Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Policies To Control Inflation
Transféré par
Diana ZuhairiDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Policies To Control Inflation
Transféré par
Diana ZuhairiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Policies to Control Inflation Identify Contractionary MP Contractionary FP Explain Lower MS rise in i/r cost of borrowing increases reduces I + C purchased
sed with loans fall in AD GPL falls Reduce G, increase T budget surplus personal disposable income and business aftertax income falls dampening effect on C and I AD falls less pressure on GPL Evaluation Inappropriate for cost-push inflation Time lag, but shorter than FP: sell bonds to public Unpredictable effect on C and I Inappropriate for cost-push inflation Time lag Unpredictable effect of taxes on C and I Poor may suffer more: need subsidies / supplementary schemes from government Cannot estimate how much to decrease AD by Administration unlikely to undertake vigorous antimonopoly / antiunion stance Large firms enjoy EOS and high rate of technological progress
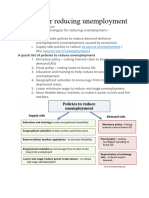
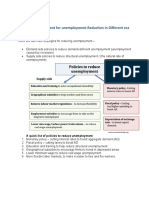
Market Policies - Manpower policy
Improve efficiency of labour markets so that any given level of AD associated with lower level of unemployment Better matching of workers to jobs, reducing labour market imbalances or bottlenecks Reduce monopoly / market power of unions and businesses less able to push up wage rates ahead of average productivity increases + reduce discretionary power of large firms to raise prices - Business: antitrust laws, remove existing legal restrictions upon entry reduce / eliminate restrictions upon foreign imports - Labour: anti-monopoly laws to unions, decentralization of collective bargaining, link portion of wages to profits wage more flexible downward
- Pro competition policy
Wage-price Policies - Wage guidepost - Price guidepost - Wage / prize freeze Welfare benefits
Wage rates rise with rat e of increase in labour productivity Prices should change to compensate for changes in unit labour costs Something like price ceiling Remove benefits people more willing to be employed increase productive capacity of country
R+d, Increase productivity increase AS education and training 1) Priorities of goals: low inflation rate SR: lower rate of economic growth and higher level of unemployment 2) Economic philosophy government subscribes to: rely on free market / intervention: dependent on degree of government intervention considered necessary
Workability and compliance: business and labour leaders have to forgo the goals of maximum profits and higher wages little voluntary cooperation Strong economic incentives could develop to evade controls Effect wage-price controls interfere with allocative function of price system Need to ensure that people are equipped with skills / are able to find jobs quickly (frictional and structural unemployment) Need to ensure jobs are available in the first place Long run measure
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Business Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageD'EverandBusiness Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantagePas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Side PoliciesDocument5 pagesSupply Side PoliciesVanessa KuaPas encore d'évaluation
- IBDP Macro 3.7 FinalDocument7 pagesIBDP Macro 3.7 FinalSandeep SudhakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Policies For Reducing UnemploymentDocument6 pagesPolicies For Reducing UnemploymentAnushkaa DattaPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of LabourDocument9 pagesSupply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of LabourkirstinrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Economics Ii Assignment QuestionDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Economics Ii Assignment QuestionChristianJerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Video NotesDocument2 pagesVideo NotesHarold WhistlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pricing in Context of Government Policy and RegulationsDocument10 pagesPricing in Context of Government Policy and Regulationsnicholas otayePas encore d'évaluation
- (2013) Abdel-Kader - What Are Structural Policies PDFDocument2 pages(2013) Abdel-Kader - What Are Structural Policies PDF0treraPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of LabourDocument6 pagesSupply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of LabourkirstinrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Socio Economic Factors Affecting Business and IndustryINCOMEDocument23 pagesSocio Economic Factors Affecting Business and IndustryINCOMEMarie Joy CentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Side PoliciesDocument6 pagesSupply Side PoliciestawandaPas encore d'évaluation
