Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Gadget Rmnet
Transféré par
Rohit PathaniaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Gadget Rmnet
Transféré par
Rohit PathaniaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction ============ QUALCOMM MSM Interface (QMI) defines the interface between MSM and attached Terminal Equipment
(TE). RmNet interface is a new logical device in QMI framework for data services. RmNet in accordance with QMI architecture defines channels for control and data transfers and for example it uses Data I/O channel for IP data transfer and control I/O channel for QMI messaging (functionality similar to AT commands). RmNet may be used in place of legacy USB modem interface. Tethered networking is one of the function from MSM which can also be supported using QMI protocol. There are other standard protocols exists such as CDC-ECM and Windows proprietary RNDIS. On the host-side system, the gadget rmnet device looks like a ethernet adapter. Hardware description ==================== QMI is a messaging protocol to expose various functionalities of MSM and one of the functionality to be tethered networking which is being exposed over QMI using RmNet protocol. This usb gadget has one bulk-in, one bulk-out and one interrupt-in endpoint. Software description ==================== The RmNet uses two function drivers which uses one interface respectively as follows: 1. SMD Interface 2. SDIO Interface SMD interface uses the Shared memory for the RmNet driver to communicate with the MSM modem processor. SDIO interface acts as a link for communication of RmNet driver with the MDM modem processor. USB INTERACTION: ---------------The RmNet function driver binds with the USB using the struct usb_function. The function is added using the usb_function_add(). Control Transfers: The RmNet handles two Class-specific control transfers: SEND_ENCAPSULATED_COMMAND and GET_ENCAPSULATED_RESPONSE. The asynchronous protocol QMI which consists of the QMI requests/responses is used for handling the transfers between the RmNet and the Host where the host sends a new QMI request before receiving the response for the current QMI request. Control & Data flow: 1. Host issues a SEND_ENCAPSULATED command to send a QMI request. SMD: If the SMD control channel has enough room to accomodate a QMI request, it is written into the SMD buffer. Otherwise, append/add that request to qmi_request queue. A tasklet is scheduled to drain all QMI requests in qmi_request queue. SDIO: Add each request in the qmi_request queue and is processed until the queue is empty. 2. Append/Add QMI response from modem to qmi_response queue. A notification on an interrupt end point is used to communicate the QMI
response to host. 3. Host issues a GET_ENCAPSULATED command to retrieve the QMI response. The response from qmi_response queue will be sent to the host. 4. After the connection is fully established data can be sent to bulk-out endpoint and data can be received from bulk-in endpoint. 5. Host can send QMI requests even after the connection is established. RmNet gadget driver is completely unaware of QMI/IP protocol. It just acts as a bridge between the modem and the PC. All the request/response queues in the driver can be accessed either from tasklet/workqueue or from interrupt context (either usb or smd/sdio interrupt handler). Hence a spinlock is used to protect all data/control req lists. SMD Interface: -------------1. Each QMI request/response can at most be 2048 bytes. Eight 2KB buffers are allocated using kmalloc for storing maximum of 8 requests/responses. 2. Four 2KB buffers are allocated using kmalloc for data transfers on each bulk endpoint. Data structures: struct qmi_buf struct rmnet_smd_info struct rmnet_dev Workqueues: rmnet_connect_work rmnet_disconnect_work Tasklets: rmnet_control_rx_tlet rmnet_control_tx_tlet rmnet_data_rx_tlet rmnet_data_tx_tlet ndler SDIO Interface: --------------1. Each QMI request/response buffer is allocated depending on the size of data to be transmitted for the request/response. 2. A 2KB network buffer is allocated for data transfer on bulk-out endpoint. The SDIO allocates the required buffer for data transfers on an bulk-in endpoint. Data structures: Buffer to handle QMI requests & responses Control & Data SMD channel private data Endpoint and driver specific data Called on device connection. Opens SMD channels; enables endpoints Called on device disconnection. Closes SMD channels.
Control transfer data reception and transmission handler Data transfer data reception and transmission ha
struct rmnet_sdio_qmi_buf struct rmnet_dev Workqueues: rmnet_connect_work rmnet_disconnect_work rmnet_control_rx_work rmnet_data_rx_work
Buffer to handle QMI requests/responses. Endpoint and driver specific data Device connection handler. Opens SDIO channels; enables and allocate buffer for endpoints Device disconnection handler. Closes SDIO channels; Frees allocated buffers. Control data reception handler. Network data reception handler.
