Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Termination of Contract
Transféré par
YANZHUDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Termination of Contract
Transféré par
YANZHUDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
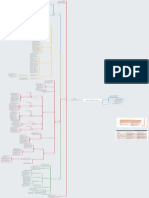
Termination of contract
Ending contract
Frustration Termination Rescission
Causes (P’s argument) 1 Intervening event 1Breach of condition 1 Mistake (Each party
(Clearly expressed as made the same mistake
2 Not contemplated by
condition/Statutory about a fundamental
both parties
implied as condition/P matter)
3 Not fault of both parties would have not entered
2 Undue influence
without strict or
4 Impossible or radically (Absence of a free and
substantial assurance)
different to original voluntary act of a
2 Serious breach of party/Could be caused by
intermediate term special relationship)
(Substantially deprived of
Exceptions: Husband and
P’s benefit)
wife/ P got independent
advice
3 Economic duress
(Pressure exerted goes
beyond legitimate)
4 Unconscionable
conduct (Covered in part
2)
Potential defence Negate 4 conditions Negate P’s argument (Not Negate P’s argument/Use
above serious enough to exemption rule
terminate)
L Schuler AG v Wickman
Machine Tool Sales
Results 1All outstanding 1 Ends from time election Ends from its beginning
obligation discharged is made
Note : Rescission is not
2 Benefits and Liabilities 2 Relieved from available in scenarios
equalised between both performing future below
parties obligation
1 Contract has been
3 Does not affect affirmed
obligations already
2 Restitution is not
accrued
available
3 Third party’s legal
rights are affected
Process 1P makes an election to Same
treat breach as ending the
contract
2 Must not be
unequivocal and be
communicated to the
party in breach
3 Party terminating
proves to be ready and
willing to perform their
part of contract
4 Cant not be revoked
Cases Taylor v Caldwell Associated Newspaper Taylor v Johnson
Ltd v Bancks
Remedies
Caused by breach of warranty or slight intermediate condition
Types P D
Damages Damage can be awarded Damage cant be awarded
1 Must be a type damage can be P would have not suffered loss but P’s loss is not caused by D
awarded (Exception: provision of by D
Loss is outside the usual course of
entertainment or enjoyment) First limb: loss is in contemplation business and unreasonable
2 Loss must be caused by breach of usual course of business
P’s contributory act counts for
3 Loss must not be too remote Second limb: within reasonable reduction of damage
contemplation of parties as a
4 Innocent party has to mitigate probable result of the breach
loss
(Consequential damage only if
notice is given)
Recovery of the contract Performed obligation under the Stipulates precise completion
price contract
Requires substantial performance
Entitled to recover the agreed price
Specific performance Dongan v Ley Lumley v Wagner
1Only when damage is not
adequate
2 Never ordered for contracts
involving personal service
Injunction Show the contravening conduct
will continue or happen again
Stop a party from doing an act
Lumley v Wagner
Restitution D has been enriched at the expense Baltic Shipping v Dillon
of P, it is unjust for D to keep the
Prevent unjust enrichment benefit
Fair and just compensation to P
Fibrosa v Fairbairn
Rectification
Mistake common to both paties
Seek order to rectify incorrect
terms
Third party’s legal right must not
be affected
Time limitation
Legal action for simple contract is
within 6 yrs
Legal action for formal contract is
within 15 yrs
Legal action for unconscionable
conduct is within 6 yrs
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Resume For PearsonDocument4 pagesResume For PearsonYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume For PearsonDocument4 pagesResume For PearsonYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- CoverDocument1 pageCoverYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Termination of ContractDocument6 pagesTermination of ContractYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Method CurriculumDocument4 pagesAccounting Method CurriculumYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Tort of NegligenceDocument5 pagesTort of NegligenceYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Tort of NegligenceDocument2 pagesTort of NegligenceYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Yan ZhuDocument1 pageYan ZhuYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Available SubjectsDocument3 pagesAvailable SubjectsYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Tort of NegligenceDocument2 pagesTort of NegligenceYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Yan ZhuDocument1 