- International Corporate FinanceDocument60 pagesInternational Corporate FinanceCarlo AgdamagPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Notes UnemploymentDocument14 pagesIB Notes UnemploymentAnderson MaradzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply-Side Policy: Improving Productivity of FactorsDocument3 pagesSupply-Side Policy: Improving Productivity of FactorsMakoy AceronPas encore d'évaluation
- Unemployment EssayDocument9 pagesUnemployment EssayJenney TatPas encore d'évaluation
- CH.7 External Economic Influences On Business AcivityDocument5 pagesCH.7 External Economic Influences On Business Acivitytaha ChniberPas encore d'évaluation
- S7b - Readings - Government Intervention in The MarketDocument4 pagesS7b - Readings - Government Intervention in The MarketOzkar Zaldivar100% (1)
- Policies For Reducing UnemploymentDocument14 pagesPolicies For Reducing UnemploymentAnushkaa DattaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 External Economic Influences On Business ActivityDocument3 pagesChapter 7 External Economic Influences On Business ActivityVakim KPas encore d'évaluation
- Policies To Control InflationDocument5 pagesPolicies To Control InflationMohsin ManzoorPas encore d'évaluation
- What Can Be Done at The Macro Level To Control Unemployment?Document3 pagesWhat Can Be Done at The Macro Level To Control Unemployment?Mohammed AshroffPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 IGCSEDocument96 pagesChapter 15 IGCSEtaj qaiserPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Fiscal Policy?Document10 pagesWhat Is Fiscal Policy?Samad Raza KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of Political Into BusinessDocument4 pagesThe Impact of Political Into BusinessAJ AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Side Policies and Policy ConflictsDocument12 pagesSupply Side Policies and Policy Conflictsnkoan12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Notes Year 11Document9 pagesEconomics Notes Year 11conorPas encore d'évaluation
- Should India Follow Demand Side or Supply Side of Macroeconomics??Document13 pagesShould India Follow Demand Side or Supply Side of Macroeconomics??Niraj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics AnswerDocument5 pagesEconomics AnswerJeeveshraj Gupta100% (1)
- Supply Side PolicyDocument6 pagesSupply Side Policyxf48qwb9gcPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiscal and Monetary PolicyDocument16 pagesFiscal and Monetary PolicyBezalel OLUSHAKINPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Question and AnswersDocument144 pagesEconomics Question and Answersmarvadomarvellous67Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Business EnvironmentDocument9 pagesAssignment Business EnvironmentDashanka WarnakulasooriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Seen - 20 MarkerDocument2 pagesPre Seen - 20 MarkerMUKESH KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Crises NoteDocument9 pagesEconomic Crises NoteAdetunbi TolulopePas encore d'évaluation
- Government As ProducerDocument56 pagesGovernment As ProducerrowobelangPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1 Demand and Supply-Side PoliciesDocument13 pages5.1 Demand and Supply-Side PoliciesMarisa VetterPas encore d'évaluation
- MacroeconomicsDocument4 pagesMacroeconomicsBurhan barchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Eceonomics ProjectDocument9 pagesBusiness Eceonomics ProjectMuhammad Waleed ArsalPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 1: Equilibrium Price 300 Quantity 640Document8 pagesTask 1: Equilibrium Price 300 Quantity 640mudassar nawazPas encore d'évaluation
- Govt Intervention and Market FailureDocument42 pagesGovt Intervention and Market FailureAsad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Onomic Policies: EconomyDocument7 pagesOnomic Policies: EconomyGunnawng sumlutPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply-Side PolicyDocument5 pagesSupply-Side PolicyElaine chenPas encore d'évaluation
- L10-Making Growth Inclusive The Impact of Fiscal Policy On EmploymentDocument45 pagesL10-Making Growth Inclusive The Impact of Fiscal Policy On EmploymentAnne Marie HordauPas encore d'évaluation
- Tax Policies and Its Economic FluctuationsDocument14 pagesTax Policies and Its Economic FluctuationsZubairPas encore d'évaluation
- Revising Macro Mind MapDocument1 pageRevising Macro Mind Mapdordon67Pas encore d'évaluation
- Taxation JunaDocument551 pagesTaxation JunaJuna DafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Increase Both Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply: Reducing Direct Tax Rates, Including Income and Corporation TaxDocument2 pagesIncrease Both Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply: Reducing Direct Tax Rates, Including Income and Corporation Taxbla blaPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply-Side PoliciesDocument2 pagesSupply-Side PoliciesSubashini ManiamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec MacrobudgetfpDocument3 pagesEc MacrobudgetfpNicholas TehPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects Income Tax Changes Economic Growth Gale Samwick PDFDocument16 pagesEffects Income Tax Changes Economic Growth Gale Samwick PDFArpit BorkarPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIC+10+ +Fiscal+Policy+and+Public+ExpendituresDocument31 pagesTOPIC+10+ +Fiscal+Policy+and+Public+ExpenditurescaylaalqueromallariPas encore d'évaluation
- Tejvan Pettinger: Poor InformationDocument6 pagesTejvan Pettinger: Poor InformationtawandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand Side PolicyDocument15 pagesDemand Side PolicyAnkit Shukla100% (1)
- Macro Economic Policy InstrumentsDocument11 pagesMacro Economic Policy InstrumentsThankachan CJPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiscal PolicyDocument10 pagesFiscal PolicyAishath Aala AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A PEST AnalysisDocument12 pagesWhat Is A PEST AnalysistanjialijlPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting The MarketDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting The Marketfelix tibawenPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 3iDocument4 pagesHW 3iEthan BoelhouwerPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Business Environment - Government Intervention & State PoliciesDocument15 pagesIndian Business Environment - Government Intervention & State PolicieschandrikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership Skills - Ferguson - 2nd Ed.Document129 pagesLeadership Skills - Ferguson - 2nd Ed.Al Jameel100% (1)
- ETHICS6375Document54 pagesETHICS6375nathaliePas encore d'évaluation
- UCSP Enrichment RemedationDocument2 pagesUCSP Enrichment RemedationAlyanna Elisse VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabulary For TOEIC - 13 - Job AdvertisingDocument2 pagesVocabulary For TOEIC - 13 - Job AdvertisingTeacher100% (2)
- Chapter 8 Location StrategiesDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Location StrategiesNivedita ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- PRC Resolution No 381Document49 pagesPRC Resolution No 381Chris Jomarie Obra100% (2)
- 2) Supervisor IsDocument6 pages2) Supervisor IsRushikesh Shinde100% (6)
- DIRECTOR FOOD AND BEVERAGE or DIRECTOR OPERATIONSDocument3 pagesDIRECTOR FOOD AND BEVERAGE or DIRECTOR OPERATIONSapi-121360454Pas encore d'évaluation
- Talon Sports Corporate Internship Report FinalDocument45 pagesTalon Sports Corporate Internship Report Finalsadaf_gul_750% (2)
- Persuasive SpeechDocument2 pagesPersuasive SpeechHannah IsabellePas encore d'évaluation
- Career CounsellingDocument36 pagesCareer CounsellingAida Ivan100% (1)
- A4-Size-Application-Form-tesda-CSS - WPS PDF Convert PDFDocument2 pagesA4-Size-Application-Form-tesda-CSS - WPS PDF Convert PDFMark Anthony DalitPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling LifeDocument169 pagesModeling LifeMatias Delera67% (3)
- Assignment On Diversity in WorkplaceDocument15 pagesAssignment On Diversity in WorkplaceWahidul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - IDocument36 pagesChapter - Iharman singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Care Officer Job DescriptionDocument4 pagesCommunity Care Officer Job DescriptionRyan SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Director Manager Operations Pharmacy in Los Angeles CA Resume Philip HoDocument2 pagesDirector Manager Operations Pharmacy in Los Angeles CA Resume Philip HoPhilipHo2Pas encore d'évaluation
- J Patrick Gallagher ResumeDocument3 pagesJ Patrick Gallagher ResumeJPatrickGallagherPas encore d'évaluation
- Budget and Budgetary Control in Kesoram Cement Industries LTDDocument42 pagesBudget and Budgetary Control in Kesoram Cement Industries LTDglorydharmaraj100% (7)
- Meaning and Definition OverheadsDocument3 pagesMeaning and Definition OverheadskunjapPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Regular Income Tax - Gross Income Aljon J. Roque, CPA, MBADocument3 pagesTopic: Regular Income Tax - Gross Income Aljon J. Roque, CPA, MBAJhon Ariel JulatonPas encore d'évaluation
- Planning and Scheduling Operations: Cooper Tire and Rubber CompanyDocument35 pagesPlanning and Scheduling Operations: Cooper Tire and Rubber CompanyLeycrow RatzingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate Layoffs Lists 2000 To 2005 Volume IIDocument310 pagesCorporate Layoffs Lists 2000 To 2005 Volume IIJaggy GirishPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching English Online: Guide ToDocument28 pagesTeaching English Online: Guide To'Cassio Costa50% (2)
- Gender Inequality in The Philippine Labor MarketDocument41 pagesGender Inequality in The Philippine Labor MarketADBGADPas encore d'évaluation
- Globalisation and IrrDocument96 pagesGlobalisation and IrrVivek YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Oct 17Document10 pagesOct 17Madelyn ViernesPas encore d'évaluation
- Catu V Rellosa PDFDocument2 pagesCatu V Rellosa PDFkatrina_petillaPas encore d'évaluation
- United Special Watchman Agency vs. CADocument6 pagesUnited Special Watchman Agency vs. CARona TumaganPas encore d'évaluation