Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CCNA NAT essentials
Transféré par
jordano1Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CCNA NAT essentials
Transféré par
jordano1Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CCNA: NAT CHEAT SHEET
CCNA: NAT CHEAT SHEET
Key Characteristics
Standard: RFC 3022 Short term solution to overcome the address requirement to connect with internet Enables an organization to use Private Addressing Scheme (defined in RFC 1918) and still connect to the internet
Private Address Space
Private IP addressing is defined in RFC 1918 according which the following IP address blocks can be used within an organization for private use: 1. 10.0.0.0 / 8 2. 172.16.0.0 / 12 3. 192.168.0.0 / 16
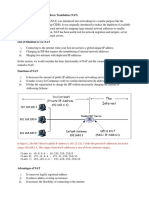
NAT Address Types
Inside Local Address: the IP Address assigned to the host on the inside network. This address is usually from the RFC 1918 Private address space. Inside Global Address: It is the IP address of an inside host (or a group of hosts) as it appears to the outside network. It is usually an address that is globally routable. Outside Local Address: the IP address assigned to an outside host as it appears to the inside network. The address is allocated from an address space routable on inside network Outside Global Address: the IP address of an outside host assigned by the owner/administrator of the host. Allocated from a globally routable address space
Types of NAT
There are 3 types: 1. Static NAT
A single local IP address is mapped to single global IP address. Also called one-to-one NAT A pool of global addresses is used to translate local IP addresses. Each inside host is assigned a global address for the duration of the session. If the session is timed-out, the specific IP address is available to use for other inside hosts Also called overloading NAT. If a large number of host need to access the internet, then static and dynamic NAT are not feasible solutions as a large number of public IP addresses will be required. PAT actually translates multiple local addresses to a single global address using different ports.
2. Dynamic NAT 3. Port Address Translation
Configuration Example: Static NAT
Router R1: interface fastethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! interface fastethernet0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside ! ip nat inside source static 192.168.1.10 172.16.1.1 R1#sh ip nat translation Pro Inside global Inside local --- 172.16.1.1 192.168.1.10 Outside local Outside global ----2
CCNA: NAT CHEAT SHEET
Configuration Example: Dynamic NAT
Router R1: interface fastethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! interface fastethernet0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside ! ip access-list standard INSIDE-HOSTS permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 ! ip nat pool NAT-POOL 155.1.1.1 155.1.1.254 netmask 255.255.255.0 ! ip nat inside source list INSIDE-HOSTS pool NAT-POOL R1#sh ip nat translation Pro Inside global --155.1.1.1 --155.1.1.2 --155.1.1.3
Inside local 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.3
Outside local -------
Outside global -------
Configuration Example: Port Address Translation
Router R1: interface fastethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! interface fastethernet0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside ! ip access-list standard INSIDE-HOSTS permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 ! ip nat inside source list INSIDE-HOSTS interface fastethernet0/0 overload R2#sh ip nat translation Pro Inside global Icmp 10.1.1.1:5 icmp 10.1.1.1:6 tcp 10.1.1.1:41683 tcp 10.1.1.1:51780
Inside local 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.3:41683 192.168.1.3:51780
Outside local 10.1.1.3:5 10.1.1.4:6 10.1.1.3:23 10.3.1.4:80
Outside global 10.3.3.3:5 10.3.3.4:6 10.3.3.3:23 10.3.3.4:80
Troubleshooting Command
1. show ip nat translation 2. show ip nat translation verbose 3. debug ip nat [detailed]
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 6 - Nat - PatDocument2 pages6 - Nat - PatDarlin DountsPas encore d'évaluation
- How Configure NatDocument5 pagesHow Configure NatAbhinav MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - 9 - NATDocument5 pagesLab - 9 - NATFarukIslamPas encore d'évaluation
- ICND2-Chapter16 Key IdeasDocument4 pagesICND2-Chapter16 Key Ideashoang nguyen baPas encore d'évaluation
- Static NAT Configuration in CiscoDocument11 pagesStatic NAT Configuration in CiscotalldesalegnPas encore d'évaluation
- NAT Configuration CommandDocument2 pagesNAT Configuration CommandPremPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Chapter 11Document4 pagesCCNA Chapter 11moves819Pas encore d'évaluation
- DHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesDHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseHasib Hamidul HaquePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7: Nat For Ipv4: Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation V7.0 (Ensa)Document47 pagesLecture 7: Nat For Ipv4: Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation V7.0 (Ensa)Poojitha NagarajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modules 6Document29 pagesModules 6Pamela VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Access The Public Internet Via Network Address Translation (NAT)Document7 pagesAccess The Public Internet Via Network Address Translation (NAT)Hotico CatalinPas encore d'évaluation
