Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2 - Math
Transféré par
reymartlaguneroDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Module 2 - Math
Transféré par
reymartlaguneroDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
University of the Philippines Baguio
Gov. Pack Road, Baguio City
National Service Training Program 2
Literacy Training Service
Baguio City National High School San Vicente Annex
Mathematics II Module for 12 December 2011
Objectives
I. To practice the students in their mathematical skills on the following topics:
a. Graphs of Linear Equations in Two Variables
b. Solution of a System of Linear Equations
c. Systems of Linear Equations Solved by Graphing
d. Systems of Linear Equations Solved by Algebraic Methods
e. Systems of Linear Equations with Fractions and Parentheses
f. Problems Involving Systems of Linear Equations
g. Problems Involving Linear Inequalities
h. Graph of Linear Inequalities
i. Graphs of Systems of Linear Inequalities
II. To enhance further and develop their understanding of mathematical concepts and
principles
III. To improve higher-order thinking skills
IV. To help them appreciate the applications of mathematics in real life situations.
Discussion
I. Graphs of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Consider the equation . Ordered pairs that satisfy the equation can be found. For example,
if y=0, a value for x, by substituting 0 for y in the equation can be found as follows,
5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5
5
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
x
y y = 2x-3
(x,y) = (3/2,0)
(x,y) = (0,-3)
(x,y) = (2,1)
(x,y) = (1,-1)
The ordered pair (
) is one of the solutions. Other ordered pairs that satisfy the equation are
( ) ( ) ( ). The graph of the equation appears below
Illustrative Example
Find at least 3 ordered pairs that satisfy the equation . Graph on the Cartesian plane.
II. Solution of a System of Linear Equations
To solve a system of linear equations is to find its solution. However, while some systems have an
infinite number of solutions, others may have only one solution or may have no solution at all.
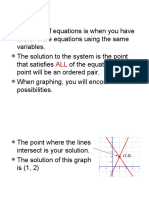
Definition: The set of all the ordered pairs of real numbers that satisfy every equation in a system of
equations is called the solution set of that system.
Observe the graphs of
drawn in the coordinate plane at the
right. The lines intersect at exactly one point
which has the coordinates (1, 1). Notice also
that the two lines have different slopes, the
one is positive, the other is negative.
5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
5
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
x
y y = 2x-1
y = 3-2x
(x,y) = (1,1)
4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
x
y y = 2x-1
y = 2x+5
2 1 1 2
2
1
1
2
x
y
2x-y=1
4x-2y=2
Now, consider the diagram on the right. Note
that the solution set is the empty set. There is no
solution because the two lines do not intersect.
Notice that the lines have the same slope 2 but
different y-intercepts, 5 and -1.
Also, consider the diagram below. Note that the
solution set of the system consists of infinite set
of points on the line formed by the graphs of
both equations. Take note also that the lines
have the same slope 2 and the same y-intercept,
-1. These lines overlap. If both sides of
are divided by 2, the result is
. These two equations are called
equivalent equations.
Definition: A system of linear equations in two variables which has
a. At least one solution is called a consistent system;
- If it has exactly one solution, then the consistent system is independent.
- If it has an infinite number of solutions, then the consistent system is dependent.
b. If it has no solution, it is called an inconsistent system.
Illustrative Example
Graph the system of equations and determine whether or not it is consistent and independent.
1. {
2. {
{
3 2 1 1 2 3 4
3
2
1
1
2
3
x
y 2x-y=2
3x+y=3
(x,y) = (1,0)
3 2 2 3 5 6 8
6
4
3
1
1
3
4
6
x
y 2x+3y=12
4x-3y=6
(x,y) = (3,2)
3 2 2 3
3
1
1
3
x
y 2x+3y=2
2x+6y=3
(x,y) = (1/2,1/3)
III. Systems of Linear Equations Solved by Graphing
One way of finding the solution of a system of linear equations is by graphing the equations on the same
set of axes. The point/s of intersection of the graphs is/are the solution/s of the system.
Illustrative Example
Solve the system of linear equations graphically.
1. {
2. {
3. {
IV. Systems of Linear Equations Solved by Algebraic Methods
To obtain a more accurate solution to systems of linear equations, the algebraic methods of solution are
resorted to.
Solution by Substitution
This method is easily applied when at least one equation gives the value of one unknown in terms of the
other.
Illustrative Examples
Solve the systems
1. {
()
()
Solution:
Substitute 4x for y in equation (1).
3x+2(4x)=11
3x+8x=11
11x=11
x=1
Substitute 1 for x in equation (2).
Y=4(1)=4
The solution is the ordered pair (1, 4).
2. {
()
()
Solution:
Substitute 8-4x for y in equation (1).
5x+3(8-4x)=3 5x+24-12x=3 -7x=-21 x=3
Substitute 3 for x in equation (2). y=8-4(3)=-4.
The solution is the ordered pair (3, -4).
3. {
()
()
Solution:
Solve for x in terms of y in equation (1).
4x-3y=11 4x=11+3y
Substitute the value of y in equation (2).
(
) ( )
Substitute the value of y in equation (1).
()
The solution is the ordered pair (
)
Solution by Comparison
This method of solving systems of linear equations uses the transitive property of equality, which states
that quantities equal to the same quantity are equal. This is used when the same unknown in the two
equations has coefficient 1. This value of the other unknown can then be found.
Illustrative Examples
Solve the systems
1. {
Solution:
Solve both equations for the variable x to find y.
x=-2y+4 (1) x=3y-1 (2)
Equate -2y+4 and 3y-1 since both are equal to x.
-2y+4=3y-1 -5y=-5 y=1.
Solve both equations for the variable y to find x.
(3)
(4)
Equate
and
since both are equal to y.
Multiplying both sides of the equation by 6, the LCD of the fractions.
(
) (
)
2. {
Solution:
Solve for y to find x.
4y=-x+2
(1)
-7y=-2x-7
(2)
Equate both values of y in equations (1) and (2).
Transitive Property of Equality
(
) (
) Multiply both sides by 28
Simplify
Solve for x to find y.
x=-4y+2 (3)
2x=7y-1 (4)
Equate both values of x in equations (3) and (4).
( ) (
. The solution is the ordered pair (
)
Solution by Elimination
This method of solving systems of linear equations depends on the addition property of equality, which
states that when two quantities are equal, adding the same number to each quantity results in equal
sums. This is used when the coefficients of one of the unknown quantities in the two equations are
equal in absolute value.
Illustrative Example
Solve the systems
1. {
Solution:
( ) ( )
If x=5, then is equal to .
The solution is the ordered pair (5, 3).
2. {
Solution:
If x=2, then
x+y=2
The solution is the ordered pair (2, 0).
V. System of Linear Equations with Fractions and Parentheses
Illustrative Examples
Solve the system.
1. {
( ) ( ) ()
( ) ()
Solution:
Simplify equation (1).
2x+2+y-3=4 2x+y=5 (3)
Simplify equation (2).
5x+5-y=0 (4)
Add equations (3) and (4).
Substitute 0 for x in equation (3).
()
The solution is the ordered pair (0, 5).
2. {
()
()
Solution:
Multiply both sides of equation (1) by 20, which is the LCD of the fractions.
4x+5y=240 (3)
Multiply both sides of equation (2) by 12, the LCD of the fractions.
4x-3y=48 (4)
Subtract equation (4) from equation (3).
Substitute 24 for y in equation (1).
The solution is the ordered pair (30, 24).
VI. Problems Involving Systems of Linear Equations
Many types of real life mathematical problems can be solved using a system of linear equations.
Illustrative Examples
1. Number Relations Problem
A stage theatre sold tickets for P500. Senior citizens received a discount of 20%, and paid only
P400. On the initial showing, the theatre sold 450 tickets and registered a total of P207, 500.
How many of each type of tickets were sold?
Solution:
2. Age Problem
Mon is three times as old as Luigi. Ten years from now, Mon will be two times as old as Luigi.
How old are they now?
Solution:
3. Uniform Motion Problem
Two cars travel toward each other from points 500 kilometers apart. The two cars meet in 4
hours. What is the average speed of each car if one car travels 15 kilometers per hour faster
than the other?
Solution:
4. Geometric Relations Problem
The sum of the measure of two angles is 180. Three times the measure of one angle is 24 less
than the measure of the other angle. What is the measure of each angle?