pageYan ZhuYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Yan ZhuDocument3 pagesYan ZhuYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Available SubjectsDocument3 pagesAvailable SubjectsYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Available SubjectsDocument3 pagesAvailable SubjectsYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Available SubjectsDocument3 pagesAvailable SubjectsYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Yan ZhuDocument1 pageYan ZhuYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Plan: Name Executive SummaryDocument11 pagesBusiness Plan: Name Executive SummaryYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Plan: Name Executive SummaryDocument11 pagesBusiness Plan: Name Executive SummaryYANZHUPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Contract PowerpointDocument119 pagesContract PowerpointToheeb BadmusPas encore d'évaluation
- Shipowner's Liability - The UK LawDocument31 pagesShipowner's Liability - The UK Lawramiolwan100% (7)
- Torts For Digest LISTDocument12 pagesTorts For Digest LISTJim ParedesPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts Essay 1Document10 pagesTorts Essay 1Zviagin & CoPas encore d'évaluation
- TORT End Sem Imp Definition and ConceptDocument30 pagesTORT End Sem Imp Definition and ConceptDev AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Consideration: The Essential Characteristic of ConsiderationDocument6 pagesConsideration: The Essential Characteristic of ConsiderationJhon KabirPas encore d'évaluation
- Contract Is A Meeting of Minds Between Two Persons Whereby One Binds HimselfDocument1 pageContract Is A Meeting of Minds Between Two Persons Whereby One Binds HimselfIan Ag-aDoctorPas encore d'évaluation
- Free ConsentDocument10 pagesFree Consentshakti ranjan mohanty100% (1)
- Exemption Clause Exemption Clause: Contract I (Universiti Malaya) Contract I (Universiti Malaya)Document4 pagesExemption Clause Exemption Clause: Contract I (Universiti Malaya) Contract I (Universiti Malaya)Bella SallehPas encore d'évaluation
- Business LawDocument6 pagesBusiness LawThor ThunderPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 The Basis of Contractual Obligation Mutual Assent and ConsiderationDocument7 pagesChapter 2 The Basis of Contractual Obligation Mutual Assent and ConsiderationGregnnecia DarrettPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Contracts - IDocument2 pages2 Contracts - IAnanthi NarayananPas encore d'évaluation
- Law On SalesDocument3 pagesLaw On SalesHPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce Laws, Contracts and Ethics: D H V T S U C E ADocument20 pagesCe Laws, Contracts and Ethics: D H V T S U C E AAllan CubacubPas encore d'évaluation
- Transfer of Property With TitleDocument10 pagesTransfer of Property With TitleHarris AdamPas encore d'évaluation
- LAW436 (Contract) - Free Consent (Voidable)Document1 pageLAW436 (Contract) - Free Consent (Voidable)Intan NadhirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 - Consideration and Object PDFDocument27 pagesLecture 4 - Consideration and Object PDFYahya MinhasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mistake (Free Consent)Document36 pagesMistake (Free Consent)Shubdhi9467% (3)
- MGT 312 Quiz 4 Chapters 11 - 15 Passed 100%Document6 pagesMGT 312 Quiz 4 Chapters 11 - 15 Passed 100%EltonPas encore d'évaluation
- Relevance of Legal Maxims - T Ax StatutesDocument20 pagesRelevance of Legal Maxims - T Ax Statutesjairaj321Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Contract-Vikash KR Basant PPT-2Document17 pagesClassification of Contract-Vikash KR Basant PPT-2Sameer SapaligaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yile Xu - MPT - in Re Field HogsDocument2 pagesYile Xu - MPT - in Re Field HogsYile XuPas encore d'évaluation
- Oblicon NotesDocument14 pagesOblicon NotesCee Silo Aban100% (1)
- Test Bank For Law For Business 14th Edition A James Barnes Eric Richards Tim Lemper 2Document44 pagesTest Bank For Law For Business 14th Edition A James Barnes Eric Richards Tim Lemper 2frankmooreepmgoaqjkb100% (28)
- 2 Contract - Consideration and IntentionDocument4 pages2 Contract - Consideration and IntentionJasline SohPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Law and Equity: Past Year Questions Paper 1Document4 pagesCommon Law and Equity: Past Year Questions Paper 1Ashif Rahman100% (2)
- All Contracts Are AgreementDocument13 pagesAll Contracts Are AgreementAzizi JaisPas encore d'évaluation
- DocxDocument11 pagesDocxAnkit VardhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tort of NegligenceDocument21 pagesTort of NegligenceAtul Verma100% (1)
- Quiz No. 6Document5 pagesQuiz No. 6Janwyne NgPas encore d'évaluation