Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun 2011: Peraturan Pemarkahan
Transféré par
Ain ShahfandiDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun 2011: Peraturan Pemarkahan
Transféré par
Ain ShahfandiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SULIT 4551/3 BIOLOGY/AT Kertas 3 Okt./ Nov.
2011 1 JAM
4551/3
PEPERIKSAAN AKHIR TAHUN 2011
BIOLOGY
Tingkatan 4 Kertas 3
Satu jam tiga puluh minit
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
Peraturan pemarkahan ini mengandungi 15 halaman bercetak
@ 2011 Hak Cipta MPSM Pahang
MARK SCHEME FINAL EXAM 2011 Form 4 ( PAPER 3)
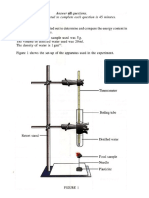
QUESTION 1 No Mark Scheme KB0603 Measuring Using Number 1(a) Able to record all the three final heights correctly Sample answer Percentage concentration of glucose / % 10 15 20 Final height of coloured liquid / cm 3 5 8 3 Score
KB0601 - Observation (b) (i) Able to state two different observations correctly P1 The concentration of glucose P2 - The final height of coloured liquid Sample answers : Horizontal observation: 1. The final height of coloured liquid is 3 cm for 10% of glucose solution. 2. At 15% of glucose solution , the final height of coloured liquid is 5 cm 3. At 20% of glucose solution , the final height of coloured liquid is 8 cm Vertical observation : 4. The final height of coloured liquid for 5% of glucose solution is higher/greater compared to 20% of glucose solution. 3
KB0604 - Making inference (b) (ii) Able to make two inferences correctly or any two Ps Criteria : P1 - Infer on concentration of glucose less/more glucose molecule for respiration P2 less/more carbon dioxide released P3 low/high activity of yeast Sample answers Horizontal observation 1. At 10% (low) concentration of glucose, less carbon dioxide is released means low activity of yeast.. 2. At 20% (high) concentration of glucose, more carbon dioxide is released means high activity of yeast. 3. 10% concentration of glucose contain less glucose molecule for respiration so less carbon dioxide is released Vertical observation 3. In lower concentration of glucose, less carbon dioxide is released means low activity of yeast compared to higher concentration of glucose //vice-versa Notes : The inferences should be correspond to the observations. inference 1observation 1 0 mark if not correspond - inference 2observation 2
KB0610-Controlling variables (c) Able to state all 3 variables and 3 methods to handle each variable. Sample answers 3
Variable Manipulated variable The concentration of nutrients/glucose Responding variable
Method to handle the variable Change the concentration of nutrients/glucose Use different concentration of nutrients/glucose Record the height of coloured
(Final) Height of coloured liquid
liquid by using a metre rule Measure and record the height of coloured liquid by using a metre rule Calculate the rate of yeast activity by using the formula = the height of coloured liquid time taken
The rate of yeast activity
Controlled variable 1.Volume of yeast suspension 2. Mass of yeast 3. Volume of glucose 4. pH 5. Light intensity 6. Temperature 7. Time taken
1. Use the same/ fix the 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. volume of 100cm3 of yeast suspension Use the same/ fix the mass of 4 g of yeast Fix the volume of glucose, 100cm3 Use the same/ fix pH at 5 Fix the light intensity Fix temperature at room temperature Fix the time taken for 10 minutes
All 6 ticks
KB0602 - Classifying (c) (ii) Able to match the apparatus and material used to obtain data for the three variables correctly Sample answers Variables Manipulated Responding Controlled Apparatus measuring cylinder metre rule electronic balance Material glucose solution coloured liquid yeast 3
KB0611-State hypothesis (d) Able to state hypothesis correctly following all criteria : P1 Manipulated variable concentration of glucose P2 Responding variable (Final) Height of coloured liquid / the rate of yeast activity H - relationship higher // inversely Sample answer 1. The higher/ lower the concentration of glucose(nutrient), the higher / greater / lower / the height of coloured liquid / the rate of yeast activity.
KB0606 Communicating data (e) (i) Able to construct a table correctly with the following aspects : 1. Able to state the 3 titles with units correctly -T 2. Able to record all data for concentration of glucose and changes in height of coloured liquid correctly. -D 3. Able to calculate and record the values for rate of yeast activity -C Sample answers Percentage concentration of glucose /% Changes in height of coloured liquid /cm Rate of the yeast activity / cmminutes-1 1- mark 1 - mark 1 - mark 3
10 15 20
2 4 7
0.2 0.4 0.7
KB0612 Relationship between space and time
(e) (ii)
Able to draw a graph of the rate of yeast activity against the concentration of glucose which satisfies the following criteria: Axes (P) both axes are labelled and uniform scales, manipulated variable on horizontal axis, correct units. Points(T)- all points correctly plotted Shape(B)- all points are connected smoothly
Sample answer Refer graph
Rate of the yeast activity / cm/minutes
10
15
20 0
Concentration of glucose(%)
KB 0608 Interpreting data (f) Able to explain the relationship between the rate of yeast activity and the concentration of glucose correctly based on the following criteria: R1- state the relationship between the rate of yeast activity and the concentration of glucose R2- state the activity of anaerobic respiration is increase/decrease R3- state the carbon dioxide released is increase/decrease Sample answer 1. When the concentration of glucose increases/decreases, the rate of yeast activity increases/decreases 2. Because of the activity of anaerobic respiration increase /decreases 3. So the released of carbon dioxide is increased/ decreased 3
KB0609 Defining by operation (g) Able to state the definition of anaerobic respiration operationally, complete and correct based on the following criteria: D1- yeast respire using glucose D2- the released of gas causes the pressure in the manometer to rise / increase the height of coloured liquid in manometer D3- concentration of nutrien affects the activity of yeast Sample answer Anaerobic respiration is yeast respire using glucose(K1) and release gas (carbon dioxide) that causes the pressure in the manometer tube to rise/ increase the height of coloured liquid in manometer (K2) and the rate of yeast activity is affected by the concentration of glucose (K3) 3
KB0605 - Predicting (h) Able to predict correctly and explain the prediction based on the following criteria: K1 manometer R K2 the height of coloured liquid is declined/ nil / 0 / below the initial height K3- the activity of yeast is declined / lowered in an alkaline medium //optimum / higher in an acidic medium Sample answer The height of coloured liquid in manometer R is declined / nil / 0 / below the initial height .This is because the activity of yeast is declined in an alkaline medium // optimum / higher in an acidic medium 3
QUESTION 2
PROBLEM STATEMENT No. Mark Scheme Score
2(i) KB061201 Able to state a problem statement relating the manipulated variable with the responding variable correctly P1 : (Type of) food samples / peanut butter and pineapple jam. P2 : energy content/value in food samples H : question form and question mark(?) Sample answer 1. Which types of food samples, the peanut butter or pineapple, has a higher energy value/content? 2. Do different types of food samples contain similar energy value / content? 3. Do peanut butter / pineapple jam has a higher energy value/content compared to pineapple jam / peanut butter?
HYPOTHESIS No. Mark Scheme Score
2 (ii) Able to state a hypothesis relating the manipulated variable to the KB061202 responding variable correctly P1 : type of food samples / peanut butter and pineapple jam P2 : energy content/value (in food samples) H : relationship Sample answer 1. Peanut butter have a higher energy value/content than pineapple jam. 2. Pineapple jam has lower energy value/content than peanut butter. 2. Different type of food samples contain different energy value /content.