- NAT 10 Lab TasksDocument4 pagesNAT 10 Lab Tasksmuhammad.mursleen025Pas encore d'évaluation
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Commands and ConfigurationsDocument4 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT) Commands and ConfigurationsNaseer IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2 10 4aDocument3 pagesLab 2 10 4asilindeanPas encore d'évaluation
- NAT IPv6Document15 pagesNAT IPv6raichhitijrPas encore d'évaluation
- Sybex CCNA 640-802 Chapter 13Document15 pagesSybex CCNA 640-802 Chapter 13xkerberosxPas encore d'évaluation
- NAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside InterfacesDocument6 pagesNAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside Interfacesimb2Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 2 Chapter 11 v5.0 Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 11 v5.0 Exam QuestionsmacebferPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNAv3.3 401Document45 pagesCCNAv3.3 401Tung HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 3 v7 Modules 6 - 8: WAN Concepts Exam AnswersDocument38 pagesCCNA 3 v7 Modules 6 - 8: WAN Concepts Exam AnswersLeandro J. HinestrozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Etwork Ddress Ranslation: Inside Local Inside GlobalDocument1 pageEtwork Ddress Ranslation: Inside Local Inside GlobalMuhammadMazidPas encore d'évaluation
- 52 Nat PatDocument5 pages52 Nat PatBHARYPas encore d'évaluation
- 29-06 Dynamic NATDocument9 pages29-06 Dynamic NATabhinaskari1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Linux Managing DNS Servers Lpic 2 m7 SlidesDocument5 pages7 Linux Managing DNS Servers Lpic 2 m7 SlidesАлександр ПяткинPas encore d'évaluation
- Twan - Tema2 - Nat For Ipv4 - ModificadaDocument57 pagesTwan - Tema2 - Nat For Ipv4 - ModificadaMiguel Angel Garcia ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA NAT ConfigurationDocument3 pagesCCNA NAT Configurationsneha77Pas encore d'évaluation
- CPE 528 Lab Six Introduction to Network Address Translation (NATDocument11 pagesCPE 528 Lab Six Introduction to Network Address Translation (NATCharles CarpenterPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 640-802 Chapter 11 Network Address TranslationDocument14 pagesCCNA 640-802 Chapter 11 Network Address TranslationNaseem AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Scaling IP Addresses: Concept QuestionsDocument5 pagesScaling IP Addresses: Concept Questionsapi-3842231Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 5: Bmit3094 Advanced Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesTutorial 5: Bmit3094 Advanced Computer Networksterence yapPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6: Nat For Ipv4: Instructor MaterialsDocument58 pagesModule 6: Nat For Ipv4: Instructor MaterialsJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Pka7 4 1Document6 pagesPka7 4 1Nerwin PagulayanPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is NATDocument9 pagesWhat Is NATBelete TilahunPas encore d'évaluation
- 24 Network Address TranslationDocument20 pages24 Network Address TranslationRakesh CharyPas encore d'évaluation
- 00 NAT IntroductionDocument27 pages00 NAT IntroductiontestoffsurfPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Address Translation: Example: NAT Address TypesDocument7 pagesNetwork Address Translation: Example: NAT Address TypesstPas encore d'évaluation
- NAT Types Explained: Dynamic, Static, PATDocument9 pagesNAT Types Explained: Dynamic, Static, PATMohammed Musharraf MohiuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- The CCNA Topics Covered in This Chapter Include: What Is NATDocument10 pagesThe CCNA Topics Covered in This Chapter Include: What Is NATvijiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionDocument5 pagesFatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionfaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nat in Voip: RequirementsDocument19 pagesNat in Voip: Requirementsgarytj21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Network Address Translation NAT TutorialDocument4 pagesNetwork Address Translation NAT Tutorialjorge jaramillo coronellPas encore d'évaluation
- NAT Network Address TranslationDocument41 pagesNAT Network Address TranslationPaul100% (1)
- CCNP Tshoot Ch10 IP Services TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesCCNP Tshoot Ch10 IP Services TroubleshootingAbdelrahim Hussam MoubayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring A Router To Dial Multiple Sites Using Isdn Bri: Document ID: 14562Document10 pagesConfiguring A Router To Dial Multiple Sites Using Isdn Bri: Document ID: 14562Buddika WijesooriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scaling IP Addresses - NATDocument22 pagesScaling IP Addresses - NATVo Ngoc HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Document4 pagesIntroduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Firemandeheavenly InamenPas encore d'évaluation
- NAT and PATDocument17 pagesNAT and PATAbhishrkPas encore d'évaluation
