distributed, and Decentralized Computing Facilitiesamazingthings2743100% (1)
- Diff Wire & Wireless Comm SlideDocument12 pagesDiff Wire & Wireless Comm SlideKila HamzahPas encore d'évaluation
- History of ComputerDocument20 pagesHistory of Computermohamed jamaPas encore d'évaluation
- DC17 Ch06Document36 pagesDC17 Ch06Nadie Lrd100% (1)
- Unit-2: Internet and E-CommerceDocument37 pagesUnit-2: Internet and E-Commercerohit soniPas encore d'évaluation
- Wide Area NetworkDocument12 pagesWide Area NetworkMarkhill Veran TiosanPas encore d'évaluation
- IT207 - Network Essentials Project (Frame Relay)Document50 pagesIT207 - Network Essentials Project (Frame Relay)CarmenLim07100% (3)
- IT Infrastructure and Network Technologies Part 2Document11 pagesIT Infrastructure and Network Technologies Part 2Junice IlaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Embedded Systems NotesDocument88 pagesEmbedded Systems NotesMadridVetticadPas encore d'évaluation
- CN Unit1 8-7-10Document20 pagesCN Unit1 8-7-10nallapatiharika0% (1)
- Windows Server 2012-70-410 SyllabusDocument4 pagesWindows Server 2012-70-410 SyllabusSenthil NathanPas encore d'évaluation
- First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes: Machine LanguageDocument2 pagesFirst Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes: Machine LanguageacciacatauraPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computers Module PDFDocument218 pagesIntroduction To Computers Module PDFTinashe ChikariPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Communication and NetworkDocument25 pagesComputer Communication and Networkmhatet_ignacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking Midterm PreparationDocument2 pagesNetworking Midterm PreparationSopharoath LyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introducing Operating Systems: Pt101 - Platform TechnologiesDocument36 pagesIntroducing Operating Systems: Pt101 - Platform TechnologiesChris ValduezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesCloud ComputingNabeela Khaled100% (1)
- Amazon Web Service CASE STUDYDocument36 pagesAmazon Web Service CASE STUDYrichaPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking LessonsDocument100 pagesNetworking LessonsSachin SadadekarPas encore d'évaluation
- UNDERSTANDING THE FACTORS OF CLOUD COMPUTING ADOPTION in MalaysiaDocument3 pagesUNDERSTANDING THE FACTORS OF CLOUD COMPUTING ADOPTION in MalaysiaMfaeez FizPas encore d'évaluation
- Next Level Communication With 5G NetworkingDocument19 pagesNext Level Communication With 5G NetworkingAmphenol-ICCPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT146 - Course SyllabusDocument2 pagesMIT146 - Course SyllabusFurqan Ali KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud ComputingDocument29 pagesCloud ComputingShilpa DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Database SystemDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Database SystemRige Mae MuescoPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network Module 1Document205 pagesComputer Network Module 1shakti139Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNADocument38 pagesCCNAGagan SardanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Introduction To Web TechnologiesDocument12 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Web TechnologiesME16 Krunal DeshmukhPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Security With Virtualized Defense andDocument6 pagesCloud Security With Virtualized Defense andmbamiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart College Campus Using IoTDocument7 pagesSmart College Campus Using IoTsri harshaphaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Hci 101Document11 pagesHci 101Divine ManaloPas encore d'évaluation
- HCIDocument22 pagesHCIHimanshu ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- CompressedDocument282 pagesCompressedBayan Al-dosriPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Ex1Document3 pagesAnswer Ex1Produttore Twistedvision0% (1)
- EC8551 CN SyllabusDocument2 pagesEC8551 CN SyllabusRagavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud, Fog and Edge Computing Security and Privacy ConcernsDocument8 pagesCloud, Fog and Edge Computing Security and Privacy ConcernsIJRASETPublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Free PDF of Computer ScienceDocument2 pagesFree PDF of Computer ScienceTerri0% (1)
- Empowerment Tech Module 1Document8 pagesEmpowerment Tech Module 1Don BesicPas encore d'évaluation
- Information Storage and RetrievalDocument5 pagesInformation Storage and RetrievalHellenNdegwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To The Internet of ThingsDocument57 pagesIntroduction To The Internet of ThingsAmjad Ali HumanistPas encore d'évaluation
- HYPERLANDocument19 pagesHYPERLANInformation SystemPas encore d'évaluation
- Network For Small OfficeDocument7 pagesNetwork For Small OfficeIndranil DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 How The Web WorksDocument38 pagesChapter 2 How The Web WorksEduard Anthony PechaycoPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer NetworksDocument57 pagesComputer NetworksSushmita Kumari100% (1)
- Introduction To Computer Network PDFDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Computer Network PDFPriyanshu KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 1 1. What Is Computer Networks?Document9 pagesActivity 1 1. What Is Computer Networks?Katrina Mae VillalunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Report On BSNL: Presented ByDocument24 pagesTraining Report On BSNL: Presented ByManu YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Cap 1-2-3-4Document228 pagesCap 1-2-3-4strummaticjonazPas encore d'évaluation
- ZigbeeDocument9 pagesZigbeelikithavonamalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Network NotesDocument6 pagesNetwork NotesNMPas encore d'évaluation
- COC 2 - Configuring of Computer Systems and NetworksDocument73 pagesCOC 2 - Configuring of Computer Systems and NetworksInfoTutorial 2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- ITC - Chapter # 11Document43 pagesITC - Chapter # 11Afaq BhuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Pan: Wireless Usb, Irda, Blue-Tooth, Ultra-Wide-Band (Uwb), Zig-Bee, and SimilarDocument5 pagesWireless Pan: Wireless Usb, Irda, Blue-Tooth, Ultra-Wide-Band (Uwb), Zig-Bee, and SimilarSaman Nilantha PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Acmp 101 Ass 4Document10 pagesAcmp 101 Ass 4KENYAN LARRYPas encore d'évaluation
- Zigbee Vs BluetoothDocument2 pagesZigbee Vs Bluetoothለዛ ፍቅርPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Computer NetworkingDocument6 pagesWireless Computer Networkingsirus starPas encore d'évaluation
- WN Chapter 4 WPANDocument27 pagesWN Chapter 4 WPANRdsharukh DaroorPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Configure ComputerDocument91 pages3 Configure ComputerBhem BoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart LED Display Board-2Document12 pagesSmart LED Display Board-2Dhiraj ChaudhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1anushka bhandarePas encore d'évaluation
- Iiot Question BankDocument28 pagesIiot Question Bankdarshan KeskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Network DesignDocument6 pagesNetwork Designমোঃ আরাফাত উল হকPas encore d'évaluation
- DWA-131 E1 Manual v5.00 (DI) PDFDocument36 pagesDWA-131 E1 Manual v5.00 (DI) PDF1981todurkarPas encore d'évaluation
- DCC Lab Manual Final Practicals PDFDocument152 pagesDCC Lab Manual Final Practicals PDFKaran LatayePas encore d'évaluation
- GPS ProjectDocument143 pagesGPS ProjectPhạm Tuấn AnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring of Computer Systems and NetworksDocument73 pagesConfiguring of Computer Systems and NetworksMark Michael BundocPas encore d'évaluation
- Networking AssignmentDocument80 pagesNetworking AssignmentSimon NdongaPas encore d'évaluation
- IEEE 802.15: Harald ØverbyDocument34 pagesIEEE 802.15: Harald ØverbyAmitKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet and Email NotesDocument96 pagesInternet and Email NotesdnlkabaPas encore d'évaluation
- IoT BluetoothDocument80 pagesIoT BluetoothPranjal YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Area NetworkDocument1 pagePersonal Area NetworkEldrich Brian CañadaPas encore d'évaluation
- 507:current and Future Devoplement in Network and Communication - LA3:5071.1 Describe The Latest Devoplement in Network and CommunicationDocument5 pages507:current and Future Devoplement in Network and Communication - LA3:5071.1 Describe The Latest Devoplement in Network and CommunicationAnonymous Se7zCDPas encore d'évaluation
- E121707-1662831818256-180949-Abdullah NetworkingDocument169 pagesE121707-1662831818256-180949-Abdullah NetworkingAbdullah NehumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Computer NetworkDocument3 pagesTypes of Computer NetworkMaricel Viloria100% (1)
- E5252 USB-BT211 Manual Win7Document41 pagesE5252 USB-BT211 Manual Win7moynihan32Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types of NetworksDocument13 pagesTypes of NetworksharmangahirPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Introduction To DCNDocument39 pages1 Introduction To DCNIndira KunduPas encore d'évaluation