Solution:
5. Mixture Problem
Mon works at a pharmaceutical company as a chemist. To meet the clients demands, he was
told to prepare 100 liters of 25% alcohol solution. He has on hand a 15% alcohol solution and a
40% alcohol solution which she thought of mixing. How many liters of each solution will be
required to make the mixture?
Solution:
6. Investment Problem
Mr. Gili invested P20, 000, part of the amount at 15% annual interest rate and the remaining
amount at 7% annual interest. At the end of the year, he earned P1, 160. How much did he
invest at each rate?
Solution:
7. Work Problem
In a Girls Home, three girls work in the embroidery section. Crissa and Donna can finish a
tablecloth in 9 day, Crissa and Noime can finish the same work in 8 days, while Donna and
Noime can finish it in 12 days. Find how long it will take each girl working alone to finish the
work.
Solution:
VII. Linear Inequalities and their Graphs
An open sentence that makes use of the symbol = is called an equation. On the other hand, an open
sentence that makes use of any of these order relation symbols is called an inequality.
Here are some examples of inequalities expressed in algebraic symbols and in sentences.
1. x plus 8 is greater than 10.
2. 2x minus six is less than 20.
3. 4x is less than or equal to 16.
4. 5x minus one is greater than or equal to 24.
5. 12x plus x is not equal to 10.
Now, try to solve the solutions of the inequalities above.
Definitions:
1. Let a, b ,c .
a. if a>b, then a+c>b+c.
b. if a>b, then a-c>b-c.
c. if a>b, then ac>bc when c>0; ac<bc when c<0.
d. If a>b, then a/c > b/c when c>0; a/c < b/c when c<0.
2. Let A, B, C
a. If
b. If
c. If
Illustrative Examples
Graph the solution set of these inequalities on a number line.
1. 2.
Solution:
VIII. Problems Involving Linear Inequalities
There are word problems that can be translated into inequalities. Consider the following sentences with
their corresponding translations.
1. A number added to 3 times a number is less than 36.
2. The sum of two consecutive even integers is greater than 56.
3. Five times a number is at least 30.
4. Three times an integer is at most 7.
Certain situations in real life can often be represented by inequalities.
Illustrative Examples
Write an inequality to represent this situation and solve (if needed).
1. The survey shows that less than 18 students in a class own a computer unit.
2. A man travelled a number of kilometers by car, and 10 times as far by plane. He covered more
than 3000 km.
3. Ruby bought 2 blouses of the same kind and at the same price. She gave P200 and got a change
of less than P5.
4. Rona is 8 years older than Larry, and the sum of their ages is less than 24. Calculate their
possible ages.
IX. Graphs of Linear Inequalities and Systems of Linear Inequalities
4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
x
y y=2x-1
4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
x
y x=-2
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
x
y 2x+y=4
y=4
6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
5
4
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
x
y 2x+y=4
-x+y=2
Illustrative Examples
1. Graph the inequality
2. Graph the inequality .
3. Find the solutions of the system of inequalities by graphing.
a. {
b. {
Solution:
1. 2.
3. a. 3. b.
Evaluation
Answer the following questions. Write your complete and neat solution on an intermediate pad paper.
1. Determine the solution by graphing and classifying the system.
a. {
b. {
c. {
2. Solve each system of equations by substitution. Check your answer.
a. {
b. {
c. {
3. Solve the following systems of linear equations using the elimination method.
a. {
b. {
( )
( )
c. {
4. The sum of two numbers is 55. Four times the smaller is less than larger. Find the numbers.
5. Mons father is 7 times as old as he is. One year ago, his father was nine times as old as he is.
Find Mons present age.
6. The length of a rectangle is 5 more than twice its width. The perimeter is 70 m. what is the area?
7. Mon bought 7 pens and 9 pencils and paid a total of P106.75. Donna purchased 3 pens and 6
pencils and paid P57.00. Find the cost of a pen and a pencil.
8. Solve the following by graphing.
a. {
b. {
Assignment:
1. If the rectangle has a length that is 3 cm less than four times its width and its perimeter is 19
cm, what are the dimensions?
2. One painter can paint a room in 12 hour and another can paint the same room in 10 hour.
How long will it take to paint the room if they work together?
3. How many liters of a 7% acid solution and how many liters of a 12% acid solution should be
mixed by a chemist to obtain 6 liters of a 10% acid solution?
4. Find the solution set of the inequality 3x-8<7.
5. A student must receive an average score of at least 90 on five examinations to earn a grade
of A in a particular course. If the students score on the first four examinations are 93, 95,
79, and 88, what must be the score on the fifth examination be for the course grade to be
A?
6. The perimeter of a rectangle must not be greater than 30 cm and the length must be 8 cm.
What is the range of values for the width?
7. The sum of two integers is 51. The larger integer is 3 more than twice the smaller integer.
Find the integers.
If you faIl to prepare, then prepare to faIl.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsD'EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary Differential Equations with Linear AlgebraD'EverandElementary Differential Equations with Linear AlgebraPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 Simultaneous EquationsDocument27 pagesTopic 1 Simultaneous EquationsAnum TauqirPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1 Numerical Methods Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesCh1 Numerical Methods Lecture NotesAbdiqani Mohamed AdanPas encore d'évaluation
- W1-1 Linear SystemsDocument26 pagesW1-1 Linear SystemsEmanuel JheadPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra Lecture Notes ch1Document10 pagesLinear Algebra Lecture Notes ch1Abdiqani Mohamed AdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra Lecture Notes Ch3Document10 pagesLinear Algebra Lecture Notes Ch3Abdiqani Mohamed AdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Systems of Linear EquationsDocument24 pagesSystems of Linear EquationsEli LoneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 5-Systems of Linear EquationsDocument46 pagesTopic 5-Systems of Linear EquationsNqobile PhokanePas encore d'évaluation
- Antonchap1 LinsystemsDocument23 pagesAntonchap1 Linsystemsapi-2612829520% (1)
- Algeb Midterm-FinalDocument71 pagesAlgeb Midterm-FinalGreen zolarPas encore d'évaluation
- Systems of Linear Equations With Two VariablesDocument34 pagesSystems of Linear Equations With Two VariablesFatima KausarPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 9 Math 8Document8 pagesModule 9 Math 8Ja NeenPas encore d'évaluation
- LAGRAMA MATH 8 - Teachers - Made (WEEK 8)Document13 pagesLAGRAMA MATH 8 - Teachers - Made (WEEK 8)Leoni Francis Lagrama100% (1)
- Solve System of Equations Using GraphingDocument42 pagesSolve System of Equations Using Graphingapi-265481804Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Grade 9 Unit 3 Solving EqautionsDocument31 pagesMaths Grade 9 Unit 3 Solving EqautionsrabiraworkisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Systems of Linear EquationsDocument4 pagesSolving Systems of Linear EquationssamsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 24-Linear Algebra (Soft Copy) Set BDocument5 pagesMath 24-Linear Algebra (Soft Copy) Set BArgie ClaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 1 Module 7 Linear ProgrammingDocument21 pagesMath 1 Module 7 Linear ProgrammingAra MaePas encore d'évaluation
- C05Document96 pagesC05tri00Pas encore d'évaluation
- System of Linear Equations - Spring - 20-21Document35 pagesSystem of Linear Equations - Spring - 20-21maimona rahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Simultaneous Linear EquationsDocument8 pagesSolving Simultaneous Linear EquationsEbookcrazePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document84 pagesChapter 5Singh KaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Systems of Linear EquationsDocument19 pagesSolving Systems of Linear Equationsapi-340728730Pas encore d'évaluation
- Systems of Equations U6Document10 pagesSystems of Equations U6Will NerPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional Maths 0606 Notes - SummarisedDocument180 pagesAdditional Maths 0606 Notes - SummarisedObert MupomokiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 System of Linear EquationsDocument10 pages5 System of Linear EquationsAllen Kyle PrielaPas encore d'évaluation