- CN - 1 Sample Lab ProgramsDocument20 pagesCN - 1 Sample Lab Programskannanperu123Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA NAT SIM Question 2: Go To CommentsDocument2 pagesCCNA NAT SIM Question 2: Go To CommentsReinor JuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Network Address Translation (NAT)Document26 pagesChapter 9 Network Address Translation (NAT)nuhonoPas encore d'évaluation
- How Network Address Translation WorksDocument8 pagesHow Network Address Translation WorksPhaniraj LenkalapallyPas encore d'évaluation
- Configure Network Address Translation - CiscoDocument13 pagesConfigure Network Address Translation - CiscoFederacion Hip Hop DominicanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Address Translation (NAT)Document16 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT)Mubarik Ali MuhumedPas encore d'évaluation
- Natting in depth guideDocument31 pagesNatting in depth guideJunior foxPas encore d'évaluation
- Nat - 6Document72 pagesNat - 6etiPas encore d'évaluation
- How NAT WorksDocument10 pagesHow NAT WorksRajPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.4.1 Basic DHCP y NAT Configuration PDFDocument12 pages7.4.1 Basic DHCP y NAT Configuration PDFANDRES FELIPE TOLOZA RESTREPOPas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityD'EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3D'EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Pas encore d'évaluation
- RNC2600 DatasheetDocument2 pagesRNC2600 DatasheetShaikh Tariq100% (1)
- Serway PSE Quick Ch21Document17 pagesSerway PSE Quick Ch21music manPas encore d'évaluation
- Secotools Pune Quad Station Laser Marking System Operating Manual Final Corrected Version - 26 PagesDocument26 pagesSecotools Pune Quad Station Laser Marking System Operating Manual Final Corrected Version - 26 Pagessudhir_abhyankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Murakami - Analysis of Stress Intensity Factors of Modes I, II and III For Inclined Surface Cracks of Arbitrary ShapeDocument14 pagesMurakami - Analysis of Stress Intensity Factors of Modes I, II and III For Inclined Surface Cracks of Arbitrary ShapeDavid C HouserPas encore d'évaluation
- MP2.1 - Rankine CycleDocument12 pagesMP2.1 - Rankine CycleRuhan Guo0% (1)
- Helios PDF HandshakeDocument2 pagesHelios PDF HandshakemilivojPas encore d'évaluation
- Charlez Rock Mechanics V1Document339 pagesCharlez Rock Mechanics V1Yehimy Cambas100% (4)
- Calculator Technique For Solving Volume Flow Rate Problems in CalculusDocument3 pagesCalculator Technique For Solving Volume Flow Rate Problems in CalculusasapamorePas encore d'évaluation
- CV Pak WonoDocument2 pagesCV Pak WonoKharismaPas encore d'évaluation
- SM G318ML Tshoo 7Document70 pagesSM G318ML Tshoo 7Martín Cabrera0% (1)
- SBC Code 301Document350 pagesSBC Code 301Marwan Mokhadder100% (6)
- Next Level Racing F GT Racing Simulator Cockpit InstructionsDocument30 pagesNext Level Racing F GT Racing Simulator Cockpit InstructionsjoanPas encore d'évaluation
- Automating commercial insurance data intake with a metamodel-driven solutionDocument5 pagesAutomating commercial insurance data intake with a metamodel-driven solutionSachin ShingotePas encore d'évaluation
- TechRef ShuntDocument32 pagesTechRef ShuntAlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Validation Evidence of The Motivation For Teaching Scale in Secondary EducationDocument12 pagesValidation Evidence of The Motivation For Teaching Scale in Secondary EducationNasr-edineOuahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Finxter Python Cheat Sheet Complex Data TypesDocument1 pageFinxter Python Cheat Sheet Complex Data Typesel rahmouni oussamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bus 172Document5 pagesBus 172api-538674995Pas encore d'évaluation
- DrillDocument18 pagesDrillvivekPas encore d'évaluation
- SVERKER-750-780 DS en V03Document8 pagesSVERKER-750-780 DS en V03Jesse WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- WorkplqceDocument116 pagesWorkplqceRaferPas encore d'évaluation
- Universal JointDocument17 pagesUniversal Jointakmalzuhri96Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01-An Approach To Improved CNC Machining Using Vision-Based SystemDocument11 pages01-An Approach To Improved CNC Machining Using Vision-Based SystemCătălina StahurschiPas encore d'évaluation
- AMD64 Architecture Programmers ManualDocument386 pagesAMD64 Architecture Programmers Manualxxx54Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Magic 2019 Catalog PDFDocument56 pagesFire Magic 2019 Catalog PDFgallegos7386Pas encore d'évaluation
- Opencv Python TutorialDocument88 pagesOpencv Python TutorialParéto BessanhPas encore d'évaluation
- CXC Elec Paper 1sDocument60 pagesCXC Elec Paper 1sapi-255989257100% (1)
- 900 BED HOSPITAL STEAM CALCULATIONDocument21 pages900 BED HOSPITAL STEAM CALCULATIONAbdel HamidPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparation and Characterization of Tin Oxide Based Transparent Conducting Coating For Solar Cell ApplicationDocument5 pagesPreparation and Characterization of Tin Oxide Based Transparent Conducting Coating For Solar Cell Applicationcrypto fanbabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions For Using WinplotDocument38 pagesInstructions For Using WinplotClaudia MuñozPas encore d'évaluation
- LIPIDS MidtermDocument8 pagesLIPIDS MidtermMariaGay Albite Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation