Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lab
Transféré par
Zuru Raya EthioDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lab
Transféré par
Zuru Raya EthioDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Exercise 07
Lab Manual
Data Communications
EXPERIMENT # 7 PSK/QPSK Measurements and Adjustments
Objective
To understand the principle of phase-shift keying (PSK) modulation. To implement the PSK/QPSK modulator.
Theory
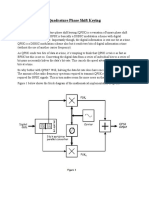
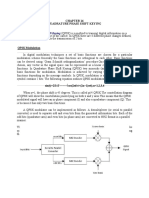
Continuing the theory of PSK from previous lab, consider the following block diagram of PSK/QPSK modulator.
Figure 7-1: Block Diagram of PSK/QPSK Modulator
The carrier signal generator provides a carrier signal (sinusoidal wave) to the phase switching network and a square wave to the timing circuit. Phase switching network provides four outputs (0, 90, 180, 270) to the inputs of data selector. The output X of data selector is determined by the select inputs A and B. There are four following cases; 1) If BA = 00 (Q1 = Q0 = low), X = Xo, the signal with phase shift 0. 2) If BA = 11 (Q1 = Q0 = high), X = X3, the signal with phase shift 180. 3) If BA = 01 (Q1 = low, Q0 = high), X = X1, the signal with phase shift 90. 4) If BA = 10 (Q1 = high, Q0= low), X = Xo, the signal with phase shift 270.
Engr. Danish Afzal
-1-
Hamdard University-HIIT
Exercise 07
Lab Manual
Data Communications
The timing circuit receives the square wave (fc) from the carrier signal generator output and produces two outputs: fc to the load control input and signal 2fc (twice the carrier frequency) to the clock input of control register as well as the sync cycle generator. These two signals of fc and 2fc and the data rate (measured in bps) of input digital information are used to determine whether the modulator operates binary PSK or QPSK mode. There are three possibilities.
1) Bit Rate = fc and no sync cycle generated. In this case the data rate is equal to the carrier frequency fc and the clock frequency is twice the carrier frequency 2fc. One bit of digital data stream is loaded into the control register two times the outputs Q0-Q1 of control register are therefore the same, 00 or 11. The output X of data selector is either X0 or X3. this system operates in PSK mode. 2) Bit Rate = 2fc and no sync cycle generated. In this case, data rate and clock frequency are equal to twice the carrier frequency, 2fc. Two bits of data stream are loaded to the control register each carrier cycle. The control register outputs Q0-Q1 may be 00, 01, 11 or 10. This system therefore operates in QPSK mode. 3) Bit Rate = fc or 2fc and sync cycle generated. If a sync cycle is required, sync cycle control circuit will produce a control signal to control the output data of control shift register, and then a sync cycle signal will present at modulator output. The format of sync cycle shown in the figure is used in our experiments. The sync cycle signal is different from the PSK/QPSK modulated signals. The sync cycle signal can be identified by the sync cycle detector in PSK/QPSK demodulator and can be viewed as an identification word.
Figure 7-2: Synchronization Cycle Engr. Danish Afzal -2Hamdard University-HIIT
Exercise 07
Lab Manual
Data Communications
Practical Circuit Description
Waveform generator chip ICL8038 serves as the carrier signal generator that produces sinusoidal and square waves. The frequency of the carrier generator is determined by the external timing resistors R2-R3 and capacitor C2 is 7.1 KHz approximately. The generated sinusoidal signal is connected to the inputs of phase switching network consisting of two non-inverting amplifiers (U2a and U2d) and two inverting amplifiers (U2b and U2c). This phase shift network provides four phase shifts 0, 90, 180 and 270 to data inputs X0, X1, X2 and X3 of data selector is determined by the state of select inputs A and B. once the output is selected the PSK/QPSK modulated signal is amplified by the non-inverting amplifier U8. The potentiometer VR5 is used to control the output amplitude of PSK/QPSK modulated signal.
The square wave present at U1 pin 9 is connected to the input of timing circuit to generate a signal with the frequency 2fc twice the carrier frequency by the frequency doubling network constructed by U4b, U4c, and U5a and associated components R21, R22, C6 and C7. The 2fc signal is connected to the clock inputs of the shift register U7 and the 4-bit binary counter U6a. The output Q0 is connected to inverters U4F and U4d and U7 pin1 (load input). The frequency of this signal is fc. The modulating signal (digital) is connected to DATA input (pin 2) of the control shift register U7. The outputs Q0-Q1 of the shift register are XORed with the signal on TP6, and then connected to the select inputs A and B of data selector.
Binary counters U6a and U6b are used to determine when to generate a sync cycle. The clock frequency of the binary counter U6a is connected to clock input of U6b, so that the clock frequency is fc/2 and the frequency of U6b Q3 is fc/32. The sync cycle is generated only in onehalf duration of Q3 output signal or fc/16.
Engr. Danish Afzal
-3-
Hamdard University-HIIT
Exercise 07
Lab Manual
Data Communications
Figure 7-3: KL94006 Module
Engr. Danish Afzal
-4-
Hamdard University-HIIT
Exercise 07
Lab Manual
Data Communications
Equipment
Module KL-92001 Module KL-94006 Oscilloscope
Procedure
A. 2fc Measurement (KL94006) 1) Connect a 500 KHz, TTL-level digital signal to DIGITAL DATA IN. 2) Connect scope CH1 IN to TP 12 and CH2 IN to TP 13. Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies in Table 7-1. Compare the phase difference between two waveforms. 3) Connect scope CH1 IN to TP15. Measure and record the waveform and frequency in Table 7-1. the frequency should be twice the carrier frequency, 2fc. B. Sync Cycle Measurement 4) Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies on the test points listed in table 7-2. C. Control Shift Register Measurement 5) Connect scope CH1 IN to TP 10 and CH2 IN to TP11. Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies in Table 7-3. 6) Repeat step 5 for digital signal frequencies 100 Hz and 1 KHz to Digital DATA IN. 7) Recover the digital signal frequency to 500 Hz D. PSK/QPSK modulated Signal Measurement 8) Connect scope CH1 IN to PSK/QPSK OUT. Measure and record the waveform with the various TIME/DIV settings in Table 7-4.
Engr. Danish Afzal
-5-
Hamdard University-HIIT
Exercise 07
Lab Manual
Data Communications
Results
2fc Measurement (KL-94006) Test Point Waveform
TP12 (CH1)
TP 13 (CH2)
TP15
Table 7-1
Engr. Danish Afzal
-6-
Hamdard University-HIIT
Exercise 07
Lab Manual
Data Communications
Sync Cycle Measurement Test Point Waveform and Frequency
TP15
TP 16
TP8
TP 17
Table 7-2
Engr. Danish Afzal
-7-
Hamdard University-HIIT
Exercise 07
Lab Manual
Data Communications
Shift Register Measurement Test Point Waveform
500 Hz
100 Hz
1 KHz
Table 7-3
Engr. Danish Afzal
-8-
Hamdard University-HIIT
Exercise 07
Lab Manual PSK/QPSK modulated signal measurement
Data Communications
Scope TIME/DIV PSK / QPSK OUT
2.5ms
1ms
500s
250s
100s
Table 7-4
Engr. Danish Afzal
-9-
Hamdard University-HIIT
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsDocument28 pages15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsSanjeev KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- QPSKDocument11 pagesQPSKCesar MachadoPas encore d'évaluation
- DCT-6000-09 QPSK - Manual Mod Sin Sol PDFDocument25 pagesDCT-6000-09 QPSK - Manual Mod Sin Sol PDFArturo TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Conditioning & Carrier Modulation Transmitter & Data Reconditioning & Carrier Demodulation ReceiverDocument49 pagesData Conditioning & Carrier Modulation Transmitter & Data Reconditioning & Carrier Demodulation ReceiverCauVong JustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4 - Communication Systems. AmplitudeDocument9 pagesLab 4 - Communication Systems. AmplitudeDiego De Castro FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 PSK DemodDocument18 pagesChapter 16 PSK DemodberkahPas encore d'évaluation
- Generation and Detection of DPSKDocument3 pagesGeneration and Detection of DPSKAmy OliverPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 04 Experiment Name-QPSK Modulation & Demodulation Aim Equipments NeededDocument10 pagesExperiment No. 04 Experiment Name-QPSK Modulation & Demodulation Aim Equipments NeededmuskanPas encore d'évaluation
- LAb 4 PSKDocument9 pagesLAb 4 PSKJoseph MagonduPas encore d'évaluation
- Generation and Detection of DPSKDocument3 pagesGeneration and Detection of DPSKAmy OliverPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 423 Report 5Document9 pagesECE 423 Report 5Ryan LanuzaPas encore d'évaluation
- DC - Experiment - No. 5Document8 pagesDC - Experiment - No. 5amol maliPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Phase Shift Keying Modulation and DemodulationDocument9 pagesDifferential Phase Shift Keying Modulation and DemodulationananthaprathimaPas encore d'évaluation
