Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Principles of Microeconomics - Notes - Introduction
Transféré par
Katherine SauerCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Principles of Microeconomics - Notes - Introduction
Transféré par
Katherine SauerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Name ______________________________________________ LECTURE NOTES
Principles of Microeconomics Dr. Sauer
Chapter 1: 10 Principles of Economics I. What is economics? Economics is the study of the ___________________________________ which have alternative uses. What do we mean by scarce? Human desires ____________________ our resources. What do we mean by resources? time, money, fresh water, your skills What do we mean by alternate uses? What are 3 things you could spend your time on? What are 3 things you could spend your money on? What are 3 careers you could pursue that would utilize your skills?
Economics studies the ___________________________ of the decisions that are made about the _____________________________________________. Decisions are made by Individuals groups firms governments _________economics focuses on the decision making of economic actors (e.g. consumers, producers). _________economics focuses on economy-wide phenomena (e.g. unemployment). II. 10 Basic Principles of Economics A. How People Make Decisions Principle #1 People Face __________________________ Infinite options for spending your time but time is scarce you face tradeoffs. Infinite options for spending your money but money is scarce you face tradeoffs. Think of a tradeoff that you recently faced. What were the options you were deciding between? Why did you go with the option you chose?
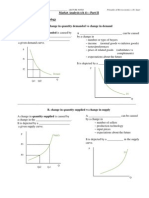
Recognizing that people face trade-offs ______________________________ tell us what decisions they will or should make. A common tradeoff for society is between efficiency and equity. efficiency = _______________________________ out of a scarce resource equity = ______________________________ resources
________________________________________________ Principle #2: The Cost of Something is What You Give Up To Get It Because people face trade-offs, making decisions requires ___________________________________ of alternative courses of action. Costs are ______________________________________ in nature. The _______________________________ of an item/action includes any money cost as well as any forgone opportunities. What is your personal opportunity cost of being in class today?
What is the opportunity cost of a college education?
What is the opportunity cost of spending tax dollars on national health care?
_____________________________________________ Principle #3: Rational People Think at the _______________________ __________________________ means only doing things when the benefits outweigh the costs. Rational people know that ________________________ in life are rarely black and white but usually involve ________________________. The term _____________________ is used to describe small incremental adjustments to an existing plan of action. (decisions are rarely all-or-nothing) While you are studying for an economics exam, you decide whether or not to study another hour. marginal benefit vs marginal cost While you are at a party, you decide whether or not to stay for a bit longer. marginal benefit vs marginal cost __________________________________ Principle #4: People Respond to Incentives An ________________________ is something that ________________________________ - the prospect of a punishment - the prospect of a reward 2
Why do we tax cigarettes?
Why do parents often give their kids allowances?
Why must I give exams and homework in this class instead of inviting you to learn the material on your honor?
___________________________________________________________________________________ B. How People Interact Principle #5: Trade Can Make Everyone Better Off _______________________ economies are based on the concepts of specialization and trade. At the _____________________ level, we specialize in a ______________, get paid to do it, and trade the money to buy other things. ___________________ specialize in the production of ______________________ and purchase the inputs needed. Trade allows _________________________ to specialize in what they do best and to enjoy a greater variety of goods and services Example: Your roommate is a better cook than you are. You are an adequate cook but a way faster cleaner than your roommate. Explain how specialization and trade could make you both better off.
Share your intended majors/careers with each other. Explain how this is a form of specialization and how you will be trading to get the other things you want in life.
______________________________ 3
Principle #6: Markets are Usually a Good Way to Organize Economic Activity ___________________________countries worked on the premise that ____________________officials were in the best position to ___________________ the economy's scarce resources. Government decides: -what goods and services were produced - how much was produced - who produced and consumed these goods and services In a ______________________________, the decisions of a central planner are replaced by the decisions of _______________________________________. Government is still needed in a market economy. ____________________________________________________________ Principle #7: Governments Can Sometimes _______________ Market Outcomes The invisible hand can work its magic only if the government enforces the _____________ and maintains the ________________________ that are key to a market economy. - property rights, sound currency, justice system Also, the market ___________________________ in all situations: 1. externalities (impact of one person's actions on the well-being of a bystander) 2. non-profitable goods 3. concentrated market power ____________________________________________________________________________________ C. How the Economy as a Whole Works Principle # 8: A Country's Standard of Living Depends on Its Ability to Produce Goods and Services Almost all variation in living standards is attributable to differences in countries' productivity. - amount of goods and services produced from each unit of labor input
Principle #9: Prices Rise When the Government Prints Too Much Money In almost all cases of large or persistent inflation, the culprit is growth in the quantity of money. When a government creates large quantities of the nation's money, the value of the money falls.
