Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Configuring Frame Relay Involves The Following Steps
Transféré par
Lê Chí ThọDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Configuring Frame Relay Involves The Following Steps
Transféré par
Lê Chí ThọDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Configuring Frame Relay involves the following steps:
Chang the encapsulation
Go in interface mode and select the Frame Relay encapsulation on the interface. There are two types of Frame Relay encapsulations: Cisco and IETF. Cisco is the default. The syntax to set your encapsulation is
encapsulation frame-relay [ietf]
Configuring the LMI type
The three LMI types are Cisco, Ansi, and Q933a. For IOS 11.2 and higher, the LMI type is automatically detected
frame-relay lmi-type [cisco | ansi | 933a]
Configuring the Frame Relay map
configuring a static Frame Relay map, is optional unless you are using subinterfaces. The Frame Relay map will map a Layer 3 address to a local DLCI. This step is optional because inverse-arp will automatically perform this map for you. The syntax for a Frame Relay map is as follows:
frame-relay map protocol address dlci [broadcast] [cisco | ietf]
Configuring subinterfaces
If you are using a routing protocol in a hub-and-spoke topology, you will probably want to use subinterfaces to avoid the split-horizon problem. To configure a subinterface, remove the IP address off the main interface and put it under the subinterface. Configuring a subinterface involves assigning it a number and specifying the type. The following command creates point-topoint subinterface serial0/0.1
Router(config)#interface serial0/0.1 point-to-point
To create a multipoint subinterface, enter multipoint instead:
Router(config)#interface serial0/0.1 multipoint
Assign IP address to subinterface
After entering one of these commands you will be taken to the subinterface configuration mode where you can enter your IP address:
Router(config-subif)#ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
If you are using a multipoint subinterface, you will need to configure frame-relay maps and you cannot rely on inverse-arp. If you are using a point-to-point subinterface, you will need to assign a DLCI to the subinterface. This is only for point-to-point subinterfaces; this is not needed on the main interface or on multipoint subinterfaces. To assign a DLCI to a point-to-point subinterface, enter the following command under the subinterface:
frame-relay interface-dlci dlci
Configuration of Frame Relay
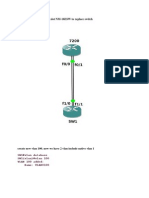
Lets practically implement whatever you learn so far. Download this pre configured topology and load it in packet tracer.
Now first configure R1. Fast Ethernet port and hostname is already configured. Double click on R1 and configure serial port for frame relay encapsulation and further create sub interface for connecting R2, R3, R4. Configure also static route for connecting remaining network.
Configure R1
R1>enable R1#configure terminal
R1(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R1(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#exit R1(config-subif)#interface serial 0/0/0.102 point-to-point R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.245 255.255.255.252 R1(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci 102 R1(config-subif)#exit R1(config)#interface serial 0/0/0.103 point-to-point R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.249 255.255.255.252 R1(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci 103 R1(config-subif)#exit R1(config)#interface serial 0/0/0.104 point-to-point R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.253 255.255.255.252 R1(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci 104 R1(config-subif)#exit R1(config)#ip route 192.168.1.64 255.255.255.224 192.168.1.246 R1(config)#ip route 192.168.1.96 255.255.255.224 192.168.1.250 R1(config)#ip route 192.168.1.128 255.255.255.224 192.168.1.254 R1(config)#exit
configure R2
R2>enable R2#configure terminal R2(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R2(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#interface serial 0/0/0.101 point-to-point R2(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.246 255.255.255.252 R2(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci 101 R2(config-subif)#exit R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.245
configure R3
R3>enable R3#configure terminal R3(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R3(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay R3(config-if)#no shutdown R3(config-if)#exit R3(config)#interface serial 0/0/0.101 point-to-point R3(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.250 255.255.255.252 R3(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci 101 R3(config-subif)#exit R3(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.249 R3(config)#
configure R4
R4>enable R4#configure terminal
R4(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R4(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay R4(config-if)#no shutdown R4(config-if)#exit R4(config)#interface serial 0/0/0.101 point-to-point R4(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.252 R4(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci 101 R4(config-subif)#exit R4(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.253 R4(config)#
now verify by doing ping from pc0 to all pc. It should be ping successfully. I have uploaded a configured topology but use it as the final resort first try yourself to configure it.
Router(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 Router(configif)#encapsulation framerelay Router(config-if)#framerelay lmitype {ansi | cisco | q933a}
Enter in interface mode Turns on Frame Relay encapsulation with the default encapsulation type of cisco
Depending on the option you select, this command sets the LMI type to the ANSI standard, the Cisco standard, or the ITU-T Q.933 Annex A standard. Router(config-if)#frame- Sets the DLCI number of 110 on the local interface and enters relay interface-dlci 110 Frame Relay DLCI configuration mode Router(config-fr-dlci)#exit Returns to interface configuration mode Router(config-if)#frame- Maps the remote IP address (192.168.100.1) to the local DLCI number (110). The optional broadcast keyword specifies that relay map ip 192.168.100.1 110 broadcasts across IP should be forwarded to this address. This is broadcast necessary when using dynamic routing protocols.
Router(config-if)#no frame-relay inverse arp Router#show frame-relay map Router#show frame-relay pvc Router#show frame-relay lmi Router#clear frame-relay counters Router#clear frame-relay inarp
Turns off Inverse ARP. Displays IP/DLCI map entries Displays the status of all PVCs configured Displays LMI statistics Clears and resets all Frame Relay counters Clears all Inverse ARP entries from the map table and Frame Relay switch
Router#debug frame-relay Used to help determine whether a router lmi are exchanging LMI packets properly
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- As Usual, I'll Use 3660 With Slot NM-16ESW To Replace SwitchDocument9 pagesAs Usual, I'll Use 3660 With Slot NM-16ESW To Replace SwitchLê Chí ThọPas encore d'évaluation
- Mpls VPN BasicDocument13 pagesMpls VPN BasicMohamed FarhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab-Iscw - Mpls VPN MultivrfDocument12 pagesLab-Iscw - Mpls VPN MultivrfLê Chí ThọPas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- EasyDCP Creator UserManualDocument73 pagesEasyDCP Creator UserManualLeandro FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- TC458-96060 StoreOnce VSA Deployment and Configuration GuideDocument89 pagesTC458-96060 StoreOnce VSA Deployment and Configuration GuideMartin AbrhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes For Installing SICAM PAS/PQS V7.00 SP2 or Later On A SICAM Station Unit V2.00/V2.10Document2 pagesNotes For Installing SICAM PAS/PQS V7.00 SP2 or Later On A SICAM Station Unit V2.00/V2.10Salvador FayssalPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Optimize Write-Back Disk - CCBoot v3.0 Diskless Boot SystemDocument7 pagesHow To Optimize Write-Back Disk - CCBoot v3.0 Diskless Boot SystemBlak Dia MondPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabraiz Pasha AS: Carrier ObjectiveDocument5 pagesTabraiz Pasha AS: Carrier Objectivejaya74mscPas encore d'évaluation
- br6000 v6 0 PBDocument2 pagesbr6000 v6 0 PBAndré Ricardo da SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- TOF Camera WhitePaperDocument10 pagesTOF Camera WhitePaperaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Viewsonic n3250w-1 User GuideDocument56 pagesViewsonic n3250w-1 User Guidefeb29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gran Turismo 5 Prologue - Manual - PS3Document19 pagesGran Turismo 5 Prologue - Manual - PS3Historia da Segunda Guerra MundialPas encore d'évaluation
- Sixth Sense TechnologyDocument6 pagesSixth Sense TechnologyRavi Shankar K BPas encore d'évaluation
- div-ESLG3Document27 pagesdiv-ESLG3Sree DurgaPas encore d'évaluation
- CycomDocument2 pagesCycomLance Hikikomori ChongPas encore d'évaluation
- Tms 320 F 2812Document154 pagesTms 320 F 2812Andre Bacilio VelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chess GPS: 12 Chapters Exploring Strategic ConceptsDocument17 pagesChess GPS: 12 Chapters Exploring Strategic ConceptsStans Wole100% (1)
- Commercial Electrical Load Calculations NECDocument4 pagesCommercial Electrical Load Calculations NECRudanekPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Architecture - Teachers NotesDocument11 pagesComputer Architecture - Teachers NotesHAMMAD UR REHMANPas encore d'évaluation
- Inductive Shrink Devices and Accessories Inductive Shrink DevicesDocument3 pagesInductive Shrink Devices and Accessories Inductive Shrink DevicesVlad LeucutaPas encore d'évaluation
- D1000Document6 pagesD1000rsudjianPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Electronics 2011-2012Document135 pagesConsumer Electronics 2011-2012Jaimichu07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Operating System Types and EvolutionDocument12 pagesOperating System Types and EvolutionMannPas encore d'évaluation
- To Perform HDL Based Design Entry and Simulation of ALUDocument6 pagesTo Perform HDL Based Design Entry and Simulation of ALUsamhita santhanamPas encore d'évaluation
- AD9259Document52 pagesAD9259chrhyd1Pas encore d'évaluation
- PC Express Laptop and Desktop Price List: Laptop SRP 0% 6MOS 0% 12MOSDocument8 pagesPC Express Laptop and Desktop Price List: Laptop SRP 0% 6MOS 0% 12MOSAndrew Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Wm-sg-sm-42 Product Spec Rev03 20170301Document31 pagesWm-sg-sm-42 Product Spec Rev03 20170301Adrian P.Pas encore d'évaluation
- CGC 400 Installation Instructions 4189340785 UK - 2013.09.24Document26 pagesCGC 400 Installation Instructions 4189340785 UK - 2013.09.24edgarcooPas encore d'évaluation
- 9P9H9DDocument31 pages9P9H9DArtful DodgerPas encore d'évaluation
- TVLCD LGDocument45 pagesTVLCD LGIonescu CristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Shop Management System NewDocument38 pagesElectrical Shop Management System NewDeva Chandran67% (3)
- D. A and B TrueDocument2 pagesD. A and B TrueAkbar FalladikaPas encore d'évaluation