VARIABLES No. 2 (iii) KB061203 Mark Scheme Able to state all three variables correctly Sample answer Manipulated variable (Type of) food samples / peanut butter and pineapple jam Responding variable The energy value of food samples Constant variable Volume of distilled water / the mass of food / Initial temperature of distilled water 3 Score
LIST OF APPARATUS AND MATERIALS No. 2(iv) KB061205 Mark Scheme Able to list all the important apparatus and materials correctly *compulsory apparatus and materials Sample answer Apparatus : boiling tubes, thermometer, retort stand, pin, measuring cylinder, Bunsen burner and electronic balance. Materials : *distilled water, *peanut butter, *pineapple jam, plasticine and cotton wool. 6-7 apparatus + 5 materials 3 Score
10
PROCEDURE
No. 2 (v) KB061204
Mark Scheme Able to describe the steps of experiment correctly based on the following aspects: K1 : Preparation of materials and apparatus (any 3) K2 : Operating the constant variable (any 1) K3 : Operating the responding variable (any 1) K4 : Operating the manipulated variable (any 1) K5 : Steps to increase reliability of results accurately (any 1) Sample answers 1. Weight and record the mass of peanut butter. 2. Fill a boiling tube with 20ml of distilled water. 3. Clamp the boiling tube to the retort stand in an upright position as shown in the diagram. 4. Record the initial temperature of the distilled water in the boiling tube. 5. Fix the peanut butter at the end of the pin. 6. Ignite the peanut butter by holding it in the flame of a Bunsen burner. Then immediately place it beneath the boiling tube to heat the water. 7. Stir the water gently with the thermometer. 8. Record the final temperature of the distilled water in the boiling tube. 9. Repeat steps 1-8 using pineapple jam to replace the peanut butter. 10. Calculate the energy value of the food samples by using the formula : Energy value = 4.2 (Jg-1 0C-1 ) x mass of water (g) x increase in temperature (0C) (kJg-1 ) Mass of food sample (g) x 1000 11. Record/tabulate all the results in the table. *K1 (any 3) 1.Weight 2. Fill the boiling tube 3. Clamp 4. Fix at the end of the pin 5. Ignite
Score
*K2 (any 1)
11
1. Fix the volume of distilled water 2. Fix the mass of food samples 3. Fix the initial temperature of water *K3 (any 1) 1. Record the initial and the final temperature of water 2. Calculate the energy value of the food samples by using the formula : Energy value = 4.2 (Jg-1 0C-1 ) x mass of water (g) x increase in temperature (0C) (kJg-1 ) Mass of food sample (g) x 1000 *K4 (any 1) 1. Repeat the experiment with another food samples 2. Use two different types of food samples. *K5 (any 1) 1. Stir the water gently with the thermometer. 2. Repeat experiment to get average reading. 3. Use an insulator shield to reduce heat loss to the surroundings. 4. To ensure that the food is oxidized completely, make sure the food is burnt completely. No. 2 (vi) Mark Scheme Able to present all the data with units correctly i. Colum 1 shows type of food1 mark ii. Colum 2 shows change in temperature----1 mark iii. Sample answer Types of food samples * Peanut butter * Mass (g) Initial temperature (oC) Final temperature (oC) Change in temperature (oC) * Energy value (J/g) / (kJ/g) * Pineapple jam* Score 2
12
Marks :
3 X 5 = 15 marks 2x1 TOTAL = 2 marks = 17 marks
END OF MARKING SCHEME PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN TAMAT
13
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Trial Kedah Biology SPM 2013 SKEMADocument11 pagesTrial Kedah Biology SPM 2013 SKEMACikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Ans Bio F4Document9 pagesAns Bio F4navaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Paper 3 Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesBiology Paper 3 Marking SchemeDRprof Rizzuan Amir100% (1)
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 3 PatDocument10 pagesSkema Jawapan Kertas 3 PatSitinorsyahidah JantanPas encore d'évaluation
- Teknik3 BioDocument77 pagesTeknik3 Bioachikgai100% (1)
- Biology Form 4 Paper 3 Quiz & AnsDocument18 pagesBiology Form 4 Paper 3 Quiz & Anskhangsiean8967% (3)
- 6 Nutrition P3aDocument9 pages6 Nutrition P3aSharifah NurainPas encore d'évaluation
- Jawapan Buku Paper 3 Group 3 and 4Document19 pagesJawapan Buku Paper 3 Group 3 and 4Azam NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- PAPER 3 BiologyDocument11 pagesPAPER 3 BiologyNg Wan LinPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO A 05A COMP Cell RespirationDocument5 pagesBIO A 05A COMP Cell RespirationVishnu SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity: ExperimentDocument12 pagesEnzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity: ExperimentsannsannPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Temperature On RespirationDocument19 pagesEffect of Temperature On RespirationLiza KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K3 SkemaDocument11 pagesTrial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K3 SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (1)
- Sugar - Fermentation Yeast LabDocument5 pagesSugar - Fermentation Yeast LabVictoria WarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Exothermic Endothermic Reaction LabDocument14 pagesExothermic Endothermic Reaction Labliza1207Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetics of Ethanol Fermentation With High Biomass Concentration Considering The Effect of TemperatureDocument13 pagesKinetics of Ethanol Fermentation With High Biomass Concentration Considering The Effect of TemperatureJhon Fernando NiñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Unit Operation 1 - Laboratory ManualDocument17 pagesFood Unit Operation 1 - Laboratory ManualVy NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Operating Condition On The Kinetic of Color Change of Concentrated PineappleDocument7 pagesEffect of Operating Condition On The Kinetic of Color Change of Concentrated Pineapplenam nguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Suggested Answer Question 1 (A) (KB0603-measuring Using Number) CriteriaDocument12 pagesSuggested Answer Question 1 (A) (KB0603-measuring Using Number) CriteriascarleticPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3 Amali Energy ValueDocument20 pagesPaper 3 Amali Energy ValueNathan Leezhao (Snatan Si Zeelhao)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sugar Fermentation in YeastDocument4 pagesSugar Fermentation in YeastVictoria WarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Method - Calculations ChemistryDocument3 pagesMethod - Calculations ChemistrygamebozPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Biology Internal Assessment 2Document12 pagesIB Biology Internal Assessment 2beslisevval89% (9)
- Cape Unit 1 Lab ManualDocument89 pagesCape Unit 1 Lab ManualAnthony HoseinPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigation 1 FactorsaffectingenzymeactivityDocument6 pagesInvestigation 1 FactorsaffectingenzymeactivityDrewPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences: Research Article Analytical ChemistryDocument7 pagesInternational Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences: Research Article Analytical ChemistryMie YaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 4 Paper 3 Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesBiology Form 4 Paper 3 Marking SchemeLAUEELANGPas encore d'évaluation
- Biologi Skema Set 11 P3Document12 pagesBiologi Skema Set 11 P3Aura Maya HasrinaHashimPas encore d'évaluation
- PAG 10.3 Learner SheetDocument3 pagesPAG 10.3 Learner SheetJoshna JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Science (Chilli Plant Experiment)Document10 pagesAssignment Science (Chilli Plant Experiment)Thomas Kai0% (1)
- Sample Peka Sains SPMDocument15 pagesSample Peka Sains SPMNor Azizah100% (1)
- Cpac 12Document3 pagesCpac 12mohammed kibriahPas encore d'évaluation
- ChE 124 Experiment 6 Results and DiscussionDocument6 pagesChE 124 Experiment 6 Results and DiscussionJacey OngPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 OsmosisDocument9 pages3.1 OsmosisQuan YingPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K3 SkemaDocument8 pagesTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K3 SkemaCikgu FaizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3 Instruction: Answer All QuestionsDocument10 pagesPaper 3 Instruction: Answer All QuestionsNoor Hafezah Mohd MokhtiarPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Biology 2010 Course WorkDocument11 pagesGCSE Biology 2010 Course WorkDermot McGuckinPas encore d'évaluation
- Spectrapak 315Document4 pagesSpectrapak 315amirouche15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essay p3 Isotonic-PotatoDocument2 pagesEssay p3 Isotonic-PotatoKhusyairy Daeng SailendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Paper 6 TipsDocument7 pagesBiology Paper 6 TipsJayakumar SankaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Kertas 3Document13 pagesSkema Kertas 3rhimalinyPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Penetration and Bacteriological Properties of FoodsDocument6 pagesHeat Penetration and Bacteriological Properties of FoodsPenny HuynhPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme Bio Paper 3 2011Document10 pagesScheme Bio Paper 3 2011Ismaliza IshakPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Enthalpy CalcDocument5 pages13 Enthalpy CalcAhmad HussienPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Answer Biology SPM PapersDocument8 pagesHow To Answer Biology SPM PapersCikgu A. KamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 2 Bubble Cap DistillationDocument7 pagesExp 2 Bubble Cap DistillationFaris HamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigating Gas Chromatography: Figure 1 Sample Gas ChromatogramDocument9 pagesInvestigating Gas Chromatography: Figure 1 Sample Gas ChromatogramPanduka EkanayakePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Spa Skill 3 GuideDocument3 pagesBiology Spa Skill 3 GuideClara SooPas encore d'évaluation
- Sugar Fermentation in Yeast 23Document7 pagesSugar Fermentation in Yeast 23Victoria WarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial SPM 2012 - Paper 3 - JPNTRG - Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesTrial SPM 2012 - Paper 3 - JPNTRG - Marking SchemeZaiton RoslanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry PAG 10.3 Learner v2.1Document3 pagesChemistry PAG 10.3 Learner v2.1Umair Choudhry0% (1)
- Takuya Yoshida, Satoru Yanachi and Yukihiko Matsumura Hiroshima University, 1-4-1 Kagamiyama, Higashi-Hiroshimashi, Hiroshima 739-8527, JapanDocument6 pagesTakuya Yoshida, Satoru Yanachi and Yukihiko Matsumura Hiroshima University, 1-4-1 Kagamiyama, Higashi-Hiroshimashi, Hiroshima 739-8527, JapanDébora NobregaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 8.11 (Practical Textbook Page 119)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 8.11 (Practical Textbook Page 119)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kertas 3 Pep Pertengahan Tahun Ting 5 Terengganu 2013Document9 pagesKertas 3 Pep Pertengahan Tahun Ting 5 Terengganu 2013vonashPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of Proportion of Different Cut-Fruits On Respiration Rate of Fruit SaladDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Proportion of Different Cut-Fruits On Respiration Rate of Fruit Saladjasmin Zotelo villanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vce Chemistry Unit 3 Sac 2 Equilibrium Experimental Report: InstructionsDocument5 pagesVce Chemistry Unit 3 Sac 2 Equilibrium Experimental Report: InstructionsJefferyPas encore d'évaluation
- Beano LabDocument12 pagesBeano Labapi-284496286Pas encore d'évaluation
- Control of Salmonella and Other Bacterial Pathogens in Low-Moisture FoodsD'EverandControl of Salmonella and Other Bacterial Pathogens in Low-Moisture FoodsRichard PodolakPas encore d'évaluation
- Alpha Beta Gamma Nuclear Decay Activity SheetDocument10 pagesAlpha Beta Gamma Nuclear Decay Activity SheetArlo RivasPas encore d'évaluation
- NFPA 329 - 2005 Handling Releases of Flammable and Combustible LiquidsDocument49 pagesNFPA 329 - 2005 Handling Releases of Flammable and Combustible LiquidsArnaldo J Brito Ñ100% (1)
- Indian Standard: Methods of Test For CablesDocument3 pagesIndian Standard: Methods of Test For CablesBilal AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- 34 Qualitative Analysis Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument11 pages34 Qualitative Analysis Formula Sheets QuizrrSwapnil SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ssab Emea Ab, Se-781 84 Borlänge, Sweden: Carbon Equivalent Etc C93-C99Document1 pageSsab Emea Ab, Se-781 84 Borlänge, Sweden: Carbon Equivalent Etc C93-C99Agustin FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Exam Questions: Unit 4Document2 pagesPractice Exam Questions: Unit 4alamphyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Powerpoint Honors - Student VersionDocument131 pagesChapter 8 Powerpoint Honors - Student VersionMario PachecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Absroption Unit in Dilute Nitric Acid ProductionDocument8 pagesAbsroption Unit in Dilute Nitric Acid ProductionFateh HakeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Silva2019 Article OptimizationOfLycopeneExtractiDocument11 pagesSilva2019 Article OptimizationOfLycopeneExtractilunosicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Mechanical Behaviour of Coconut Shell Reinforced Polymer Matrix CompositeDocument6 pagesStudy of Mechanical Behaviour of Coconut Shell Reinforced Polymer Matrix CompositeRing MasterPas encore d'évaluation
- The1+carbo+ach221+21415, Nokey 1Document18 pagesThe1+carbo+ach221+21415, Nokey 1Shailah Leilene Arce BrionesPas encore d'évaluation
- Getting Started in Steady StateDocument24 pagesGetting Started in Steady StateamitPas encore d'évaluation
- Chelatin-Sa: Sarex ChemicalsDocument2 pagesChelatin-Sa: Sarex Chemicalssivanesan seeranganPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test-03 For AIATS-05Document16 pagesPractice Test-03 For AIATS-05Urja Moon0% (1)
- DLL Science 8 Q3Document3 pagesDLL Science 8 Q3IAN BERNARDOPas encore d'évaluation
- DS4B - (1988) Physical Constants of Hydrocarbon and Non-Hydrocarbon CompoundsDocument216 pagesDS4B - (1988) Physical Constants of Hydrocarbon and Non-Hydrocarbon CompoundsJacques Strappe0% (1)
- Oxygen Scavengers For Food Packaging ApplicationsDocument9 pagesOxygen Scavengers For Food Packaging ApplicationsbiswasblrPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 6 Combined Gas Law 4th EdDocument11 pages11 6 Combined Gas Law 4th Edapi-267245178Pas encore d'évaluation
- A-En MoviPol-5 IMDocument58 pagesA-En MoviPol-5 IMFabien CazesPas encore d'évaluation
- nbr002 1612 PDFDocument32 pagesnbr002 1612 PDFRanjith RPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Polymer Chemistry?Document8 pagesWhat Is Polymer Chemistry?ハジャ 咲良Pas encore d'évaluation
- Technological Advancements in The Drying of Fruits and Vegetables: A ReviewDocument14 pagesTechnological Advancements in The Drying of Fruits and Vegetables: A ReviewMaria MadanPas encore d'évaluation
- Supplement 10 TS Calibration ECSPP ECBSDocument16 pagesSupplement 10 TS Calibration ECSPP ECBSKingston Rivington100% (1)
- Junction BreakdownDocument41 pagesJunction BreakdownKamal Jeet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Ti Corrosion in AlkalineDocument10 pagesTi Corrosion in AlkalineGeetha ThiruvengadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Data Sheet Hovadur CCNB Eh: Agreed Properties at 20 °C (Condition: Hardened, Solution Heat Treated Respectively)Document4 pagesMaterial Data Sheet Hovadur CCNB Eh: Agreed Properties at 20 °C (Condition: Hardened, Solution Heat Treated Respectively)AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Identification of The Best Model and Parameters For T-Y-X Equilibrium Data of Ethanol-Water MixtureDocument7 pagesIdentification of The Best Model and Parameters For T-Y-X Equilibrium Data of Ethanol-Water MixtureMeghana SPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrology - Final Examination (1S, 2023-2024)Document2 pagesHydrology - Final Examination (1S, 2023-2024)fathima camangianPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparatory Problems SolutionsDocument38 pagesPreparatory Problems SolutionsĐạt Trần VănPas encore d'évaluation
- Senscient ELDS - Hydrogen Sulphide - Data Sheet Rev6Document2 pagesSenscient ELDS - Hydrogen Sulphide - Data Sheet Rev6Vincent GabrielPas encore d'évaluation