Principle #10: Society Faces a Short-Run Trade-off between Inflation and Unemployment Over the short run, many economic policies push inflation and unemployment in opposite directions. This short-run trade-off plays a key role in the analysis of the business cycle.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Module 1 Answer KJSMDocument24 pagesModule 1 Answer KJSMKier MahusayPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Systems Notes: There Are - Economic Systems. The Big Economic QuestionsDocument1 pageEconomic Systems Notes: There Are - Economic Systems. The Big Economic QuestionsHannah DonleyPas encore d'évaluation
- G11-Entrepreneurship Answer Sheets Module 1: Understanding The 4Ms of OperationsDocument3 pagesG11-Entrepreneurship Answer Sheets Module 1: Understanding The 4Ms of OperationsFergus GerodiasPas encore d'évaluation
- LESSON#1: Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesDocument3 pagesLESSON#1: Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesCatherine Bercasio Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Guided Notes - Planning For ExpensesDocument5 pagesGuided Notes - Planning For ExpensesrebaamoshyPas encore d'évaluation
- Las EntrepDocument45 pagesLas EntrepMonina LegaspiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Parkin Samantha Chapter 2 - Measuring Your Financial Health and Making A PlanDocument6 pages5 Parkin Samantha Chapter 2 - Measuring Your Financial Health and Making A Planapi-245262597100% (1)
- Retail MarketingDocument3 pagesRetail MarketingcentumahmednagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Cornell Notes OutlineDocument3 pagesInvestment Cornell Notes OutlinelivyPas encore d'évaluation
- Busines Plan FinalDocument24 pagesBusines Plan FinalVictoria Quebral Carumba100% (1)
- How A Newbie Can Start Building Wealth Through Real Estate WorksheetDocument1 pageHow A Newbie Can Start Building Wealth Through Real Estate WorksheetMoose112Pas encore d'évaluation
- Creating Topic Sentences From Supporting Ideas 2022 1Document1 pageCreating Topic Sentences From Supporting Ideas 2022 1Nice reysPas encore d'évaluation
- APPLIED Periodical TEST 2nd SemDocument3 pagesAPPLIED Periodical TEST 2nd SemOne ClickPas encore d'évaluation
- SocSci1b Reviewer BlankedDocument9 pagesSocSci1b Reviewer BlankedJustin Era ApeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Step 1 - Prospecting: Name: Agent CodeDocument31 pagesStep 1 - Prospecting: Name: Agent CodealiPas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific Management". - Scientific Management".Document1 pageScientific Management". - Scientific Management".nimhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Beyond The Walkaround Workbook ADocument40 pagesBeyond The Walkaround Workbook AMarian BobocPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 0Document4 pagesWorksheet 0Ambrose OnapaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Trust Edge: Executive Training InstituteDocument8 pagesThe Trust Edge: Executive Training InstituteFelipe AcevedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Entrepreneurial Competencies of An Entrepreneur: Module 2-WorksheetDocument5 pagesPersonal Entrepreneurial Competencies of An Entrepreneur: Module 2-WorksheetMikhail CompetentePas encore d'évaluation
- Entrep Activity 02Document4 pagesEntrep Activity 02KaisenPas encore d'évaluation
- Engleski Jezik 1 - Primer ZadatkaDocument2 pagesEngleski Jezik 1 - Primer ZadatkaIva AvramovicPas encore d'évaluation
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument16 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPRomnick SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- G11-Entrepreneurship Answer SheetsDocument3 pagesG11-Entrepreneurship Answer SheetsFergus Gerodias100% (4)
- Edited - 1st Partial Exam LRCI 2Document3 pagesEdited - 1st Partial Exam LRCI 2Marilu MaciasPas encore d'évaluation
- HowToMakeALotOfMoney&HelpALotOfPeople Workbook PDFDocument13 pagesHowToMakeALotOfMoney&HelpALotOfPeople Workbook PDFWILMARPas encore d'évaluation
- The Busy Persons Guide To Achieving More Workbook EDITABLEDocument13 pagesThe Busy Persons Guide To Achieving More Workbook EDITABLEKatarina StankovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Entrep Quiz No. 01Document2 pagesEntrep Quiz No. 01Roxan Binarao-BayotPas encore d'évaluation
- Handouts CVP AnalysisDocument6 pagesHandouts CVP AnalysisAissa OrbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-1 Economics WorksheetDocument6 pagesCh-1 Economics WorksheetFenil ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Guided Notes - Production CurvesDocument7 pagesGuided Notes - Production CurvesyogurtkingyahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Tle10 Afa Agricrop q1 Mod1 Entrepreneurialskillsincropproduction v5Document24 pagesTle10 Afa Agricrop q1 Mod1 Entrepreneurialskillsincropproduction v5Jelly Ace Almond TeaPas encore d'évaluation
- First Test First QuarterDocument2 pagesFirst Test First QuarterMa'am Carla Kristina CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Igcse Business Studies Revision Sheets (For Year 10 & Year 11)Document54 pagesIgcse Business Studies Revision Sheets (For Year 10 & Year 11)Aryan AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- SLM Chs 10 Pecs FinalDocument9 pagesSLM Chs 10 Pecs FinalJose Intraboy Arais Tabugoc Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sales Action Plan: Establish Your ObjectiveDocument5 pagesSales Action Plan: Establish Your ObjectiveGretchen Plants Home ScentsPas encore d'évaluation
- Questioon STDocument3 pagesQuestioon STYared TerefePas encore d'évaluation
- Prelim Quizzes ENTREP F2fDocument5 pagesPrelim Quizzes ENTREP F2fZekainah AduanaRocellozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bisnis WellingtonDocument4 pagesBisnis WellingtonWilson TakatinPas encore d'évaluation
- LAS TVE 10 wk1 FOPDocument6 pagesLAS TVE 10 wk1 FOPMedalla MocorroPas encore d'évaluation
- ECONOMICS - Guided Reading and Study GuideDocument308 pagesECONOMICS - Guided Reading and Study GuideThorng Meng76% (21)
- Survey PotentialDocument3 pagesSurvey PotentialShanilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Lesson Plan: Time: Subject: FormDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Time: Subject: FormNurAiniNasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet Entrepreneuship Module 8 2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet Entrepreneuship Module 8 2Eleah Melly TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- 01.end of Unit Test U1Document3 pages01.end of Unit Test U1ELISA.HIPOLITO.TPas encore d'évaluation
- Deepening Activity For Practical Research 2 1Document1 pageDeepening Activity For Practical Research 2 1Rica MhonttPas encore d'évaluation
- Motivating Workers: Textbook, Chapter 6 (PG 64-76)Document10 pagesMotivating Workers: Textbook, Chapter 6 (PG 64-76)Vincent ChurchillPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Do Consumers Purchase - Video and Notes - StudentDocument11 pagesWhy Do Consumers Purchase - Video and Notes - StudentShah ShamsPas encore d'évaluation
- TFD SoFi Worksheet V1-1Document2 pagesTFD SoFi Worksheet V1-1Andrei LeontePas encore d'évaluation
- First Asian International Systems College, IncDocument4 pagesFirst Asian International Systems College, IncMelanie MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1XOLCHITPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Plan GenappealDocument30 pagesBusiness Plan GenappealMatteo LopesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pec Booklet Module TleDocument8 pagesPec Booklet Module TleMARIO BUENAVENTEPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Q1-EntrepDocument11 pages5 Q1-Entrepimong4577Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prelim Exam For PrintingDocument3 pagesPrelim Exam For PrintingLea AndreleiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module in Ege 17 EppDocument25 pagesModule in Ege 17 EppRoma Amor EstomoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1670393256-Money - Makeup ExamDocument2 pages1670393256-Money - Makeup Examsaphira evani maliqaPas encore d'évaluation
- Weeks 3-4 - 3rd Quarter - Business SimulationmoduleDocument13 pagesWeeks 3-4 - 3rd Quarter - Business Simulationmodulemycah hagadPas encore d'évaluation
- Guided Notes - Business StructuresDocument7 pagesGuided Notes - Business StructuresrebaamoshyPas encore d'évaluation
- So You Are Finally Done: 6 Ways To Make Money Online(& How To Start)D'EverandSo You Are Finally Done: 6 Ways To Make Money Online(& How To Start)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Wellness Programming: An Administrative PerspectiveDocument16 pagesFinancial Wellness Programming: An Administrative PerspectiveKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionDocument3 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Worksheet - IntroductionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Worksheet - IntroductionKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Document4 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Document17 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine Sauer100% (1)
- Intermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduDocument5 pagesIntermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Summary TemplateDocument1 pageModel Summary TemplateKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesDocument8 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Document4 pagesChapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Katherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceDocument7 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch02 S D and EquilibriumDocument7 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch02 S D and EquilibriumKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsDocument3 pagesReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerDocument6 pagesReading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- PM Income Tax History QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Income Tax History QuestionsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- This Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingDocument5 pagesThis Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 MathDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter08 MathKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- ReadingNotes Chapter01 StatsDocument5 pagesReadingNotes Chapter01 StatsKatherine Sauer100% (1)
- Chapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes - Big Mac IndexDocument2 pagesLecture Notes - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- PM Iceland Krona QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Iceland Krona QuestionsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- PM Guilds QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Guilds QuestionsKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes - TaxesDocument3 pagesLecture Notes - TaxesKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 3 Information SheetDocument1 pageExam 3 Information SheetKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - Big Mac IndexDocument11 pagesLecture - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Taxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerDocument21 pagesTaxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 2 Information SheetDocument3 pagesExam 2 Information SheetKatherine SauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Financial Markets English X PDFDocument84 pagesIntroduction To Financial Markets English X PDFPreeti ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Credit Suisse and The CDS Streisand Effect - Financial TimesDocument12 pagesCredit Suisse and The CDS Streisand Effect - Financial TimesNoman BouaoudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Market Segmentation Targeting Dan Positio PDFDocument16 pagesAnalisis Market Segmentation Targeting Dan Positio PDFdavidkurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I-Mefa Final NotesDocument24 pagesUnit I-Mefa Final NotesMuskan TambiPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Politics MODULE 3Document26 pagesPhilippine Politics MODULE 3jonas arsenue100% (1)
- DocxDocument20 pagesDocxGuineverePas encore d'évaluation
- Error CorrectionDocument8 pagesError CorrectionCharlie Magne G. SantiaguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Kim and Common Application Form - Equity SchemesDocument89 pagesKim and Common Application Form - Equity Schemesarghya000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Finance and Capital MarketsDocument53 pagesFinance and Capital MarketsMUNAWAR ALIPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 566Document6 pagesQuiz 566Haris NoonPas encore d'évaluation
- IMC AssignmentDocument7 pagesIMC AssignmentAmardeep RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Wu2018 JournalDocument27 pagesWu2018 JournalSyafrie MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Practitioner Guide To Forex Market-Part 1Document10 pagesPractitioner Guide To Forex Market-Part 1acreddiPas encore d'évaluation
- Facture Sweat BalenciagaDocument1 pageFacture Sweat Balenciagaspeak.luminonPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Market Update 14.12.2021Document1 pageDaily Market Update 14.12.2021Fuaad DodooPas encore d'évaluation
- Sol Man - Pas 2 InventoriesDocument3 pagesSol Man - Pas 2 InventoriesDaniella Mae ElipPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Activity 1Document3 pages12 Activity 1Razel AntiniolosPas encore d'évaluation
- Economicmodel of Roic Eva WaccDocument29 pagesEconomicmodel of Roic Eva Waccbernhardf100% (1)
- Business Plan in Entrepreneur: Submitted By: Joshua Jocame Submitted To: Glaiza SiasonDocument13 pagesBusiness Plan in Entrepreneur: Submitted By: Joshua Jocame Submitted To: Glaiza SiasonAlma Jane SoteloPas encore d'évaluation
- Rural MarketingDocument378 pagesRural Marketingpun_nisPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional FibreDocument10 pagesFunctional Fibresofia NunesPas encore d'évaluation
- XIMIVOUGE - LITE - FeasibilityDocument9 pagesXIMIVOUGE - LITE - FeasibilityPranav TubajiPas encore d'évaluation
- SYBMS Sem 3 SyllabusDocument7 pagesSYBMS Sem 3 SyllabusRavi KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Private Equity and Private Debt Investments in IndiaDocument76 pagesPrivate Equity and Private Debt Investments in Indiagoyal.rohit8089Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution StarbucksDocument3 pagesSolution StarbucksMrityunjay Kumar PandayPas encore d'évaluation
- Olson Power and ProsperityDocument6 pagesOlson Power and ProsperitymaryserranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect Topic 3.2 DisinvestmentDocument23 pagesLect Topic 3.2 DisinvestmentKertik SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Geography Template CreativeDocument14 pagesGeography Template Creativealexandra mpPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Sofr FuturesDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Sofr FuturesGeorge LiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Coca Cola Mini CaseDocument1 pageCoca Cola Mini CaseDania Sekar WuryandariPas encore d'évaluation