Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Semester - 8 GTU Syllabus
Transféré par
Panchal Dhaval MDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Semester - 8 GTU Syllabus
Transféré par
Panchal Dhaval MDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
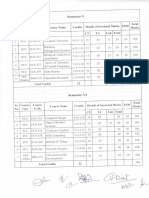
Semester VIII
SR. NO. SUBJECT TEACHING SCHEME (HOURS) THEORY 1 2 3 4 Distributed Systems Parallel Processing Elective-II Project Work 4 4 4 0 TUTORIAL 0 0 0 0 PRACTICAL 2 2 2 12 6 6 6 12 CREDITS
TOTAL
12
18
30
Elective 2
1. Artificial Intelligence 2. VLSI & HDL Prog. 3. Advance Computer Network
Subject Name: Distributed System Sr No 1. Course Content Distributed computing: History, Forms of computing, Monolithic, Distributed, Parallel, Cooperative Strengths and weaknesses of distributed computing, OS basics, Programs and processes, Concurrent programming Interconnection networks Cache hit-rate model, Cache coherency , Static and Dynamic networks , Internet mega computer-Network resources and their identifications, OLE/ COM , Distributed objects and CORBA, RPC and Rendezvous , Internet agents , Porting of applications- accessibility, scalability, security, fault tolerance Intercrosses communication Archetypal IPC program interface, Event synchronization, Timeouts and threading, Deadlock and timeouts, Data representation, Data encoding, Text based protocols, Request response protocols, Event and sequence diagram, Connection vs. connectionless IPC Distributed computing paradigms Paradigms, Message passing, Client server, Peer to peer, Message system, Remote procedure call model, Distributed objects, Object space, Mobile agent, Network services, Collaborative application (groupware),Abstraction, Tradeoffs: abstraction vs. overhead, Scalability, cross-platform Distributed Objects Message passing vs distributed objects, Archetypal distributed object architecture, Distributed object systems, Remote procedure calls, Java RMI architecture, Client side Server side, Object registry, API for Java RMI, Remote interface, Server side software Client side software, RMI vs. socket API Advanced RMI Client callback, Client side, Server side, Stub downloading, RMI Security manager, Instantiation of a Security manager, Java security policy file, Specifying stub downloading and a security policy file, Algorithms for building RMI application, Allowing for Stub downloading Advanced Distributed Computing Paradigms Message Queue system paradigm, Point to point, Publish/Subscribe, Mobile Agents, Basic architecture, Advantages, Mobile agent framework Total Hrs
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
systems, Network services Textbook: 1) Distributed Computing: Principles and Applications, M. L. Liu, Pearson/Addison-Wesley, 2) A. Taunenbaum, Distributed Systems: Principles and Paradigms 3) G. Coulouris, J. Dollimore, and T. Kindberg, Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design, Pearson Education References: 1. M. Singhal, N. Shivaratri, Advanced Concepts in Operating Systems, TMH Subject Name: Parallel Processing Sr No 1. Course Content Introduction. Parallel Processing Shared Memory Multiprocessing Distributed Shared Memory Message Passing Parallel Computers - Using Parallelism Utilizing Temporal Parallelism Utilizing Data Parallelism Comparison Of Temporal And Data Parallel Processing Data Parallel Processing With Specialized Processors Tools And Languages. Processes & Shared Memory Programming Processes - Shared Memory Programming General Model Of Shared Memory Programming Forking-Creating Processes Joining Processes - Process Model Under UNIX. Basic Parallel Programming Techniques. Loop Splitting Ideal Speedup Spin-Locks, Contention And Self-Scheduling. Scheduling. Loop Scheduling Variations On Loop Scheduling Expression Scheduling Self-Scheduling Variations On Self-Scheduling Indirect Scheduling Block Scheduling Special Scheduling. Barriers And Race Conditions. The Barrier Calls Expression Splitting. Programmability Issues. Operating System Support Types Of Operating Systems Parallel Programming Models Software Tools. 6. Thread-Based Implementation. Thread Management Example With Threads Attributes Of Threads Total Hrs
2.
3.
4.
5.
Mutual Exclusion With Threads Mutex Usage Of Threads Thread Implementation Events And Condition Variables Deviation Computation With Threads Java Threads. 7. Distributed Computing I: Message Passing Model. Message Passing Model General Model Programming Model PVM. Distributed Computing II: Remote Procedure Call Parameter Passing Locating The Server Semantics In The Presence Of Failures Security Problem Areas Java Remote Method Invocation DCE Developing Applications In DCE. Algorithms For Parallel Machines. Models Of Computation Analysis Of Parallel Algorithms Prefix Computation Histogram Computation Parallel Reduction Quadrature Problem Sorting Searching - Matrix Multiplication Parallel Sorting Algorithms Solving Linear Systems Probabilistic Algorithms. Semaphores And Events. Semaphores, Events.
8.
9.
10.
Practical and Term work The Practical and Term work will be based on the topics covered in the syllabus. Minimum 10 experiments should be carried out. Text Books: 1 Introduction To Parallel Programming - By Steven Brawer 2 Introduction To Parallel Processing By M.Sasikumar, Dinesh Shikhare And P. Ravi Prakash 3 Parallel Computers Architecture And Programming By V. Rajaraman And C. Siva Ram Murthy
Subject Name: Artificial Intelligence Sr No 1. Course Content Problems And State Space Search: The AI Problems, The Underlying Assumption, What Is An AI Techniques, The Level Of The Model, Criteria For Success, Some General References, One Final Word. Problems, Problem Spaces And Search : Defining The Problems As A State Space Search, Production Systems, Production Characteristics, Production System Characteristics, And Issues In The Design Of Search Programs, Additional Problems. Heuristic Search Techniques: Generate-And-Test, Hill Climbing, Best-First Search, Problem Reduction, Constraint Satisfaction, Means-Ends Analysis. Knowledge Representation Issues: Representations and Mappings, Approaches to Knowledge Representation. Using Predicate Logic: Representation Simple Facts in Logic, Representing Instance and Isa Relationships, Computable Functions and Predicates, Resolution. Representing Knowledge Using Rules: Procedural versus Declarative Knowledge, Logic Programming, Forward Versus Backward Reasoning. Symbolic Reasoning under Uncertainty: Introduction to Non-monotonic Reasoning, Logics for Nonmonotonic Reasoning. Statistical Reasoning: Probability and Bays Theorem, Certainty Factors and Rule-Base Systems, Bayesian Networks, Dempster-Shafer Theory, Fuzzy Logic. Weak Slot-And-Filler Structure: Semantic Nets, Frames. Advance Topics Game Playing: Overview, And Example Domain The Blocks World, Components Of A Planning System, Goal Stack Planning, Nonlinear Planning Using Constraint Posting, Hierarchical Planning, Reactive Systems, Other Planning Techniques. Natural Language Processing Introduction, Syntactic Processing, Semantic Analysis, Semantic Analysis, Discourse and Pragmatic Processing. Total Hrs
2.
3.
4.
5.
6. 7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Connectionist Models Introduction: Hopfield Networld, Learning In Neural Networld, Application of Neural Networks, Recurrent Networks, Distributed Representations, Connectionist AI and Symbolic AI. Expert Systems An Introduction To Expert System, Explanation Facilities, Expert System Developments Process, knowledge Acquisition. Introduction to Prolog Introduction To Prolog: Syntax & Numeric Function, Basic List Manipulation Functions In Prolog, Functions, Predicates & Conditional, Input, Output & Local Variables, Iteration & Recursion, Property Lists & Arrays, Miscellaneous Topics, LISP & Other AI Programming Languages.
13.
14.
Practical and Term work The Practical and Term work will be based on the topics covered in the syllabus. Text Book: 1 Artificial Intelligence -By Elaine Rich And Kevin Knight (2nd Edition) Tata Mcgraw-Hill 2 Introduction to Prolog Programming By Carl Townsend References: 1 Artificial Intelligence And Expert System, Development -By D.W.Rolston Mcgraw-Hill International Edition. 2 Artificial Intelligence And Expert Systems -By D.W.Patterson 3 PROLOG Programming For Artificial Intelligence -By Ivan Bratko( Addison-Wesley) 4 Programming With PROLOG By Klocksin And Mellish.