Two SMD/SDIO channels (control and data) are used as communication channels between Modem and Apps processor. The driver opens the SMD/SDIO channels on USB device connection. Data is either read from/written to the channels as one complete packet. SMD/SDIO provides a notification whenever the Modem processor completes read/write of a packet. Based on these SMD/SDIO notifications all the pending read/write requests will be handled. Tasklets(SMD)/Workqueues(SDIO) are used to get the requests done. There is another variant of rmnet driver called rmnet_smd_sdio which is used on some boards. This driver allows the transport (SMD/SDIO) to be chosen at runtime. This is required because either MDM processor or MODEM processor is only active at a time for data transfers. As SMD and SDIO interfaces are different, different endpoint completion handlers are used. This driver leverage the existing rmnet over smd and rmnet over sdio drivers. The control messages (QMI) always routed over SDIO. After the control messages exchange, user space will come to know about the available data transport (SMD/SDIO). User space notify the same to driver and the corresponding transport is activated. It is assumed that transport will not change while a USB cable is connected. Rmnet over SMD and rmnet over SDIO doesn't expose any of its interfaces to either kernelspace or userspace. But rmnet over smd/sdio expose a sysfs interface for userspace to notify the available transport to driver. The sysfs file can be found at /sys/class/usb_composite/rmnet_smd_sdio/transport The below command activates the SMD transport echo 0 > /sys/class/usb_composite/rmnet_smd_sdio/transport The below command activates the SDIO transport echo 1 > /sys/class/usb_composite/rmnet_smd_sdio/transport -EINVAL is returned if a write is attempted to transport when a USB cable is not connected.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- PQMII Power Quality Meter Communications Guide: MultilinDocument96 pagesPQMII Power Quality Meter Communications Guide: Multilinanon_820693557Pas encore d'évaluation
- OMNI Flow Computers Peer-to-Peer BasicsDocument11 pagesOMNI Flow Computers Peer-to-Peer Basicssyed jeelani ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager 7.0 TCP and Udp Port UsageDocument12 pagesCisco Unified Communications Manager 7.0 TCP and Udp Port UsagePhyo Min TunPas encore d'évaluation
- rs2gprs enDocument11 pagesrs2gprs enftonelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Gfs-384 m10 Modbus TCPDocument25 pagesGfs-384 m10 Modbus TCPPham LongPas encore d'évaluation
- Peer To Peer Basics: Last Updated: 09-April-2009 TB-980401BDocument12 pagesPeer To Peer Basics: Last Updated: 09-April-2009 TB-980401BSofyan HadiPas encore d'évaluation
- APP Connect QuestionsDocument6 pagesAPP Connect Questionskandula nagababuPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam PutraDocument20 pagesFinal Exam PutracrabmoetPas encore d'évaluation
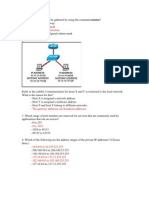
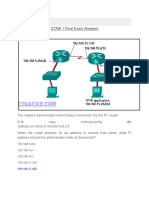
- CCNA3 - Answers Chapter 2 v.4.0: Updated Daily New Updated Mar 01 2009 by Quocvuong EmailDocument6 pagesCCNA3 - Answers Chapter 2 v.4.0: Updated Daily New Updated Mar 01 2009 by Quocvuong EmailWalter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco 1 Reviewer For Final ExamDocument9 pagesCisco 1 Reviewer For Final ExamAlPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Comm & Networking 1 (Upgraded) Created By:AnonymousDocument56 pagesData Comm & Networking 1 (Upgraded) Created By:AnonymousJitlee PapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment On NetworksDocument7 pagesAssignment On NetworksLimitless StatusPas encore d'évaluation
- IoT in Five Days - v1.1 20160627 (1) - 1-160-128-136Document9 pagesIoT in Five Days - v1.1 20160627 (1) - 1-160-128-136pham phuPas encore d'évaluation
- CP1L / CP1H / CJ2M Modbus/TCP Adapter Application and Setup GuideDocument18 pagesCP1L / CP1H / CJ2M Modbus/TCP Adapter Application and Setup GuideJorgeManriquePas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 1 Final Exam AnswersDocument80 pagesCCNA 1 Final Exam AnswersTatenda BizurePas encore d'évaluation
- Questionario 2Document37 pagesQuestionario 2Evelyta Sanz100% (1)
- Modbus InformationDocument37 pagesModbus InformationJuampi PizarroPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 1 RS Introduction To Networks Final Exam v50 2013Document15 pagesCCNA 1 RS Introduction To Networks Final Exam v50 2013daniel_afpPas encore d'évaluation
- Examen Final Ccna1 v5.0Document23 pagesExamen Final Ccna1 v5.0Kristian Marlon PrietoPas encore d'évaluation
- Peer-to-Peer Basics: Date: 05 22 03 Author(s) : Kenneth D. ElliottDocument12 pagesPeer-to-Peer Basics: Date: 05 22 03 Author(s) : Kenneth D. ElliottapisituPas encore d'évaluation
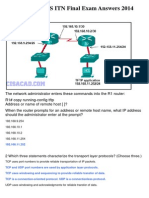
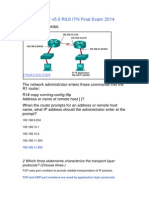
- CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014Document22 pagesCCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014jonmicPas encore d'évaluation
- Smith Meter: Modbus & Modbus/TCP CommunicationsDocument32 pagesSmith Meter: Modbus & Modbus/TCP CommunicationsAli Ben BrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- OPC & NetworkingDocument60 pagesOPC & NetworkingAnil Nair100% (2)
- TCP and Udp PDFDocument11 pagesTCP and Udp PDFUsman ZeeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Serial - Ethernet ModuleDocument22 pagesSerial - Ethernet ModuleJAC 91Pas encore d'évaluation
- Serialized DLMS Over TCP PRIME GatewayDocument12 pagesSerialized DLMS Over TCP PRIME GatewayVPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevent Data Loss When Updating S7-1200 PLC ProgramDocument124 pagesPrevent Data Loss When Updating S7-1200 PLC Programee01096Pas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Methods (Protocols, Format & Language) For The Substation Automation & Control by MUHAMMAD UZAIR (Project Report of Course 586 B)Document10 pagesCommunication Methods (Protocols, Format & Language) For The Substation Automation & Control by MUHAMMAD UZAIR (Project Report of Course 586 B)Nima MahmoudpourPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To All Participants: Plastics MachineryDocument78 pagesWelcome To All Participants: Plastics MachineryjupudiguptaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1. Background: Datagram CommunicationDocument8 pages1.1. Background: Datagram CommunicationPrithwish GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming With TCP/IP - Best PracticesDocument31 pagesProgramming With TCP/IP - Best PracticesmrwanzPas encore d'évaluation
- Fudamentos de Redes Final ExamDocument11 pagesFudamentos de Redes Final ExamEnriquePas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 1+2+3+4 v5Document87 pagesCCNA 1+2+3+4 v5Ajmal QalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network 4Document10 pagesComputer Network 4dooharistide2Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 1 Exam Final en AnglaisDocument54 pagesCCNA 1 Exam Final en AnglaisRoland FoyemtchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Using DMA Module in Kinetis Devices (Complete)Document27 pagesUsing DMA Module in Kinetis Devices (Complete)futuromp3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual 5020MGC 04 04Document54 pagesManual 5020MGC 04 04consultachPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter5 p1Document63 pagesChapter5 p1radeeyjdPas encore d'évaluation
- Android RilDocument14 pagesAndroid RilJohnson JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- CC3502 Computer Networks: Multiplexing and IP Address Tutorial SolutionsDocument4 pagesCC3502 Computer Networks: Multiplexing and IP Address Tutorial Solutionsmgayanan100% (1)
- Study Guide ExpandedDocument7 pagesStudy Guide ExpandedGabby ShearerPas encore d'évaluation
- Ping utility and network device fundamentalsDocument7 pagesPing utility and network device fundamentalsSanjeev RajPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 1 FINAL Exam Answers v5.0 2013Document0 pageCCNA 1 FINAL Exam Answers v5.0 2013CCNA5.NETPas encore d'évaluation
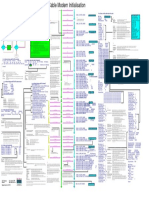
- Cisco CM - Initialization-Pdf-Wallchart PDFDocument1 pageCisco CM - Initialization-Pdf-Wallchart PDFjjmazueraPas encore d'évaluation
- AcromatModbusTCP IPDocument42 pagesAcromatModbusTCP IPManuel Domínguez MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Protocolo ModbusDocument34 pagesProtocolo ModbusErnesto Rivas GaytánPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3 Dichotomy of Parallel Computing PlatformsDocument6 pages2.3 Dichotomy of Parallel Computing PlatformsNaira ElazabPas encore d'évaluation
- AF-6 Series Drives Modbus RTUDocument12 pagesAF-6 Series Drives Modbus RTUshijub_001Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction to NetworksDocument48 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction to NetworksRazvan AlexandruPas encore d'évaluation