- PSKDocument4 pagesPSKTushar PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- EXPT 04 - 4-PSK Modulation & DemodulationDocument6 pagesEXPT 04 - 4-PSK Modulation & Demodulationanika tabassumPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase Shift Keying: Exp - No:01Document74 pagesPhase Shift Keying: Exp - No:01Sumit PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Lab ManualDocument43 pagesDC Lab ManualSowmya KharviPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manual Autonomous Pvp-12Document57 pagesDepartment of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manual Autonomous Pvp-12Ravi JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- LAb 1Document8 pagesLAb 1nazmyPas encore d'évaluation
- WTM Microwave DigitalDocument16 pagesWTM Microwave DigitalrrohuuPas encore d'évaluation
- QPSKDocument12 pagesQPSKATUL SACHAN100% (1)
- Experiment No. 03 Experiment Name-PSK Modulation AIM Equipments RequiredDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 03 Experiment Name-PSK Modulation AIM Equipments RequiredmuskanPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 3Document7 pagesExp 3Tejaswini APas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Electronic and Information Engineering Communication Laboratory Phase Shift Keying (PSK) & Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)Document11 pagesDepartment of Electronic and Information Engineering Communication Laboratory Phase Shift Keying (PSK) & Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)AnupamJosePas encore d'évaluation
- Research Article: A Four Quadrature Signals' Generator With Precise Phase AdjustmentDocument7 pagesResearch Article: A Four Quadrature Signals' Generator With Precise Phase Adjustmentaamir.nedian4139Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Ask, PSK, FSKDocument15 pages2 Ask, PSK, FSKI AM A PROGRAMMERPas encore d'évaluation
- PSK Qam2 PDFDocument43 pagesPSK Qam2 PDFKim Kenneth UgayPas encore d'évaluation
- Bapatla Engineering College Digital Communications Lab EC-451Document30 pagesBapatla Engineering College Digital Communications Lab EC-451nithyamnvPas encore d'évaluation
- Submitted By:: Muhammad Maab Nawaz FA21-EEE-021Document7 pagesSubmitted By:: Muhammad Maab Nawaz FA21-EEE-021M4MAAB GAMINGPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Communications Lab: List of ExperimentsDocument50 pagesDigital Communications Lab: List of ExperimentsNeel SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadrature Phase Shift Keying - 1Document15 pagesQuadrature Phase Shift Keying - 1RANA RAMEEZPas encore d'évaluation
- Wicomm T QPSKDocument13 pagesWicomm T QPSKvithyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kulliyyah of EngineeringDocument11 pagesKulliyyah of EngineeringHitesh MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- DC - Experiment - No. 4Document9 pagesDC - Experiment - No. 4amol maliPas encore d'évaluation
- A Differential QPSK Modem Using The TMS320C6711 DSKDocument5 pagesA Differential QPSK Modem Using The TMS320C6711 DSKSamia AkhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Manual Final PDFDocument25 pagesDC Manual Final PDFAsma FirdousePas encore d'évaluation
- PSK Modulator: Experiment #Document6 pagesPSK Modulator: Experiment #Kumar Adithya Myla0% (1)
- Digital Modulation Techniques For Mobile and Personal Communication SystemsDocument8 pagesDigital Modulation Techniques For Mobile and Personal Communication Systemsdava2007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Phase Shift KeyingDocument7 pagesDifferential Phase Shift Keyingtaherakhans100% (1)
- A New Miniaturized Electronic Pill (Epille®) For Mass Medical Application With Bi-Directional Communication SystemDocument4 pagesA New Miniaturized Electronic Pill (Epille®) For Mass Medical Application With Bi-Directional Communication SystemMarka ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 1612Document3 pagesCH 1612Kylle Bryan FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of Digital QPSK Modulator by Using VHDL / MatlabDocument5 pagesImplementation of Digital QPSK Modulator by Using VHDL / Matlabblesson123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital IQ DemodulatorDocument3 pagesDigital IQ DemodulatoraboashoorPas encore d'évaluation
- DCLabDocument31 pagesDCLabani rohiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Frequency Shift Keying FSKDocument10 pagesFrequency Shift Keying FSKapi-19937584Pas encore d'évaluation
- New DC Lab ManualDocument53 pagesNew DC Lab Manualsriram128Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Modulation PDFDocument41 pagesDigital Modulation PDFPabitraMandalPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul ASK Mod - DemodDocument45 pagesModul ASK Mod - DemodfarrasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3: 16QAM Modulator/Demodulator: (Frant Oana, 1232E)Document12 pagesLab 3: 16QAM Modulator/Demodulator: (Frant Oana, 1232E)s_g_andreiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ManualDocument56 pagesLab ManualNarendra ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bangladesh University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument14 pagesBangladesh University of Engineering & TechnologyShouvik MusavvirPas encore d'évaluation
- ASK DemodulatorDocument24 pagesASK DemodulatorKrista JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Telecom - Exp - 10 - QAM, MSK, & GMSKDocument15 pagesTelecom - Exp - 10 - QAM, MSK, & GMSKrakibPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Digital Modulation and Forward Error CorrectionDocument74 pagesPresentation On Digital Modulation and Forward Error CorrectionJitendra ChuughPas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsD'EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei U2000 CommandsDocument6 596 pagesHuawei U2000 CommandsWalid ChakrounPas encore d'évaluation
- Philips MC 235 B Service ManualDocument36 pagesPhilips MC 235 B Service ManualTrabelssi RamziPas encore d'évaluation
- Moshells BasicsDocument39 pagesMoshells BasicsWilliam Cj LyngdohPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution QuizDocument3 pagesSolution Quizdjun033Pas encore d'évaluation
- MHA 850 MHZ DatasheetDocument3 pagesMHA 850 MHZ DatasheetDavid TesztPas encore d'évaluation
- Ashdown Pedal ManualDocument2 pagesAshdown Pedal ManualAndré LückmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment1 SP MultimediaDocument2 pagesAssignment1 SP MultimediaRendy Christian SiahaanPas encore d'évaluation
- R1-AD Datasheet v1.1 (Eng)Document4 pagesR1-AD Datasheet v1.1 (Eng)forseil100% (1)
- RSRP Vs RSRQ Vs Sinr PDFDocument13 pagesRSRP Vs RSRQ Vs Sinr PDFUsman SiddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- AIR-AP1832I-E-K9 DatasheetDocument3 pagesAIR-AP1832I-E-K9 DatasheetC KPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Radio Optimization ZTEDocument64 pagesGSM Radio Optimization ZTESyed Muhammad Kamran50% (2)
- PDD Functionnal OverviewDocument6 pagesPDD Functionnal OverviewtarsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Plan Company Law 7th Sem B. A. LL.B-1Document5 pagesLecture Plan Company Law 7th Sem B. A. LL.B-1Kshamaa KshamaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metoda Proracuna MTU SignalaDocument28 pagesMetoda Proracuna MTU SignalaGoran LevačićPas encore d'évaluation
- Service Manual: iF210S iF211S iF221SDocument37 pagesService Manual: iF210S iF211S iF221SMarcelo LilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Telewave Power MonitoringDocument9 pagesTelewave Power MonitoringCarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Adc Dac and Sensor InterfacingDocument17 pagesAdc Dac and Sensor InterfacingMahreenPas encore d'évaluation
- PeakvueDocument68 pagesPeakvueChe Khairuddin100% (1)
- S & S 2 MarksDocument30 pagesS & S 2 MarkspriyajegaPas encore d'évaluation
- EMI and ESD StandardDocument10 pagesEMI and ESD StandardHendra Prima PawitraPas encore d'évaluation
- QP-WR115N: 150Mbps Wireless N RouterDocument54 pagesQP-WR115N: 150Mbps Wireless N RouterDiego Fernando CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- BCS Tut QuestionsDocument3 pagesBCS Tut Questions3176RACHANA CHOUGULE0% (1)
- RF BasicsDocument61 pagesRF BasicsBilal HabibPas encore d'évaluation
- LLZ PracticeDocument82 pagesLLZ PracticeChiranjivi KuthumiPas encore d'évaluation
- N2qv-Wu2x-N5dx CQ Magazine May 2018Document6 pagesN2qv-Wu2x-N5dx CQ Magazine May 2018Tariq Mundiya0% (1)
- 71 139826 Sailor 6210 6215 VHF DSC Class D Letter Lo PDFDocument2 pages71 139826 Sailor 6210 6215 VHF DSC Class D Letter Lo PDFjaliltaghdarehPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound System Gain StructureDocument22 pagesSound System Gain StructurewfshamsPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Wireless-Wired Alarm System-2Document2 pagesGSM Wireless-Wired Alarm System-2Mada NafeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dismantled POQ Template: Good/Broken/DamageDocument3 pagesDismantled POQ Template: Good/Broken/DamageAhmed IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- MFHF Equipment Test Procedure (TRM-1500 Tokyo Keiki) - WIDocument2 pagesMFHF Equipment Test Procedure (TRM-1500 Tokyo Keiki) - WILawrence De VeraPas encore d'évaluation