- Math8 Q1 Module-7 MELC-15161718Document12 pagesMath8 Q1 Module-7 MELC-15161718Terence GabionPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 11 PowerpointDocument62 pagesCH 11 PowerpointRolando QuintanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Overview:: Property of Diocesan Schools of UrdanetaDocument18 pagesTopic: Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Overview:: Property of Diocesan Schools of UrdanetaDanica Feliciano Lorenzo100% (1)
- Day Assignment-Worth 10 Points, Due March 14: Can OneDocument19 pagesDay Assignment-Worth 10 Points, Due March 14: Can OneAlexander Kim WaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Ae 106 Modules Module 1: Linear Equations in One Variable Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesAe 106 Modules Module 1: Linear Equations in One Variable Learning OutcomesAcry LeaksPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A System of Equations?Document17 pagesWhat Is A System of Equations?Towhid RishadPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebraic Solution of Simultaneous Linear Equations PDFDocument11 pagesAlgebraic Solution of Simultaneous Linear Equations PDFAmeer AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Topical Revision Notes Additional Mathematics O Level PDFDocument186 pagesTopical Revision Notes Additional Mathematics O Level PDFShamvil Raza100% (5)
- L1 System-PrintDocument17 pagesL1 System-PrintkkkPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 FM101Document43 pagesWeek 1 - Lecture 1-3 FM101Labiba ZainPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Systems of Linear Equations and InequalitiesDocument20 pagesModule 2 Systems of Linear Equations and InequalitiesjeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 8 Lesson 11 System of Linear EquationsDocument44 pagesMath 8 Lesson 11 System of Linear EquationsAllah Rizza MarquesesPas encore d'évaluation
- Systems - of - EquationsDocument39 pagesSystems - of - EquationsAnonymous 5aPb088W100% (1)
- Equations 1. The Equation Formula: Mathg12 Euclid Stage 3 Class 1 NotesDocument8 pagesEquations 1. The Equation Formula: Mathg12 Euclid Stage 3 Class 1 NotesHappy DolphinPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Systems of Equations: M.Enban Madhu Shankar II M.SC MathsDocument23 pagesSolving Systems of Equations: M.Enban Madhu Shankar II M.SC MathsGANAPATHY.SPas encore d'évaluation
- System of Linear EquationsDocument14 pagesSystem of Linear EquationsKristel AndreaPas encore d'évaluation
- System of Linear EquationsDocument75 pagesSystem of Linear Equationsnoli_ediPas encore d'évaluation
- System Og Linear EquationDocument36 pagesSystem Og Linear EquationG19 Sauro Denise AngelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Iqra Nazir@ucp Edu PKDocument7 pagesIqra Nazir@ucp Edu PKAMIR ALIPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet X ADocument47 pagesFormula Sheet X Ayashikachandel15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Simultaneous Equations Using The Inverse Matrix: PrerequisitesDocument20 pagesSolving Simultaneous Equations Using The Inverse Matrix: PrerequisitesPrithviraj NetkePas encore d'évaluation
- Kuttler LinearAlgebra AFirstCourse 2021A (020 040)Document21 pagesKuttler LinearAlgebra AFirstCourse 2021A (020 040)Fernanda Ortega LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Equation Dinesh KumarDocument20 pagesLinear Equation Dinesh KumarVibhu GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- U7 Systems of EquationsDocument6 pagesU7 Systems of EquationsPatricia GamarroPas encore d'évaluation
- X - y 1 y X - 1 y 2x - 4Document4 pagesX - y 1 y X - 1 y 2x - 4Remalyn Quinay CasemPas encore d'évaluation
- 1system of Linear EquationsDocument64 pages1system of Linear EquationsJoelar OndaPas encore d'évaluation
- Systems of Linear EccuationsDocument14 pagesSystems of Linear EccuationsRaulPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1: Linear Systems With Two Variables and Their SolutionsDocument16 pages3.1: Linear Systems With Two Variables and Their SolutionsJea Mae G. BatiancilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2 - PPT 2 - AMG 211 (Equations and Inequalities)Document49 pagesWeek 2 - PPT 2 - AMG 211 (Equations and Inequalities)not funny didn't laughPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 8. Quarter 1. Week 7-8Document4 pagesMath 8. Quarter 1. Week 7-8Rose Angela Mislang UliganPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Variable SolutionDocument8 pagesThree Variable Solutionmech_lalit2k77856Pas encore d'évaluation
- PC Solve Linear SystemsDocument15 pagesPC Solve Linear SystemsHector R.100% (1)
- Lecture - 1 - System of Linear Equations - Matrix Algebra-Part1Document20 pagesLecture - 1 - System of Linear Equations - Matrix Algebra-Part1Ahmed SayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Principal Examiner Feedback Summer 2016: Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Statistics (2ST01) Higher Paper 1HDocument14 pagesPrincipal Examiner Feedback Summer 2016: Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Statistics (2ST01) Higher Paper 1HHeavenly SinPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Solutions To Enderton LogicDocument16 pagesSome Solutions To Enderton LogicJason100% (1)
- Ccie R&s Expanded-BlueprintDocument12 pagesCcie R&s Expanded-BlueprintAftab AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Angelina JolieDocument14 pagesAngelina Joliemaria joannah guanteroPas encore d'évaluation
- JOB Performer: Q .1: What Is Permit?Document5 pagesJOB Performer: Q .1: What Is Permit?Shahid BhattiPas encore d'évaluation
- d10 Sandra Darby FinalDocument3 pagesd10 Sandra Darby FinalFirstCitizen1773Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bomba Manual Hidraulica - P 19 LDocument2 pagesBomba Manual Hidraulica - P 19 LBruno PachecoPas encore d'évaluation
- IELTS Letter Writing TipsDocument7 pagesIELTS Letter Writing Tipsarif salmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Denial of LOI & LOP For Ayurveda Colleges Under 13A For AY-2021-22 As On 18.02.2022Document1 pageDenial of LOI & LOP For Ayurveda Colleges Under 13A For AY-2021-22 As On 18.02.2022Gbp GbpPas encore d'évaluation
- " Suratgarh Super Thermal Power Station": Submitted ToDocument58 pages" Suratgarh Super Thermal Power Station": Submitted ToSahuManishPas encore d'évaluation
- Plantas Con Madre Plants That Teach and PDFDocument15 pagesPlantas Con Madre Plants That Teach and PDFJetPas encore d'évaluation
- Portland Cement: Standard Specification ForDocument9 pagesPortland Cement: Standard Specification ForHishmat Ezz AlarabPas encore d'évaluation
- Medha Servo Drives Written Exam Pattern Given by KV Sai KIshore (BVRIT-2005-09-ECE)Document2 pagesMedha Servo Drives Written Exam Pattern Given by KV Sai KIshore (BVRIT-2005-09-ECE)Varaprasad KanugulaPas encore d'évaluation
- IJISRT23JUL645Document11 pagesIJISRT23JUL645International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhagwan Mahavir College of Architecture: Topic: Lacing, Batteneing, BracingDocument14 pagesBhagwan Mahavir College of Architecture: Topic: Lacing, Batteneing, BracingJai MenDparaPas encore d'évaluation
- NST 029Document123 pagesNST 029Riaz Ahmad BhattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Résumé Emily Martin FullDocument3 pagesRésumé Emily Martin FullEmily MartinPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce Project 1Document7 pagesCe Project 1emmaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS)Document13 pagesSAP Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS)SAFETY VOFPLPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture No. 11Document15 pagesLecture No. 11Sayeda JabbinPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics SS3 2ND Term SchemeDocument2 pagesGeneral Mathematics SS3 2ND Term Schemesam kaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ProposalDocument2 pagesProject Proposalqueen malik80% (5)
- 103-Article Text-514-1-10-20190329Document11 pages103-Article Text-514-1-10-20190329Elok KurniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualDocument53 pagesBlackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualSydney Adam SteelePas encore d'évaluation
- Defenders of The Empire v1.4Document13 pagesDefenders of The Empire v1.4Iker Antolín MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- BGP PDFDocument100 pagesBGP PDFJeya ChandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Historical Roots of The "Whitening" of BrazilDocument23 pagesHistorical Roots of The "Whitening" of BrazilFernandoMascarenhasPas encore d'évaluation
- Directorate of Technical Education, Maharashtra State, MumbaiDocument57 pagesDirectorate of Technical Education, Maharashtra State, MumbaiShubham DahatondePas encore d'évaluation
- Arte PoveraDocument13 pagesArte PoveraSohini MaitiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes - Introduction To Big DataDocument8 pagesLecture Notes - Introduction To Big Datasakshi kureley0% (1)