- Hct6000 Tcpip OptionDocument14 pagesHct6000 Tcpip OptionGerman DfrPas encore d'évaluation
- Login access methods and router configuration questionsDocument6 pagesLogin access methods and router configuration questionschennai11Pas encore d'évaluation
- AT89S8252 In-System ProgrammingDocument38 pagesAT89S8252 In-System ProgrammingPramod JainPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 ECM700 - Modbus Protocol V6.5Document22 pages03 ECM700 - Modbus Protocol V6.5Chanatip de LaohasomPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding the OSI model layers and TCP/IP configurationDocument6 pagesUnderstanding the OSI model layers and TCP/IP configurationjohn deveyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 CCNA 3Document6 pagesChapter 2 CCNA 3beloved54321Pas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksD'EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedD'EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedPas encore d'évaluation
- C# programming introductionDocument46 pagesC# programming introductionVincentius Yosephat Suryo100% (2)
- DPDKDocument2 pagesDPDKshri1527Pas encore d'évaluation
- HDMI USB CaptureDocument4 pagesHDMI USB CaptureAlfi TapaiPas encore d'évaluation
- EeupdateDocument12 pagesEeupdateІгорPas encore d'évaluation
- Device driver and status reportDocument5 pagesDevice driver and status reportVikiNorrisPas encore d'évaluation
- System ProgrammingDocument26 pagesSystem ProgrammingMohan Rao MamdikarPas encore d'évaluation
- UVProbe TutorialDocument142 pagesUVProbe TutorialAnand H SPas encore d'évaluation
- DX DiagDocument35 pagesDX DiagRichardPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Report On Fire WireDocument34 pagesSeminar Report On Fire Wirenjpatel9100% (2)
- Qubee ManualDocument9 pagesQubee ManualJohn MillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser Model Interface Reference ManualDocument18 pagesLaser Model Interface Reference ManualManny Mendoza100% (1)
- LabVIEW Robotics Programming Guide ForDocument65 pagesLabVIEW Robotics Programming Guide ForJuan de Dios Alardín HernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- Middleware SystemsDocument5 pagesMiddleware Systemsdameantd0310Pas encore d'évaluation
- 110758-W2-US LCR-Meter Operating Instructions enDocument13 pages110758-W2-US LCR-Meter Operating Instructions enadamatozPas encore d'évaluation
- AUTOSAR TR ReleaseOverviewAndRevHistoryDocument49 pagesAUTOSAR TR ReleaseOverviewAndRevHistorySiddu Shiva KadiwalPas encore d'évaluation
- DX DiagDocument8 pagesDX DiagNafiza Hasin MisuPas encore d'évaluation
- Check Driver InstallationDocument4 pagesCheck Driver InstallationZachary CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- tr8 (Ooooo)Document4 pagestr8 (Ooooo)Aro rovoPas encore d'évaluation
- Device Tree Learning (DTS) by SSMDocument7 pagesDevice Tree Learning (DTS) by SSMSiba SsmPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Systems and Utility Programs 1Document27 pagesOperating Systems and Utility Programs 1osmokoPas encore d'évaluation
- DX DiagDocument17 pagesDX DiaghoulanPas encore d'évaluation
- Win Dump HwidDocument18 pagesWin Dump HwidWing Chung ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Two: Communication Diagnostics With Cat ETDocument34 pagesLesson Two: Communication Diagnostics With Cat ETramiro rodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Essentials Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2018 2019 Version 6.0 100% IT Essentials Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2018 2019 Version 6.0 100%Document7 pagesIT Essentials Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2018 2019 Version 6.0 100% IT Essentials Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2018 2019 Version 6.0 100%Egy RenataPas encore d'évaluation
- برنامج Driver Genius Professional Edition v6Document3 pagesبرنامج Driver Genius Professional Edition v6SGH31000Pas encore d'évaluation
- AUTOSARFSDocument3 pagesAUTOSARFSNirav DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Stellarisware API User GuideDocument326 pagesStellarisware API User Guide13579krmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ezurio Bluetooth Driver PDFDocument2 pagesEzurio Bluetooth Driver PDFBobbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Soundscape Getting Started V 100Document51 pagesSoundscape Getting Started V 100nifnifnafnafPas encore d'évaluation
- DX DiagDocument35 pagesDX DiagSanzMilanoPas encore d'évaluation