Subject Name: VLSI & HDL Programming Sr No 1. Course Content Introduction: Overview of VLSI design mythology, VLSI design flow, Design hierarchy, Concept of regularity, Modularity ,and Locality, VLSI design style, Design quality, package technology, ,computer aided design technology. Fabrication of MOSFET: Introduction, Fabrication Process flow: Basic steps, C-MOS n-Well Process, Layout Design rules, full custom mask layout design. MOS Transistor:The Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) structure, The MOS Total Hrs
2.
3.
System under external bias, Structure &Operation of MOS transistor, MOSFET Current-Voltage characteristics, MOSFET scaling & small-geometry effects, MOSFET capacitances 4. MOS inverters: Static characteristics: Introduction, Resistive load Inverter, Inverter with n-type MOSFET load (Enhancement & Depletion type MOSFET load), CMOS Inverter MOS inverters Switching characteristics and Interconnect Effects: Introduction, Delay-time definitions, Calculation of Delay times, Inverter design with delay constraints, Estimation of Interconnect Parasitics, Calculation of interconnect delay, Switching Power Dissipation of CMOS Inverters Combinational MOS Logic circuits. :Introduction, MOS logic circuits with Depletion nMOS Loads, CMOS logic circuits, Complex logic circuits, CMOS Transmission Gates (TGs) Sequential MOS Logic circuits :Introduction, Behaviour of Bistable elements, The SR latch circuit, Clocked latch & Flip-flop circuit, CMOS D-latch & Edgetriggered flip-flop Dynamic Logic Circuits :Introduction, Basic Principles of pass transistor circuits, Voltage Bootstrapping, Synchronous Dynamic Circuit Techniques, CMOS Dynamic Circuit Techniques, High-performance Dynamic CMOS circuits Chip I/P and O/P circuits :On chip Clock Generation and Distribution, Latch Up and its Prevention Design for testability :Introduction, Fault types and models, Controllability and observability, Ad Hoc Testable design techniques, Scan based techniques, built-in Self Test (BIST) techniques, current monitoring IDDQ test
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Text Book : 1. Book: CMOS Digital Integrated circuits Analysis and Design by Sung Mo kang, Yusuf Leblebici, TATA McGraw-Hill Pub. Company Ltd. Third Edition. Reference Books: (1) Basic VLSI Design By Pucknell & Eshraghian, PHI,3rd ed. (2) Introduction to VLSI Systems by Mead C & Conway, Addison Wesley (3) Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective By Jan M. Rabaey, PHI
Subject Name: Advance Computer Network Sr No 1. Course Content Broadband Wide Area Networking; SDH, Frame Relay and ATM Bandwidth-On-Demand Technologies, Limitations of Traditional Fixed Capacity Networks Packet Switching; First and Subsequent Generations, In-Band vs. Out-of-Band Control Methods Congestion Control, Flow Control & Throughput Cell Relay and ATM Internetworking ATM Features, Adaptation Layers & Cell Structure, Virtual Path, Switching and Traffic Shaping ATM Classes of Service and Traffic Partitioning , LANE, MPOA and PNNI Developments Distributed Computing and The NFS The distributed computing environment architecture , Intra-cell communication and threads The network file system, Remote procedure calls and distributed processes The Next Generation Protocols IP and TCP performance issues, Limitations of current generation TCP and IP Ipv4 pressure points that demand solutions , Internet protocol version 6 features Addressing options and strategies , Ipv6 extension headers, options and features TCP next generation issues and header details, Changes to ICMP and DNS Transition to Next Generation Protocols Mobile IP; Technology and Applications, Requirements of mobile, portable and ubiquitous computing , Radio propagation issues, Evolving device features and form factors Quality of Service and Real-Time Application Issues Quality of service; motivation, issues and options, Integrated vs. Differentiated services Multi-protocol label switching , Real time protocol; features and applications Multicast The Multicast Backbone (MBONE), Relating IP multicast to IEEE 802.1, Multicast tunnels MBONE routing challenges, Voice Over IP Technical and economic opportunities, Configuration models, Packet delay issues Total Hrs
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Voice encoding methods, Signaling and revenue coordination issues TDMA and CDMA; Features Compared and Contrasted TDMA and CDMA concepts/issues/features/limitations, Global system for mobile (GSM) technical features, Enhanced data rates for GSM and TDMA/136 evolution (EDGE) Comparing suitability for supporting data applications Mobile IP; Concepts and Issues Disconnecting from fixed infrastructure, Mobile computing addressing issues Overview; IP connectivity with a mobile unit, Functions of the mobile agent, home agent and foreign agent, Tunnel delivery methods Wireless Application Protocol The case for an unwired web architecture, The WAP architecture; concepts and features WAP data presentation; cards and decks, The wireless application environment, Protocols elements of WAP, Bearer services that support WAP Partial Mobility with Wireless Local Loops Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA), Applications of wireless subscriber loops Broadband wireless; LMDS, MMDS and related technologies, Applications, economics and market for WLL
10.
11.
12.
Practical and Term work The practical and Term work will be based on the topics covered in the syllabus. Minimum 5 experiments should be carried out. Reference: 1. Internetworking with ISDN, Frame Relay & ATM -By William Stallings 2. ATM - protocols, applications and standards -By Hueber et al 3. Internetworking with TCP/IP : volume 1 & 3 -By Douglas Comer 4. Computer Networks-By A. Tanenbaum 5. Unix Network Programming - 1 & 2 -By Richard Stevens 6. WAP Specifications www.wapforum.org Various RFCs, Technical Journals, Papers & Internet Drafts
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Network Coding: Fundamentals and ApplicationsD'EverandNetwork Coding: Fundamentals and ApplicationsMuriel MedardPas encore d'évaluation
- UGC-NET Computer ScienceDocument8 pagesUGC-NET Computer ScienceVikrant Sehgal100% (2)
- SylabiiDocument6 pagesSylabiiashit kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Computer System Design: An IntroductionD'EverandPrinciples of Computer System Design: An IntroductionÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Example Dealer Process Flow and VIMS 3GDocument2 pagesExample Dealer Process Flow and VIMS 3GWilson ClaveriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Iecep EstDocument16 pagesIecep EstRystelle ArganaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyber Security Lab ManualDocument73 pagesCyber Security Lab ManualANNANAHMED SHAIKH50% (2)
- AAA SessionDocument17 pagesAAA SessionRoyal RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Multicore Software Development Techniques: Applications, Tips, and TricksD'EverandMulticore Software Development Techniques: Applications, Tips, and TricksÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (2)
- Sem-4 CSEDocument7 pagesSem-4 CSEdattpatel2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Semester Mtce 701 A Knowledge Based System Design: ReferencesDocument8 pages3 Semester Mtce 701 A Knowledge Based System Design: ReferencesZeeshan KhursheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus CS-0000 V Sem All SubjectDocument11 pagesSyllabus CS-0000 V Sem All Subject12ashivangtiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Week Wise Syllabus 1st SemesterDocument7 pagesWeek Wise Syllabus 1st SemesterRehman Ahmad ChPas encore d'évaluation
- Final MCA 2016-19 Batch SyallbusDocument42 pagesFinal MCA 2016-19 Batch SyallbusChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Sem Syllabus CEDocument13 pages8 Sem Syllabus CEBhavin PalanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd CSE IT New Syllabus 2019 20Document19 pages3rd CSE IT New Syllabus 2019 20Harsh Vardhan HBTUPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE - 5th Semester NotesDocument5 pagesCSE - 5th Semester NotesShubham ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Java Programming Course Outline: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesJava Programming Course Outline: ObjectivesjpsahooPas encore d'évaluation
- RGPV Syllabus Cbgs Cs 6 Sem All Subjects PDFDocument12 pagesRGPV Syllabus Cbgs Cs 6 Sem All Subjects PDFelectronPas encore d'évaluation
- M.Tech (Computer Engineering) (Full Time) : Semester IDocument16 pagesM.Tech (Computer Engineering) (Full Time) : Semester ITarun AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Program: Computer & Data Science: Analytical ActivityDocument18 pagesProgram: Computer & Data Science: Analytical ActivityTamenePas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering - PGDocument31 pagesDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering - PGMegha BheemaraoPas encore d'évaluation
- B.TECH. II Semester-4 L T P C CS 401: Operating Systems 3 0 2 4Document6 pagesB.TECH. II Semester-4 L T P C CS 401: Operating Systems 3 0 2 4Onkar JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- MCTA - 301 (A) Data Mining and Warehousing: Reference BooksDocument8 pagesMCTA - 301 (A) Data Mining and Warehousing: Reference BookssurajamitPas encore d'évaluation
- Cse First Year SyllabusDocument4 pagesCse First Year SyllabusEr Gaurav PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fifth Semester: BTCS 501 Computer Networks - IIDocument6 pagesFifth Semester: BTCS 501 Computer Networks - IIPrincess deepikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajasthan Technical University, Kota Detailed Syllabus For B.Tech.Document21 pagesRajasthan Technical University, Kota Detailed Syllabus For B.Tech.Dolly HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Thapar MCA Syllabus PDFDocument53 pagesThapar MCA Syllabus PDFsunnykinger100% (2)
- 8th Sem SyllabusDocument4 pages8th Sem SyllabusShwetank GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- CB-401 Operating Systems: Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, BhopalDocument19 pagesCB-401 Operating Systems: Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, BhopalshubhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Askinfos 6th CompDocument10 pagesAskinfos 6th Compsaurabh150Pas encore d'évaluation
- MSC IT SyllabusDocument69 pagesMSC IT Syllabusbirbal93% (15)
- Syllabus Bca - Iiird YearDocument8 pagesSyllabus Bca - Iiird YearTheRHKapadiaCollegePas encore d'évaluation
- Semester-V BCA 501-Software Engineering (BCA V)Document8 pagesSemester-V BCA 501-Software Engineering (BCA V)Anitha VeeramanePas encore d'évaluation
- VII Semester VTU SyllabusDocument7 pagesVII Semester VTU SyllabusantoshdyadePas encore d'évaluation
- 5th Sem SyllabusDocument4 pages5th Sem SyllabusMathew RejiPas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Computer Architecture & Peripherals: Duration 3 Hours 3 1 2 6 70 22Document7 pagesAdvance Computer Architecture & Peripherals: Duration 3 Hours 3 1 2 6 70 22Yogendra AgnihotriPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE BTech Third YearDocument14 pagesCSE BTech Third Yearhalfblood8400Pas encore d'évaluation
- MG University Mca 4th Sem SyllabusDocument18 pagesMG University Mca 4th Sem Syllabusnoblesivankutty100% (1)
- C 4 Pnuuiost 85 K 8 Q 6 U 4 Szqiwcerccakq 9Document11 pagesC 4 Pnuuiost 85 K 8 Q 6 U 4 Szqiwcerccakq 9mahdi.alsaadi7Pas encore d'évaluation
- University of Mysore Directorate of Outreach and Online ProgramsDocument15 pagesUniversity of Mysore Directorate of Outreach and Online ProgramsdeepsdesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Elective - I: Python Programming LanguageDocument12 pagesElective - I: Python Programming LanguageTanayyPas encore d'évaluation
- TcsDocument12 pagesTcsapi-3729768100% (1)
- C++ Language: (No. of HRS: 09)Document6 pagesC++ Language: (No. of HRS: 09)Clyde JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- 5th Sem SyllabusDocument5 pages5th Sem SyllabusAnkit SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Bca 6th Sem Syllabus UemjDocument19 pages6 Bca 6th Sem Syllabus Uemjapi-351162654Pas encore d'évaluation
- BTech CSE Third Year SyllabusDocument5 pagesBTech CSE Third Year SyllabusAnkush KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bca I Year SyllabusDocument9 pagesBca I Year SyllabusLol HahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of Master of Computer MCADocument31 pagesSyllabus of Master of Computer MCAThesavyPas encore d'évaluation
- BDBC ContentDocument32 pagesBDBC ContentManoj YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- M.Tech (CSE)Document10 pagesM.Tech (CSE)krishna_reddy517Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati Department of Computer ScienceDocument6 pagesSri Venkateswara University, Tirupati Department of Computer ScienceANKISETTI BHARATHKUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Parallel and Distributed SystemsDocument3 pagesParallel and Distributed Systemsarungupta652Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5th-Sem Syllabus T.U.Document25 pages5th-Sem Syllabus T.U.Roshan PaudelPas encore d'évaluation
- BE Sem 8th Syllabus For Mid Sem ExamDocument7 pagesBE Sem 8th Syllabus For Mid Sem ExamaspdjPas encore d'évaluation
- M.tech. (ICT) Part I (Semester I & II)Document22 pagesM.tech. (ICT) Part I (Semester I & II)Babita ChopraPas encore d'évaluation
- M. Tech 1st Year 2nd SemDocument7 pagesM. Tech 1st Year 2nd Sem9866726771Pas encore d'évaluation
- MG University Btech CS 6th SemesterDocument20 pagesMG University Btech CS 6th SemesterAntony RealPas encore d'évaluation
- Kerala University s8 Syllabus 2008 SchemeDocument29 pagesKerala University s8 Syllabus 2008 SchemeJijo PJPas encore d'évaluation
- Cognitive Radio Communication and Networking: Principles and PracticeD'EverandCognitive Radio Communication and Networking: Principles and PracticePas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Evaluation by Simulation and Analysis with Applications to Computer NetworksD'EverandPerformance Evaluation by Simulation and Analysis with Applications to Computer NetworksPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Best PracticesDocument66 pagesBluetooth Best PracticesseyazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring ActivePassive RACDocument3 pagesConfiguring ActivePassive RACNonstop NonPas encore d'évaluation
- Trackers para UtorrentDocument7 pagesTrackers para UtorrentFranklin CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Veva1200 1210 User Guide For UK BTP - Apr 30 07 - 0Document2 pagesVeva1200 1210 User Guide For UK BTP - Apr 30 07 - 0cross1avalPas encore d'évaluation
- Name Synopsis Description: Curl (Options) (URL... )Document35 pagesName Synopsis Description: Curl (Options) (URL... )yo goloPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Fall2011Document450 pagesBook Fall2011yuqiao1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unix Handbook For Oracle DBA: Flavia D'SouzaDocument53 pagesUnix Handbook For Oracle DBA: Flavia D'SouzaMabu DbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Airfiber AF-11FX UG PDFDocument58 pagesAirfiber AF-11FX UG PDFKevin RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Shellshock LabDocument5 pagesShellshock LabpavanhugarPas encore d'évaluation
- Eagle - Smint - WebDocument2 pagesEagle - Smint - WebrewritingPas encore d'évaluation
- OM4 Provides An Opportunity To Future-Proof Cabling Infrastructure. OM4 Is Completely Backwards-Compatible With Existing OM3 SystemsDocument2 pagesOM4 Provides An Opportunity To Future-Proof Cabling Infrastructure. OM4 Is Completely Backwards-Compatible With Existing OM3 Systemsaldebaran0473Pas encore d'évaluation
- Linkedin Chat - January 30th 2013Document17 pagesLinkedin Chat - January 30th 2013Tweet Binder100% (1)
- Instruction Sheet 1032-500Document29 pagesInstruction Sheet 1032-500Wagner Pereira Lima PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- AngularJS Mastery Code Like A Pro GuideDocument56 pagesAngularJS Mastery Code Like A Pro Guidebp499Pas encore d'évaluation
- CICS Transaction ConnectionDocument102 pagesCICS Transaction Connectiongborja8881331Pas encore d'évaluation
- Zipato Zipatile Data Sheet 1.3Document2 pagesZipato Zipatile Data Sheet 1.3panchoPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual VirtualCOMport IrCOMM2KdriverDocument3 pagesManual VirtualCOMport IrCOMM2Kdriverosto72Pas encore d'évaluation
- Att, Attn, Fao ..Document4 pagesAtt, Attn, Fao ..s.v.k.rajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Moxa Application - Total IEC61850 MMS Solution For Substation Retrofits 2018Document2 pagesMoxa Application - Total IEC61850 MMS Solution For Substation Retrofits 2018Michael Parohinog GregasPas encore d'évaluation
- sx60-100 QSG Us 090817Document74 pagessx60-100 QSG Us 090817negrau72Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Call Manager en Packet TracerDocument4 pagesCisco Call Manager en Packet TracerJairo González MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- FortiGate 80E SeriesDocument6 pagesFortiGate 80E SeriesAndrés HomePas encore d'évaluation
- Pravesh Chadda: Purpose StatementDocument4 pagesPravesh Chadda: Purpose StatementPankaj Chadda100% (1)
- DigiJED StudentsDocument7 pagesDigiJED StudentsArtem NAzPas encore d'évaluation
- Cipt180lgDocument102 pagesCipt180lgsa100100Pas encore d'évaluation
- Windows Server 2003 Vs 2008Document2 pagesWindows Server 2003 Vs 2008simadrigiriPas encore d'évaluation